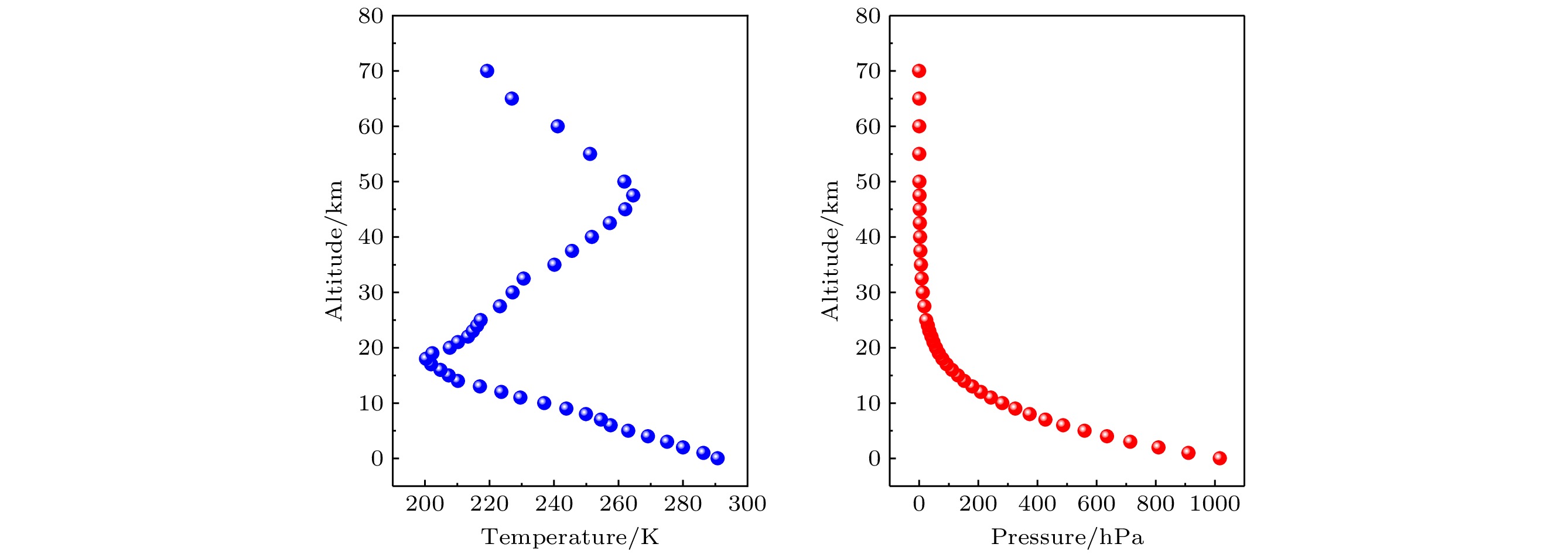
-
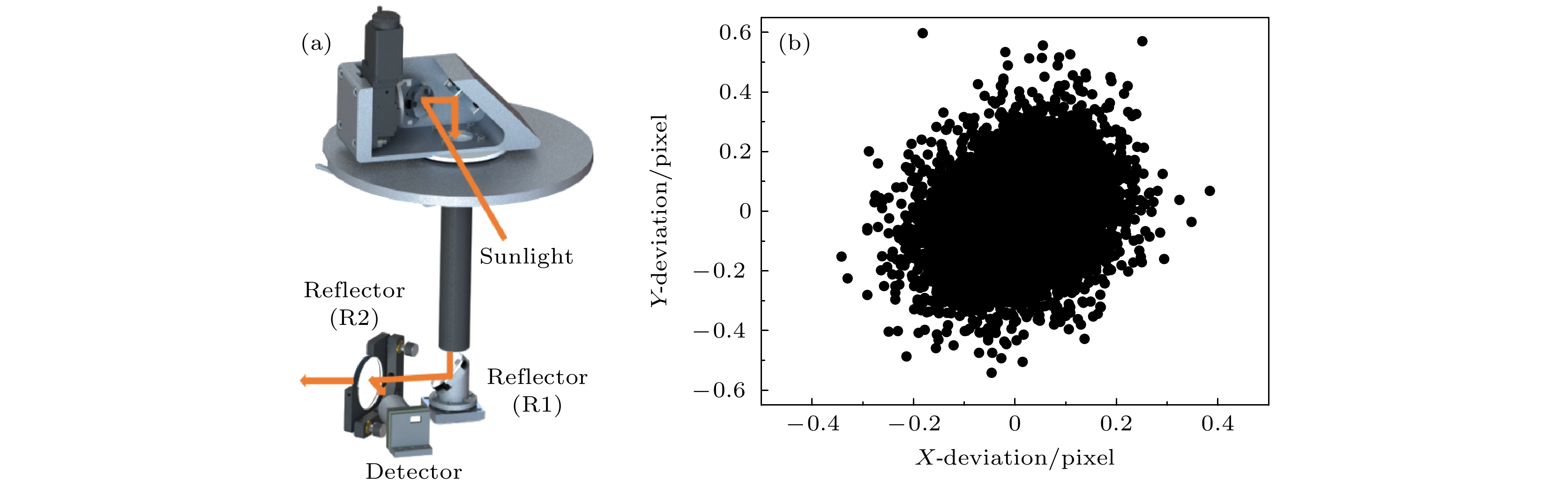
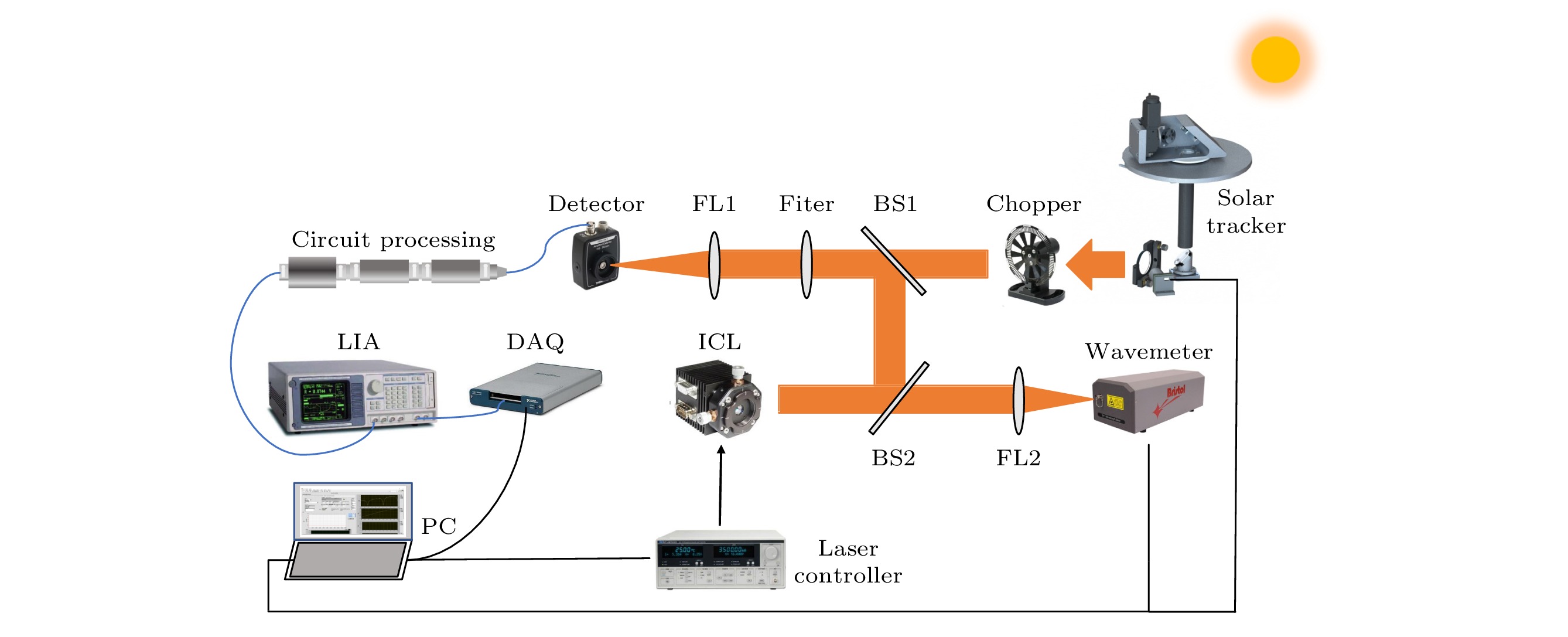
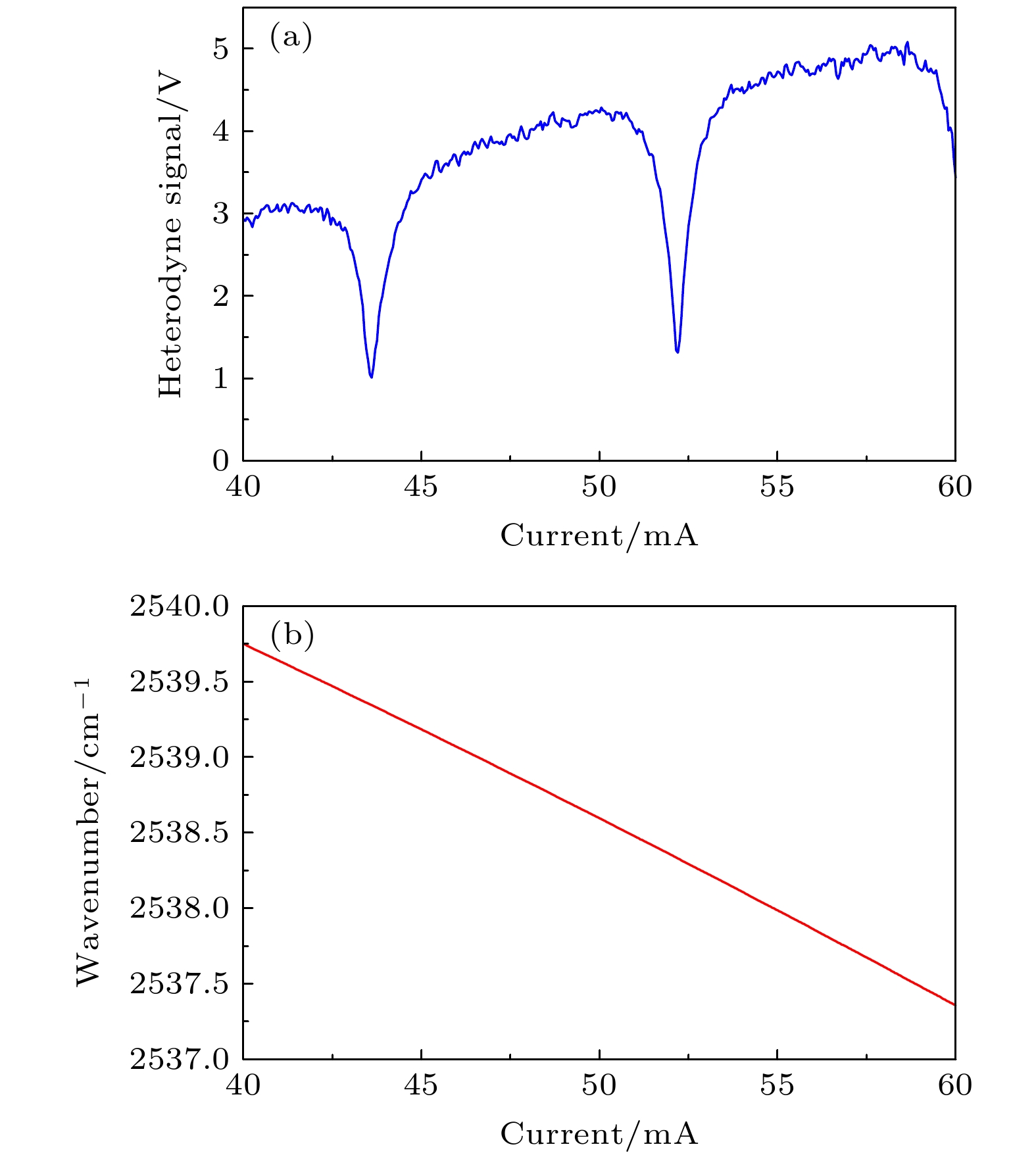
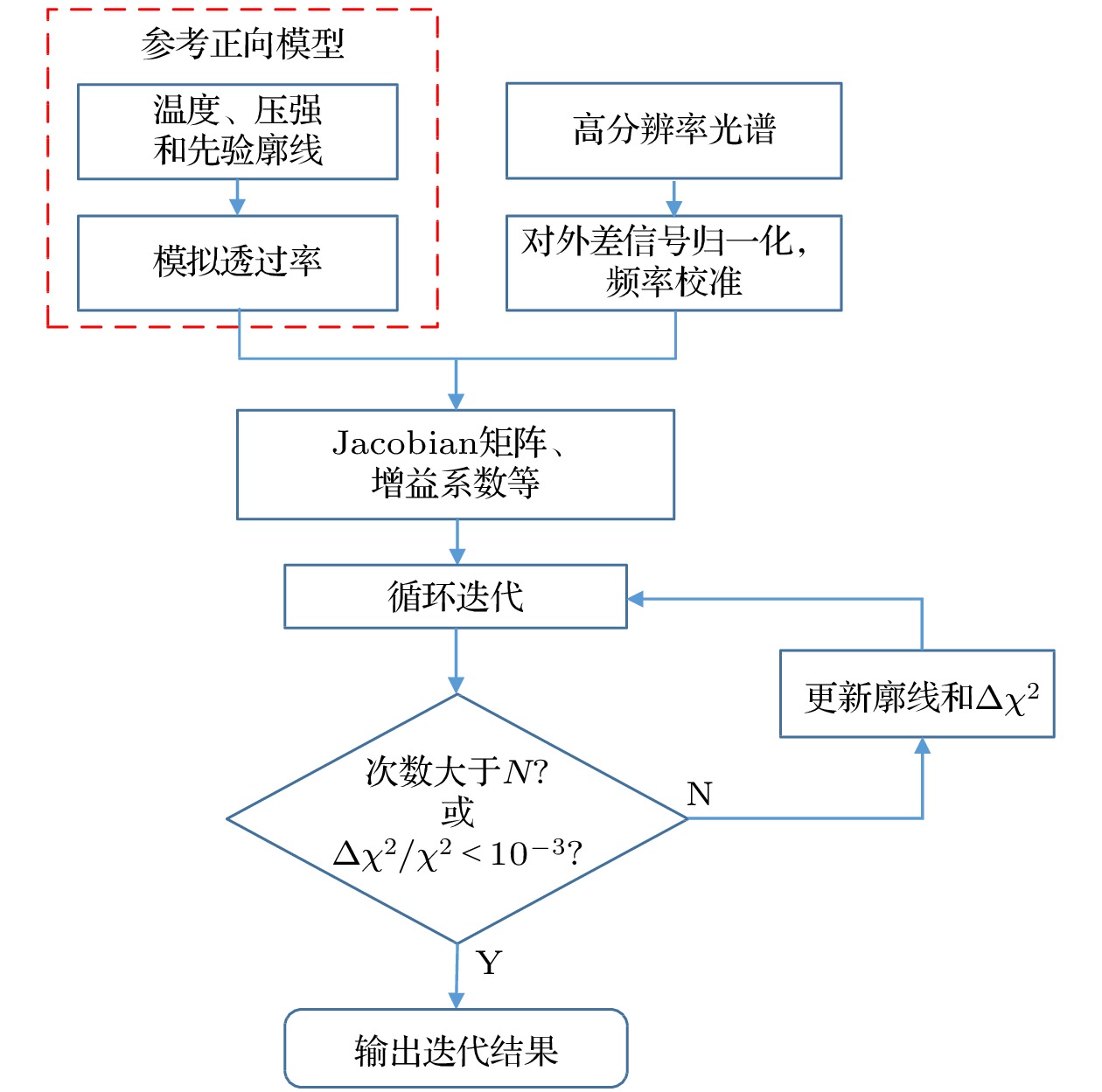
aser heterodyne spectroscopy detection has rapidly developed in recent years due to its high spectral resolution, small size, and light weight. It can be used to measure the atmospheric greenhouse gas vertical profile and calibrate the carbon satellite ground. This paper reports a laser heterodyne system for measuring atmospheric N2O, with a 3.939-µm interband cascade laser used as a local oscillator light source. A homemade high-precision solar tracker collects sunlight as a laser heterodyne signal source. The tracking accuracy reaches 7 arcsec, and the spectral resolution of the laser heterodyne system arrives at 0.004 cm–1. The atmospheric N2O absorption spectrum in Hefei area (31.902°N, 117.167°E) is measured, and two strong absorption peaks respectively at 288.336 and 2539.344 cm–1 are obtained. In addition, the wavelength calibration of the absorption signal, and the entire atmospheric transmittance spectrum of N2O molecules are obtained, and the signal-to-noise ratio is 93. The high-resolution spectrum data are normalized and frequency is corrected, and the N2O atmospheric concentration profile is obtained by using the reference forward model and the optimal estimation algorithm. The standard deviation of volume fraction is in a range of 0.000031—0.0026 ppm, and the corresponding relative error range is 0.009%—0.83%. The research results show that the laser heterodyne system built in this work can be used to measure the absorption spectrum of N2O in the atmosphere and realize the inversion of the N2O profile, which provides a guarantee for long-term observation of atmospheric N2O concentration.
[1] 向亮, 高庆先, 周锁铨, 陈永立 2009 气候变化研究进展 5 278
Xiang L, Gao Q X, Zhou S Q, Chen Y L 2009 Adv. Clim. Change Res. 5 278
[2] 邵君宜, 林兆祥, 刘林美, 龚威 2017 66 104206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao J Y, Lin Z X, Liu L M, Gong W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 104206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王薇, 刘文清, 张天舒 2014 光学学报 34 0130003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Liu W Q, Zhang T S 2014 Acta Opt. Sin. 34 0130003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao Y J, Wexler A S, Hase F, Pan Y, Mitloehner F M 2016 J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 7 1719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Clarke G B, Wilson E L, Miller J H, et al. 2014 Meas. Sci. Technol. 25 055204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Palmer P I, Wilson E L, Villanueva G L, et al. 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 2579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Weidmann D, Tsai T R, Macleod N A, et al. 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tsai T R, Rose R A, Weidmann D, et al. 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 8779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wilson E L, McLinden M L, Miller J H, et al. 2013 Appl. Phys. B 114 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wilson E L, DiGregorio A J, Villanueva G, et al. 2019 Appl. Phys. B 125 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rodin A, Klimchuk A, Nadezhdinskiy A, et al. 2014 Opt. Express 22 13825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 谈图, 曹振松, 王贵师, 等 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 1516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan T, Cao Z S, Wang G S, et al. 2015 Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 35 1516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang J, Wang G, Tan T, et al. 2019 Opt. Express 27 9610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Parvitte B, Zéninari V, Thiébeaux C, et al. 2004 Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 60 1193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gisi M, Hase F, Blumenstock T 2011 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 4 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Siegman A E 1966 Appl. Opt. 5 1588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张尚露, 黄印博, 卢兴吉, 曹振松, 戴聪明, 刘强, 高晓明, 饶瑞中, 王英俭 2019 光谱学与光谱分析 39 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang S L, Huang Y B, Lu X j, Cao Z S, Dai C M, Liu Q, Gao X M, Zhong R R, Wang Y J 2019 Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 39 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rodgers C D 2000 Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practise (1st Ed.) (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing)
[19] Rodgers C D 1990 J. Geophys. Res. 95 5587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Weidmann D, Reburn W J, Smith K M 2007 Appl. opt. 46 7162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 3.9 µm激光外差系统的参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting of 3.9 µm laser heterodyne system.
参数 数值 太阳光传输效率 0.305 滤波带宽/MHz 60 太阳温度/K 5773 测量波长/m 3.939 积分时间/s 0.3 -
[1] 向亮, 高庆先, 周锁铨, 陈永立 2009 气候变化研究进展 5 278
Xiang L, Gao Q X, Zhou S Q, Chen Y L 2009 Adv. Clim. Change Res. 5 278
[2] 邵君宜, 林兆祥, 刘林美, 龚威 2017 66 104206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao J Y, Lin Z X, Liu L M, Gong W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 104206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王薇, 刘文清, 张天舒 2014 光学学报 34 0130003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Liu W Q, Zhang T S 2014 Acta Opt. Sin. 34 0130003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao Y J, Wexler A S, Hase F, Pan Y, Mitloehner F M 2016 J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 7 1719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Clarke G B, Wilson E L, Miller J H, et al. 2014 Meas. Sci. Technol. 25 055204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Palmer P I, Wilson E L, Villanueva G L, et al. 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 2579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Weidmann D, Tsai T R, Macleod N A, et al. 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tsai T R, Rose R A, Weidmann D, et al. 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 8779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wilson E L, McLinden M L, Miller J H, et al. 2013 Appl. Phys. B 114 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wilson E L, DiGregorio A J, Villanueva G, et al. 2019 Appl. Phys. B 125 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rodin A, Klimchuk A, Nadezhdinskiy A, et al. 2014 Opt. Express 22 13825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 谈图, 曹振松, 王贵师, 等 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 1516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan T, Cao Z S, Wang G S, et al. 2015 Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 35 1516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang J, Wang G, Tan T, et al. 2019 Opt. Express 27 9610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Parvitte B, Zéninari V, Thiébeaux C, et al. 2004 Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 60 1193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gisi M, Hase F, Blumenstock T 2011 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 4 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Siegman A E 1966 Appl. Opt. 5 1588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 张尚露, 黄印博, 卢兴吉, 曹振松, 戴聪明, 刘强, 高晓明, 饶瑞中, 王英俭 2019 光谱学与光谱分析 39 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang S L, Huang Y B, Lu X j, Cao Z S, Dai C M, Liu Q, Gao X M, Zhong R R, Wang Y J 2019 Spectrosc. Spectral Anal. 39 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rodgers C D 2000 Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practise (1st Ed.) (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing)
[19] Rodgers C D 1990 J. Geophys. Res. 95 5587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Weidmann D, Reburn W J, Smith K M 2007 Appl. opt. 46 7162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8738
- PDF Downloads: 133
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: