-
Melting of the dielectric phase change material inside a closed square enclosure is numerically investigated. The fully coupled equations including Navier-Stokes equations, Poisson's equation, charge conservation equation and the energy equation are solved using the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). Strong charge injection from a high temperature vertical electrode is considered and the basic characteristics of fluid flow, charge transport and heat transfer in solid-liquid phase change process under the coupling of Coulomb force and buoyancy force are systematically studied. Emphasis is put on analysing the influence of multiple non-dimensional parameters, including electric Rayleigh number T, Stefan number
$Ste$ , mobility number M, and Prandtl number$Pr$ on electrohydrodynamic (EHD) solid-liquid phase change. The numerical results show that comparing with the melting process driven by buoyancy force, the applied electric field will not only change the flow structure in liquid region and the evolution of the liquid-solid interface, but also increase the heat transfer efficiency of dielectric phase change material and thus enhance the solid-liquid phase change process. In particular, we find that this phenomenon becomes more pronounced when T is larger. Further, the dimensionless parameter$\varPhi$ is introduced to characterize the effect of EHD enhanced solid-liquid phase change, and the results indicate that the effect of EHD enhancement solid-liquid phase change is weakened with the increase of Stefan number$Ste$ , However the change of$Ste$ does not make much difference in EHD enhancement solid-liquid phase change for a sufficiently high electric Rayleigh number T, and it is attributed to the fully developed convection cells at a very early stage of the melting process. Moreover, it is found that the effect of EHD enhancement solid-liquid phase change is negatively related to the mobility number M and that the effect of Prandtl number$Pr$ on the EHD enhancement solid-liquid phase change largely depends on the mobility number M, which is due to the simultaneous influence of electric field force and buoyancy force. In general, the electric field has a significant influence on the melting process of dielectric phase change material, especially at high T,$Pr$ and low$Ste$ , M. And quantitatively, in all tested cases, a maximum melting time saves about 86.6% at$T=1000$ ,$Ra=10000$ ,$M=3$ ,$Pr=20$ , and$Ste=0.1$ .[1] Luo X, Wang J H, Dooner M, Clarke J 2015 Appl. Energy 137 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H S, Cong T N, Yang W, Tan C Q, Li Y L, Ding Y L 2009 Prog. Nat. Sci. 19 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 霍宇涛 2018 博士学位论文 (徐州: 中国矿业大学)
Huo Y T 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] Ren Q L, Meng F L, Guo P H 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 121 1214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵耀 2018 博士学位论文 (上海: 上海交通大学)
Zhao Y 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University) (in Chinese)
[6] Sharma A, Tyagi V V, Chen C R, Buddhi D 2009 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 13 318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Agyenim F, Hewitt N, Eames P, Smyth M 2010 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 14 615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ren Q L 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 180 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Stritih U 2004 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 47 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lacroix M, Benmadda M 1997 Numer. Heat Tranfer, Part A 31 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ji C Z, Qin Z, Low Z H, Dubey S, Choo F H, Duan F 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 129 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Khodadadi J M, Hosseinizadeh S F 2007 Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 34 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Feng Y C, Li H X, Li L X, Bu L, Wang T 2015 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 81 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiao X, Zhang P, Li M 2014 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 81 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张涛, 余建祖 2007 制冷学报 6 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T, Yu J Z 2007 J. Refrigeration 6 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan L W, Zhu Z Q, Zeng Y, Ding Q, Liu M J 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 95 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fan L W, Zhu Z Q, Liu M J, Xu C L, Zeng Y, Lu H, Tao Y Z 2016 J. Heat Transfer-Trans. ASME 138 122402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Oh Y K, Park S H, Cha K O 2001 KSME Int. J. 15 1882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Oh Y K, Park S H, Cho Y I 2002 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45 4631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nakhla D, Sadek H, Cotton J S 2015 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 81 695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Rashidi S, Bafekr H, Masoodi R, Languri M E 2017 J. Electrostat. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Atten P, Mc Cluskey F, Pérez A 1988 IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation 23 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Traoré P, Pérez A T, Koulova D, Romat H 2010 J. Fluid Mech. 658 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu J, Traoré P, Zhang M, Pérez A T, Vázquez P A 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 92 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 陈凤, 彭耀, 宋耀祖, 陈民 2007 工程热 4 679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen F, Peng Y, Song Y Z, Chen M 2007 J. Eng. Therm. 4 679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao M, Cheng P, Quan X 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 67 984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sadek H, Ching C Y, Cotton J 2010 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53 3721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 陈春天, 杨嘉祥, 张颖, 李静 2004 工程热 2 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen C T, Yang J X, Zhang Y, Li J 2004 J. Eng. Therm. 2 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李典, 王太, 陈烁, 谢英柏, 刘春涛 2020 工程热 41 2752
Li D, Wang T, Chen L, Xie Y B, Liu C T 2020 J. Eng. Therm. 41 2752
[30] 危卫, 张云伟, 顾兆林 2013 科学通报 58 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei W, Zhang Y W, Gu Z L 2013 Chin. Sci. Bull. 58 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Nakhla D, Thompson E, Lacroix B, Cotton J S 2018 J. Electrostat. 92 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Luo K, Pérez A T, Wu J, Yi H L, Tan H P 2019 Phys. Rev. E 100 013306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 卢才磊 2020 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Lu C L 2020 M. D. Thesis (Haerbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[34] Selvakumar R D, Liu Q, Luo K, Traoré P, Wu J 2021 Int. J. Multiphase Flow 136 103550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Nakhla D, Cotton J S 2021 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 167 120828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Luo K, Wu J, Pérez A T, Yi H L, Tan H P 2019 Phys. Rev. Fluids 4 083702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Huang R Z, Wu H Y 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 294 346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 罗康 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Luo K 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Haerbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[39] Chen S, Doolen G D 1998 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Wang L, Zhao Y, Yang X G, Shi B C, Chai Z H 2019 Appl. Math. Model. 71 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] 黄昌盛, 张文欢, 侯志敏, 陈俊辉, 李明晶, 何南忠, 施保昌 2011 科学通报 56 2434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang C S, Zhang W H, Hou Z M, Chen J H, Li M J, He N Z, Shi B C 2011 Chin. Sci. Bull. 56 2434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 李洋, 苏婷, 梁宏, 徐江荣 2018 67 224701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Su T, Liang H, Xu J R 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 224701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 梁宏 2015 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Liang H 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[44] 李庆, 余悦, 唐诗 2020 科学通报 65 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Yu Y, Tang S 2020 Chin. Sci. Bull. 65 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 朱炼华, 郭照立 2015 计算物理 32 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu L H, Guo Z L 2015 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 32 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 刘高洁, 郭照立, 施保昌 2016 65 014702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu G J, Guo Z L, Shi B C 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 吴健, 张蒙齐, 田方宝 2018 力学学报 50 1458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J, Zhang M Q, Tian F B 2018 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 50 1458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Luo K, Wu J, Yi H L, Tan H P 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 023309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Wang L, Wei Z C, Li T F, Chai Z H, Shi B C 2021 Appl. Math. Model 95 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Guo Z L, Shi B C, Wang N C 2000 J. Comput. Phys. 165 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 046308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Chai Z H, Shi B C 2008 Appl. Math. Model. 32 2050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Lu J H, Lei H Y, Dai C S 2019 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 135 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Huang R Z, Wu H Y 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 315 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2002 Phys. Fluids 14 2007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Huang R Z, Wu H Y, Cheng P 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 59 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
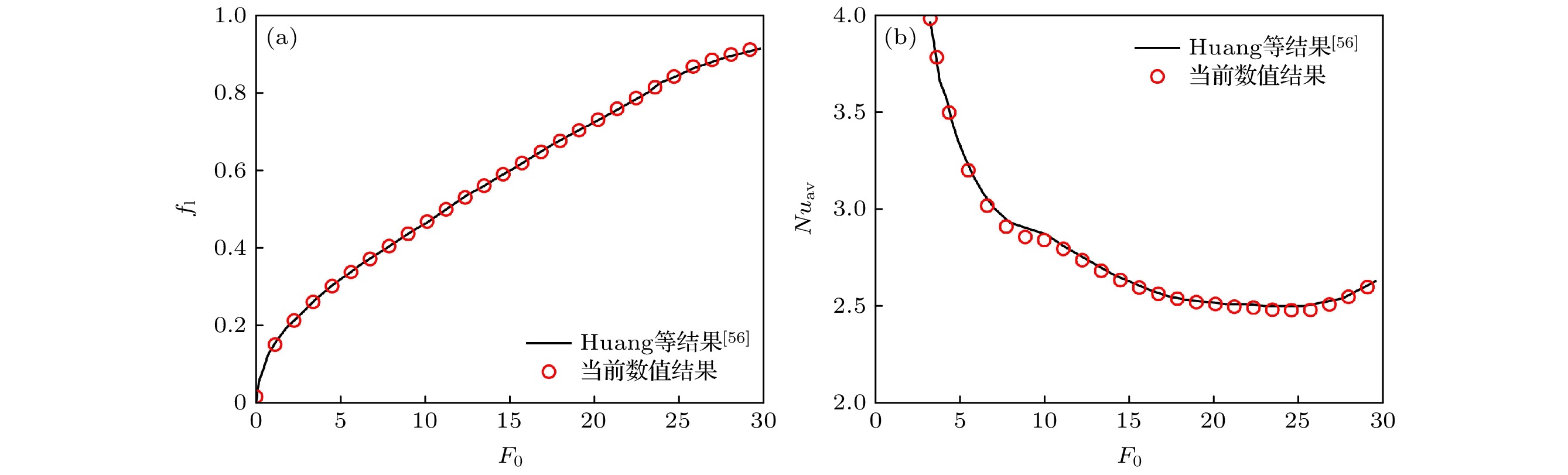
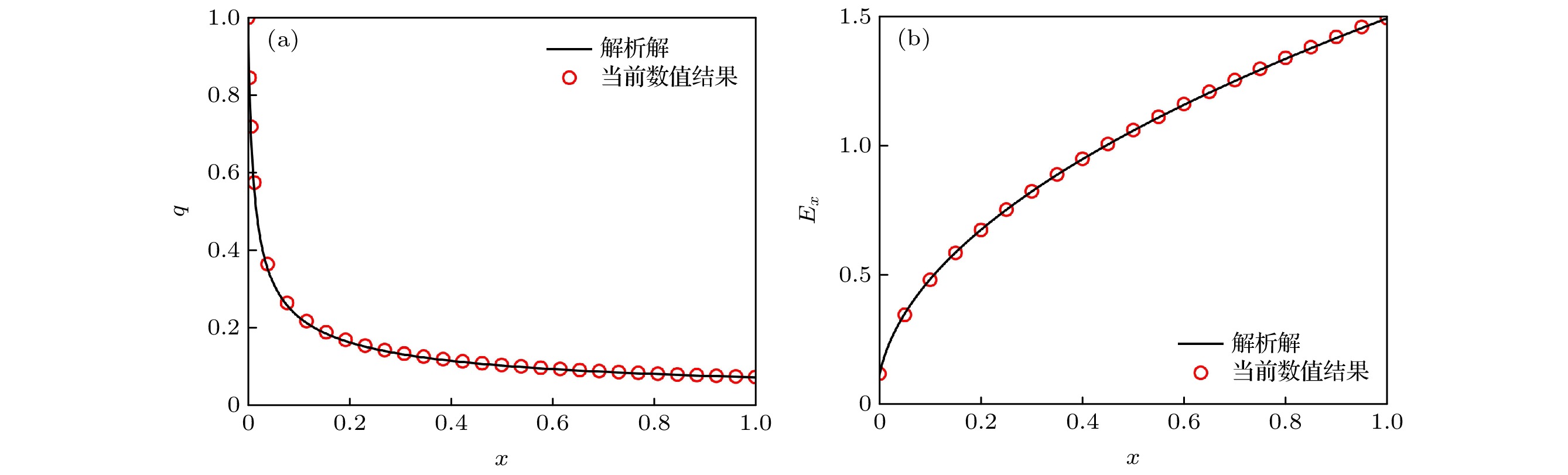
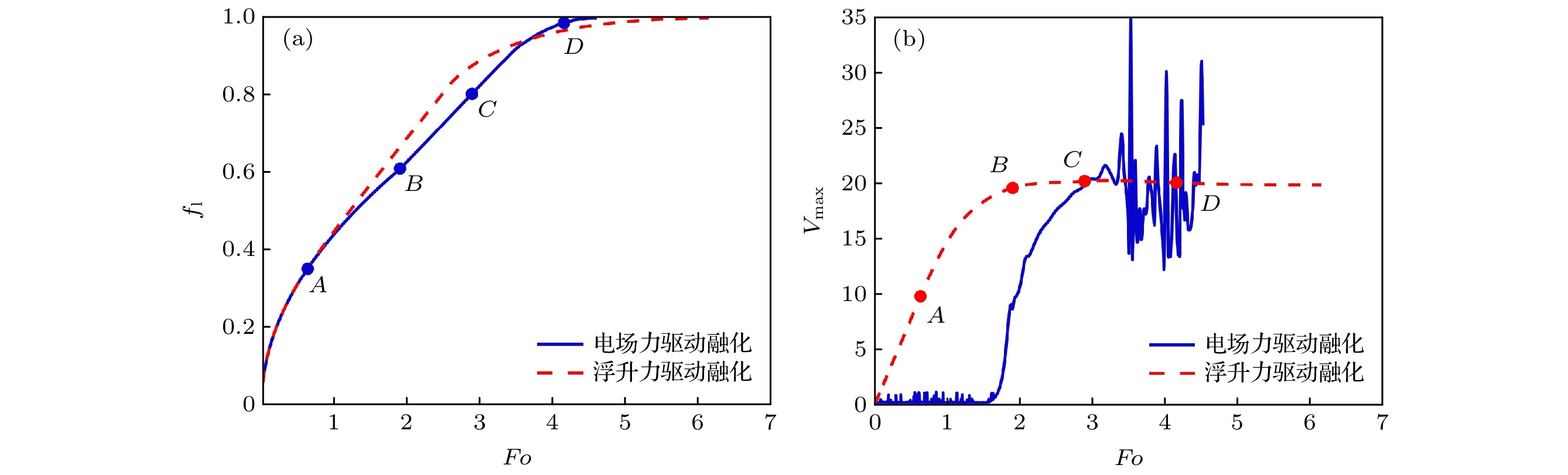
图 4 PCM熔化过程中(a)液体体积分数
$f_{\rm l}$ 和(b)液相最大速度$V_{\rm max}$ 随时间的变化趋势. 图中点A, B, C和D分别对应时刻$Fo=0.63$ ,$1.90$ ,$2.90$ 和$4.16$ Figure 4. Time evolutions of (a) the liquid fraction and (b) the maximum fluid velocity. Points A, B, C and D correspond to the dimensionless time
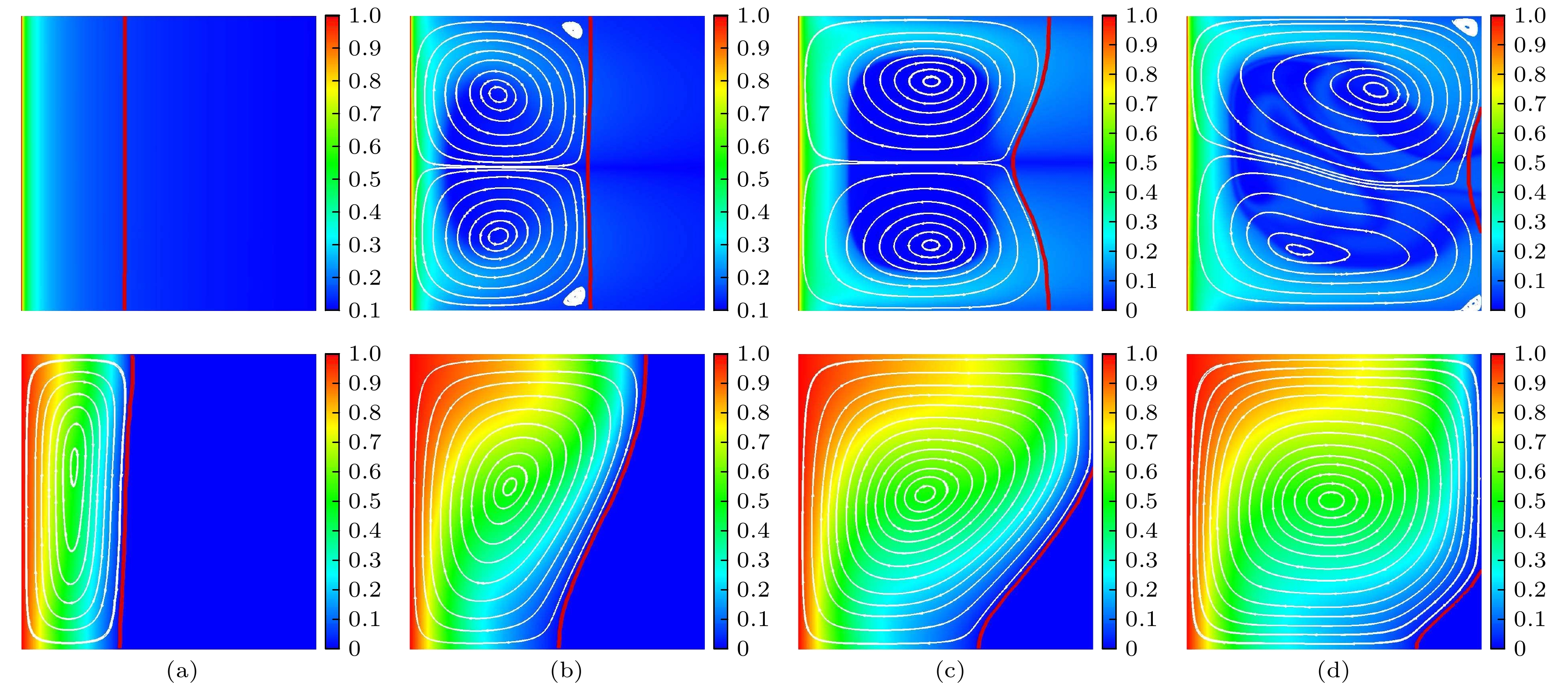
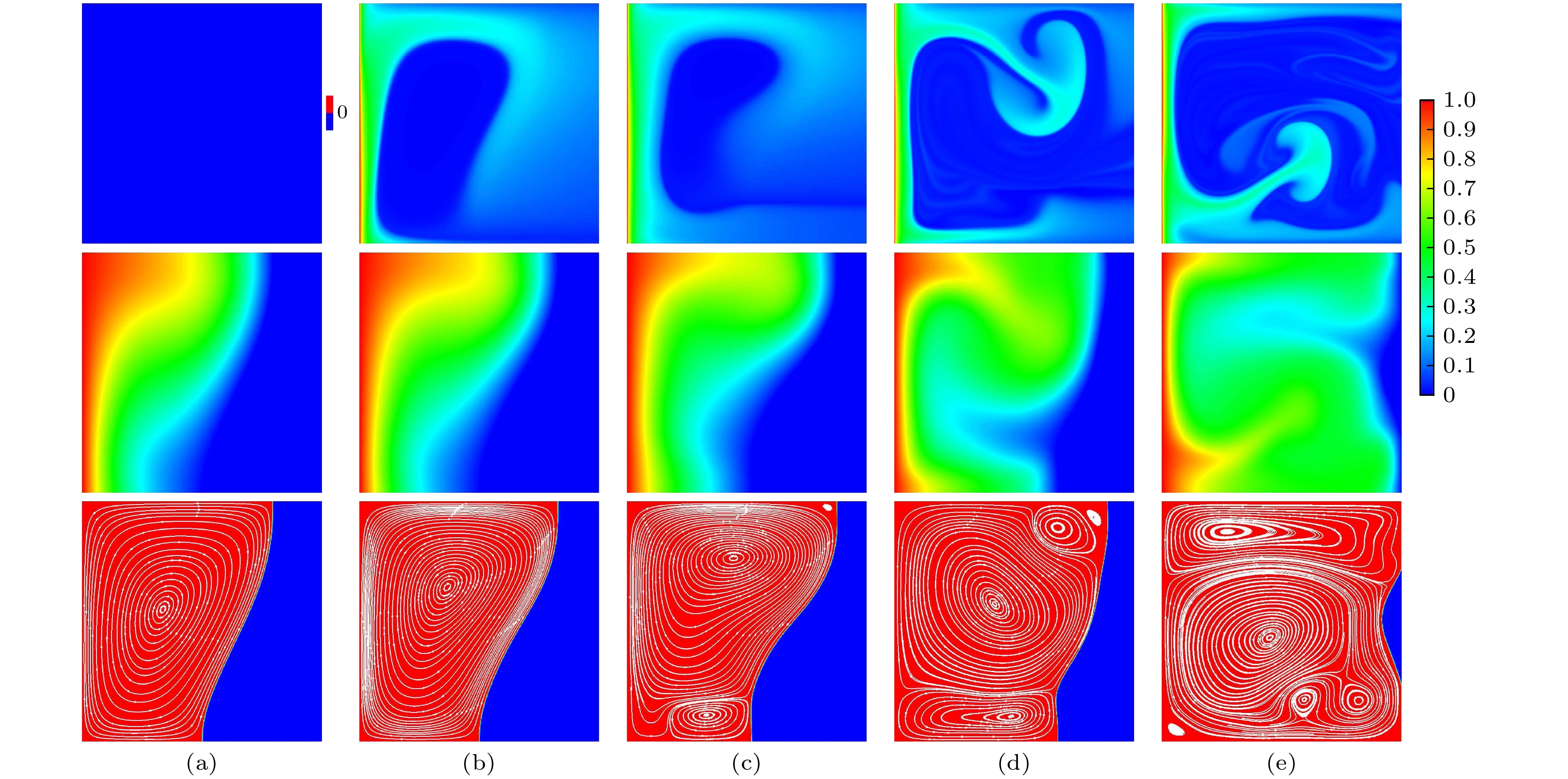
$Fo=0.36$ ,$1.90$ ,$2.90$ and$4.16$ , respectively.图 5 电场力驱动下PCM熔化到不同时刻电荷密度、流场以及相界面分布(上)和浮升力驱动下PCM熔化到不同时刻温度、流场以及相界面分布(下) (a)
$Fo=0.63$ ; (b)$Fo=1.90$ ; (c)$Fo=2.90$ ; (d)$Fo=4.16$ Figure 5. Distributions of charge density (temperature), fluid field and liquid-solid interface of PCM at four representative time of (a)
$Fo=0.63$ , (b)$Fo=1.90$ , (c)$Fo=2.90$ and (d)$Fo=4.16$ in presence of electric field force (top) and buoyancy force (bottom)图 7 不同电瑞利数下
$Fo=1.9$ 时电荷密度(上)、温度(中)以及流场(下)分布: (a)$T=0$ ; (b)$T=400$ ; (c)$T=800$ ; (d)$T=1600$ ; (e)$T=2400$ Figure 7. Distribution of the charge density (top), temperature (middle) and streamlines (bottom) at
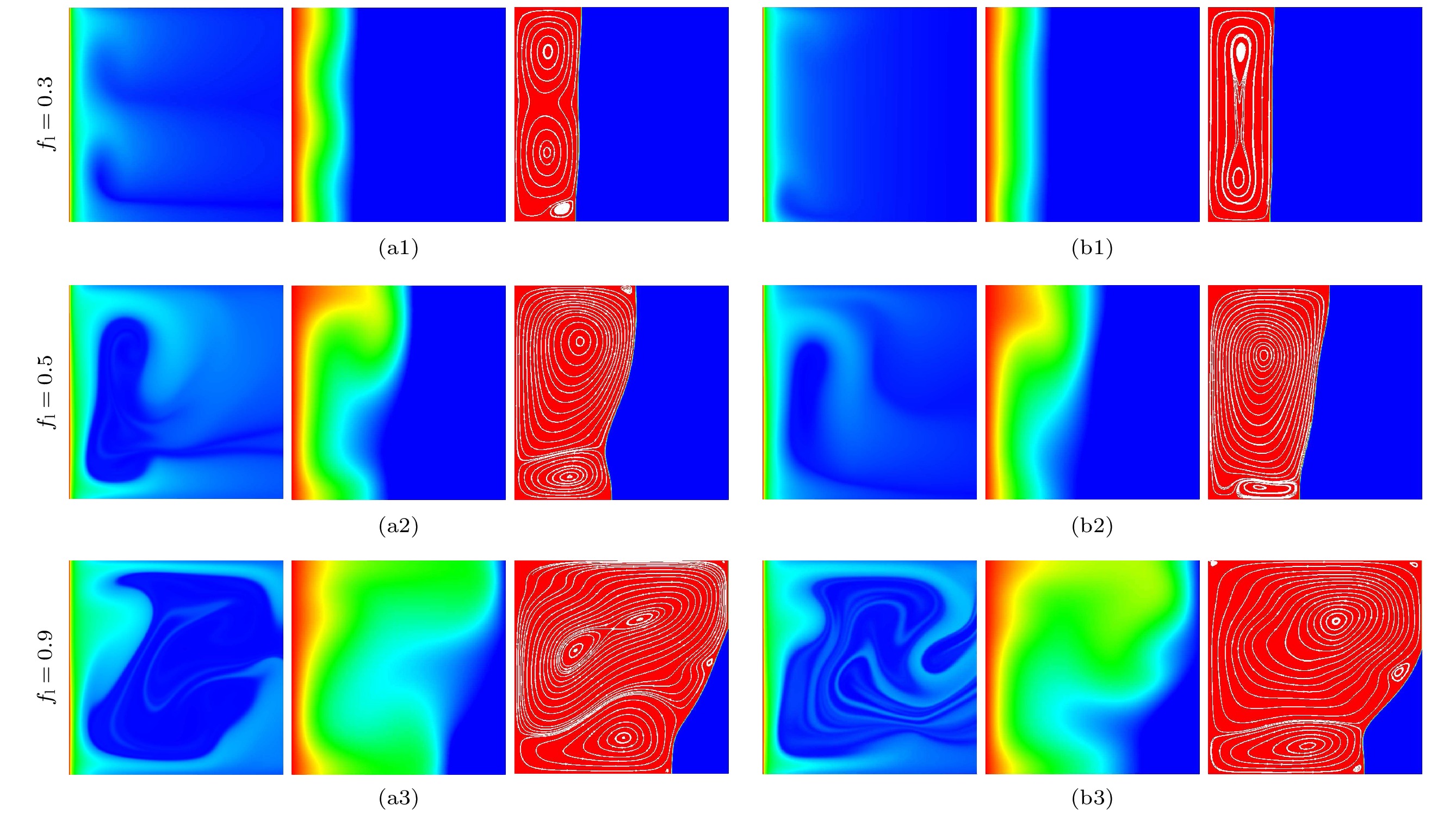
$Fo=1.9$ under different electrical Rayleigh numbers: (a)$T=0$ ; (b)$T=400$ ; (c)$T=800$ ; (d)$T=1600$ ; (e)$T=2400$ .图 10
$T=1000$ 时, 不同的斯蒂芬数下, PCM熔化到$f_{\rm l}=0.3$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.5$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.9$ 时电荷密度、温度以及流场分布 (a)$Ste= $ $ 0.05$ ; (b)$Ste=0.1$ Figure 10. With
$T=1000$ , distributions of charge density, temperature field and streamlines of PCM melting at$f_{\rm l}=0.3$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.5$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.9$ for different Stefan number: (a)$Ste=0.05$ ; (b)$Ste=0.1$ .图 11
$T=3200$ 时, 不同的斯蒂芬数下, PCM熔化到$f_{\rm l}=0.3$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.5$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.9$ 时电荷密度、温度以及流场分布 (a)$Ste= $ $ 0.05$ ; (b)$Ste=0.1$ Figure 11. With
$T=3200$ , distributions of charge density, temperature field and streamlines of PCM melting at$f_{\rm l}=0.3$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.5$ ,$f_{\rm l}=0.9$ for different Stefan number: (a)$Ste=0.05$ ; (b)$Ste=0.1$ . -
[1] Luo X, Wang J H, Dooner M, Clarke J 2015 Appl. Energy 137 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H S, Cong T N, Yang W, Tan C Q, Li Y L, Ding Y L 2009 Prog. Nat. Sci. 19 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 霍宇涛 2018 博士学位论文 (徐州: 中国矿业大学)
Huo Y T 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] Ren Q L, Meng F L, Guo P H 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 121 1214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵耀 2018 博士学位论文 (上海: 上海交通大学)
Zhao Y 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University) (in Chinese)
[6] Sharma A, Tyagi V V, Chen C R, Buddhi D 2009 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 13 318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Agyenim F, Hewitt N, Eames P, Smyth M 2010 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 14 615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ren Q L 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 180 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Stritih U 2004 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 47 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lacroix M, Benmadda M 1997 Numer. Heat Tranfer, Part A 31 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ji C Z, Qin Z, Low Z H, Dubey S, Choo F H, Duan F 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 129 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Khodadadi J M, Hosseinizadeh S F 2007 Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 34 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Feng Y C, Li H X, Li L X, Bu L, Wang T 2015 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 81 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiao X, Zhang P, Li M 2014 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 81 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张涛, 余建祖 2007 制冷学报 6 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T, Yu J Z 2007 J. Refrigeration 6 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan L W, Zhu Z Q, Zeng Y, Ding Q, Liu M J 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 95 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fan L W, Zhu Z Q, Liu M J, Xu C L, Zeng Y, Lu H, Tao Y Z 2016 J. Heat Transfer-Trans. ASME 138 122402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Oh Y K, Park S H, Cha K O 2001 KSME Int. J. 15 1882
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Oh Y K, Park S H, Cho Y I 2002 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45 4631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nakhla D, Sadek H, Cotton J S 2015 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 81 695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Rashidi S, Bafekr H, Masoodi R, Languri M E 2017 J. Electrostat. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Atten P, Mc Cluskey F, Pérez A 1988 IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation 23 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Traoré P, Pérez A T, Koulova D, Romat H 2010 J. Fluid Mech. 658 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu J, Traoré P, Zhang M, Pérez A T, Vázquez P A 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 92 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 陈凤, 彭耀, 宋耀祖, 陈民 2007 工程热 4 679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen F, Peng Y, Song Y Z, Chen M 2007 J. Eng. Therm. 4 679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao M, Cheng P, Quan X 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 67 984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sadek H, Ching C Y, Cotton J 2010 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53 3721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 陈春天, 杨嘉祥, 张颖, 李静 2004 工程热 2 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen C T, Yang J X, Zhang Y, Li J 2004 J. Eng. Therm. 2 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李典, 王太, 陈烁, 谢英柏, 刘春涛 2020 工程热 41 2752
Li D, Wang T, Chen L, Xie Y B, Liu C T 2020 J. Eng. Therm. 41 2752
[30] 危卫, 张云伟, 顾兆林 2013 科学通报 58 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei W, Zhang Y W, Gu Z L 2013 Chin. Sci. Bull. 58 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Nakhla D, Thompson E, Lacroix B, Cotton J S 2018 J. Electrostat. 92 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Luo K, Pérez A T, Wu J, Yi H L, Tan H P 2019 Phys. Rev. E 100 013306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 卢才磊 2020 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Lu C L 2020 M. D. Thesis (Haerbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[34] Selvakumar R D, Liu Q, Luo K, Traoré P, Wu J 2021 Int. J. Multiphase Flow 136 103550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Nakhla D, Cotton J S 2021 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 167 120828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Luo K, Wu J, Pérez A T, Yi H L, Tan H P 2019 Phys. Rev. Fluids 4 083702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Huang R Z, Wu H Y 2015 J. Comput. Phys. 294 346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 罗康 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Luo K 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Haerbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[39] Chen S, Doolen G D 1998 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Wang L, Zhao Y, Yang X G, Shi B C, Chai Z H 2019 Appl. Math. Model. 71 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] 黄昌盛, 张文欢, 侯志敏, 陈俊辉, 李明晶, 何南忠, 施保昌 2011 科学通报 56 2434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang C S, Zhang W H, Hou Z M, Chen J H, Li M J, He N Z, Shi B C 2011 Chin. Sci. Bull. 56 2434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 李洋, 苏婷, 梁宏, 徐江荣 2018 67 224701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Su T, Liang H, Xu J R 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 224701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 梁宏 2015 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Liang H 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[44] 李庆, 余悦, 唐诗 2020 科学通报 65 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Yu Y, Tang S 2020 Chin. Sci. Bull. 65 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 朱炼华, 郭照立 2015 计算物理 32 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu L H, Guo Z L 2015 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 32 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 刘高洁, 郭照立, 施保昌 2016 65 014702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu G J, Guo Z L, Shi B C 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 吴健, 张蒙齐, 田方宝 2018 力学学报 50 1458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J, Zhang M Q, Tian F B 2018 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 50 1458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Luo K, Wu J, Yi H L, Tan H P 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 023309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Wang L, Wei Z C, Li T F, Chai Z H, Shi B C 2021 Appl. Math. Model 95 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Guo Z L, Shi B C, Wang N C 2000 J. Comput. Phys. 165 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 046308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Chai Z H, Shi B C 2008 Appl. Math. Model. 32 2050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Lu J H, Lei H Y, Dai C S 2019 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 135 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Huang R Z, Wu H Y 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 315 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2002 Phys. Fluids 14 2007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Huang R Z, Wu H Y, Cheng P 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 59 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7082
- PDF Downloads: 127
- Cited By: 0























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: