-
Liquid iron is the major component of planetary cores. Its structure and dynamics under high pressure and temperature is of great significance in studying geophysics and planetary science. However, for experimental techniques, it is still difficult to generate and probe such a state of matter under extreme conditions, while for theoretical method like molecular dynamics simulation, the reliable estimation of dynamic properties requires both large simulation size and ab initio accuracy, resulting in unaffordable computational costs for traditional method. Owing to the technical limitation, the understanding of such matters remains limited. In this work, combining molecular dynamics simulation, we establish a neural network potential energy surface model to study the static and dynamic properties of liquid iron at its extreme thermodynamic state close to core-mantle boundary. The implementation of deep neural network extends the simulation scales from one hundred atoms to millions of atoms within quantum accuracy. The estimated static and dynamic structure factor show good consistency with all available X-ray diffraction and inelastic X-ray scattering experimental observations, while the empirical potential based on embedding-atom-method fails to give a unified description of liquid iron across a wide range of thermodynamic conditions. We also demonstrate that the transport property like diffusion coefficient exhibits a strong size effect, which requires more than at least ten thousands of atoms to give a converged value. Our results show that the combination of deep learning technology and molecular modelling provides a way to describe matter realistically under extreme conditions.
-
Keywords:
- molecular dynamics /
- neural network /
- extreme condition /
- dynamic properties
[1] Vočadlo L 2015 Treatise on Geophysics 2.06—Earth’s Core: Iron and Iron Alloys (Amsterdam: Elsevier) pp117–147
[2] Dziewonski A M, Anderson D L 1981 Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wagner F W, Sohl F, Hussmann H, Grott M, Rauer H 2011 Icarus 214 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dai J, Kang D, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Yuan J 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 175701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dai J, Hou Y, Kang D, Sun H, Wu J, Yuan J 2013 New J. Phys. 15 045003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Q, Sun T, Zhang Y G, Xian J W, Vocadlo L 2021 J. Chem. Phys. 155 194505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] González L E, González D J 2023 J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 128 e2022JB025119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ramakrishna K, Lokamani M, Baczewski A, Vorberger J, Cangi A 2023 Phys. Rev. B 107 115131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kang D, Zeng Q, Zhang S, Wang X, Dai J 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Behler J, Parrinello M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 146401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bartok A P, Payne M C, Kondor R, Csanyi G 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 136403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Thompson A P, Swiler L P, Trott C R, Foiles S M, Tucker G J 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 285 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang L, Han J, Wang H, Car R, E W 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 143001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang L 2018 arXiv: 180509003 [physics.comp-ph
[15] Zhang Y, Gao C, Liu Q, Zhang L, Wang H, Chen M 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 122704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X, Gao X, Zhao Y, Lin D, Chu W, Song H 2020 Comput. Phys. Commun. 250 107057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zeng Q, Yu X, Yao Y, Gao T, Chen B, Zhang S, Kang D, Wang H, Dai J 2021 Phys. Rev. Research 3 033116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen B, Zeng Q, Wang H, Zhang S, Kang D, Lu D, Dai J 2021 arXiv: 200613136 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci
[19] Chen B, Zeng Q, Yu X, Chen J, Zhang S, Kang D, Dai J 2022 arXiv: 220801830 [astro-ph.EP
[20] Yang F, Zeng Q, Chen B, Kang D, Zhang S, Wu J, Yu X, Dai J 2022 Chin. Phys. Lett. 39 116301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zeng Q, Chen B, Zhang S, Kang D, Wang H, Yu X, Dai J 2023 arXiv: 230813863 [physics.comp-ph
[22] Hosokawa S, Inui M, Matsuda K, Ishikawa D, Baron A Q R 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kuwayama Y, Morard G, Nakajima Y, Hirose K, Baron A Q R, Kawaguchi S I, Tsuchiya T, Ishikawa D, Hirao N, Ohishi Y 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 165701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Inui M, Maruyama K, Kajihara Y, Nakada M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 180201(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Morard G, Boccato S, Rosa A D, Anzellini S, Miozzi F, Henry L, Garbarino G, Mezouar M, Harmand M, Guyot F, Boulard E, Kantor I, Irifune T, Torchio R 2018 Geophys. Res. Lett. 45 2018GL079950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Perdew J, Burke J, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Holzwarth N, Tackett A, Matthews G 2001 Comput. Phys. Commun. 135 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Marqués M, González L E, González D J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Marqués M, González L E, González D J 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang H, Zhang L, Han J, E W 2018 Comput. Phys. Commun. 228 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zeng J, Zhang D, Lu D, Mo P, Li Z, Chen Y, Rynik M, Huang L, Li Z, Shi S, Wang Y, Ye H, Tuo P, Yang J, Ding Y, Li Y, Tisi D, Zeng Q, Bao H, Xia Y, Huang J, Muraoka K, Wang Y, Chang J, Yuan F, Bore S L, Cai C, Lin Y, Wang B, Xu J, Zhu J X, Luo C, Zhang Y, Goodall R E A, Liang W, Singh A K, Yao S, Zhang J, Wentzcovitch R, Han J, Liu J, Jia W, York D M, E W, Car R, Zhang L, Wang H 2023 J. Chem. Phys. 159 054801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Sun Y, Zhang F, Mendelev M I, Wentzcovitch R M, Ho K M 2022 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119 e2113059119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 液态铁的能量、受力与压强在训练集上的预测偏差 (a)
$ \sigma_{E}=7.36\; {\rm meV/atom}$ ; (b)$ \sigma_{f} = 0.36\; {\rm eV/\AA}$ ; (c)$ \sigma_{p} = 0.41\; {\rm GPa}$ Figure 2. DP-predicted energy per atom, force, and pressures versus the true KS-DFT calculations in the testing dataset: (a)
$ \sigma_{E}= $ $ 7.36\; {\rm meV/atom} $ ; (b)$ \sigma_{f}=0.36\; {\rm eV/\AA} $ ; (c)$ \sigma_{p}=0.41\; {\rm GPa} $ 图 3 液态铁的静态结构因子 (a) p = 0 GPa, T = 1873 K; (b) p = 21 GPa, T = 2600 K; (c) p = 40 GPa, T = 3000 K; (d) p = 53 GPa, T = 3300 K; (e) p = 74 GPa, T = 3600 K; (f) p = 106 GPa, T = 4250 K; 彩色点为DPMD计算结果, 灰色点为Inui等[24](常压)和Kuwayama等[23] (高温高压)的实验测量结果, 灰色虚线为基于EAM势的CMD计算结果
Figure 3. Static structure factor of liquid iron: (a) p = 0 GPa, T = 1873 K; (b) p = 21 GPa, T = 2600 K; (c) p = 40 GPa, T = 3000 K; (d) p = 53 GPa, T = 3300 K; (e) p = 74 GPa, T = 3600 K; (f) p = 106 GPa, T = 4250 K. Colored circles indicate the results from DPMD simulation, the gray square denotes the experimental measurements by Inui et al.[24] and Kuwayaka et al.[23], the gray dashed line denotes the results from CMD simulation with EAM potential
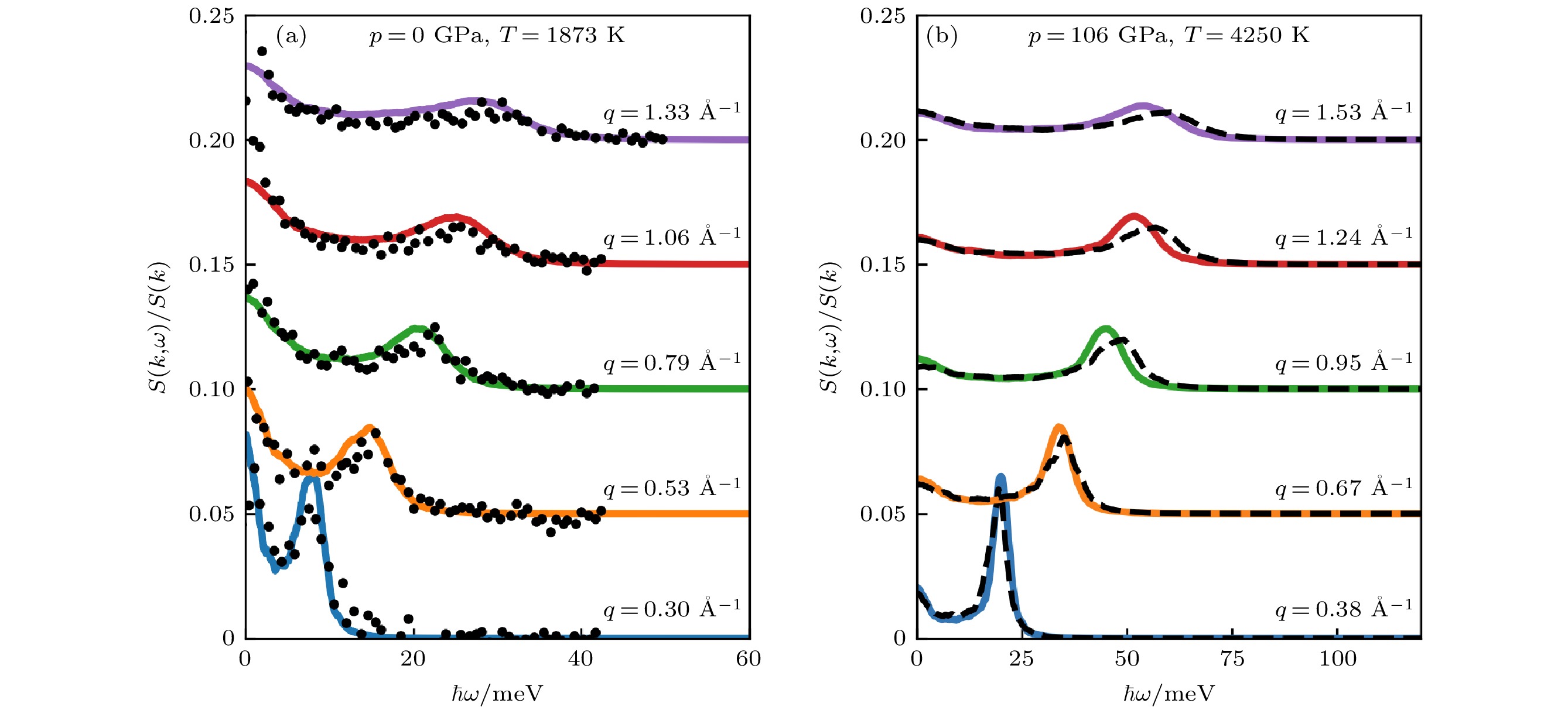
图 4 (a)常压和(b)核幔边界条件下液态铁的动态结构因子, 彩色实线为DPMD计算结果, 黑色圆圈为Hosokawa等[22]的非弹性X射线散射实验测量结果, 黑色虚线为基于Sun等[33]开发的EAM势计算的结果
Figure 4. Dynamic structure factor of liquid iron under (a) ambient pressure condition and (b) core-mantle boundary condition. Colored lines indicate the results from DPMD simulation, the black circles denote the experimental measurements by Hosokawa et al.[22], the black dashed lines denote the CMD simulation with EAM potential developed by Sun et al[33]
图 5 液态铁的扩散系数 (a) p = 0 GPa, T = 1873 K; (b) p = 96 GPa, T = 3800 K; 彩色点为DPMD计算结果, 实线为线性关系的拟合结果, 黑色三角为González等[7]的AIMD计算结果
Figure 5. Self-dissufion coefficient of liquid iron: (a) p = 0 GPa, T = 1873 K; (b) p = 96 GPa, T = 3800 K. Colored circles denote the results from DPMD simulation, colored solid lines denote the fitting curve for removal of size effect, and the balck triangle denotes the previous AIMD calcualtion by González et al[7]
-
[1] Vočadlo L 2015 Treatise on Geophysics 2.06—Earth’s Core: Iron and Iron Alloys (Amsterdam: Elsevier) pp117–147
[2] Dziewonski A M, Anderson D L 1981 Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wagner F W, Sohl F, Hussmann H, Grott M, Rauer H 2011 Icarus 214 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dai J, Kang D, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Yuan J 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 175701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dai J, Hou Y, Kang D, Sun H, Wu J, Yuan J 2013 New J. Phys. 15 045003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Q, Sun T, Zhang Y G, Xian J W, Vocadlo L 2021 J. Chem. Phys. 155 194505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] González L E, González D J 2023 J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 128 e2022JB025119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ramakrishna K, Lokamani M, Baczewski A, Vorberger J, Cangi A 2023 Phys. Rev. B 107 115131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kang D, Zeng Q, Zhang S, Wang X, Dai J 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Behler J, Parrinello M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 146401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bartok A P, Payne M C, Kondor R, Csanyi G 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 136403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Thompson A P, Swiler L P, Trott C R, Foiles S M, Tucker G J 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 285 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang L, Han J, Wang H, Car R, E W 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 143001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang L 2018 arXiv: 180509003 [physics.comp-ph
[15] Zhang Y, Gao C, Liu Q, Zhang L, Wang H, Chen M 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 122704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X, Gao X, Zhao Y, Lin D, Chu W, Song H 2020 Comput. Phys. Commun. 250 107057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zeng Q, Yu X, Yao Y, Gao T, Chen B, Zhang S, Kang D, Wang H, Dai J 2021 Phys. Rev. Research 3 033116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen B, Zeng Q, Wang H, Zhang S, Kang D, Lu D, Dai J 2021 arXiv: 200613136 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci
[19] Chen B, Zeng Q, Yu X, Chen J, Zhang S, Kang D, Dai J 2022 arXiv: 220801830 [astro-ph.EP
[20] Yang F, Zeng Q, Chen B, Kang D, Zhang S, Wu J, Yu X, Dai J 2022 Chin. Phys. Lett. 39 116301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zeng Q, Chen B, Zhang S, Kang D, Wang H, Yu X, Dai J 2023 arXiv: 230813863 [physics.comp-ph
[22] Hosokawa S, Inui M, Matsuda K, Ishikawa D, Baron A Q R 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 174203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kuwayama Y, Morard G, Nakajima Y, Hirose K, Baron A Q R, Kawaguchi S I, Tsuchiya T, Ishikawa D, Hirao N, Ohishi Y 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 165701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Inui M, Maruyama K, Kajihara Y, Nakada M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 180201(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Morard G, Boccato S, Rosa A D, Anzellini S, Miozzi F, Henry L, Garbarino G, Mezouar M, Harmand M, Guyot F, Boulard E, Kantor I, Irifune T, Torchio R 2018 Geophys. Res. Lett. 45 2018GL079950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Perdew J, Burke J, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Holzwarth N, Tackett A, Matthews G 2001 Comput. Phys. Commun. 135 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Marqués M, González L E, González D J 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Marqués M, González L E, González D J 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang H, Zhang L, Han J, E W 2018 Comput. Phys. Commun. 228 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zeng J, Zhang D, Lu D, Mo P, Li Z, Chen Y, Rynik M, Huang L, Li Z, Shi S, Wang Y, Ye H, Tuo P, Yang J, Ding Y, Li Y, Tisi D, Zeng Q, Bao H, Xia Y, Huang J, Muraoka K, Wang Y, Chang J, Yuan F, Bore S L, Cai C, Lin Y, Wang B, Xu J, Zhu J X, Luo C, Zhang Y, Goodall R E A, Liang W, Singh A K, Yao S, Zhang J, Wentzcovitch R, Han J, Liu J, Jia W, York D M, E W, Car R, Zhang L, Wang H 2023 J. Chem. Phys. 159 054801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Sun Y, Zhang F, Mendelev M I, Wentzcovitch R M, Ho K M 2022 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119 e2113059119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8907
- PDF Downloads: 319
- Cited By: 0














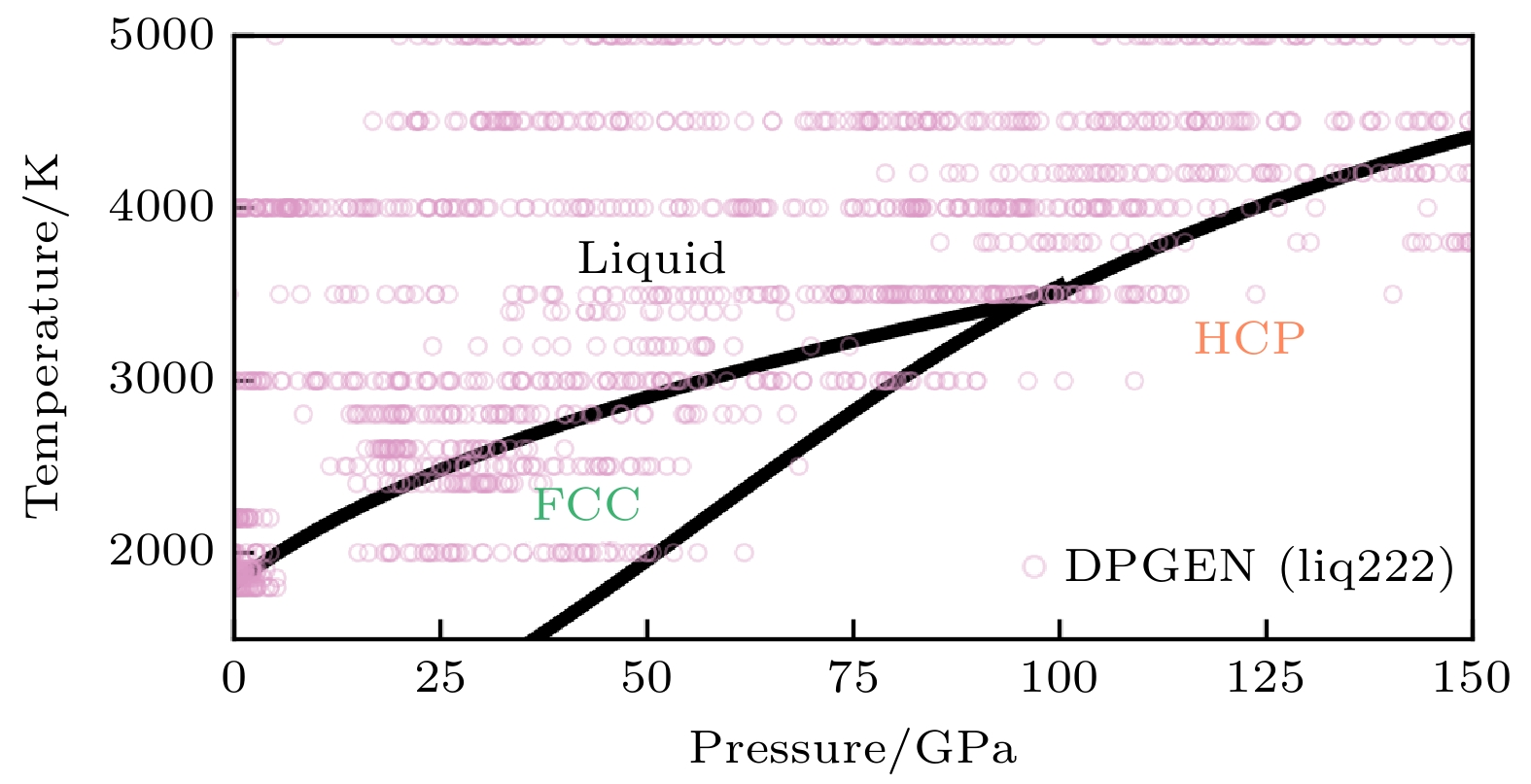
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: