-
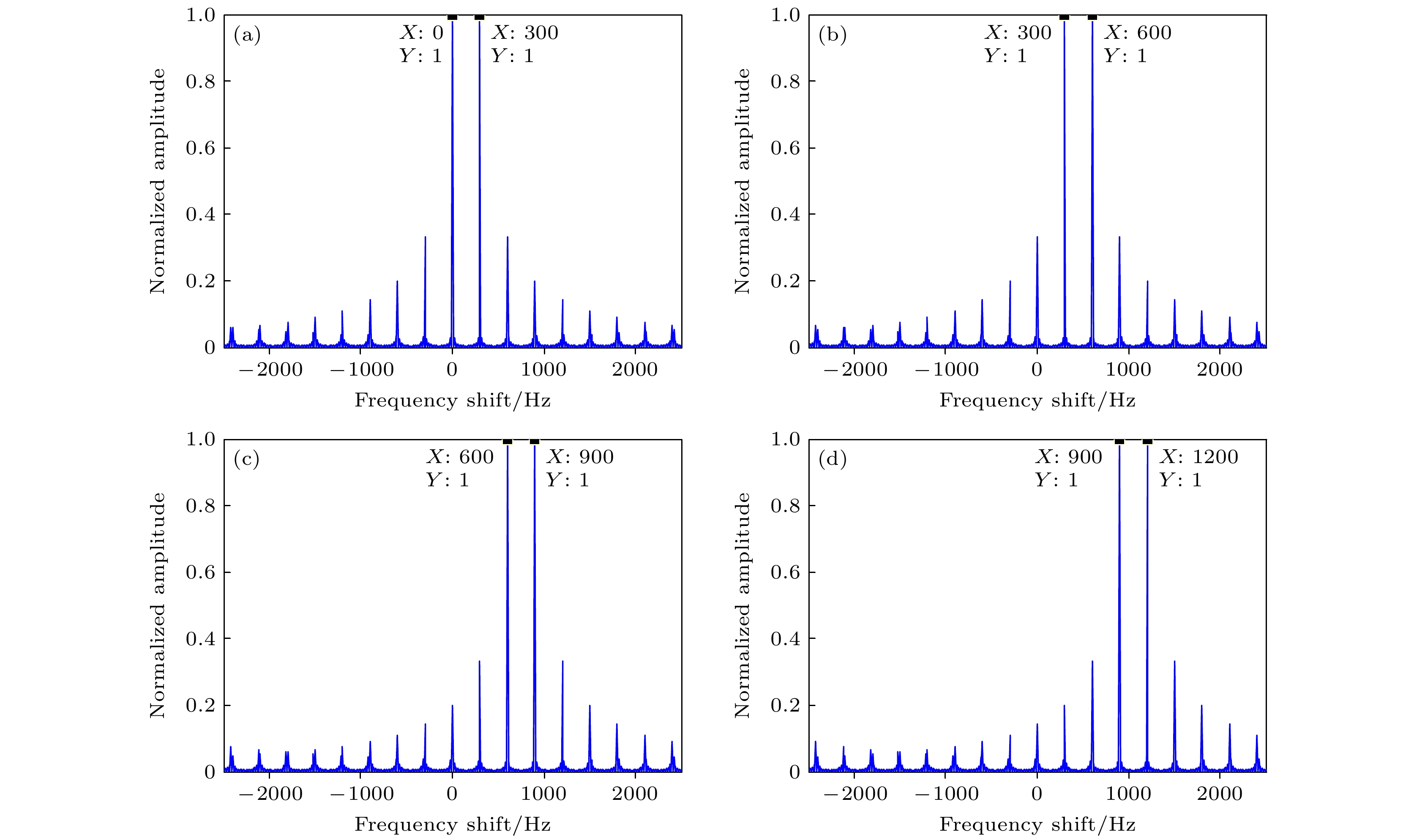
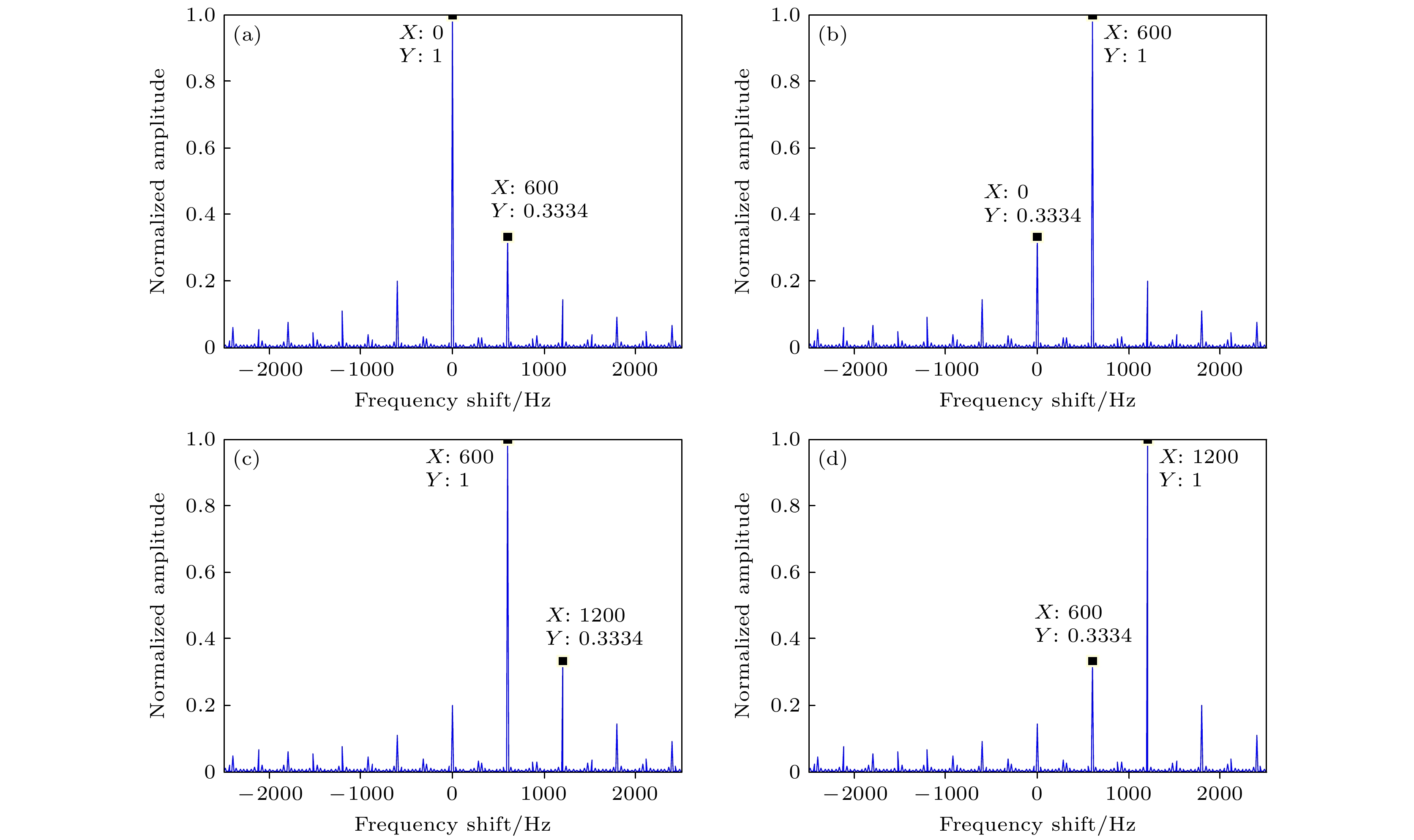
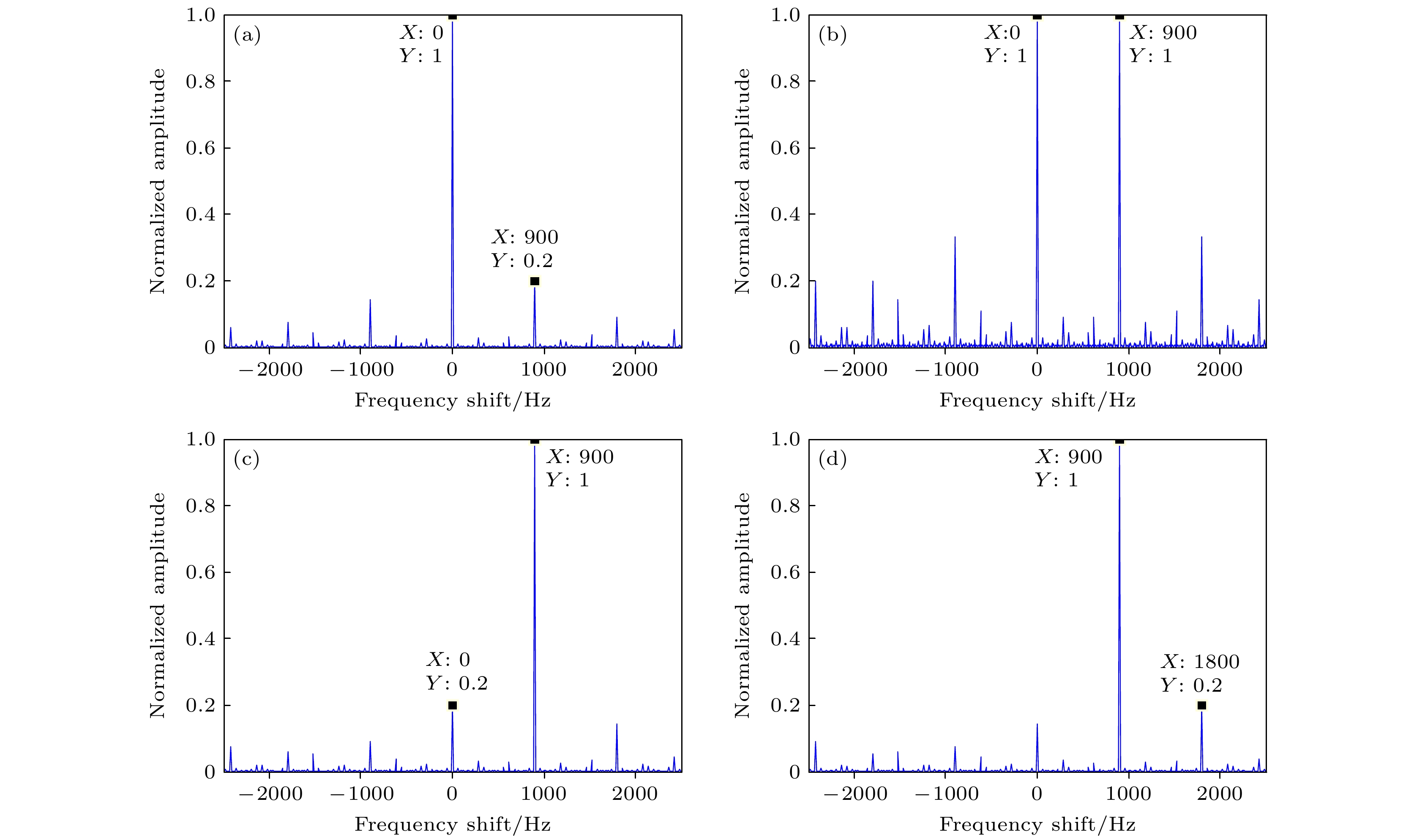
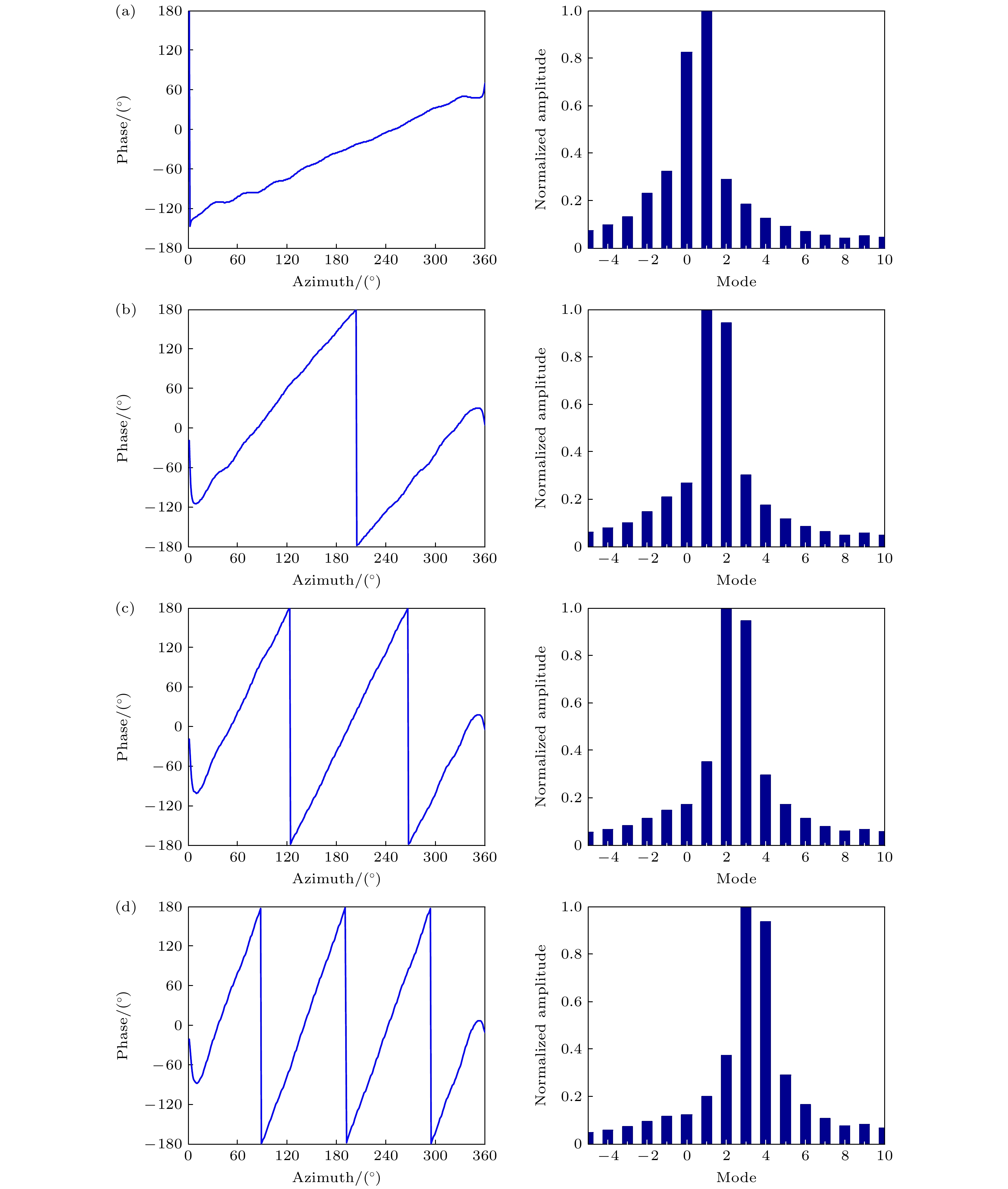
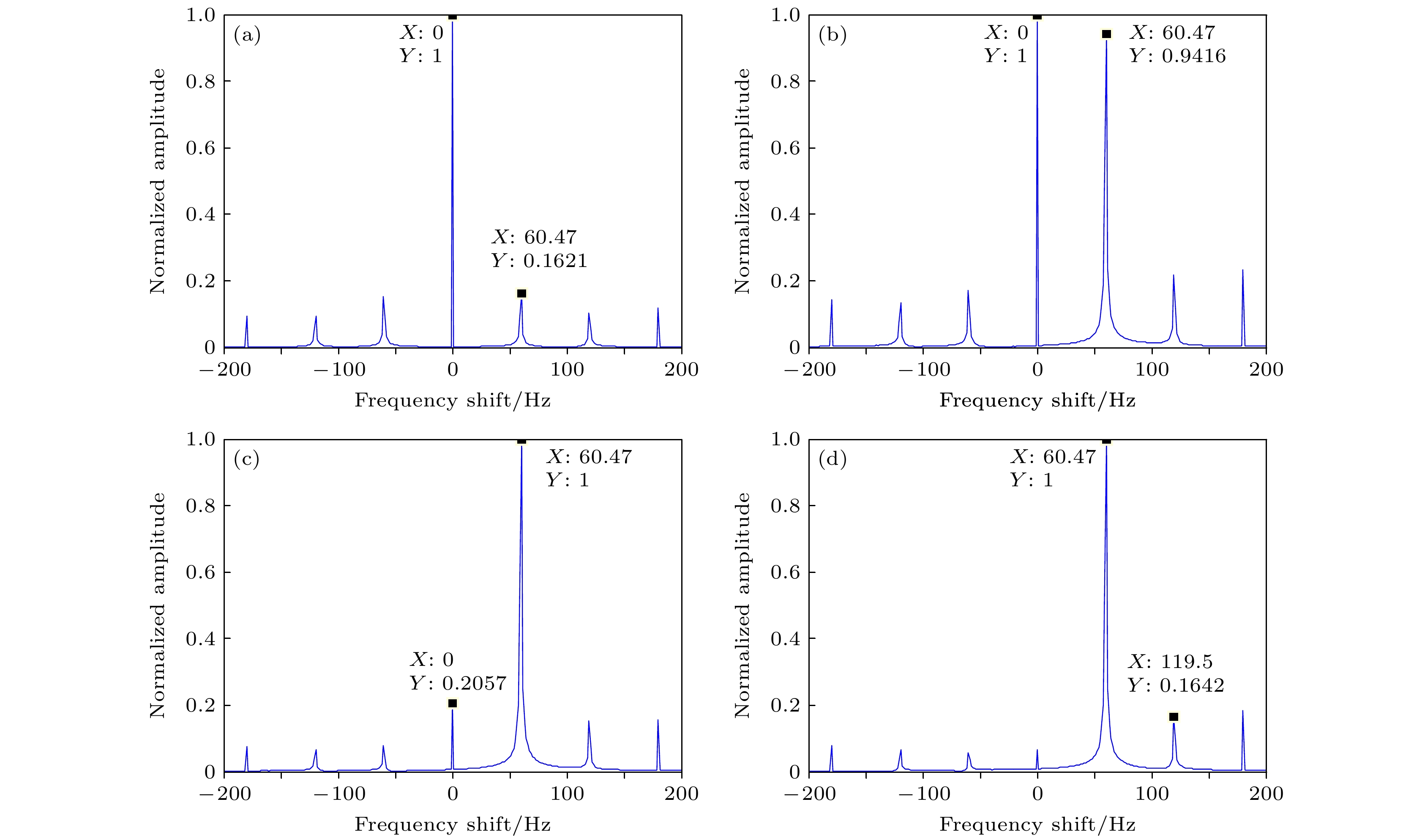
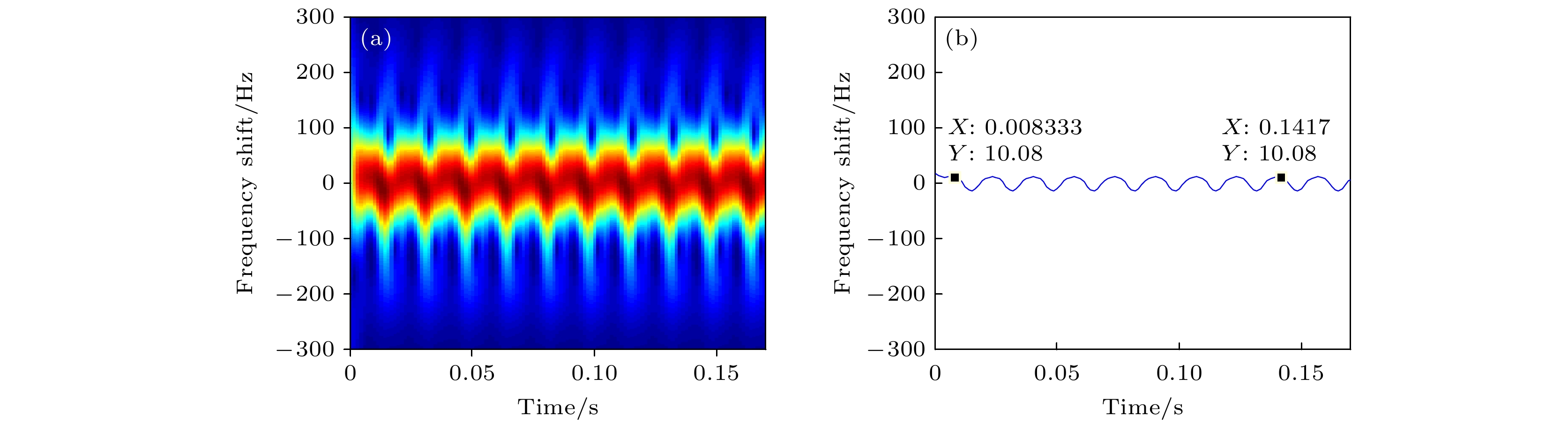
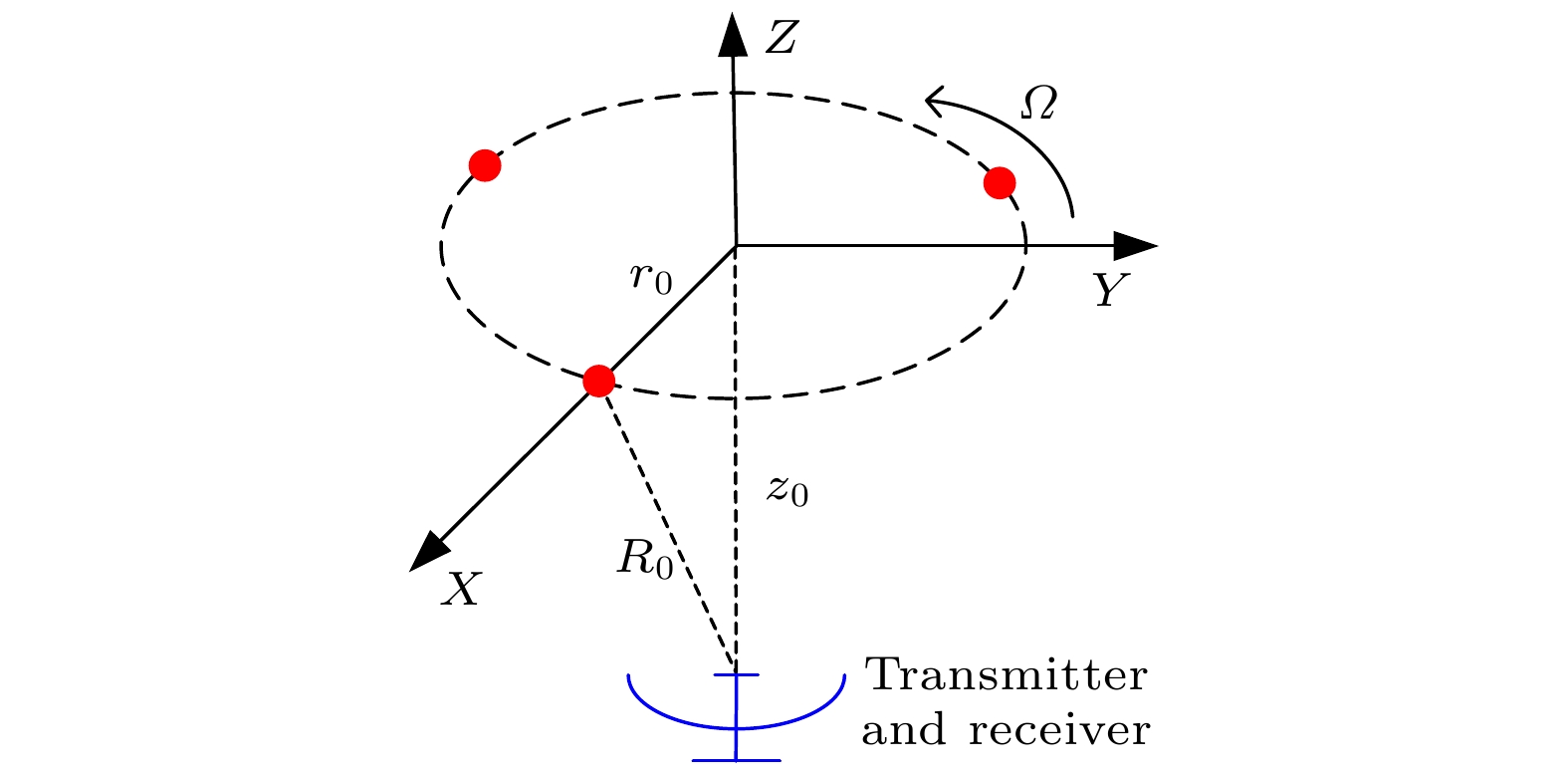
Rotational Doppler effect is an important phenomenon when the vortex electromagnetic wave carrying orbital angular momentum is used to detect a rotating target. Compared with the traditional plane wave case, rotational Doppler effect enables the vortex electromagnetic wave to detect the spin motion along the rotation axis of target. However, there are still some blind zones when the integer orbital angular momentum beams are used to detect specific spinning objects. To expand the application scope of detection scheme based on the rotational Doppler effect, according to the time-frequency analysis, in this paper we study the method of estimating the rotation speed of spinning objects under the normal incidence and oblique incidence of fractional orbital angular momentum beams. Firstly, based on the ideal scattering point model, the echo models are derived under the normal incidence and oblique incidence of integer orbital angular momentum beam and fractional orbital angular momentum beam, respectively, as well as theoretical time-frequency curves. Then taking the three-dimensional practical object for example, the echo under the incidence of fractional orbital angular momentum beams and its time-frequency graph are achieved by using the momentum method and short-time Fourier transform. The time-frequency ridge and its fluctuation period are extracted from the time-frequency graph, thereby estimating the spinning speed of target. The results show that the fractional orbital angular momentum beams can be used to estimate the rotation speed of spinning objects effectively, whether it is normal incidence or oblique incidence, thereby solving the problem about the detection blind zone of integer orbital angular momentum beams, and improving the applicability in detecting spin motion.
-
Keywords:
- rotational Doppler effect /
- fractional orbital angular momentum /
- oblique incidence /
- time-frequency analysis
[1] Allen L, Beijersbergen M W, Spreeuw R J C, Woerdman J P 1992 Phys. Rev. A 45 8185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Courtial J, Dholakia K, Robertson D A, Allen L, Padgett M J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 3217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Courtial J, Robertson D A, Dholakia K, Allen L, Padgett M J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 4828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thide B, Forozesh K, Carozzi T D, Isham B 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yin B H, He Z, Chen R S 2019 Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 34 1637
[6] Thide B, Then H, Sjoholm J, Palmer K, Bergman J, Carozzi, T D, Istomin Ya N, Ibragimov N H, Khamitova R 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 087701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu K, Cheng Y Q, Yang Z C, Wang H Q, Qin Y L, Li X 2015 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 14 711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang C, Chen D, Jiang X F 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 15412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhao M Y, Gao X L, Xie M T, Zhai W S, Xu W J, Huang S G, Gu W Y 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zheng J Y, Zheng S L, Shao Z L, Shao Z L, Zhang X M 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 164907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gong T, Cheng Y Q, Li X, Chen D C 2018 IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon. Lett. 28 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou Z L, Cheng Y Q, Liu K, Wang H Q, Qin Y L 2019 IEEE Sens. Lett. 3 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yin B H, He Z, Chen R S 2022 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70 9971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo Y, Chen Y J, Zhu Y Z, Li W Y, Zhang Q 2019 IET Radar Sonar Navig. 14 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李瑞, 李开明, 张群, 梁佳, 罗迎 2021 电子与信息学报 43 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R, Li K M, Zhang Q, Liang J, Luo Y 2021 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 43 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王煜, 刘康, 王建秋, 王宏强, 程永强 2021 雷达学报 10 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Liu K, Wang J Q, Wang H Q, Cheng Y Q 2021 J. Radars 10 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lavery M P J, Speirits F C, Barnett S M, Padgett M J 2013 Science 431 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zheng S L, Hui X N, Jin X F, Chi H, Zhang X M 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 1530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berry M V 2004 J. Opt. A:Pure Appl. Opt. 6 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu H Y, Wang Y, Wang J Q, Liu K, Wang H Q 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Allen L, Beijersbergen M W, Spreeuw R J C, Woerdman J P 1992 Phys. Rev. A 45 8185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Courtial J, Dholakia K, Robertson D A, Allen L, Padgett M J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 3217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Courtial J, Robertson D A, Dholakia K, Allen L, Padgett M J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 4828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mohammadi S M, Daldorff L K S, Bergman J E S, Karlsson R L, Thide B, Forozesh K, Carozzi T D, Isham B 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yin B H, He Z, Chen R S 2019 Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 34 1637
[6] Thide B, Then H, Sjoholm J, Palmer K, Bergman J, Carozzi, T D, Istomin Ya N, Ibragimov N H, Khamitova R 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 087701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu K, Cheng Y Q, Yang Z C, Wang H Q, Qin Y L, Li X 2015 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 14 711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang C, Chen D, Jiang X F 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 15412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhao M Y, Gao X L, Xie M T, Zhai W S, Xu W J, Huang S G, Gu W Y 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zheng J Y, Zheng S L, Shao Z L, Shao Z L, Zhang X M 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 164907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gong T, Cheng Y Q, Li X, Chen D C 2018 IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon. Lett. 28 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou Z L, Cheng Y Q, Liu K, Wang H Q, Qin Y L 2019 IEEE Sens. Lett. 3 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yin B H, He Z, Chen R S 2022 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70 9971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo Y, Chen Y J, Zhu Y Z, Li W Y, Zhang Q 2019 IET Radar Sonar Navig. 14 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李瑞, 李开明, 张群, 梁佳, 罗迎 2021 电子与信息学报 43 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R, Li K M, Zhang Q, Liang J, Luo Y 2021 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 43 547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王煜, 刘康, 王建秋, 王宏强, 程永强 2021 雷达学报 10 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Liu K, Wang J Q, Wang H Q, Cheng Y Q 2021 J. Radars 10 740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lavery M P J, Speirits F C, Barnett S M, Padgett M J 2013 Science 431 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zheng S L, Hui X N, Jin X F, Chi H, Zhang X M 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 1530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berry M V 2004 J. Opt. A:Pure Appl. Opt. 6 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu H Y, Wang Y, Wang J Q, Liu K, Wang H Q 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4955
- PDF Downloads: 107
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: