-
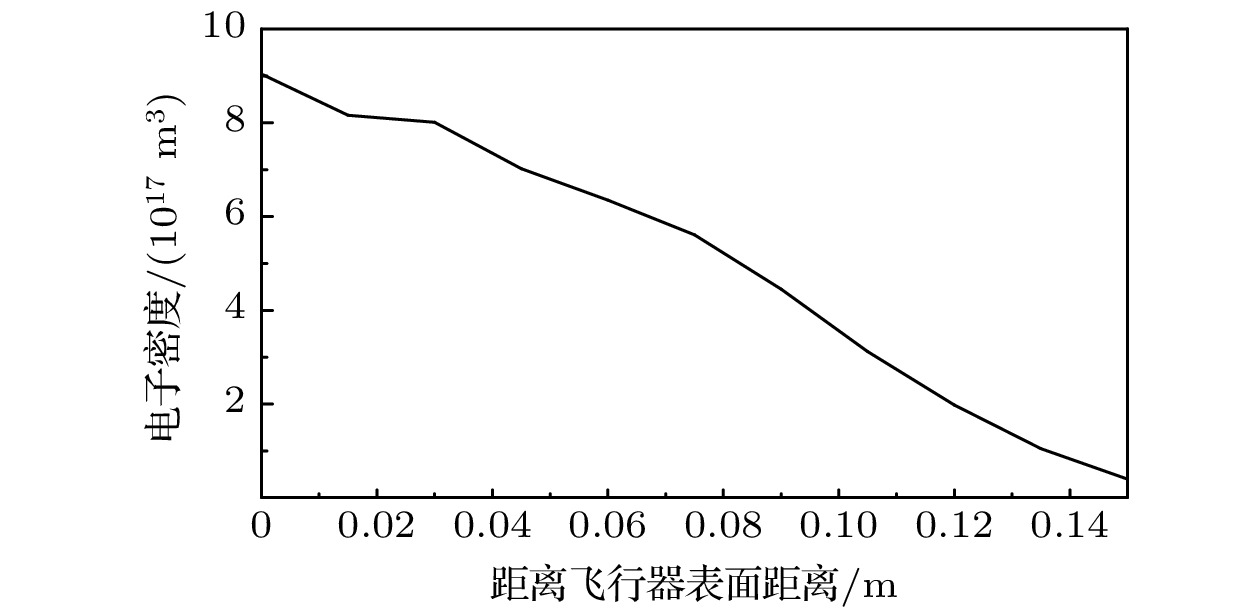
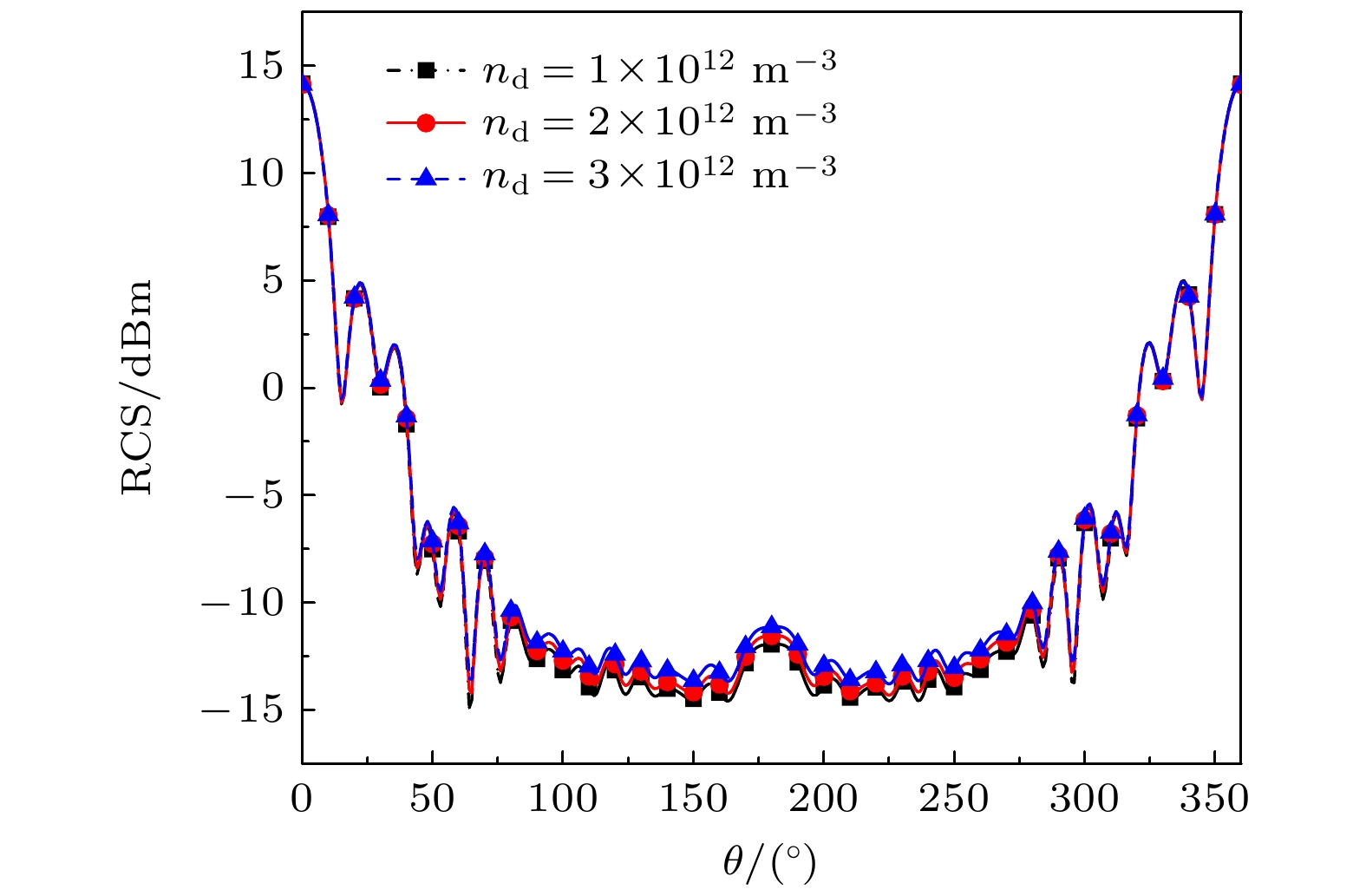
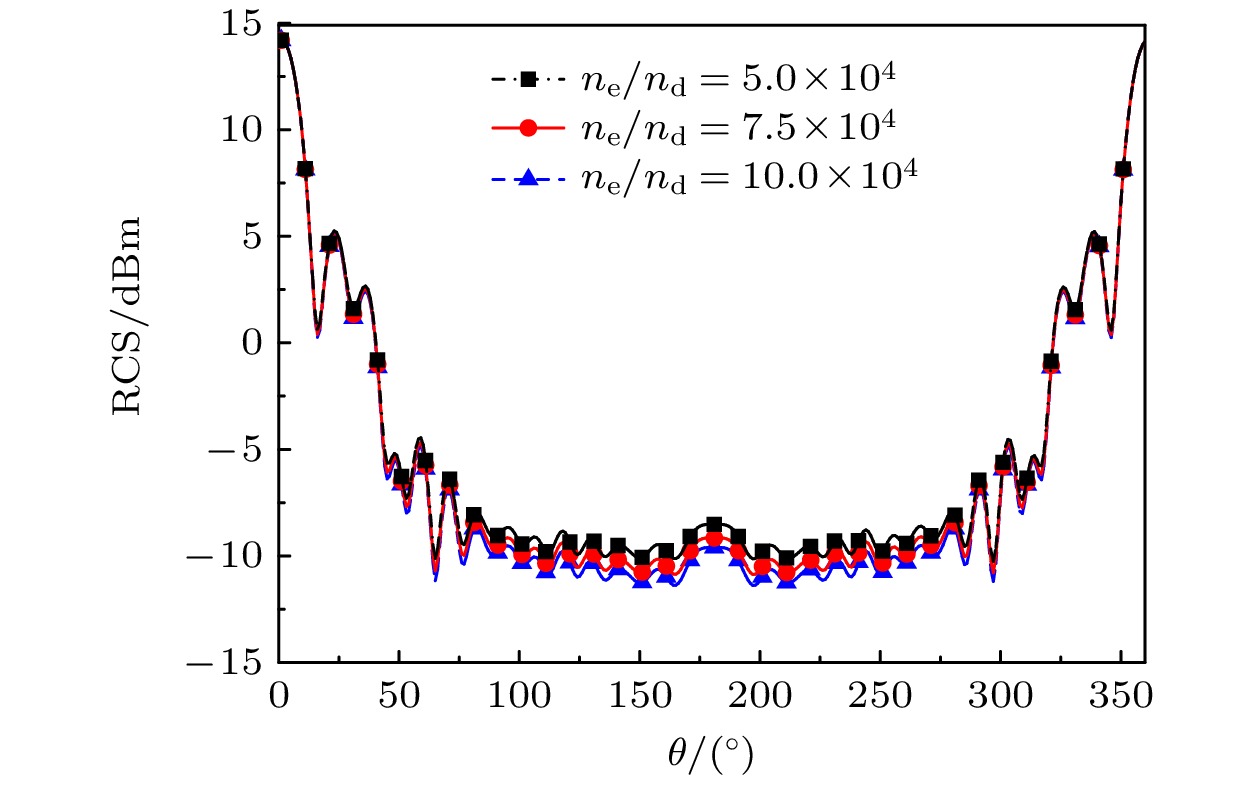
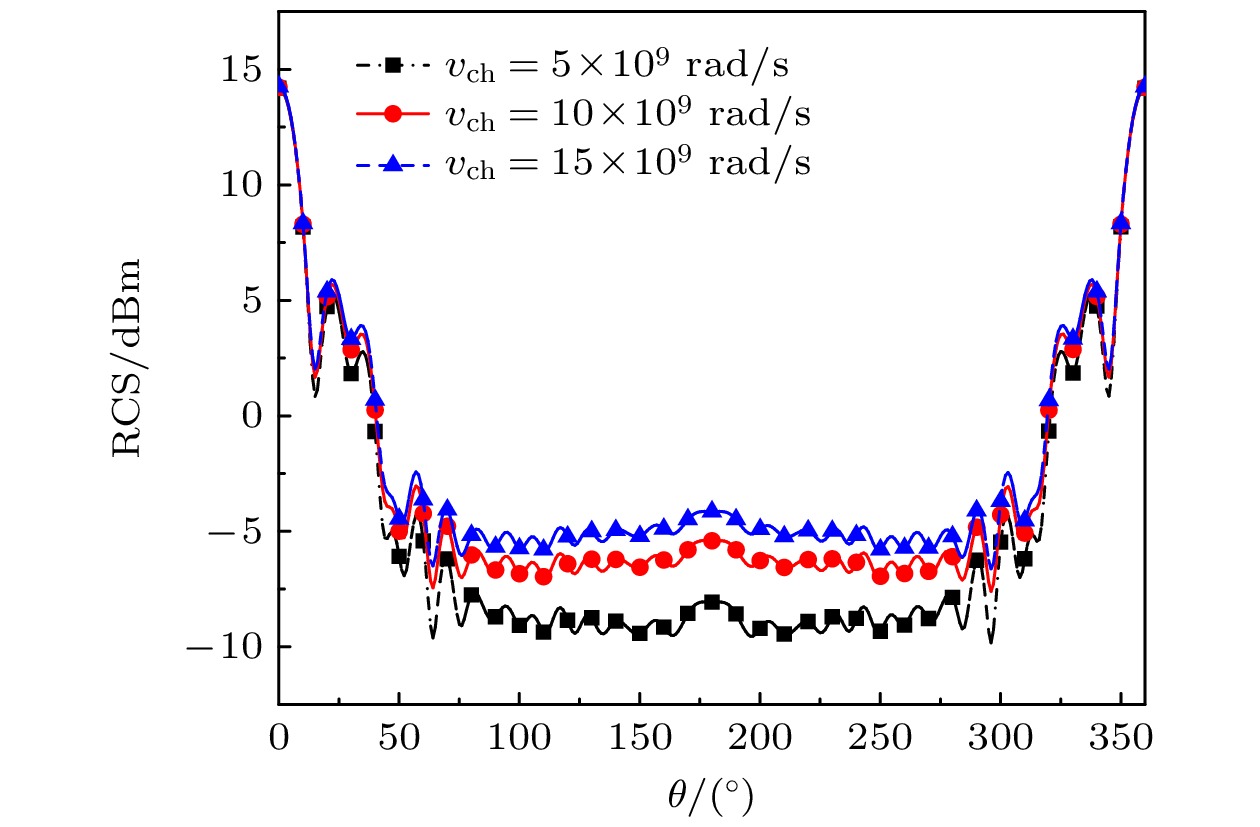
Dusty plasma is a multi-particle system of dust particles suspended in plasma, which is generally composed of free electrons, ions, and dust particles. It is widely found in natural space and aerospace equipment, such as the Earth’s ionosphere, rocket tail flame, and sheath of the hypersonic vehicle. The dust particles will interact with free electrons and ions in the plasma so that the dust particles are charged. They also significantly change the characteristics of dusty plasma, showing some phenomena different from those in ordinary plasma, such as dust acoustic solitary waves and dust void. Electromagnetic (EM) waves will interact with dusty plasma, which results in the attenuation of EM wave signal and the change of phase and other serious effects, and the phenomenon of “blackout” appears. This is very unfavorable for the guidance and control system of the vehicle. The generation of “blackout” is related to the dynamics of dusty plasma and the analysis and research of EM characteristics, so studying the scattering characteristics of dusty plasma is of great significance. First, starting from the Boltzmann equation, the iterative expression of finite-difference time-domain under the Fokker-Planck-Landau (FPL) collision model of fully ionized non-uniform dusty plasma is derived. The expression of the conductivity of the fully ionized dusty plasma under the FPL collision model is obtained by combining the collision effect and charging effect of the dusty plasma. By using the Z-transform finite-difference time-domain method, the radar cross section (RCS) of the dusty plasma coated metal blunt cone in two dimensions is calculated. The effects of dust particle density, dust particle radius, ratio of electron density to dust particle density, dust particle charging frequency, and EM wave incident angle on the scattering characteristics of the mental blunt cone are analyzed. The results show that the Debye shielding effect is weakened and RCS is increased with the increase of the radius of dust particles in the fully ionized non-uniform dusty plasma. In addition, it is affected by the collision effect and charging effect of dusty plasma, which will have a great influence on the RCS of the target. These results provide a theoretical basis for studying the EM waves scattering problem of fully ionized non-uniform dusty plasma and the communication problems in near space.
-
Keywords:
- Boltzmann equation /
- dusty plasma /
- Z-transform finite-difference time-domain method /
- radar cross section
[1] 孙俊国, 张宗国, 董焕河, 杨红卫 2019 68 210201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J G, Zhang Z G, Dong H H, Yang H W 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 210201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z Y, Guo L X, Li J T 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 045203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yan J, Feng F, Liu F C, Dong L F, He Y F 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 林麦麦, 付颖捷, 宋秋影, 于腾萱, 文惠珊, 蒋蕾 2022 71 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin M M, Fu Y J, Song Q Y, Yu T X, Wen H S, Jiang L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 黄峰, 叶茂福, 王龙 2004 科学通报 49 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang F, Ye M F, Wang L 2004 Chin. Sci. Bull. 49 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 崔平远, 窦强, 高艾 2014 宇航学报 35 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui P Y, Dou Q, Gao A 2014 J. Astr. 35 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tsytovich V N 2015 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 55 664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sotnikov V I, Leboeuf J N, Mudaliar S 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 2208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Motie I, Bokaeeyan M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 023707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 金铭, 韦笑, 吴洋, 张羽淮, 余西龙 2015 64 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin M, Wei X, Wu Y, Zhang Y H, Yu X L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo L X, Chen W, LI J T, Ren Y, Liu S H 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 053707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dan L, Guo L X, Li J T 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 013707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dan L, Gou L X, Li J T, Chen W, Yan X, Huang Q Q 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 093703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mousseau V A, Knoll D A 1997 J. Comput. Phys. 136 308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li H, Wu J, Zhou Z, Yuan C 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 073702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bendib A, Bendib-Kalache K, Cros B, Maynard G 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 043208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bendib A, Bendib K, Sid A 1997 Phys. Rev. E 55 7522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jia J S, Yuan C X, Liu S, Yue F, Gao R L, Wang Y, Zhou Z X, Wu J, Li H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 043302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 葛德彪, 闫玉波 2011 电磁波时域有限差分方法 (第三版) (西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社) 第259页
Ge D B, Yan Y B 2011 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves (3rd Ed.) (Xi’an: Xidian University Press) p259 (in Chinese)
[20] 魏兵, 葛德彪, 王飞 2008 57 6290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei B, Ge D B, Wang F 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ren Y, Guo L X, Chen W, Liu S H 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 093515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王飞, 魏兵 2013 62 084106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F, Wei B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Demarest K, Huang Z B, Plumb R 1996 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 44 1150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Britt C L 1989 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 37 1181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang H F, Li J T, Bian Z, Guo L X 2022 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 50 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu S H, Zhu C K, Guo L X, Li J T, Dan L, Wang Z Y 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 023701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 等离子体与尘埃等离子体相关参数
Table 1. Related parameters of plasma and dusty plasma.
参数 等离子体 尘埃等离子体 $n_{\text{d}}/(10^{12}~\text{m}^{-3})$ 0 1 $r_{\text{d}} /{\text{μ}{\rm m}}$ 0 5 $T_{\rm e}/(10^{4}~\text{K})$ 1 1 ${\varphi /{\left( {^\circ } \right)} }$ 0 0 表 2 全电离尘埃等离子体的计算参数
Table 2. Calculated parameters of fully ionized dusty plasma.
-
[1] 孙俊国, 张宗国, 董焕河, 杨红卫 2019 68 210201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J G, Zhang Z G, Dong H H, Yang H W 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 210201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z Y, Guo L X, Li J T 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 045203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yan J, Feng F, Liu F C, Dong L F, He Y F 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 林麦麦, 付颖捷, 宋秋影, 于腾萱, 文惠珊, 蒋蕾 2022 71 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin M M, Fu Y J, Song Q Y, Yu T X, Wen H S, Jiang L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 095203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 黄峰, 叶茂福, 王龙 2004 科学通报 49 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang F, Ye M F, Wang L 2004 Chin. Sci. Bull. 49 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 崔平远, 窦强, 高艾 2014 宇航学报 35 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui P Y, Dou Q, Gao A 2014 J. Astr. 35 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tsytovich V N 2015 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 55 664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sotnikov V I, Leboeuf J N, Mudaliar S 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 2208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Motie I, Bokaeeyan M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 023707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 金铭, 韦笑, 吴洋, 张羽淮, 余西龙 2015 64 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin M, Wei X, Wu Y, Zhang Y H, Yu X L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo L X, Chen W, LI J T, Ren Y, Liu S H 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 053707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dan L, Guo L X, Li J T 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 013707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dan L, Gou L X, Li J T, Chen W, Yan X, Huang Q Q 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 093703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mousseau V A, Knoll D A 1997 J. Comput. Phys. 136 308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li H, Wu J, Zhou Z, Yuan C 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 073702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bendib A, Bendib-Kalache K, Cros B, Maynard G 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 043208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bendib A, Bendib K, Sid A 1997 Phys. Rev. E 55 7522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Jia J S, Yuan C X, Liu S, Yue F, Gao R L, Wang Y, Zhou Z X, Wu J, Li H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 043302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 葛德彪, 闫玉波 2011 电磁波时域有限差分方法 (第三版) (西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社) 第259页
Ge D B, Yan Y B 2011 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves (3rd Ed.) (Xi’an: Xidian University Press) p259 (in Chinese)
[20] 魏兵, 葛德彪, 王飞 2008 57 6290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei B, Ge D B, Wang F 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ren Y, Guo L X, Chen W, Liu S H 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 093515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王飞, 魏兵 2013 62 084106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F, Wei B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Demarest K, Huang Z B, Plumb R 1996 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 44 1150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Britt C L 1989 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 37 1181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang H F, Li J T, Bian Z, Guo L X 2022 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 50 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu S H, Zhu C K, Guo L X, Li J T, Dan L, Wang Z Y 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 023701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6614
- PDF Downloads: 93
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: