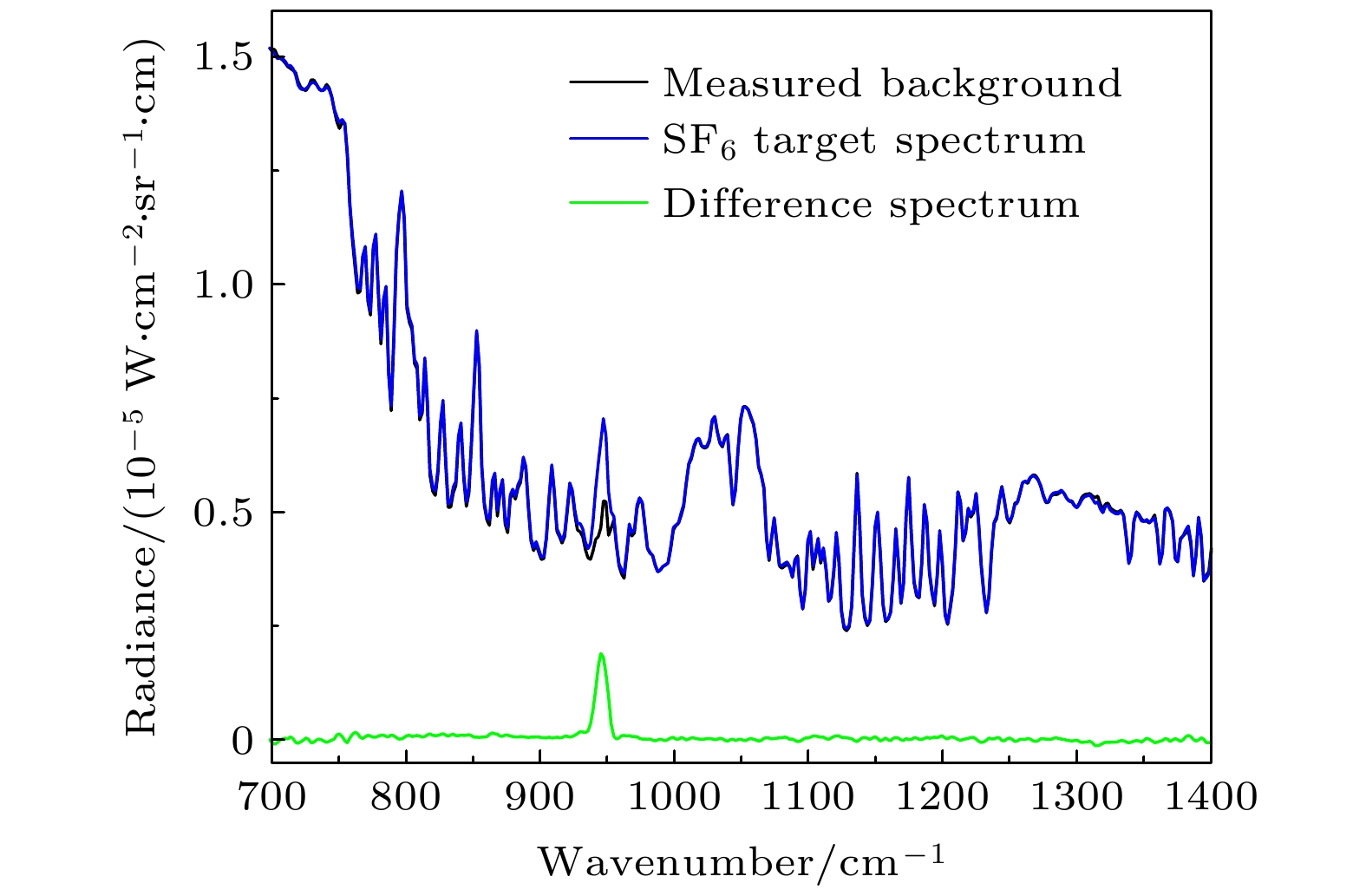
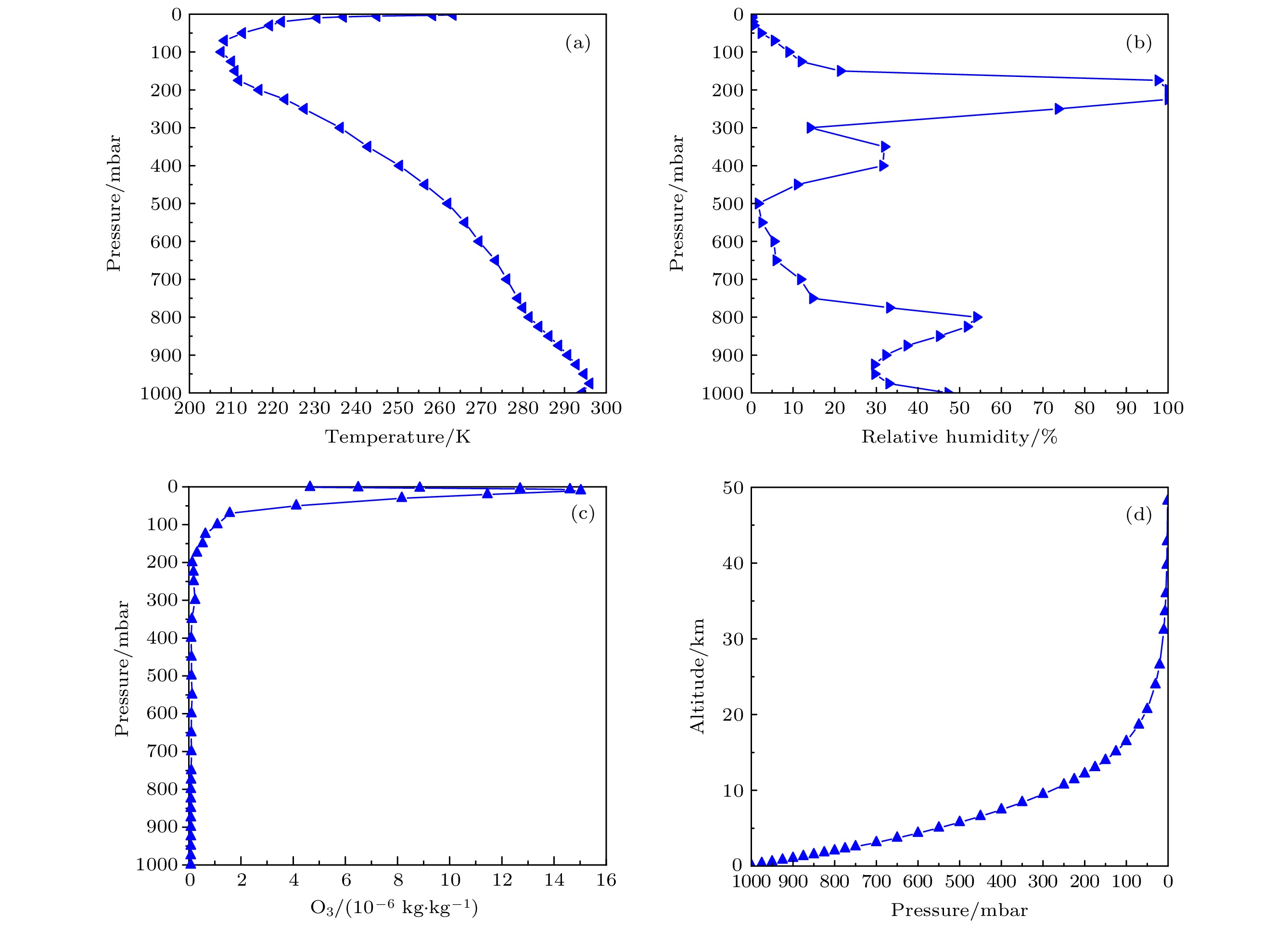
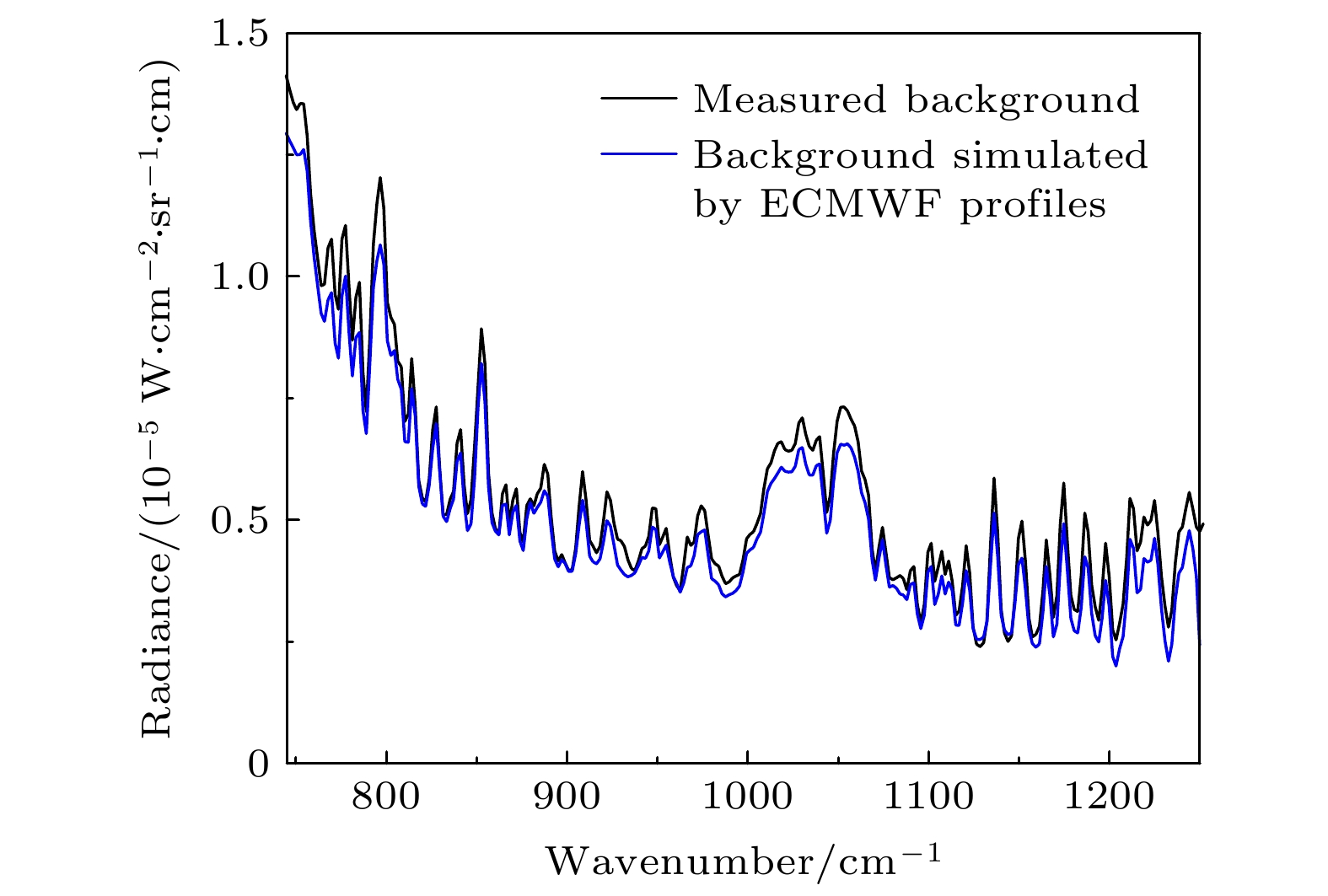
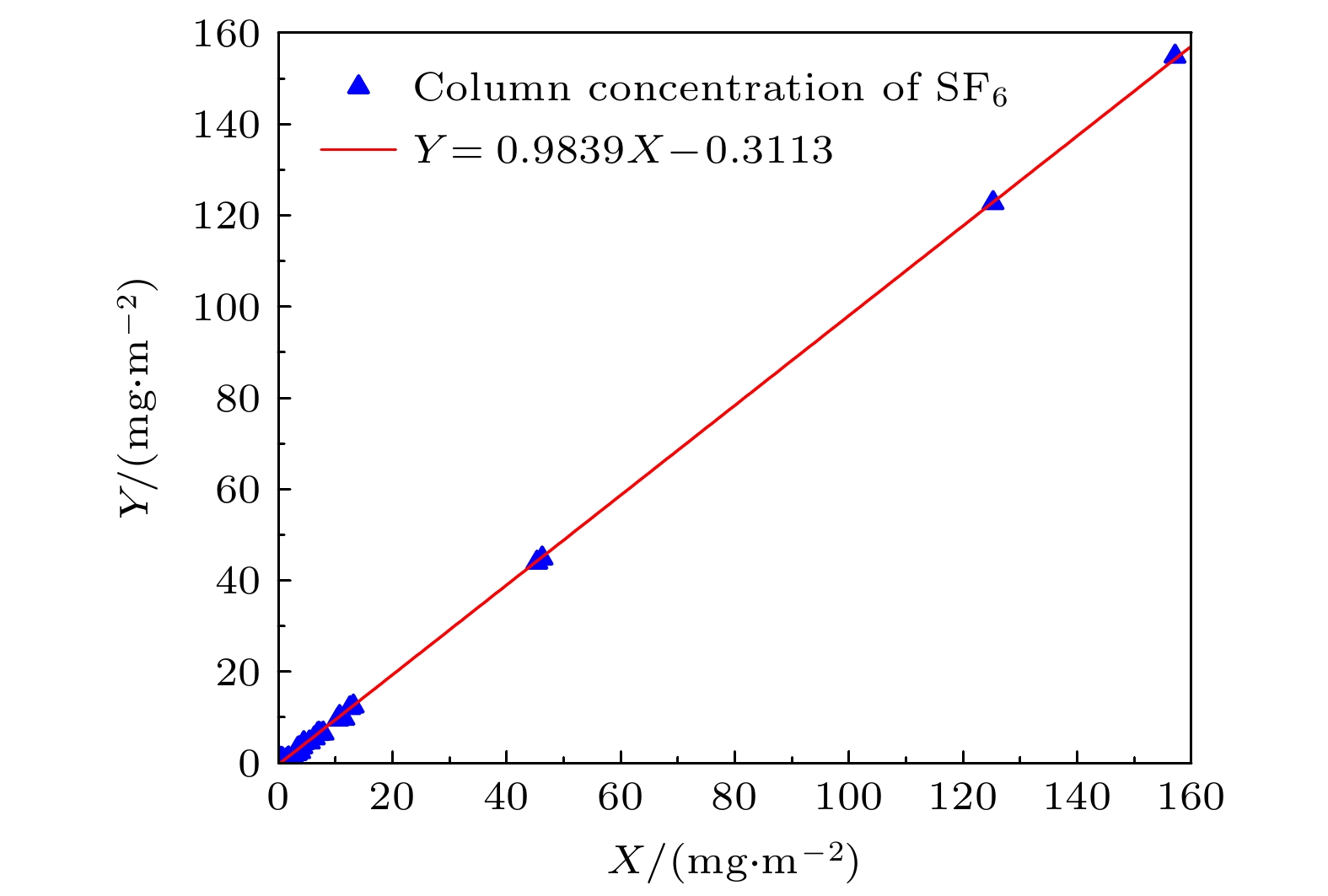
-
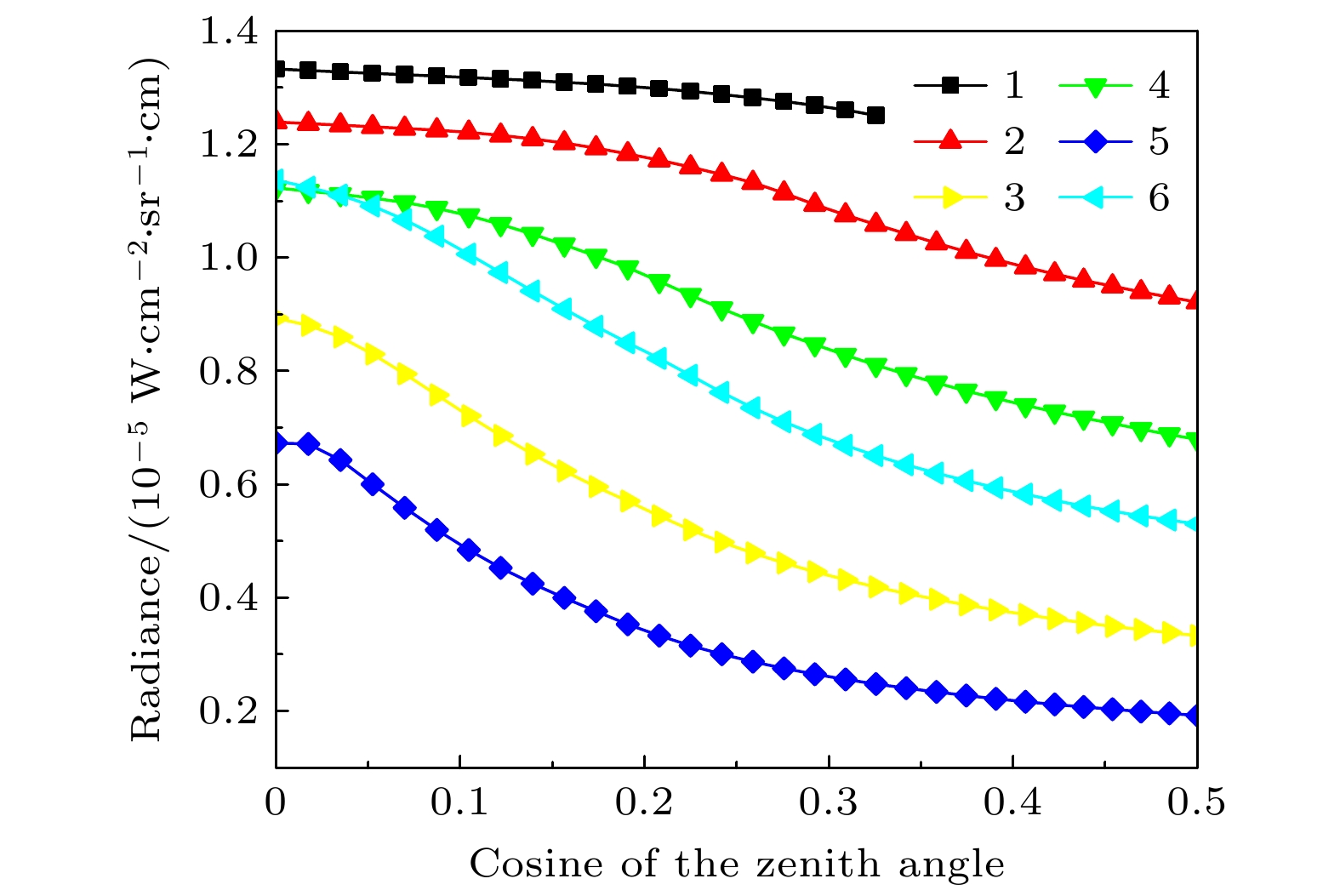
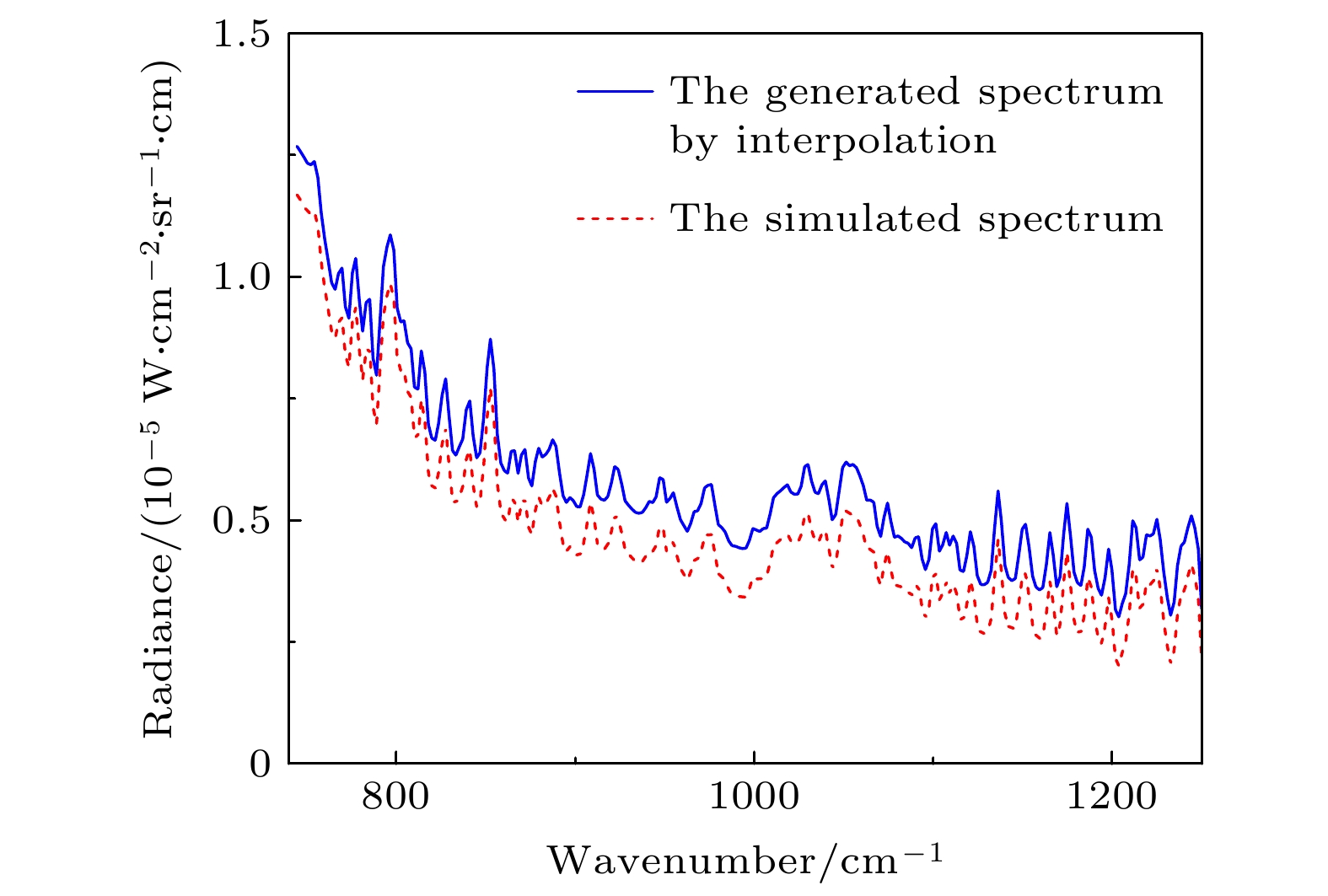
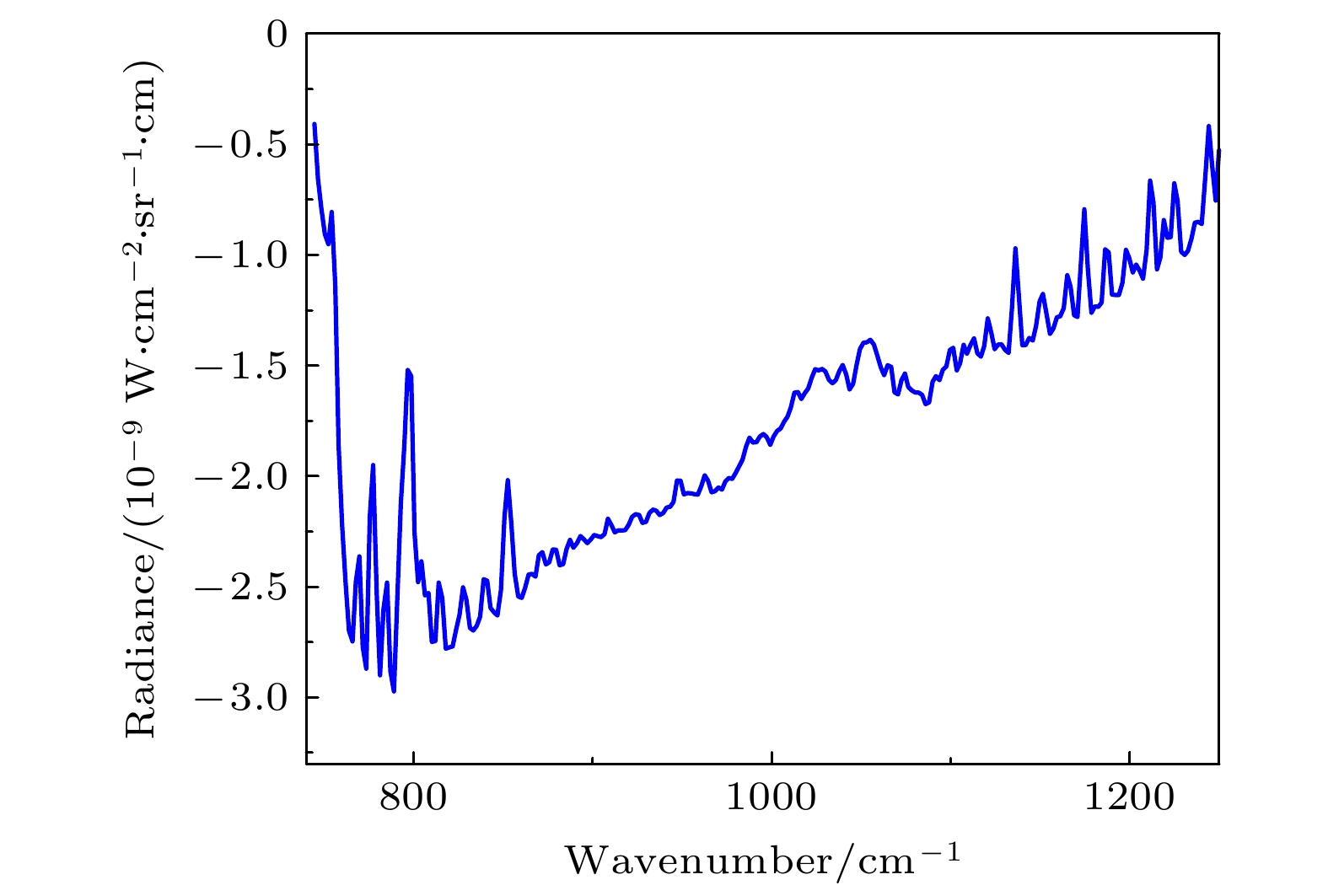
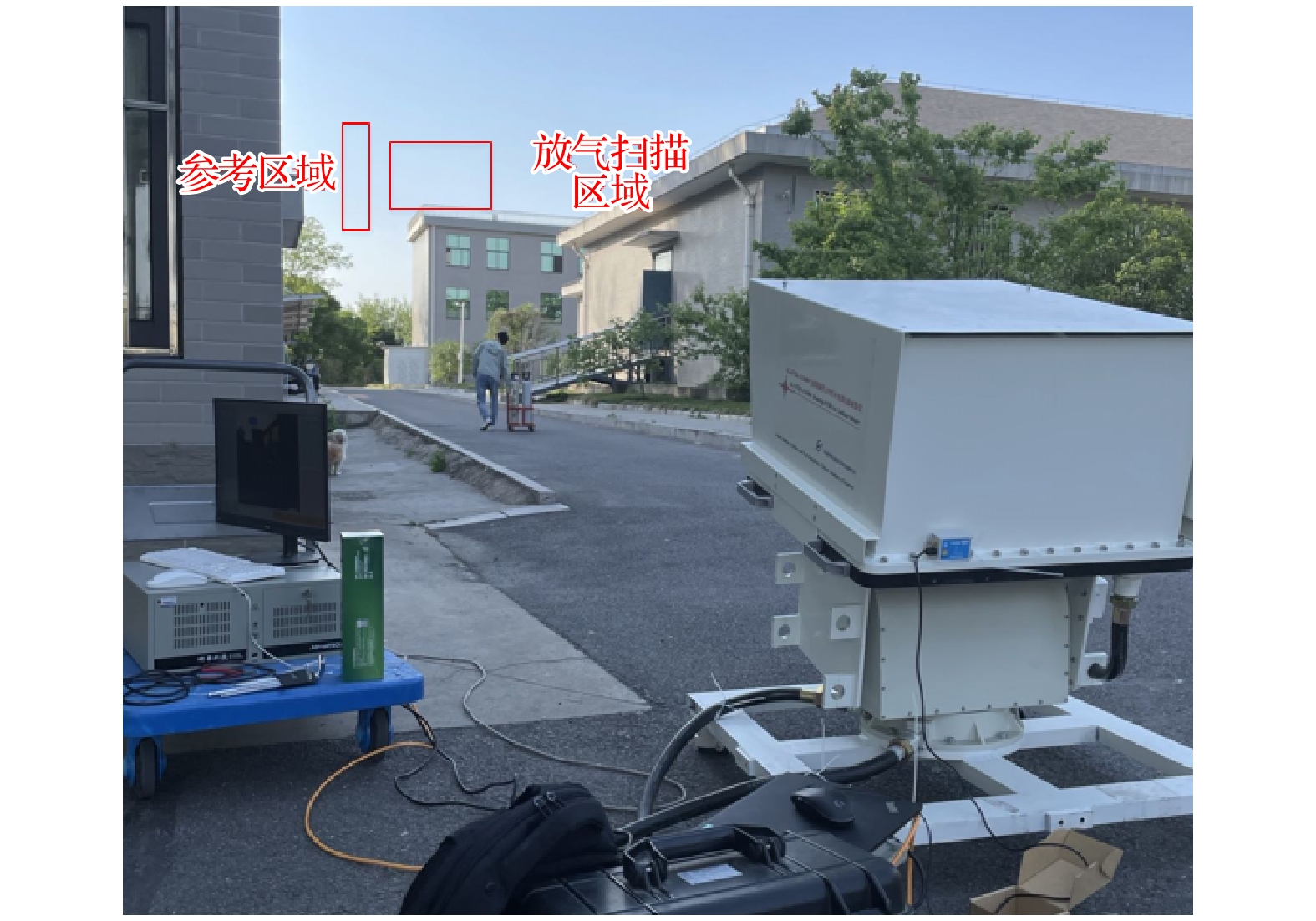
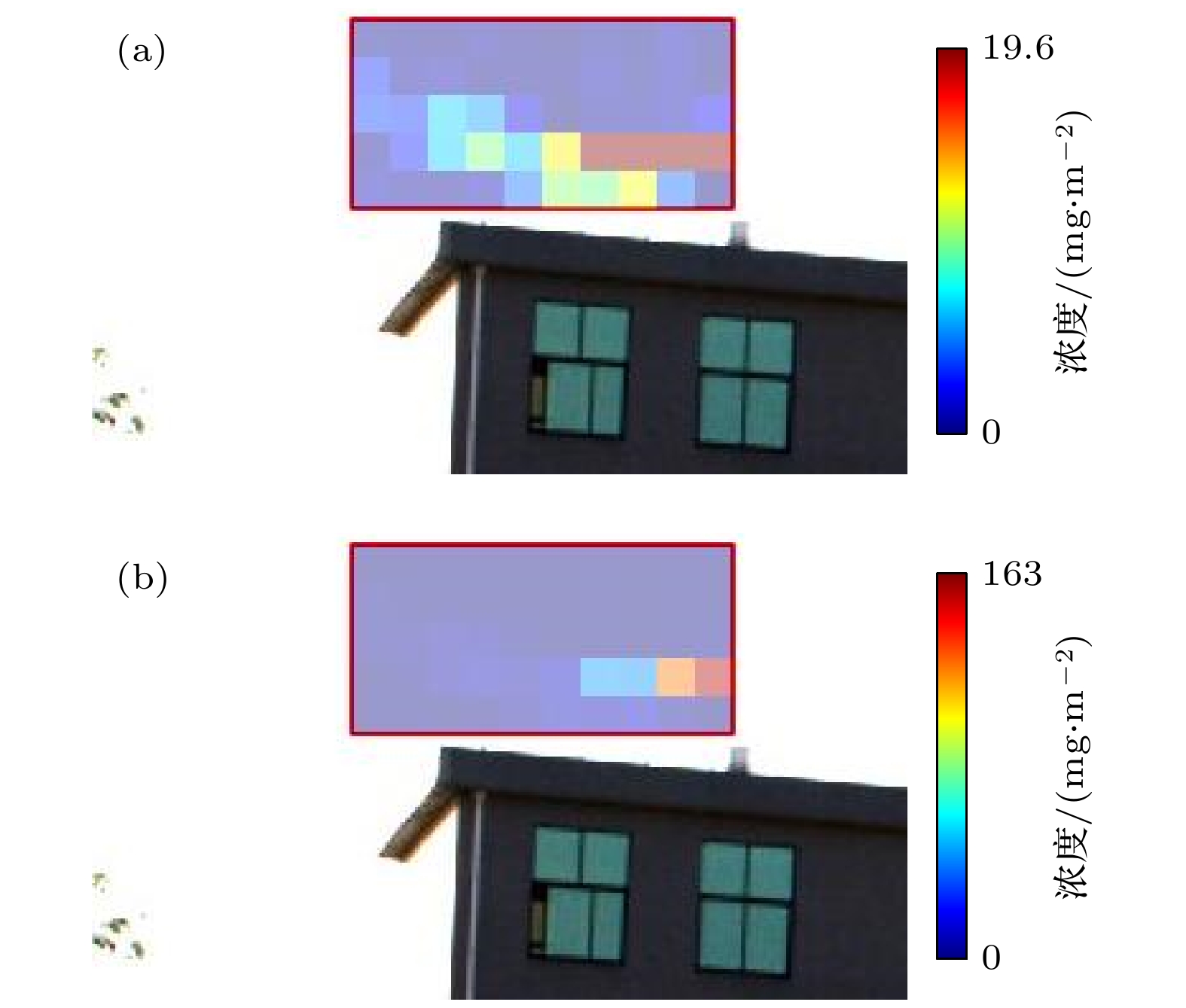
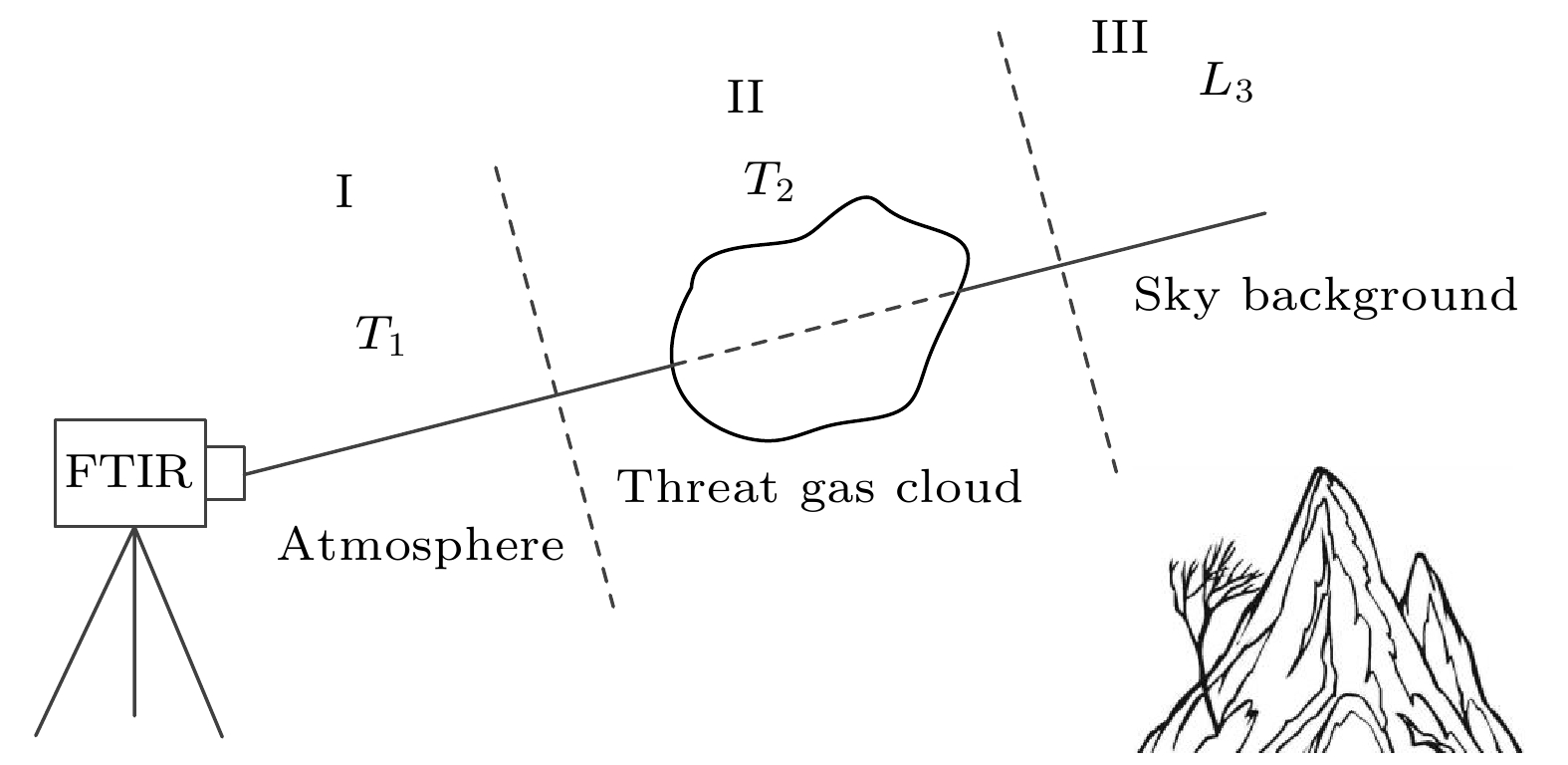
天空向下热红外辐射具有随时空变化而变化的特性, 当扫描傅里叶变换红外遥测成像系统以天空为背景对目标气云进行成像扫描时, 各扫描像素对应的背景辐射差异较大且没有恒定的基线, 因而影响目标气云透过率的精确反演. 针对这类问题, 提出了基于大气廓线合成背景的目标气云透过率反演方法, 首先采用实测地点的温度、湿度、压强和臭氧廓线及大气模式生成天空红外背景, 以解决化工园区内难以实时测量纯净天空红外背景谱的问题, 其次验证了天空红外背景与天顶角余弦逐波数存在连续可导的关系, 使得少量具有天顶角梯度的天空红外背景即可快速插值生成任意仰角位置的天空红外背景谱. 本文以中分辨率大气辐射传输模型(MODTRAN)软件仿真和SF6气体的遥测成像实验进行了方法验证, 所提方法可以快速生成梯度仰角内任意角度对应的天空红外背景谱, 准确反演出各扫描像素的目标气云透过率, 反演得到的SF6柱浓度气云分布与实际分布一致, 相关性达到0.99979.The sky infrared background radiation varies greatly with spatial distribution and time. When scanning Fourier transform infrared remote sensing imaging system scans the target gas cloud with the sky as the background, the background radiation corresponding to each scanned pixel is different, and the background does not have a constant baseline. It is extremely difficult to obtain the background spectrum of each pixel in real time, which affects the inversion accuracy of the target gas cloud transmittance. An inversion method of target gas cloud transmittance based on atmospheric profile synthesis background is proposed in this work. The temperature, humidity, pressure, and ozone profiles of the measured locations and the atmospheric model are used to generate the sky infrared background in order to solve the problem, i.e. the difficulty in measuring the clean sky infrared background spectrum in the chemical industry park. This paper proposes that there is a continuous derivable relationship between the sky infrared background spectrum and the cosine of zenith angle at each wavenumber, so a small amount of sky infrared background spectrum with a zenith angle gradient can quickly generate a sky infrared background spectrum at any elevation angle. The proposed method is verified by the moderate resolution atmospheric radiative transfer model (MODTRAN) software simulation and the remote sensing imaging experiment of SF6 gas. The proposed method can quickly generate the sky infrared background spectrum corresponding to any angle within a gradient elevation angle and accurately invert the target gas cloud transmittance at each pixel. The results show that the distribution trend of the column concentration of the SF6 gas cloud is consistent with the actual distribution, and the correlation is 0.99979.
-
Keywords:
- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy /
- synthetic background /
- transmittance inversion /
- gas cloud scanning imaging
[1] Hu Y Y, Xu L, Shen X C, Jin L, Xu H Y, Deng Y S, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 9396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 焦洋, 徐亮, 高闽光, 金岭, 童晶晶, 李胜, 魏秀丽 2013 62 140705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao Y, Xu L, Gao M G, Jin L, Tong J J, Li S, Wei X L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 140705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sabbah S, Rusch P, Gerhard J H, Harig R 2013 Proc. SPIE 8743 370
[4] Liou K N 2002 An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation (Vol. 84) (Elsevier)
[5] Chen M H, Yuan C S, Wang L C 2015 Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 15 1110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smith T E L, Wooster M J, Tattaris M, Griffith D W T 2011 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 4 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Stremme W, Krueger A, Harig R, Grutter M 2012 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 5 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Theriault J M, Puckrin E, Lavoie H, Turcotte C S, Bouffard F, Dube D 2004 Proc. SPIE 5584 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Flanigan D F 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 7027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Evans W F, Puckrin E, McMaster D 2002 Proc. SPIE 4574 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 高闽光, 刘文清, 张天舒, 刘诚, 刘建国, 魏庆农, 陆亦怀, 王亚萍, 朱军, 徐亮 2006 光谱学与光谱分析 26 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao M G, Liu W Q, Zhang T S, Liu C, Liu J G, Wei Q N, Lu Y H, Wang Y P, Zhu J, Xu L 2006 Spectrosc. Spec. Anal. 26 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Harig R 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Harig R, Rusch P, Peters H, Gerhard J, Braun R, Sabbah S, Beecken J 2009 Proc. SPIE 7475 74750Z
[14] Li D C, Cui F X, Wang A J, Li Y Y, Wu J, Qiao Y L 2020 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 58 8649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 夏旻惠, 智协飞 2020 大气科学学报 43 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia M H, Zhi X F 2020 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 43 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 崔方晓, 李大成, 吴军, 王安静, 李扬裕 2019 光学学报 39 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui F X, Li D C, Wu J, Wang A J, Li Y Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 迟晓铭, 肖安山, 朱亮, 贾润中, 李明骏, 高少华, 王国龙, 丁德武, 朱胜杰 2021 安全、健康和环境 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chi X M, Xiao A S, Zhu L, Jia R Z, Li M J, Gao S H, Wang G L, Ding D W, Zhu S J 2021 Safety Health Environ. 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Flanigan D F 1996 Appl. Opt. 35 6090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berk A, Conforti P, Kennett R, et al. 2014 6th IEEE GRSS Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing Lausanne June 25, 2014 p1
[20] 冯明春, 徐亮, 刘文清, 刘建国, 高闽光, 魏秀丽 2016 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Gao M G, Wei X L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Keller W, Borkowski A 2019 J. Geod. 93 1251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 MODTRAN大气模式
Table 1. Atmospheric models of MODTRAN.
模型序号 大气模式 边界层温度/K 1 热带 299.7 2 中纬度夏季 294.2 3 中纬度冬季 272.2 4 亚极地夏季 287.2 5 亚极地冬季 257.2 6 美国标准大气(1976) 288.2 表 2 ECMWF部分数据字段
Table 2. Some data fields of ECMWF.
序号 字段 注释 1 Longitude 经度(°) 2 Latitude 纬度(°) 3 Time 时间(h) 4 Pressure level 压强(mbar) 5 Temperature 温度(K) 6 Relative humidity 相对湿度(%) 7 Ozone mass mixing ratio 臭氧(kg/kg) 8 Geopotential 海拔参数(m2/s2) 表 3 插值生成谱与仿真谱的均方根(单位: 10–10 W/(cm2·sr·cm1))
Table 3. Root mean square error between the generated spectrum by interpolation and the simulated spectrum (unit: 10–10 W/(cm2·sr·cm1)).
模型序号 天顶角/(°) 84.5 78.5 71.5 64.5 1 2.92 1.6 35.03 Nan 2 1.77 0.93 12.47 1.0 3 4.81 21.26 0.38 0.18 4 4.59 32.97 4.41 1.05 5 4.76 1.57 0.43 0.12 6 3.41 18.56 0.44 0.39 -
[1] Hu Y Y, Xu L, Shen X C, Jin L, Xu H Y, Deng Y S, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 9396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 焦洋, 徐亮, 高闽光, 金岭, 童晶晶, 李胜, 魏秀丽 2013 62 140705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao Y, Xu L, Gao M G, Jin L, Tong J J, Li S, Wei X L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 140705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sabbah S, Rusch P, Gerhard J H, Harig R 2013 Proc. SPIE 8743 370
[4] Liou K N 2002 An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation (Vol. 84) (Elsevier)
[5] Chen M H, Yuan C S, Wang L C 2015 Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 15 1110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smith T E L, Wooster M J, Tattaris M, Griffith D W T 2011 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 4 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Stremme W, Krueger A, Harig R, Grutter M 2012 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 5 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Theriault J M, Puckrin E, Lavoie H, Turcotte C S, Bouffard F, Dube D 2004 Proc. SPIE 5584 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Flanigan D F 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 7027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Evans W F, Puckrin E, McMaster D 2002 Proc. SPIE 4574 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 高闽光, 刘文清, 张天舒, 刘诚, 刘建国, 魏庆农, 陆亦怀, 王亚萍, 朱军, 徐亮 2006 光谱学与光谱分析 26 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao M G, Liu W Q, Zhang T S, Liu C, Liu J G, Wei Q N, Lu Y H, Wang Y P, Zhu J, Xu L 2006 Spectrosc. Spec. Anal. 26 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Harig R 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Harig R, Rusch P, Peters H, Gerhard J, Braun R, Sabbah S, Beecken J 2009 Proc. SPIE 7475 74750Z
[14] Li D C, Cui F X, Wang A J, Li Y Y, Wu J, Qiao Y L 2020 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 58 8649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 夏旻惠, 智协飞 2020 大气科学学报 43 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia M H, Zhi X F 2020 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 43 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 崔方晓, 李大成, 吴军, 王安静, 李扬裕 2019 光学学报 39 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui F X, Li D C, Wu J, Wang A J, Li Y Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 迟晓铭, 肖安山, 朱亮, 贾润中, 李明骏, 高少华, 王国龙, 丁德武, 朱胜杰 2021 安全、健康和环境 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chi X M, Xiao A S, Zhu L, Jia R Z, Li M J, Gao S H, Wang G L, Ding D W, Zhu S J 2021 Safety Health Environ. 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Flanigan D F 1996 Appl. Opt. 35 6090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berk A, Conforti P, Kennett R, et al. 2014 6th IEEE GRSS Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing Lausanne June 25, 2014 p1
[20] 冯明春, 徐亮, 刘文清, 刘建国, 高闽光, 魏秀丽 2016 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Gao M G, Wei X L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Keller W, Borkowski A 2019 J. Geod. 93 1251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6838
- PDF下载量: 84
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: