-
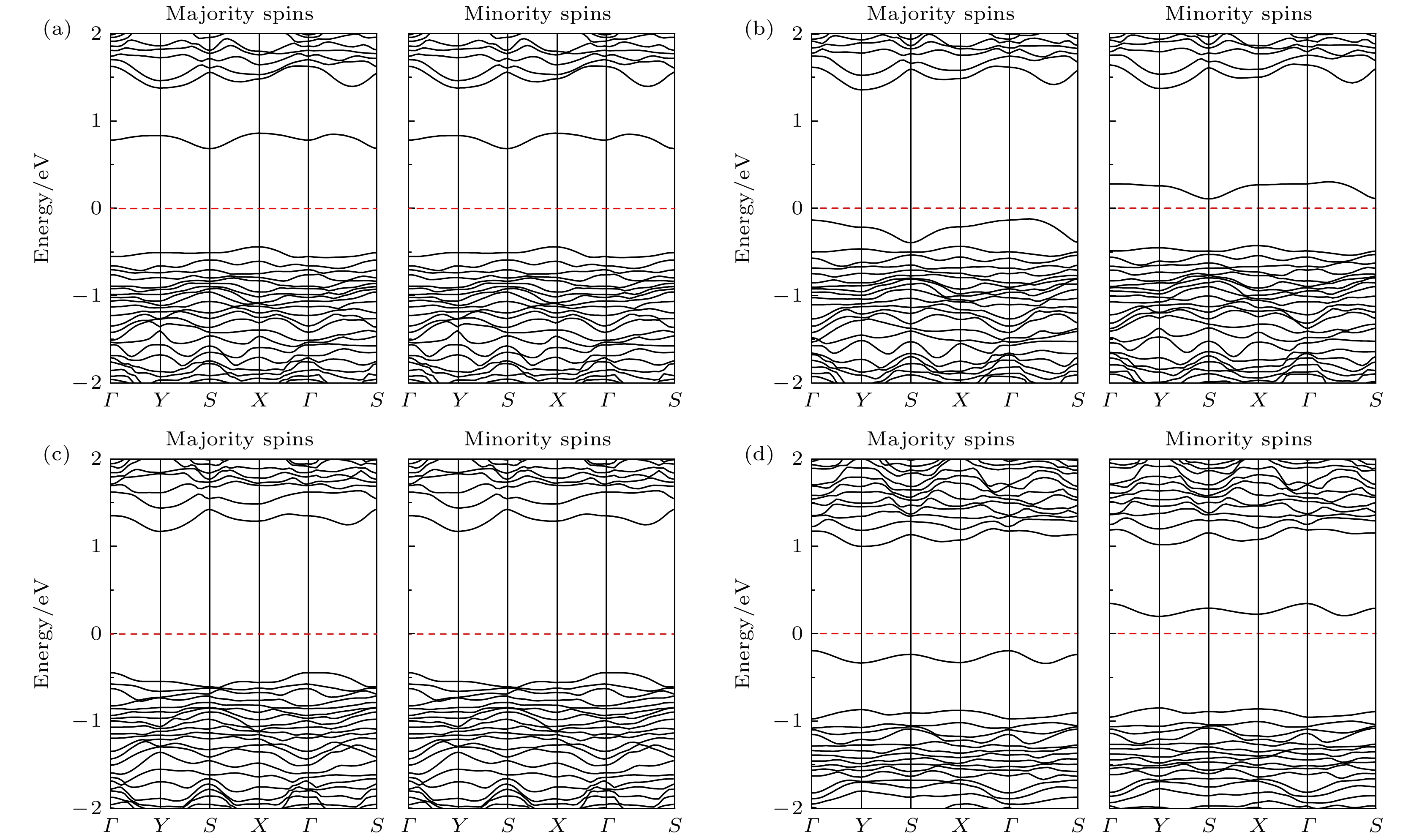
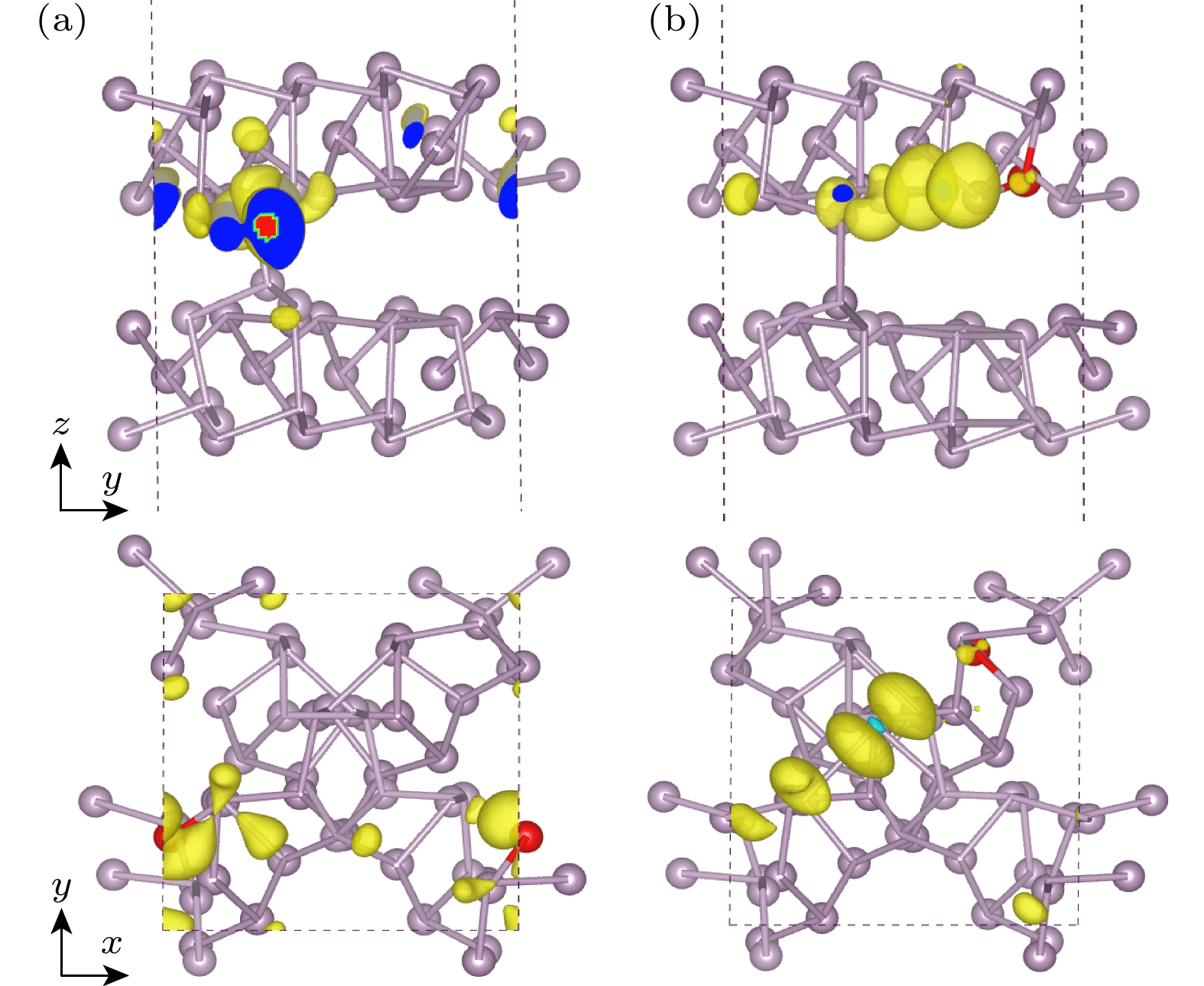
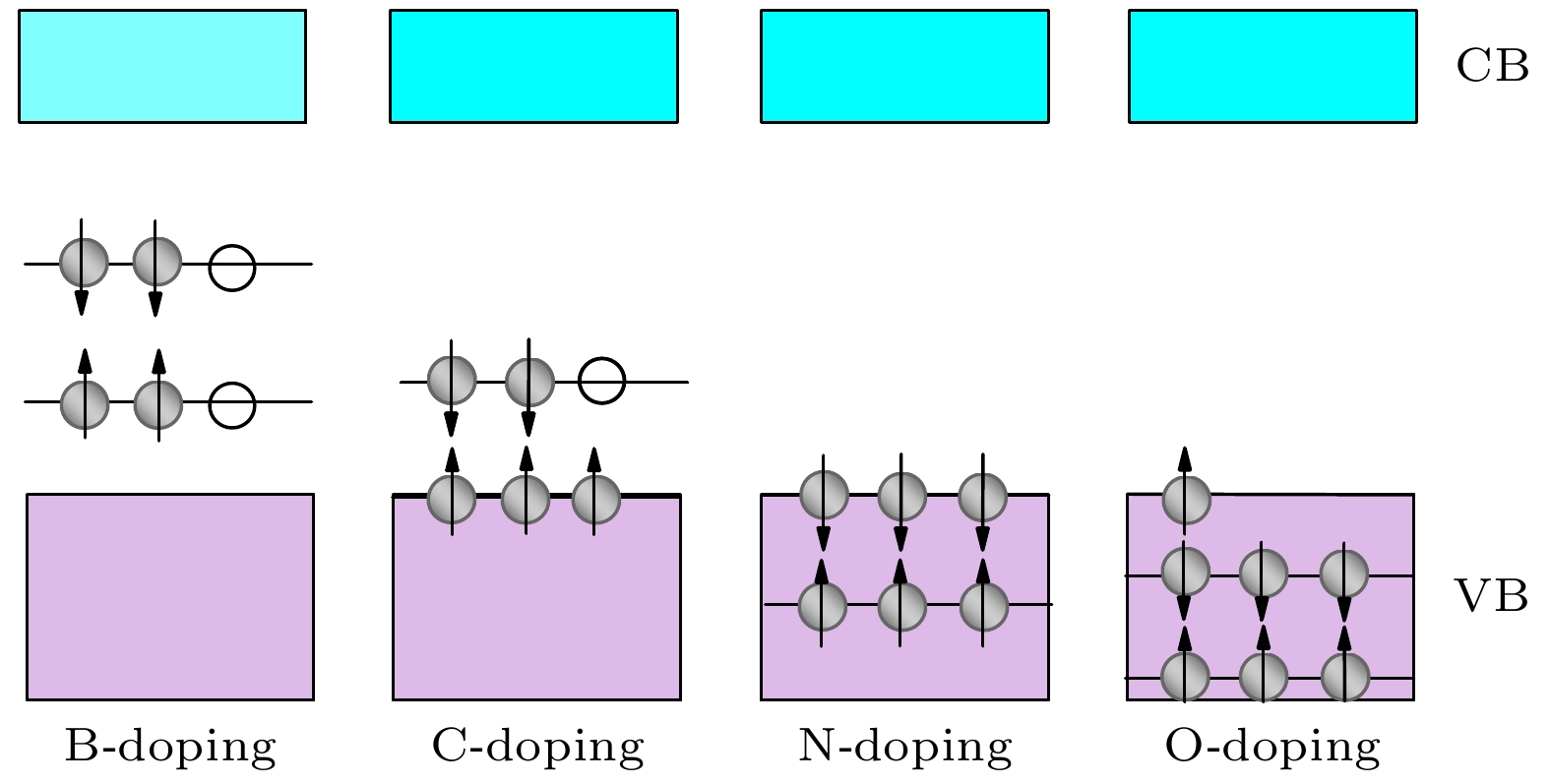
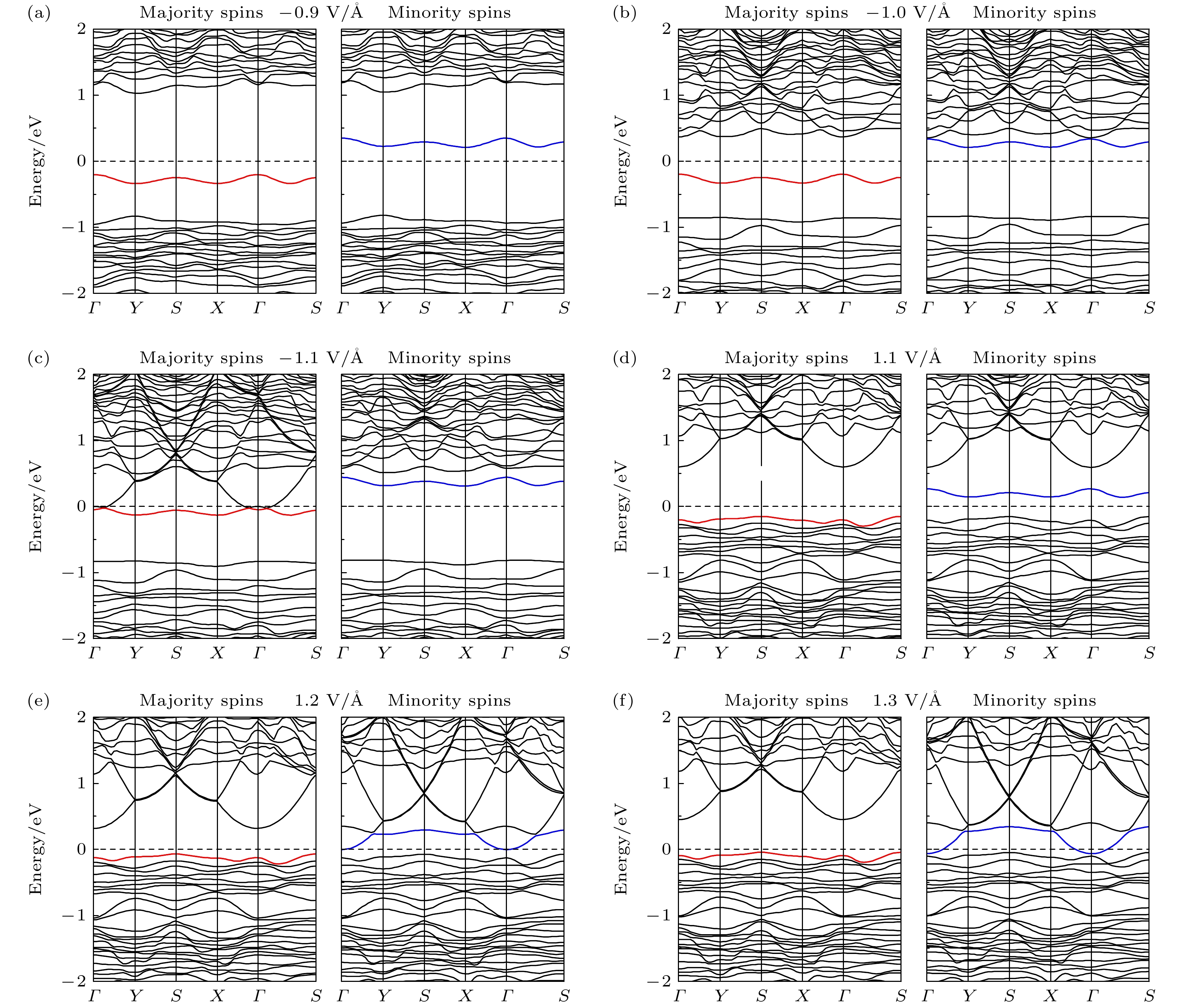
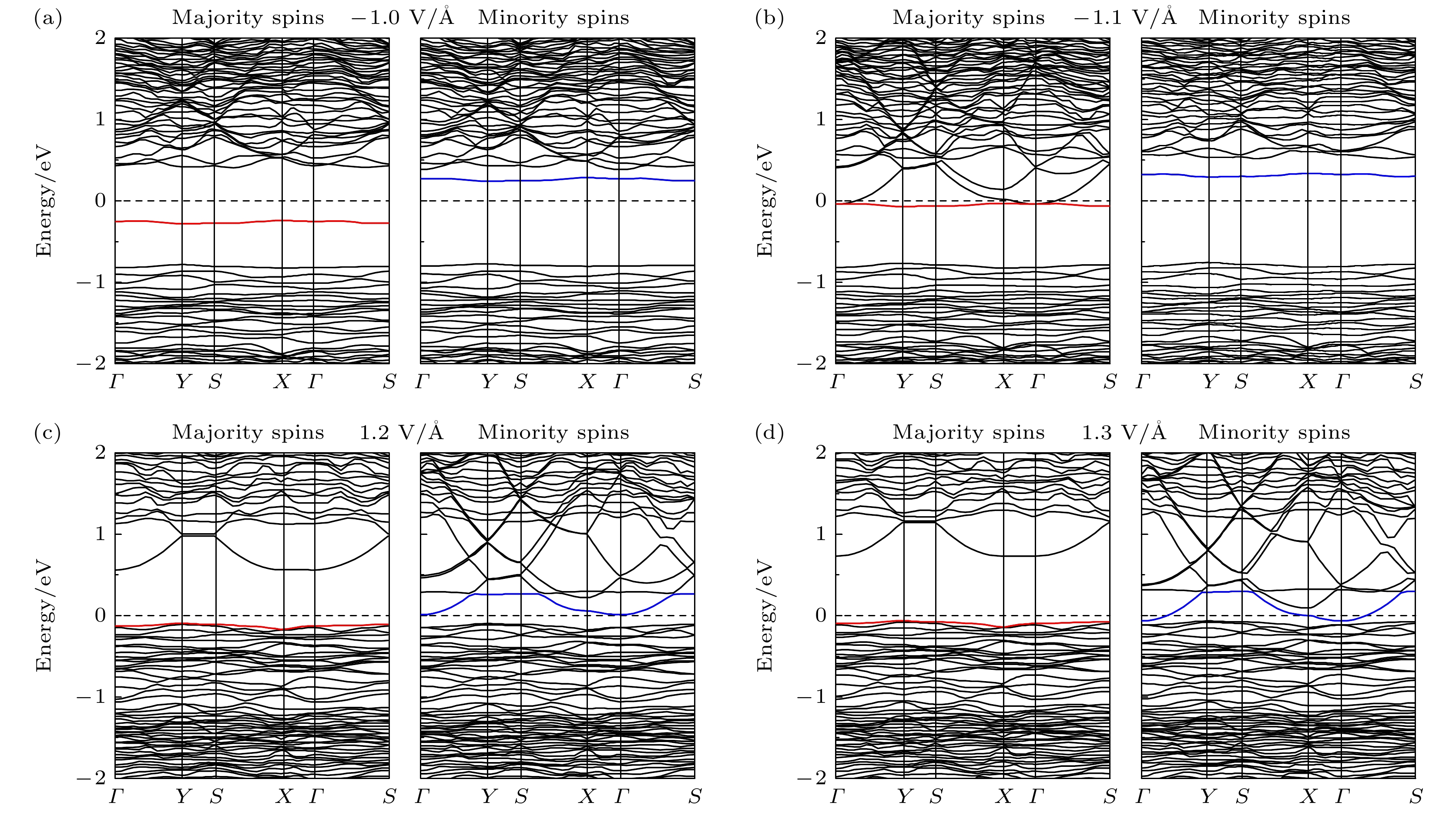
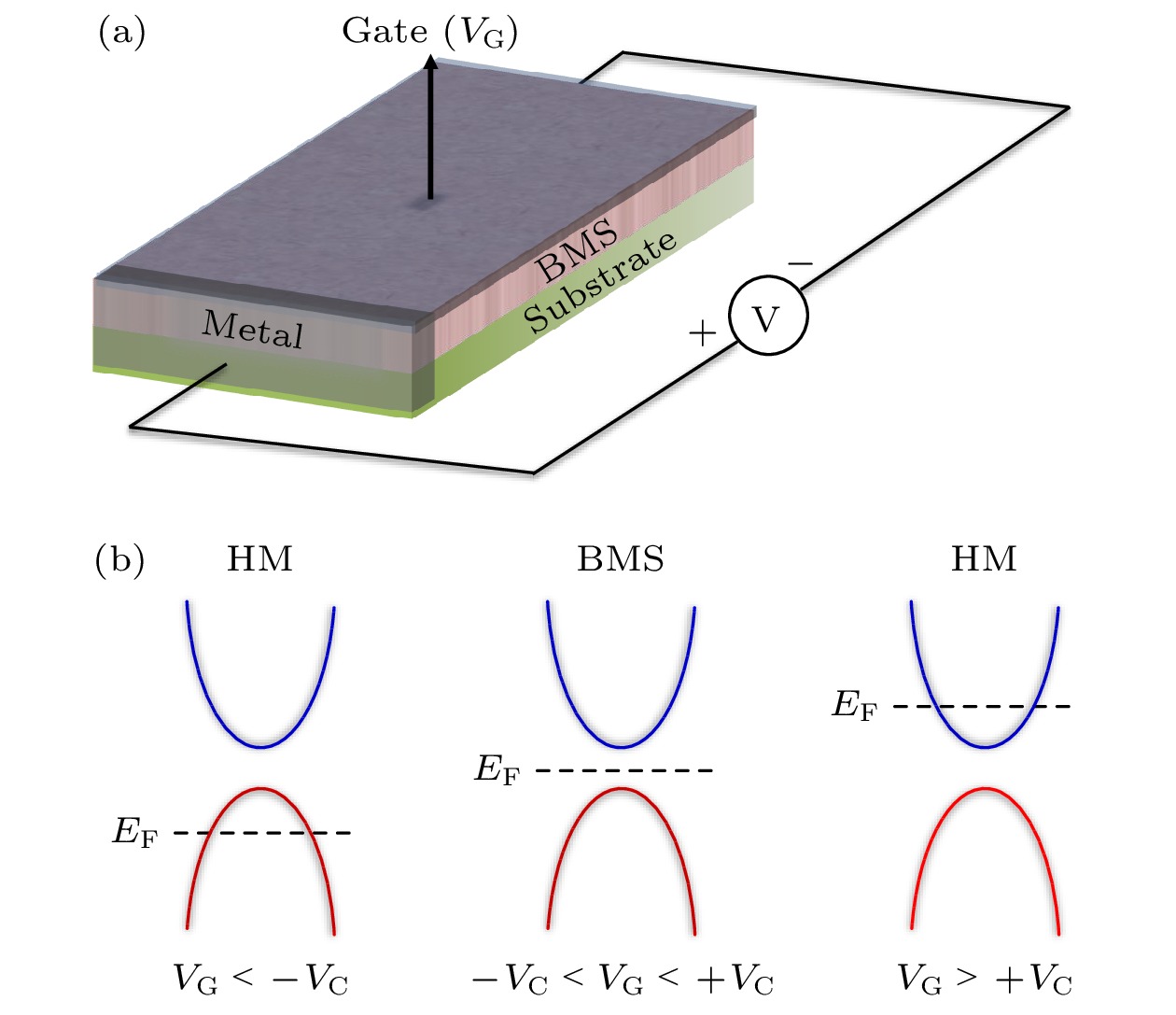
Hittorf’s violet phosphorene is a novel two-dimensional material with stable structure and excellent optoelectronic properties. Studying the doping effect helps to understand its physical essence and is of great significance in further developing nanoelectronic devices. In this paper, the first-principles method based on density functional theory is used to study the electromagnetic properties of the non-metallic element B-, C-, N-, and O-doped single-layer violet phosphene. The results show that there is no magnetism after having doped boron and nitrogen, and the system still behaves as a nonmagnetic semiconductor, while carbon doping and oxygen doping cause spin splitting, and the violet phosphorene transforms from a nonmagnetic semiconductor to a bipolar magnetic semiconductor, and its spin density is mainly distributed in the P atom and gap region, rather than on the impurity. The direction of spin polarization of its carrier can be reversed by adjusting the electric field of O-doped violet phosphorene. When a certain size of forward or reverse electrostatic field is applied, the band dispersion becomes stronger, and the O-doped violet phosphorene transforms into a half-metallic magnet with 100% downward or upward spin polarization at the Fermi level. The field effect spin filter based on O-doped violet phosphorene can reverse the direction of spin-polarized current by changing the direction of the gate voltage. This study shows that O-doped violet phosphorene is expected to be an ideal candidate material for two-dimensional spin field-effect transistors, bipolar magnetic spintronic devices, dual channel field effect spin filters, and field-effect spin valves.
-
Keywords:
- violet phosphorene /
- doping /
- bipolar magnetic semiconductor /
- half-metallic magnet
[1] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S V, Grigorieva I V, Firsov A A 2004 Science 306 666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ni Z Y, Liu Q H, Tang K C, Zheng J X, Zhou J, Qin R, Gao Z X, Yu D P, Lu J 2012 Nano Lett. 12 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen L, Liu C C, Feng B, He X, Cheng P, Ding Z, Meng S, Yao Y, Wu K 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 056804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chiappe D, Grazianetti C, Tallarida G, Fanciulli M, Molle A 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 5088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhu C, Shao R, Chen S, Cai R, Wu Y, Yao L, Xia W, Nie M, Sun L, Gao P, Xin H L, Xu F 2019 Small Methods 3 1900061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu G, Wu X, Xu Y, Cheng H, Meng J, Yu Q, Shi X, Zhang K, Chen W, Chen S 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1806492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Feng B, Sugino O, Liu R Y, Zhang J, Yukawa R, Kawamura M, Iimori T, Kim H, Hasegawa Y, Li H, Chen L, Wu K, Kumigashira H, Komori F, Chiang T C, Meng S, Matsuda I 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 096401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kiraly B, Liu X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Mannix A J, Fisher B L, Yakobson B I, Hersam M C, Guisinger N P 2019 ACS Nano 13 3816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiao J, Kong X, Hu Z X, Yang F, Ji W 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Chen Q, Tong Y, Wang J 2016 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55 11437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen Z, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Liu W, Cui Y, Tao X, Zhang D 2019 Electrochimica Acta 295 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tsai H S, Lai C C, Hsiao C H, Medina H, Su T Y, Ouyang H, Chen T H, Liang J H, Chueh Y L 2015 ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 7 13723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schusteritsch G, Uhrin M, Pickard C J 2016 Nano Lett. 16 2975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lu Y L, Dong S, Zhou W, Dai S, Zhou B, Zhao H, Wu P 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 11967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang L, Huang H, Zhang B, Gu M, Zhao D, Zhao X, Li L, Zhou J, Wu K, Cheng Y, Zhang J 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 132 1090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang B, Wang Z, Huang H, Zhang L, Gu M, Cheng Y, Wu K, Zhou J, Zhang J 2020 J. Mater. Chem. A 8 8586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dai S, Zhou W, Liu Y, Lu Y L, Sun L, Wu P 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 448 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Han R, Qi M, Mao Z, Lin X, Wu P 2021 Appl. Surf. Sci. 541 148454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xue R, Han R, Lin X, Wu P 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 608 155240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lin X, Mao Z, Dong S, Jian X, Han R, Wu P 2021 Physica E 127 114524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Han R, Qi M, Dong S, Mao Z, Lin X, Wu P 2021 Physica E 129 114667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lu Y L, Dong S, Li J, Wu Y, Zhao H 2022 Physica E 138 115068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Baumer F, Ma Y, Shen C, Zhang A, Chen L, Liu Y, Pfister D, Nilges T, Zhou C 2017 ACS Nano 11 4105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lu Y L, Dong S, He H, Li J, Wang X, Zhao H, Wu P 2019 Comput. Mater. Sci. 163 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 谭兴毅, 王佳恒, 朱祎祎, 左安友, 金克新 2014 63 207301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan X Y, Wang J H, Zhu Y Y, Zuo A Y, Jin K X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 207301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Khan I, Hong J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 023056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zheng H, Zhang J, Yang B, Du X, Yan Y 2015 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 16341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yang L, Mi W, Wang X 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 662 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 R558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kresse G, Hafner J 1994 Phys. Rev. B 49 14251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Blochl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Grimme S 2006 J. Comput. Chem. 27 1787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lu Y L, Dong S, Zhou W, Liu Y, Zhao H, Wu P 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 441 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Safari F, Fathipour M, Goharrizi A Y 2018 J. Comput. Electron. 17 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jónsson H 2006 Comput. Mater. Sci. 36 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
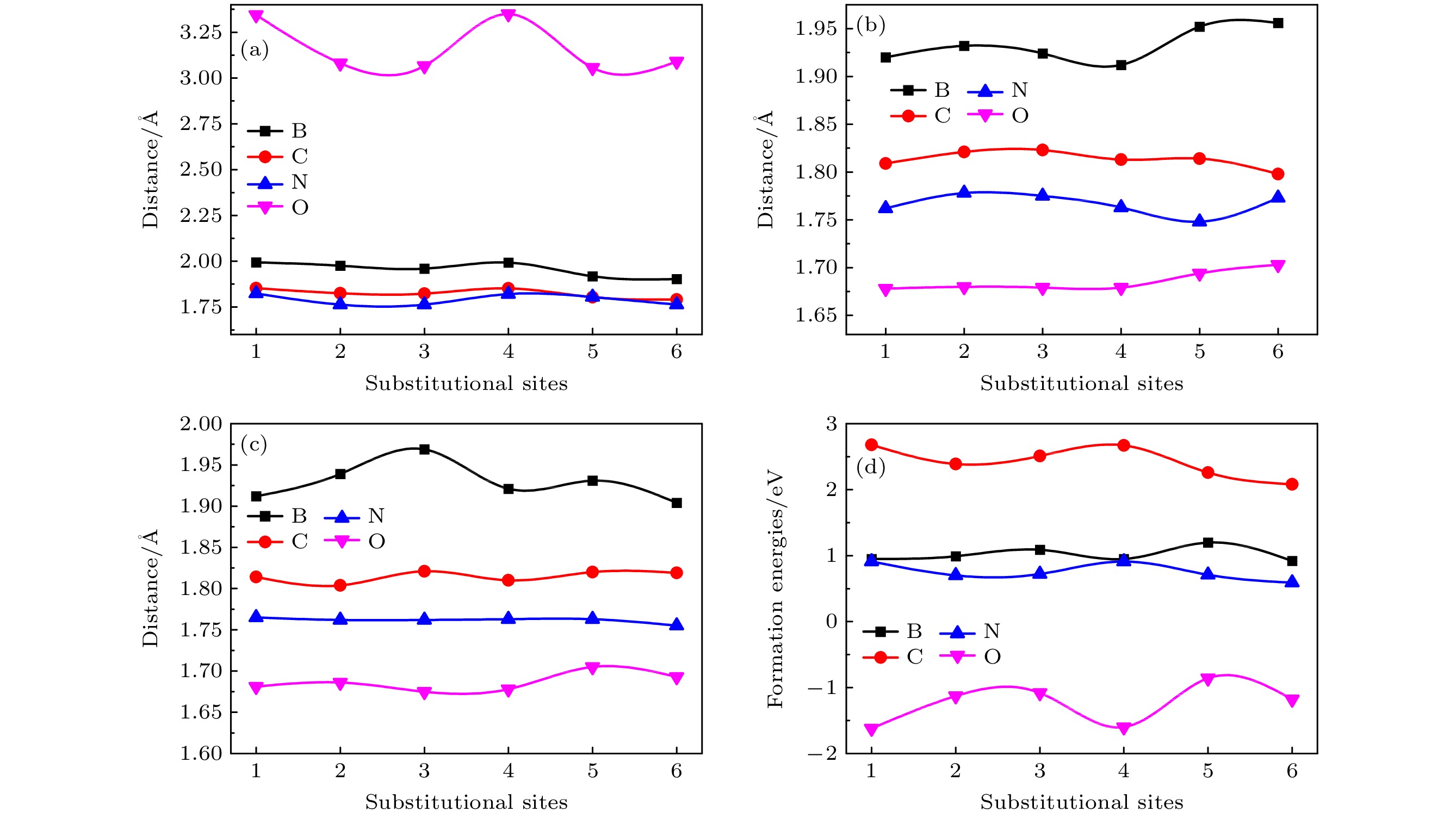
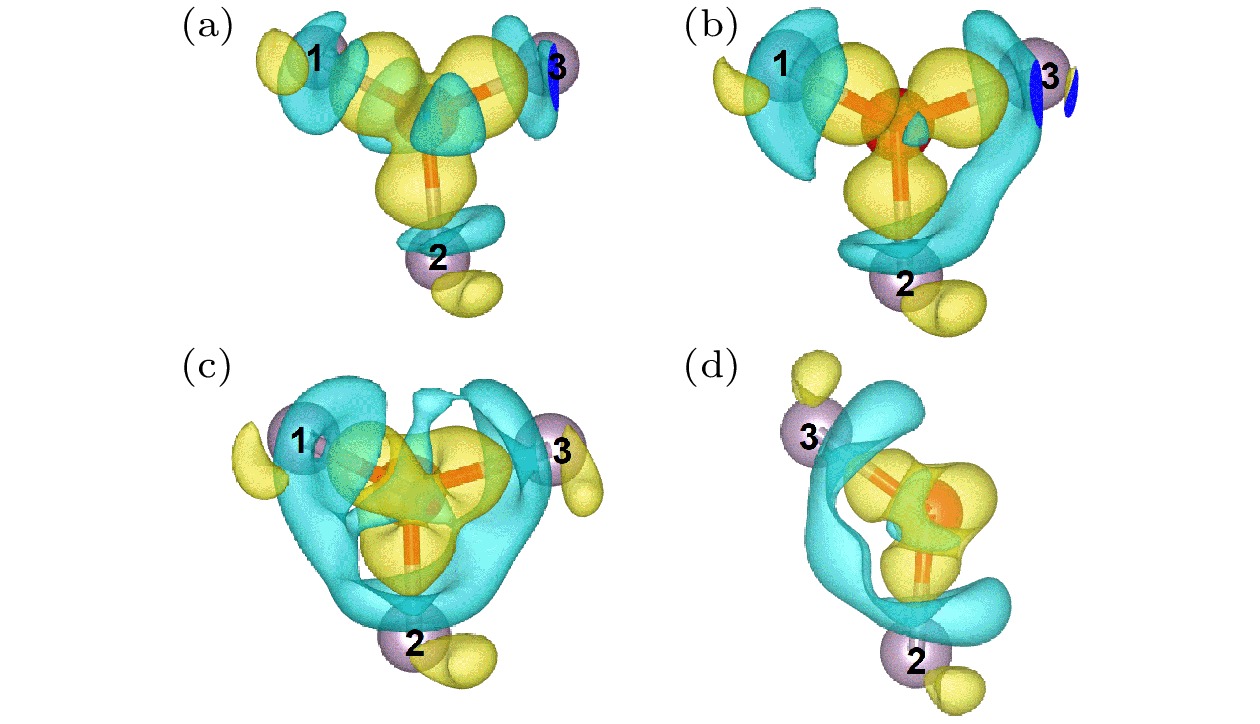
图 1 不同掺杂位点掺杂单层紫磷烯的几何结构模型. 紫色和红色小球分别表示磷原子和掺杂原子. 标记的1, 2和3分别代表与杂质原子距离最近的3个磷原子P1, P2和P3
Figure 1. Geometric structure of the doped Hittorf’s violet phosphorene with different doping sites. The violet and red spheres represent the phosphorus atoms and the dopant atom, respectively. The marked 1, 2, and 3 denote the sites of three nearest-neighboring P atoms P1, P2, and P3.
表 1 非金属原子掺杂单层紫磷烯的总磁矩Mtot, 非金属原子X的局部磁矩MX, 磷原子的局部磁矩MP以及间隙区域的局部磁矩Mint
Table 1. Total magnetic moment Mtot, the partial magnetic moment of the dopant MX, the P atoms MP, and the interstitial region Mint, respectively.
掺杂体系 Mtot/μB MX/μB MP/μB Mint/μB B掺杂 0 0 0 0 C掺杂 0.988 0.262 0.229 0.497 N掺杂 0 0 0 0 O掺杂 0.991 0.012 0.471 0.520 表 2 掺杂紫磷烯中X, P1, P2和P3原子的Bader电荷值
Table 2. Bader charges of the dopant X, P1, P2, and P3 atoms, respectively.
掺杂体系 X P1 P2 P3 B掺杂 2.73 5.11 5.11 5.10 C掺杂 5.50 4.44 4.55 4.50 N掺杂 6.81 4.37 4.37 4.35 O掺杂 7.38 — 4.26 4.25 -
[1] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S V, Grigorieva I V, Firsov A A 2004 Science 306 666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ni Z Y, Liu Q H, Tang K C, Zheng J X, Zhou J, Qin R, Gao Z X, Yu D P, Lu J 2012 Nano Lett. 12 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen L, Liu C C, Feng B, He X, Cheng P, Ding Z, Meng S, Yao Y, Wu K 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 056804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chiappe D, Grazianetti C, Tallarida G, Fanciulli M, Molle A 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 5088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhu C, Shao R, Chen S, Cai R, Wu Y, Yao L, Xia W, Nie M, Sun L, Gao P, Xin H L, Xu F 2019 Small Methods 3 1900061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu G, Wu X, Xu Y, Cheng H, Meng J, Yu Q, Shi X, Zhang K, Chen W, Chen S 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1806492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Feng B, Sugino O, Liu R Y, Zhang J, Yukawa R, Kawamura M, Iimori T, Kim H, Hasegawa Y, Li H, Chen L, Wu K, Kumigashira H, Komori F, Chiang T C, Meng S, Matsuda I 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 096401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kiraly B, Liu X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Mannix A J, Fisher B L, Yakobson B I, Hersam M C, Guisinger N P 2019 ACS Nano 13 3816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiao J, Kong X, Hu Z X, Yang F, Ji W 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Chen Q, Tong Y, Wang J 2016 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55 11437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen Z, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Liu W, Cui Y, Tao X, Zhang D 2019 Electrochimica Acta 295 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tsai H S, Lai C C, Hsiao C H, Medina H, Su T Y, Ouyang H, Chen T H, Liang J H, Chueh Y L 2015 ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 7 13723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schusteritsch G, Uhrin M, Pickard C J 2016 Nano Lett. 16 2975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lu Y L, Dong S, Zhou W, Dai S, Zhou B, Zhao H, Wu P 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 11967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang L, Huang H, Zhang B, Gu M, Zhao D, Zhao X, Li L, Zhou J, Wu K, Cheng Y, Zhang J 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 132 1090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang B, Wang Z, Huang H, Zhang L, Gu M, Cheng Y, Wu K, Zhou J, Zhang J 2020 J. Mater. Chem. A 8 8586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dai S, Zhou W, Liu Y, Lu Y L, Sun L, Wu P 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 448 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Han R, Qi M, Mao Z, Lin X, Wu P 2021 Appl. Surf. Sci. 541 148454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xue R, Han R, Lin X, Wu P 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 608 155240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lin X, Mao Z, Dong S, Jian X, Han R, Wu P 2021 Physica E 127 114524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Han R, Qi M, Dong S, Mao Z, Lin X, Wu P 2021 Physica E 129 114667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lu Y L, Dong S, Li J, Wu Y, Zhao H 2022 Physica E 138 115068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Baumer F, Ma Y, Shen C, Zhang A, Chen L, Liu Y, Pfister D, Nilges T, Zhou C 2017 ACS Nano 11 4105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lu Y L, Dong S, He H, Li J, Wang X, Zhao H, Wu P 2019 Comput. Mater. Sci. 163 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 谭兴毅, 王佳恒, 朱祎祎, 左安友, 金克新 2014 63 207301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan X Y, Wang J H, Zhu Y Y, Zuo A Y, Jin K X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 207301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Khan I, Hong J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 023056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zheng H, Zhang J, Yang B, Du X, Yan Y 2015 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 16341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yang L, Mi W, Wang X 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 662 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 R558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kresse G, Hafner J 1994 Phys. Rev. B 49 14251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Blochl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Grimme S 2006 J. Comput. Chem. 27 1787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lu Y L, Dong S, Zhou W, Liu Y, Zhao H, Wu P 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 441 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Safari F, Fathipour M, Goharrizi A Y 2018 J. Comput. Electron. 17 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jónsson H 2006 Comput. Mater. Sci. 36 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4038
- PDF Downloads: 149
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: