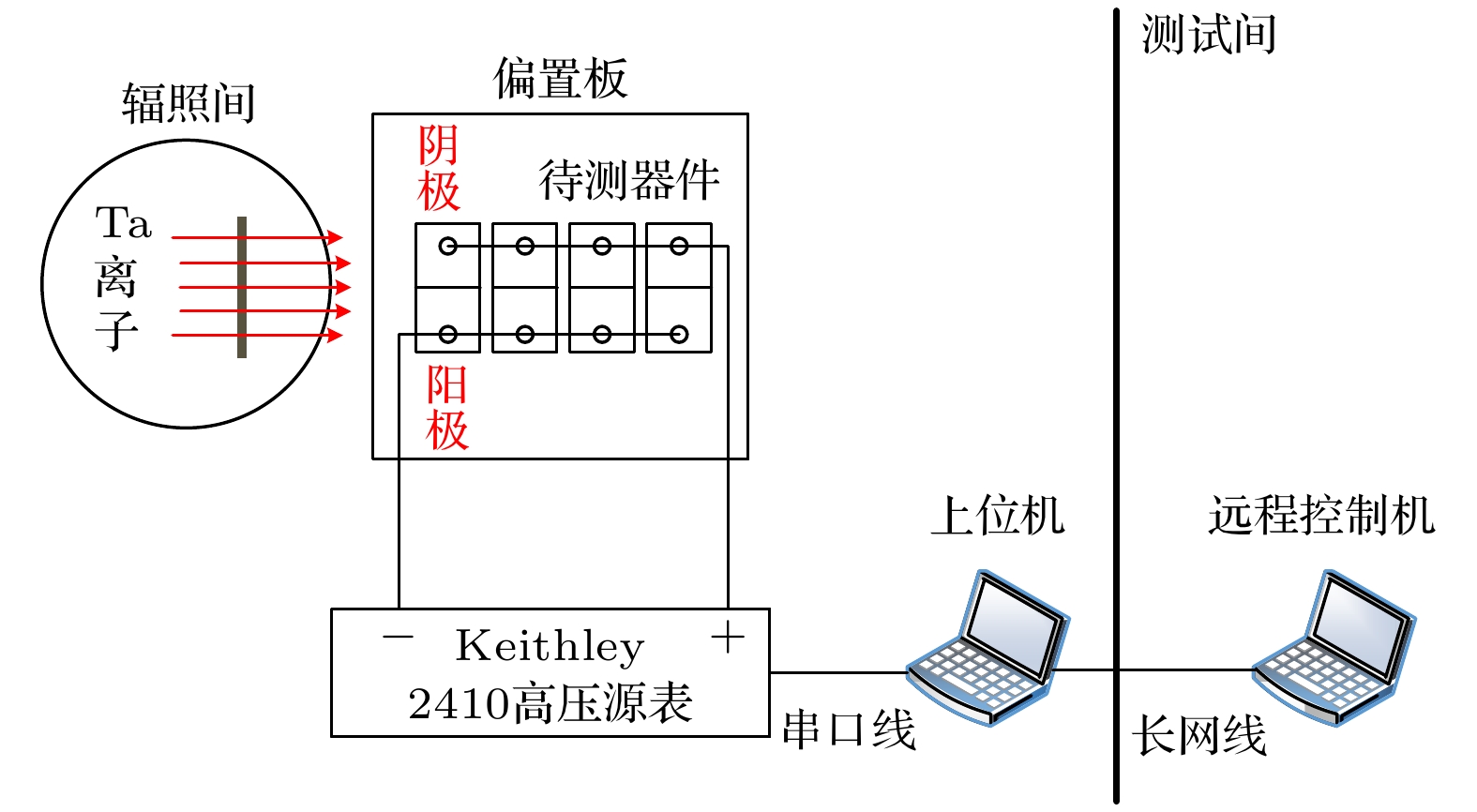
-
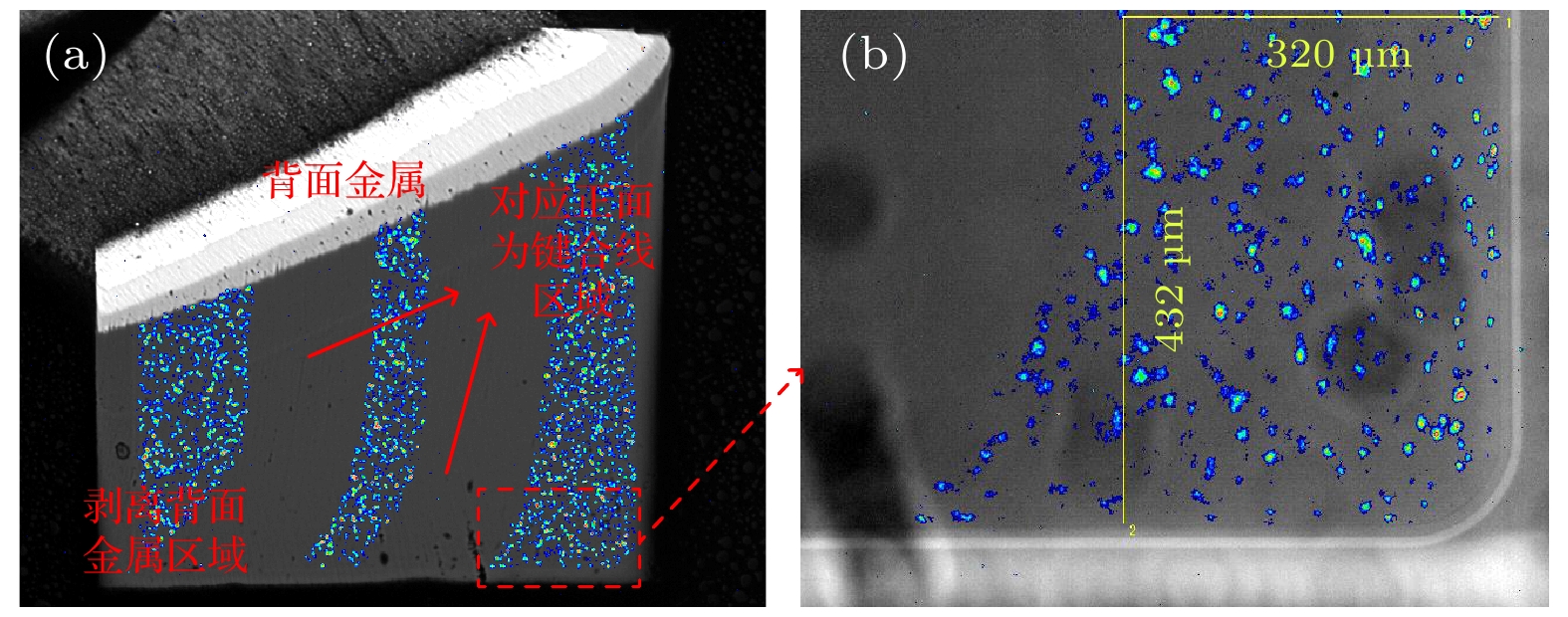
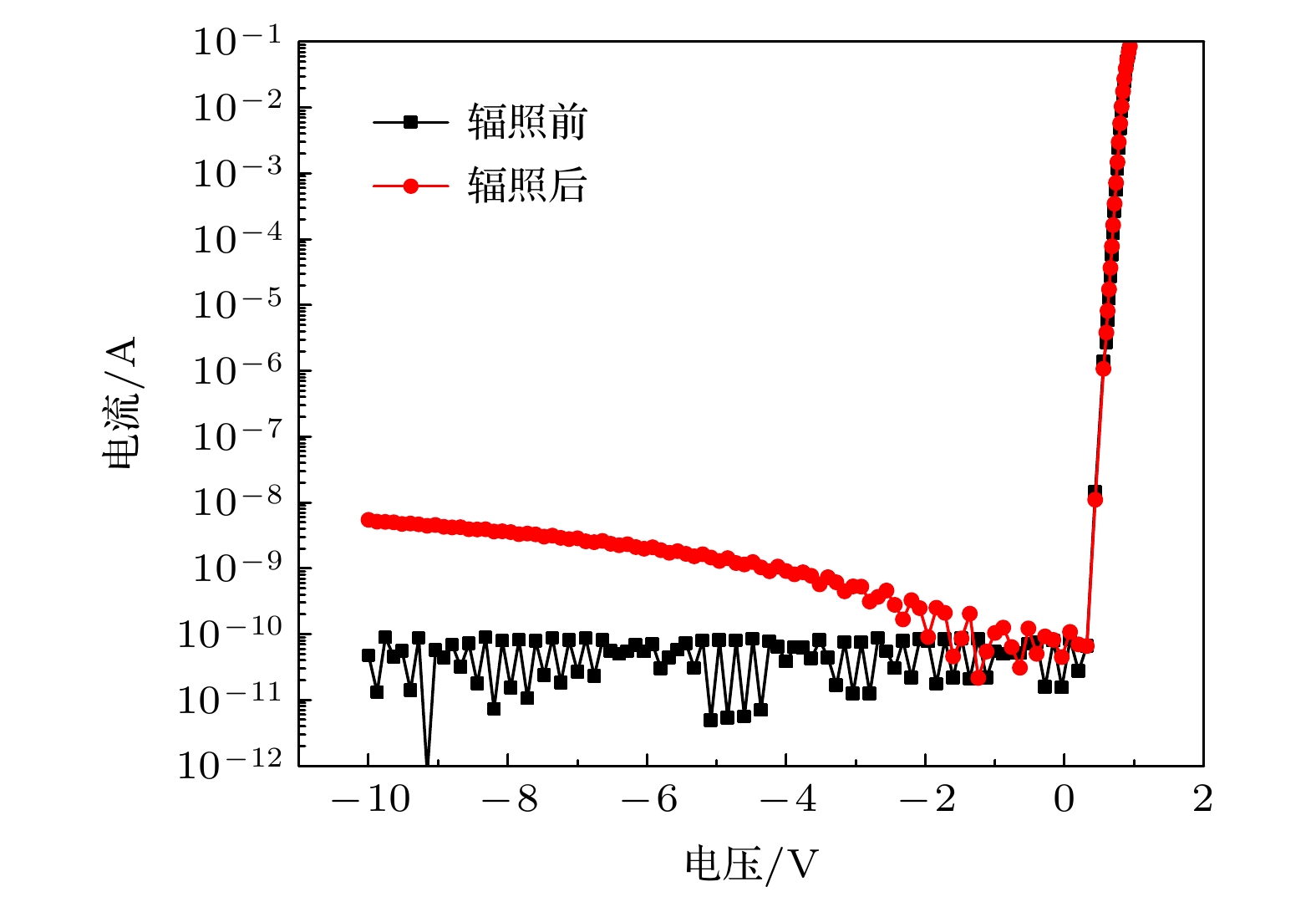
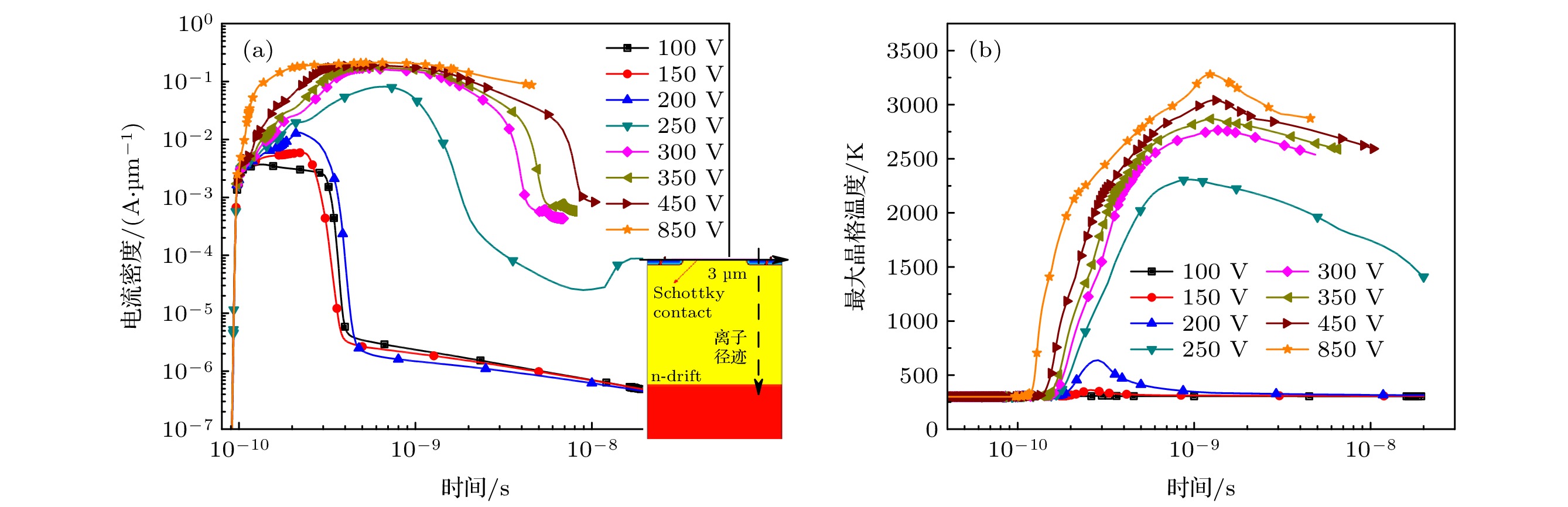
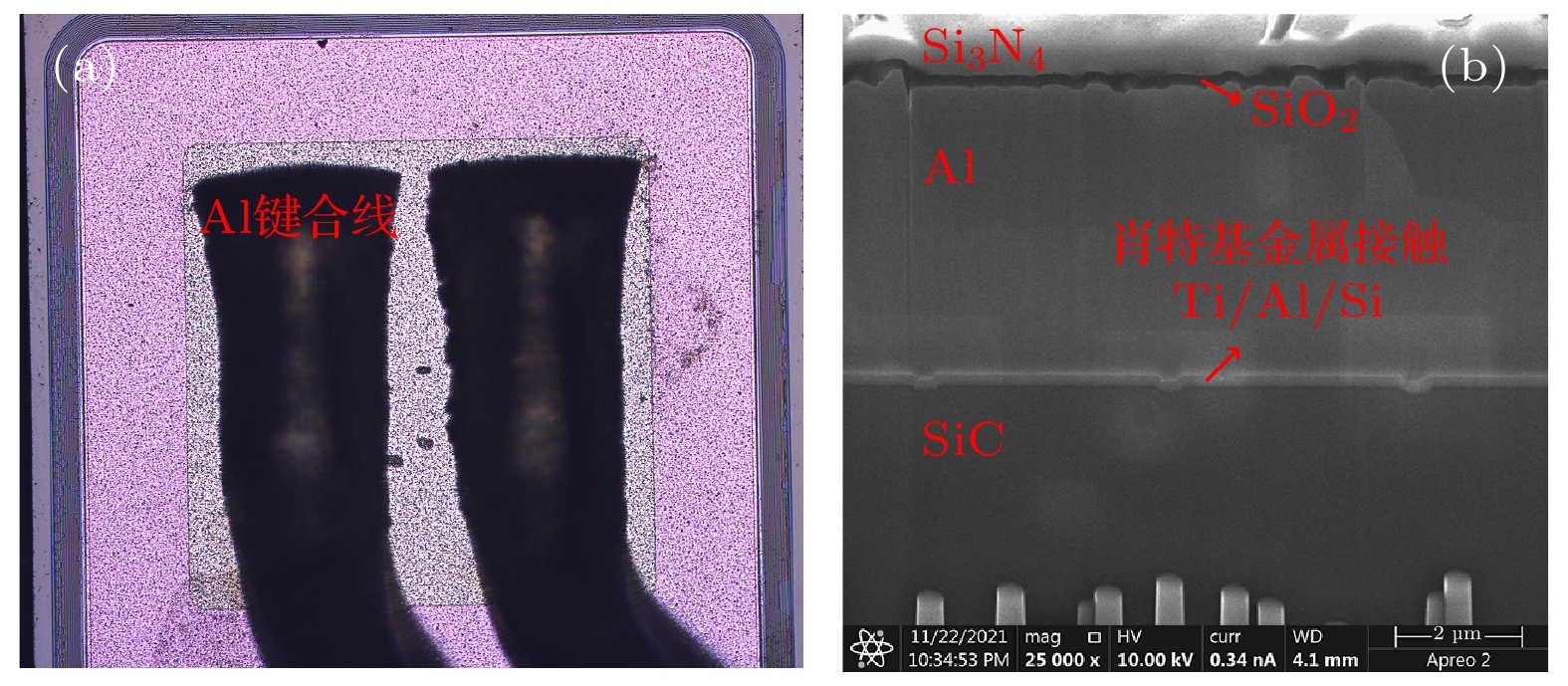
In this paper, the failure mode and mechanism of silicon carbide (SiC) Schottky barrier diode (SBD) irradiated by high-energy tantalum (Ta) ions are studied. The experimental results show that the reverse bias voltage during irradiation is the key factor causing the failure of SiC SBDs. When the reverse bias of the device is 400 V, the heavy ions will cause the single event burnout (SEB), and a “hole” formed by the melting of SiC material appears in the irradiated device. When the reverse bias is 250–300 V, the failure is manifested as the off state leakage current increases with the ion fluence. The higher the bias voltage of the device, the higher the leakage increase rate caused by heavy ions. For the devices with increased leakage, the leakage channels caused by heavy ions are found in the whole active region, based on microscopic analysis. The TCAD simulation results show that the incidence of heavy ions will lead the lattice temperature to increase in the device, and the maximum lattice temperature increases with bias voltage increasing. When the bias voltage is large enough, the local lattice temperature inside the device reaches the melting point of SiC material, resulting in SEB. When the bias voltage is relatively low, the lattice temperature is lower than the melting point of SiC material, so it will not cause burnout. However, the maximum lattice temperature in the device is concentrated near the Schottky junction, and the melting point of Schottky metal is much lower than that of SiC material. This may lead the Schottky junction to damage locally and eventually produce leakage path.
-
Keywords:
- SiC power device /
- Schottky barrier diode /
- heavy ion radiation effect
[1] Casady J B, Johnson R W 1996 Solid-State Electron. 39 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kimoto T, Cooper J A 2014 Fundamentals of Silicon Carbide Technology: Growth, Characterization, Devices and Applications (Singapore: John Wiley & Sons Press) p16
[3] 张林, 肖剑, 邱彦章, 程鸿亮 2011 60 056106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L, Xiao J, Qiu Y Z, Cheng H L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 056106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ino K, Miura M, Nakano Y, Aketa M, Kawamoto N 2019 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC) Xi'an, China, June 12–14 2019 p1
[5] 张鸿, 郭红霞, 潘霄宇, 雷志锋, 张凤祁, 顾朝桥, 柳奕天, 琚安安, 欧阳晓平 2021 70 162401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Guo H X, Pan X Y, Lei Z F, Zhang F Q, Gu Z Q, Liu Y T, Ju A A, Ouyang X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 162401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yu C H, Wang Y, Bao M T, Li X J, Yang J Q, Tang Z H 2021 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 68 5034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu C H, Wang Y, Li X J, Liu C M, Luo X, Cao F 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 65 5434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] McPherson J A, Kowal P J, Pandey G K, Chow T P, Ji W, Woodworth A A 2019 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 66 474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ball D R, Hutson J M, Javanainen A, Lauenstein J M, Galloway K F, Johnson R A, Alles M L, Sternberg A L, Sierawski B D, Witulski A F, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Akturk A, McGarrity J M, Goldsman N, Lichtenwalner D, Hull B, Grider D, Wilkins R 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Witulski A F, Ball D R, Galloway K F, Javanainen A, Lauenstein J M, Sternberg A L, Schrimpf R D 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou X, Jia Y, Hu D, Wu Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 66 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Soelkner G, Kaindl W, Treu M, Peters D 2007 Mater. Sci. Forum 556 851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Martinella C, Natzke P, Alia R G, Kadi Y, Niskanen K, Rossi M, Jaatinen J, Kettunen H, Tsibizov A, Grossner U, Javanainen A 2022 Microelectron. Rel. 128 114423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Martinella C, Ziemann T, Stark R, Tsibizov A, Voss K O, Alia R G, Kadi Y, Grossner U, Javanainen A 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Javanainen A, Galloway K F, Nicklaw C, Bosser A L, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Lauenstein J M, Pintacuda F, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Weller R A, Virtanen A 2017 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 64 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mizuta E, Kuboyama S, Abe H, Iwata Y, Tamura T 2014 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 61 1924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Javanainen A, Muinos H V, Nordlund K, Djurabekova F, Galloway K F, Turowski M, Schrimpf R D 2018 IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 18 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 于庆奎, 张洪伟, 孙毅, 梅博, 魏志超, 李晓亮, 王贺, 吕贺, 李鹏伟, 曹爽, 唐民 2019 现代应用物理 10 010602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Q K, Zhang H W, Sun Y, Mei B, Wei Z C, Li X L, Wang H, Li P W, Cao S, Tang M 2019 Modern Appl. Phys. 10 010602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Synopsys 2014 Sentaurus Device User Guide (Mountain View, CA: Synopsys Inc.) p53
[22] Shoji T, Nishida S, Hamada K, Tadano H 2014 Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 53 04EP03
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Casady J B, Johnson R W 1996 Solid-State Electron. 39 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kimoto T, Cooper J A 2014 Fundamentals of Silicon Carbide Technology: Growth, Characterization, Devices and Applications (Singapore: John Wiley & Sons Press) p16
[3] 张林, 肖剑, 邱彦章, 程鸿亮 2011 60 056106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L, Xiao J, Qiu Y Z, Cheng H L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 056106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ino K, Miura M, Nakano Y, Aketa M, Kawamoto N 2019 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC) Xi'an, China, June 12–14 2019 p1
[5] 张鸿, 郭红霞, 潘霄宇, 雷志锋, 张凤祁, 顾朝桥, 柳奕天, 琚安安, 欧阳晓平 2021 70 162401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Guo H X, Pan X Y, Lei Z F, Zhang F Q, Gu Z Q, Liu Y T, Ju A A, Ouyang X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 162401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yu C H, Wang Y, Bao M T, Li X J, Yang J Q, Tang Z H 2021 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 68 5034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu C H, Wang Y, Li X J, Liu C M, Luo X, Cao F 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 65 5434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] McPherson J A, Kowal P J, Pandey G K, Chow T P, Ji W, Woodworth A A 2019 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 66 474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ball D R, Hutson J M, Javanainen A, Lauenstein J M, Galloway K F, Johnson R A, Alles M L, Sternberg A L, Sierawski B D, Witulski A F, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Akturk A, McGarrity J M, Goldsman N, Lichtenwalner D, Hull B, Grider D, Wilkins R 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Witulski A F, Ball D R, Galloway K F, Javanainen A, Lauenstein J M, Sternberg A L, Schrimpf R D 2018 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 65 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou X, Jia Y, Hu D, Wu Y 2019 IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 66 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Soelkner G, Kaindl W, Treu M, Peters D 2007 Mater. Sci. Forum 556 851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Martinella C, Natzke P, Alia R G, Kadi Y, Niskanen K, Rossi M, Jaatinen J, Kettunen H, Tsibizov A, Grossner U, Javanainen A 2022 Microelectron. Rel. 128 114423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Martinella C, Ziemann T, Stark R, Tsibizov A, Voss K O, Alia R G, Kadi Y, Grossner U, Javanainen A 2020 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 67 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Javanainen A, Galloway K F, Nicklaw C, Bosser A L, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Lauenstein J M, Pintacuda F, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Weller R A, Virtanen A 2017 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 64 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mizuta E, Kuboyama S, Abe H, Iwata Y, Tamura T 2014 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 61 1924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Javanainen A, Muinos H V, Nordlund K, Djurabekova F, Galloway K F, Turowski M, Schrimpf R D 2018 IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 18 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 于庆奎, 张洪伟, 孙毅, 梅博, 魏志超, 李晓亮, 王贺, 吕贺, 李鹏伟, 曹爽, 唐民 2019 现代应用物理 10 010602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Q K, Zhang H W, Sun Y, Mei B, Wei Z C, Li X L, Wang H, Li P W, Cao S, Tang M 2019 Modern Appl. Phys. 10 010602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Synopsys 2014 Sentaurus Device User Guide (Mountain View, CA: Synopsys Inc.) p53
[22] Shoji T, Nishida S, Hamada K, Tadano H 2014 Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 53 04EP03
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9437
- PDF Downloads: 165
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: