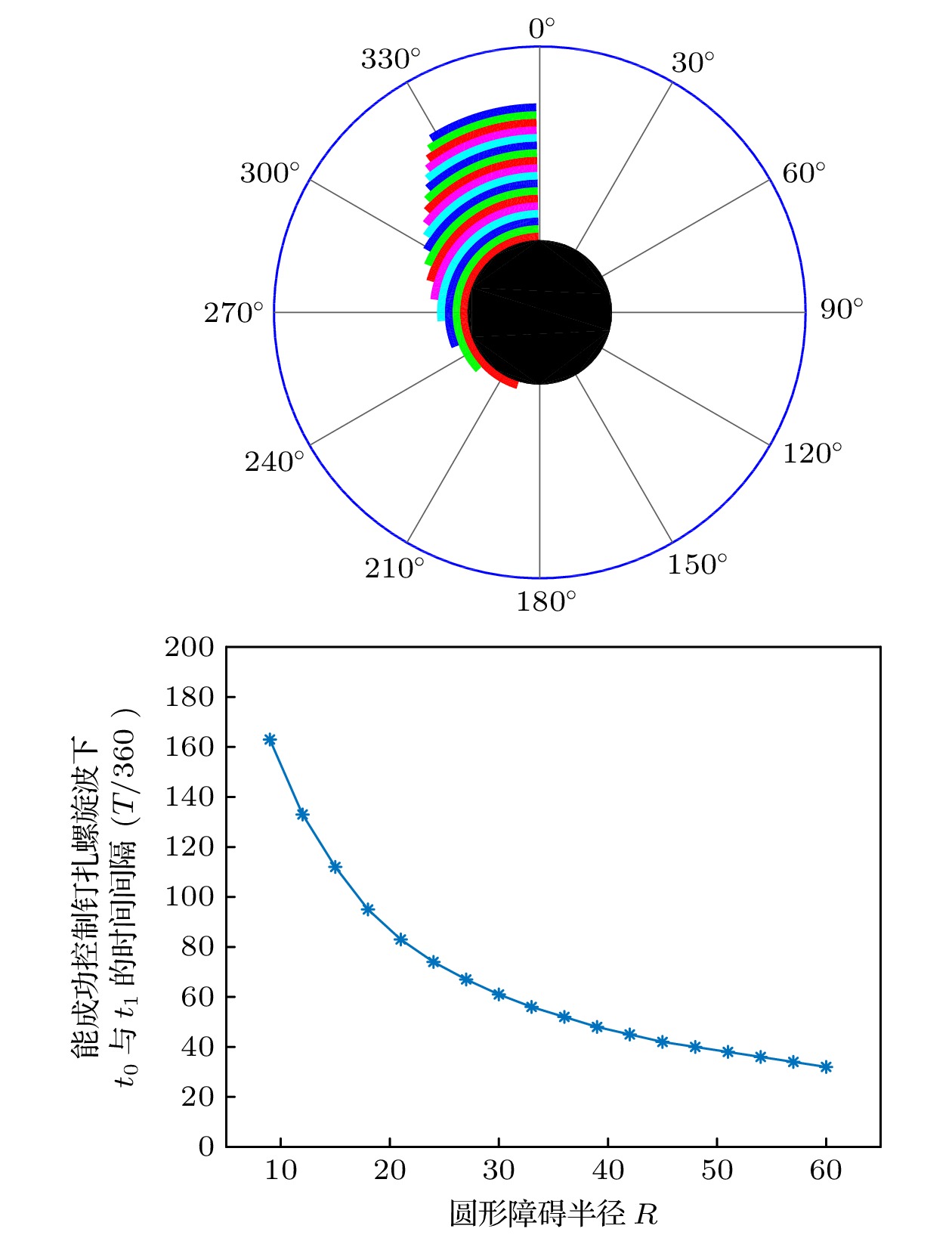
-
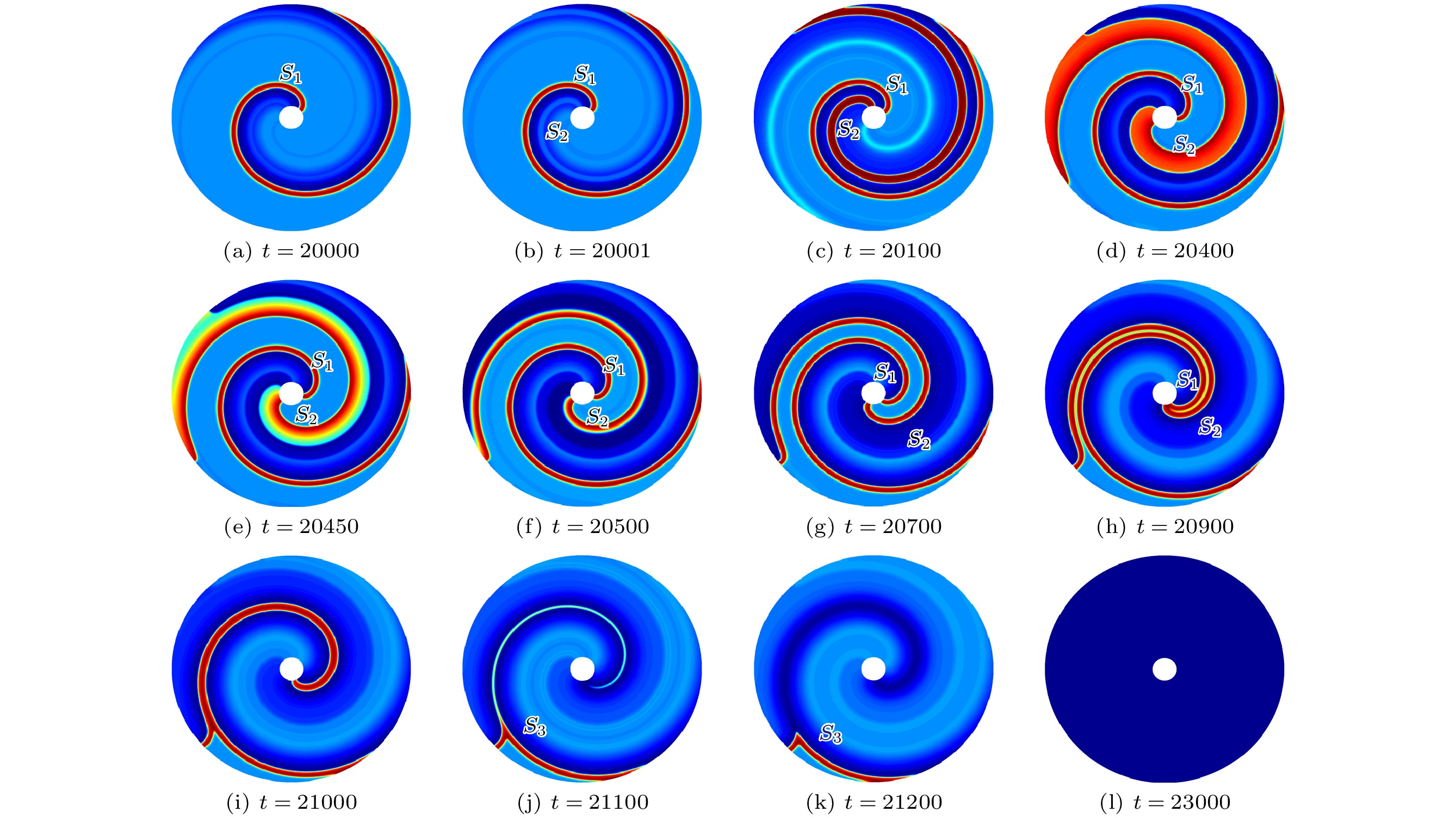
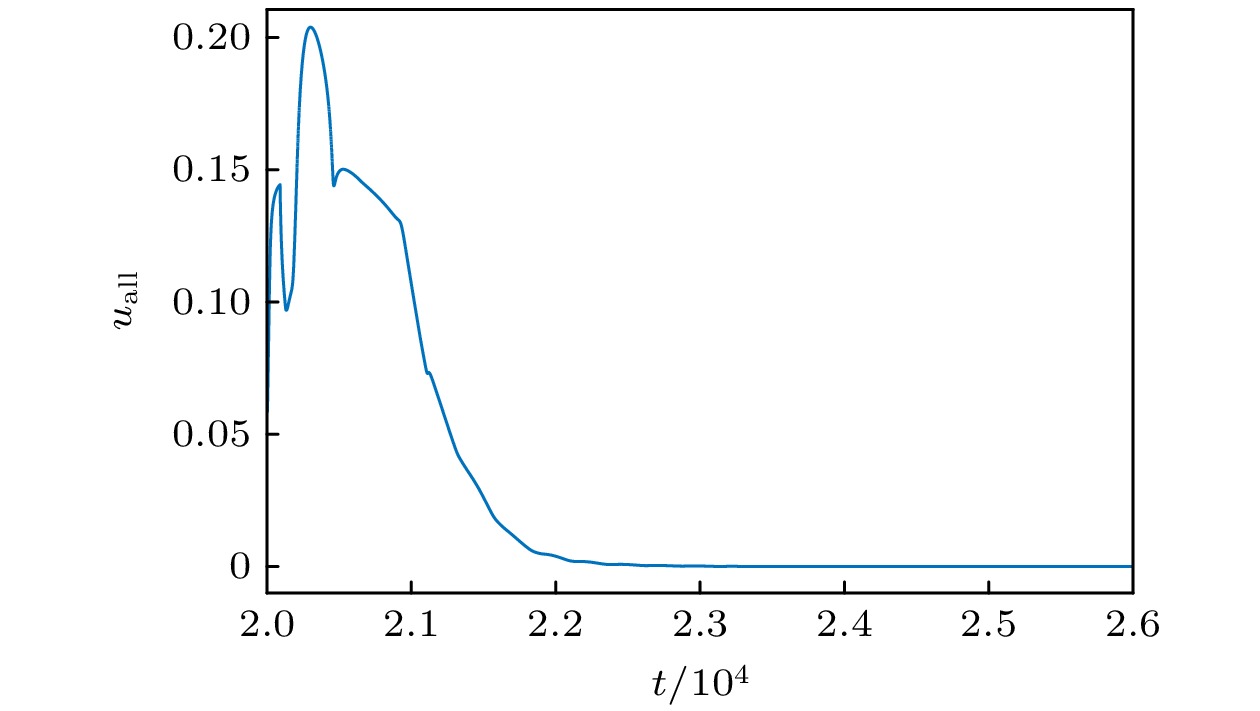
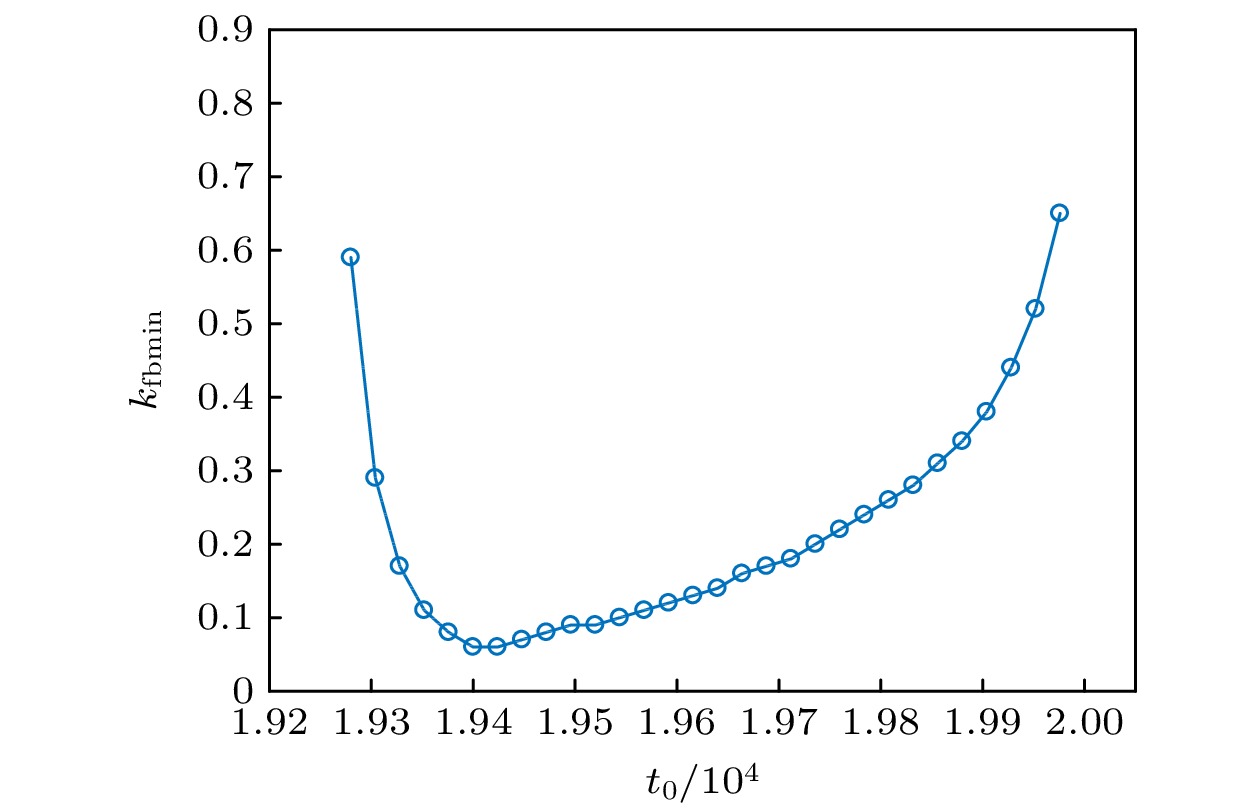
螺旋波是心室跳动过速和纤维性颤动的根源, 钉扎螺旋波相对于自由螺旋波来说更难消除. 本文采用格子Boltzmann方法求解, 以FitzHugh-Nagumo模型为对象, 研究了使用反馈控制法消除钉扎螺旋波. 数值结果表明, 无论钉扎螺旋波钉在圆形障碍物还是矩形障碍物上, 反馈控制法对其都具有很好的控制作用. 此外, 通过数值模拟系统研究了可激性系数、反馈控制信号幅度、记录反馈信号时间和障碍物的大小对钉扎螺旋波的控制情况. 研究表明, 钉扎螺旋波消除有三种情况. 首先, 反馈控制信号幅度和可激性系数与钉扎螺旋波消除所需的时间有关, 反馈控制信号幅度越大或可激性系数越小, 钉扎螺旋波消除越快. 其次, 障碍物大小和可激性系数影响着能成功消除钉扎螺旋波下记录反馈信号时间与加入反馈控制时间之间对应的时间间隔. 最后, 在保持加入反馈控制时间不变的情况下, 记录反馈信号时间影响着能成功消除钉扎螺旋波所需的最小反馈控制信号幅度.
-
关键词:
- 反馈控制法 /
- 钉扎螺旋波 /
- FitzHugh-Nagumo模型 /
- 格子Boltzmann方法
Spiral waves are common in nature and have received a lot of attention. Spiral wave is the source of ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, and pinned spiral wave is less likely to be eliminated than free spiral wave. Therefore, it is important to find an effective method to control the pinned spiral wave. In this work, we investigate the feedback control approach to eliminating pinned spiral wave based on the lattice Boltzmann method, by using the FitzHugh-Nagumo model as an object. The numerical results show that the feedback control method has a good control effect on the pinned spiral wave no matter whether it is pinned on a circular or rectangular obstacle. In addition, the excitability coefficient, amplitude of feedback control, recording feedback signal time and obstacle size are systematically investigated by numerical simulation. The study shows that there are three cases of pinned spiral wave cancellation. Firstly, the amplitude of feedback control and excitability coefficient are related to the time required to eliminate the pinned spiral wave, and the larger the amplitude of feedback control signal or the smaller the excitability coefficient, the faster the cancellation of the pinned spiral waveis. Secondly, the size of the obstacle and the excitability coefficient affect the time interval between the time of recording the feedback signal and the time of adding the feedback control that can successfully control the pinned spiral wave. Finally, the recorded feedback signal time affects the minimum amplitude of feedback control required to successfully eliminate the pinned spiral wave, while the added feedback control time is constant. According to the discussion in this paper, it can be seen that the feedback control method has a good control effect on the pinned spiral wave.-
Keywords:
- feedback control approach /
- pinned spiral waves /
- FitzHugh-Nagumo model /
- lattice Boltzmann method
[1] Winfree A T 1972 Science 175 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rotermund H H, Jakubith S, Von Oertzen A, Ertl G 1991 Phys. Rev. Lett. 66 3083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Witkowski F X, Leon L J, Penkoske P A, Giles W R, Spano M L, Ditto W L, Winfree A T 1998 Nature 392 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zakin A N, Zhabotinsky A M 1970 Nature 225 535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Valderrábano M, Kim Y, Yashima M, Wu T, Karagueuzian H S, Chen P S 2000 J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou X, Levine H, Kessler D A 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 R800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Steinbock O, Müller S C 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 1506
[8] Fu Y Q, Zhang H, Cao Z 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 046206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ponboonjaroenchai B, Srithamma P, Kumchaiseemak N, et. al. 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 901 012027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen J X, Peng L, Ma J 2014 EPL 107 38001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yuan G Y, Gao Z, Yan S 2021 Nonlinear Dyn. 104 2583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yuan G Y, Yang S P, Wang G R, Chen S G 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 1674
[13] Hou Z M, Shi B C, Chai Z H 2017 Comput. Math. Appl. 74 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chai Z H, Shi B C 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 023306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi B C, Guo Z L 2009 Phys. Rev. E 79 016701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Higuera F J, Succi S 1989 EPL 8 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F 1952 J. Physiol. 117 500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] FitzHugh R 1961 Biophys. J 1 445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Courtemanche M, Skaggs W, Winfree A T 1990 Phys. D 41 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liang H, Wu H 2008 J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103 1570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Concha A, Garrido R 2015 J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 10 021023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 何雅玲, 王勇, 李庆 2009 格子Boltzmann 方法的理论及应用(北京: 科学出版社) 第123—126页
He Y L, Wang Y, Li Q 2009 Lattice Boltzmann Method: Theory and Applications (Beijing: Science Press) pp123–126
-
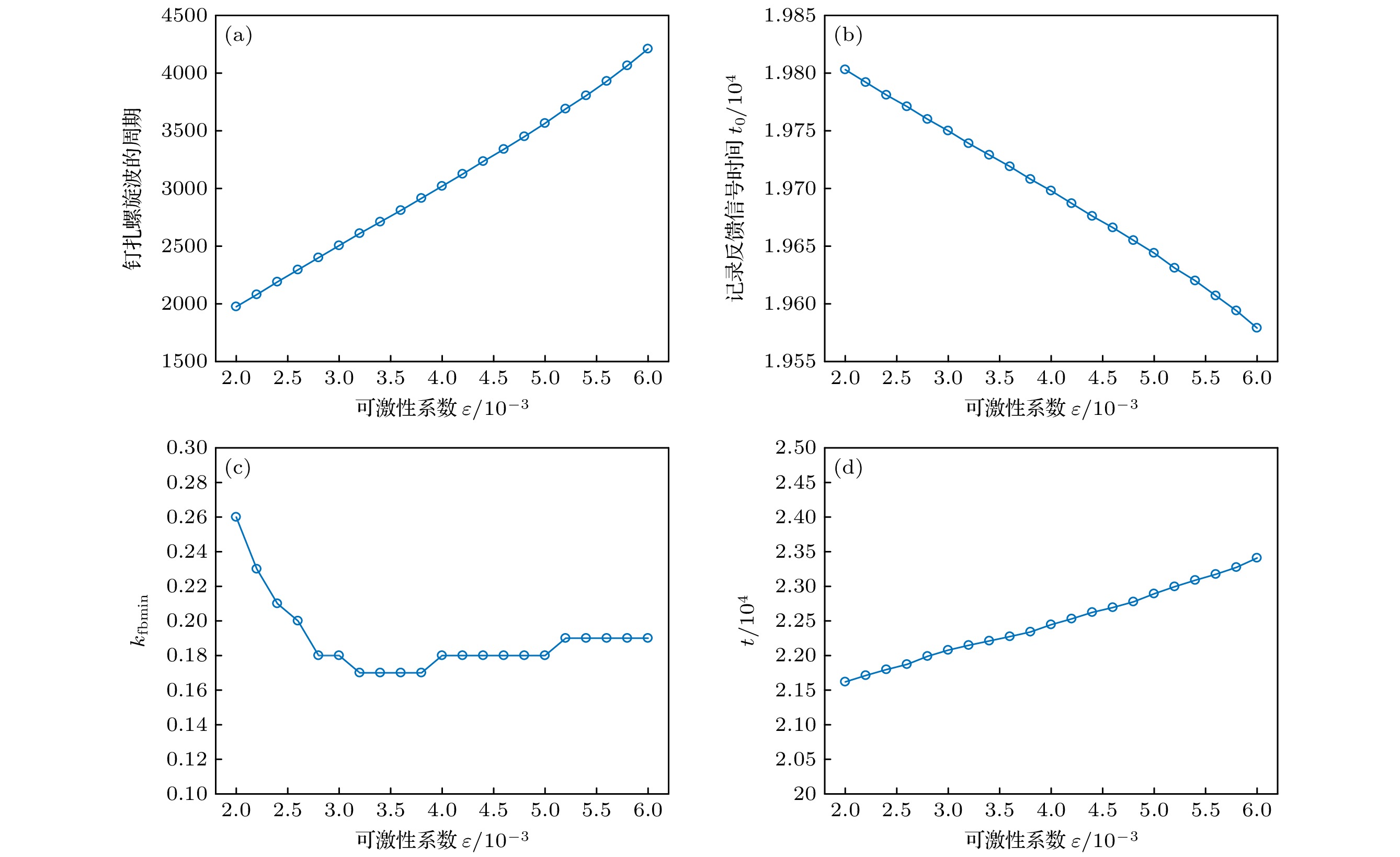
图 8 (a)钉扎螺旋波的周期随可激性系数$ \varepsilon $的变化; (b)记录反馈信号时间$ t_0 $随可激性系数$ \varepsilon $的变化; (c)$ k_{{\mathrm{fbmin}}} $随可激性系数$ \varepsilon $的变化; (d)钉扎螺旋波的控制时间t随可激性系数$ \varepsilon $的变化
Fig. 8. (a) Variation of the period of the pinned spiral wave with $ \varepsilon $; (b) variation of the time of recording the feedback signal with $ \varepsilon $; (c) variation of $ k_{{\mathrm{fbmin}}} $ with $ \varepsilon $; (d) variation of the time required to eliminate the pinned spiral wave with $ \varepsilon $
表 1 不同半径下钉扎螺旋波的波长及相对误差(1200×1200网格和1600×1600网格下)
Table 1. Wavelengths and relative errors of pinned spiral waves at different radius (under 1200×1200 grids and 1600×1600 grids).
半径 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1200×1200网格下的波长 5.031 5.552 6.055 6.575 7.602 8.275 8.871 9.451 1600×1600网格下的波长 5.041 5.582 6.071 6.602 7.633 8.345 8.912 9.502 相对误差 0.0020 0.0054 0.0026 0.0041 0.0041 0.0081 0.0046 0.0047 -
[1] Winfree A T 1972 Science 175 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rotermund H H, Jakubith S, Von Oertzen A, Ertl G 1991 Phys. Rev. Lett. 66 3083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Witkowski F X, Leon L J, Penkoske P A, Giles W R, Spano M L, Ditto W L, Winfree A T 1998 Nature 392 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zakin A N, Zhabotinsky A M 1970 Nature 225 535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Valderrábano M, Kim Y, Yashima M, Wu T, Karagueuzian H S, Chen P S 2000 J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou X, Levine H, Kessler D A 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 R800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Steinbock O, Müller S C 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 1506
[8] Fu Y Q, Zhang H, Cao Z 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 046206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ponboonjaroenchai B, Srithamma P, Kumchaiseemak N, et. al. 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 901 012027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen J X, Peng L, Ma J 2014 EPL 107 38001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yuan G Y, Gao Z, Yan S 2021 Nonlinear Dyn. 104 2583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yuan G Y, Yang S P, Wang G R, Chen S G 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 1674
[13] Hou Z M, Shi B C, Chai Z H 2017 Comput. Math. Appl. 74 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chai Z H, Shi B C 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 023306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi B C, Guo Z L 2009 Phys. Rev. E 79 016701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Higuera F J, Succi S 1989 EPL 8 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F 1952 J. Physiol. 117 500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] FitzHugh R 1961 Biophys. J 1 445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Courtemanche M, Skaggs W, Winfree A T 1990 Phys. D 41 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liang H, Wu H 2008 J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103 1570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Concha A, Garrido R 2015 J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 10 021023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 何雅玲, 王勇, 李庆 2009 格子Boltzmann 方法的理论及应用(北京: 科学出版社) 第123—126页
He Y L, Wang Y, Li Q 2009 Lattice Boltzmann Method: Theory and Applications (Beijing: Science Press) pp123–126
计量
- 文章访问数: 3749
- PDF下载量: 100
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: