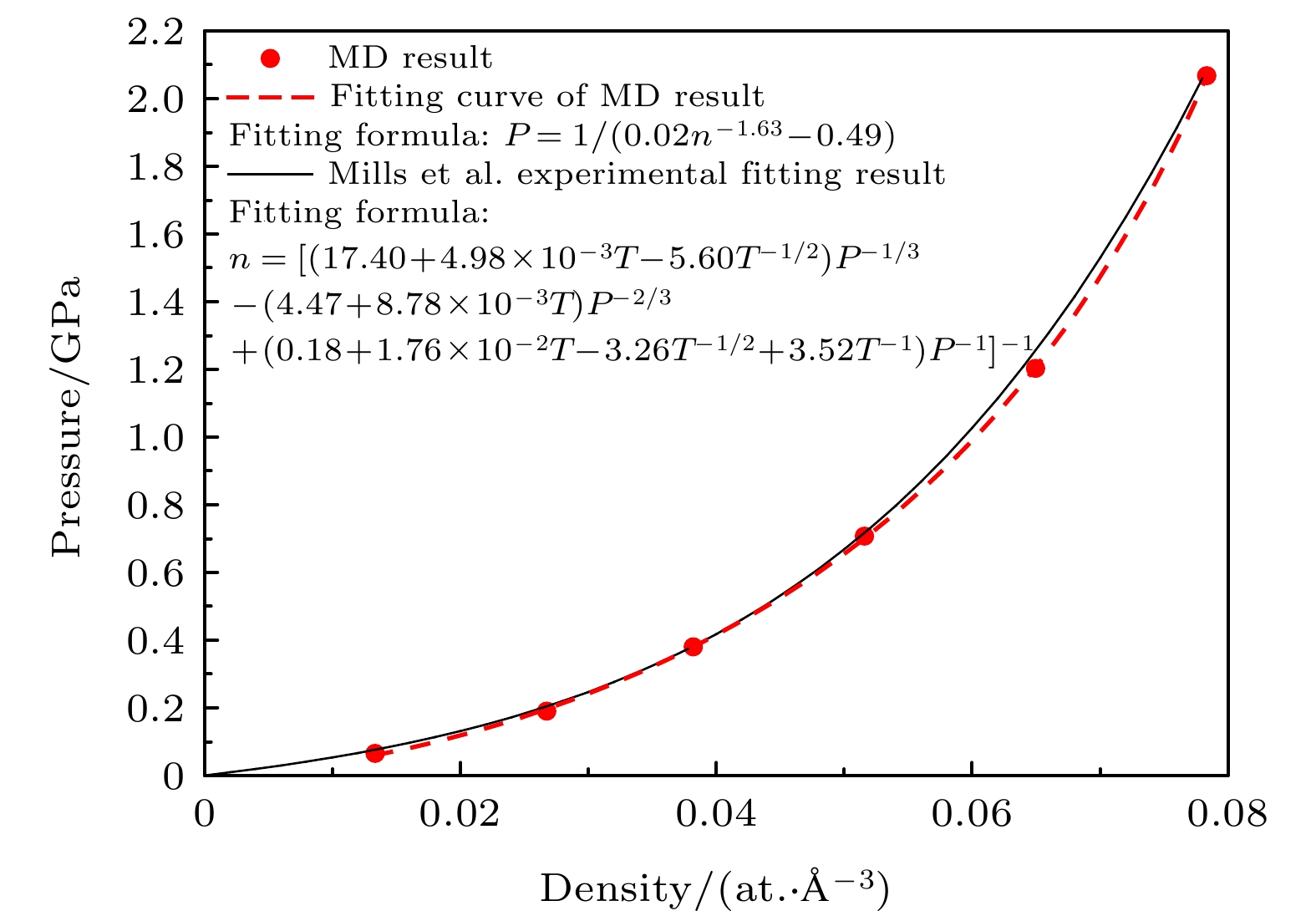
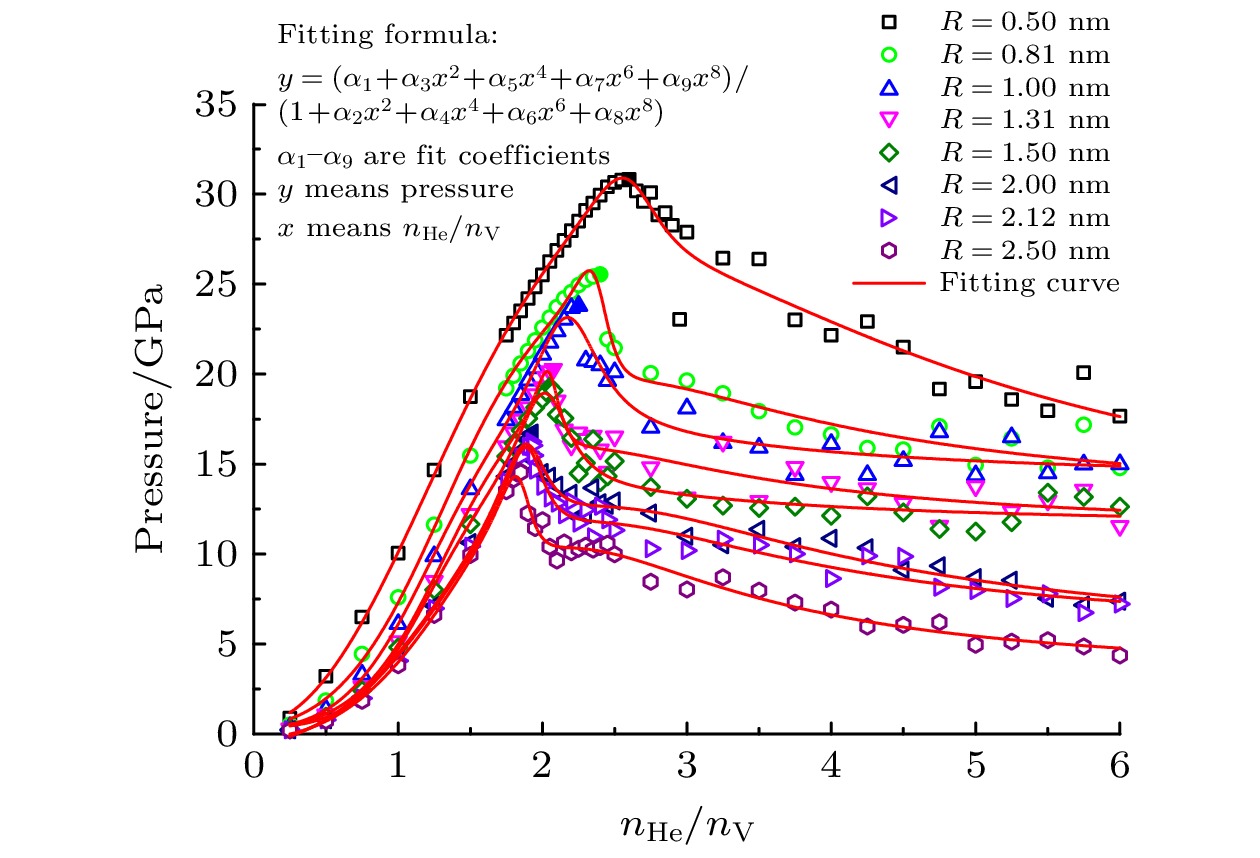
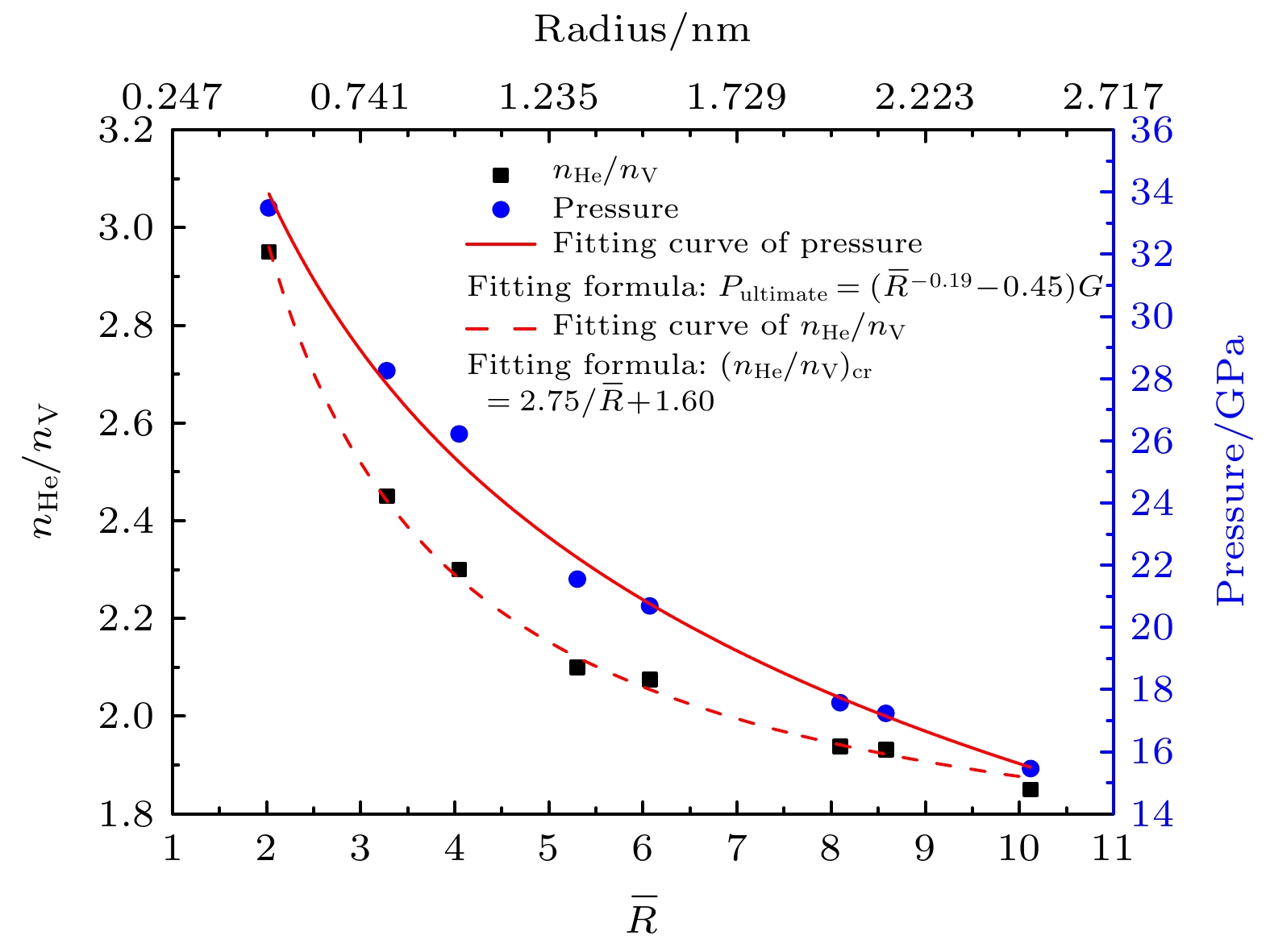
-
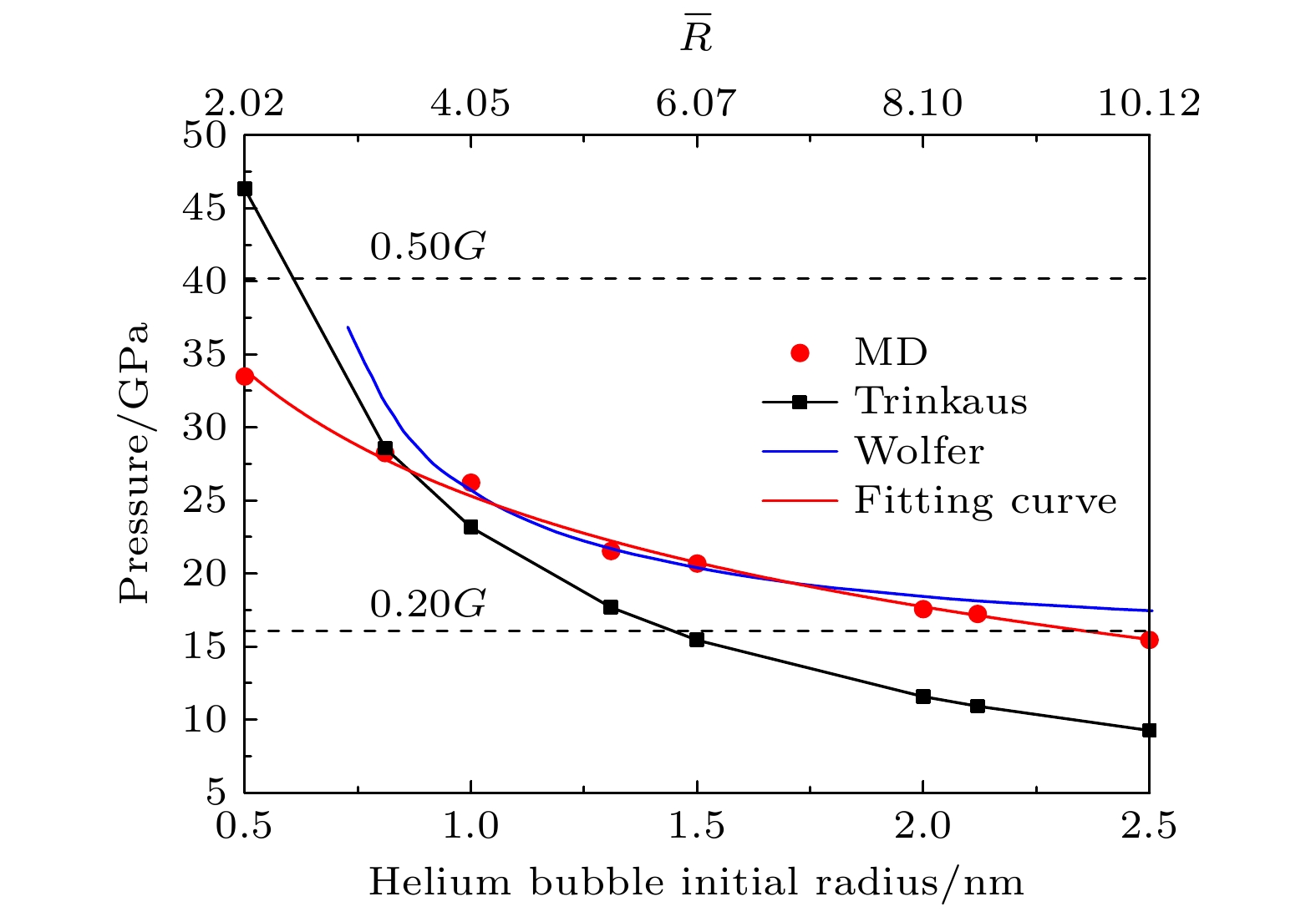
In order to understand further the micro-mechanism of helium bubble punching out of the dislocation loop in α-Fe, it is necessary to study the ultimate pressure characteristics of helium bubble punching out of the dislocation loop. In this paper, a cubic representative volume element (RVE) model of the metal-helium bubble is established. For eight types of spherical helium bubbles with different initial radii, molecular dynamics simulations are carried out with the initial helium-to-vacancy ratio serving as a variable and the ultimate pressure of helium bubble and the critical helium-to-vacancy ratio at the beginning of dislocation loop formation in each model are obtained. The results show that for helium bubbles with dimensionless radius ranging from 2 to 10, both the ultimate pressure and the critical helium-to-vacancy ratio of helium bubble punching out of the dislocation loop decrease nonlinearly with the increase of initial helium bubble radius. The relationships of the ultimate pressure and the critical helium-to-vacancy ratio with the initial radius of helium bubble are fitted respectively according to the simulation results and the fitted two equations are in good agreement with the results of previous theoretical studies. The critical helium-to-vacancy ratio required for helium bubble punching out of the dislocation loop in α-Fe has an obvious size effect. For the helium bubble in the late nucleation stage (e.g. helium bubble with an initial radius of 0.81 nm) and non-ideal gas stage (e.g. helium bubble with an initial radius ranging from 1.00 nm to 2.50 nm), the critical helium-to-vacancy ratios for punching out of the dislocation loop are the same as the initial helium-to-vacancy ratio corresponding to the peak pressure point of helium bubble. But for early or middle nucleation stage, such as helium bubble with an initial radius of 0.50 nm, the critical helium-to-vacancy ratio for punching out of the dislocation loop is about 13.46% greater than the initial helium-to-vacancy ratios corresponding to the peak pressure points. At the initial moment (0 ps), in the cross section passing through the center of cubic RVE, the shear stress is concentrated, and the maximum shear stress of Fe atom array around the helium bubble is located at the intersection points (i.e. at 45°) of diagonal and helium bubble boundary, and it is distributed symmetrically with respect to the double fold lines of the cross section parallel to the sides. Both the range of shear stress concentrating area and the maximum shear stress increase with the initial helium-to-vacancy ratio increasing. The dislocation loop’s punching direction corresponds to the direction of the maximum shear stress. The research in this paper can deepen the understanding of the physical properties of helium bubbles in metals and lay a useful foundation for the subsequent analyzing of the effects of helium bubbles on the macroscopic physical and mechanical properties of materials.
-
Keywords:
- α-Fe /
- helium bubble /
- initial helium-to-vacancy ratio /
- ultimate pressure
[1] 王佩璇, 宋家树 2002 材料中的氦及氚渗透 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第1−52页
Wang P X, Song J S 2002 Helium and Permeation of Tritium in Materials (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp1−52
[2] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Barnes R S 1965 Nature 206 1307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang Z J, Allen F I, Shan Z W, Hosemann P 2016 Acta Mater. 121 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 彭述明, 王和义 2015 氚化学与工艺学 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第1−51页
Peng S M, Wang H Y 2015 Tritium Chemistry and Technology (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp1−51
[6] 刘远东, 尹益辉, 谭云, 孙颖, 梅军 2011 中国科学 技术科学 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Yin Y H, Tan Y, Sun Y, Mei J 2011 Sci. China Tech. Sci. 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘远东, 尹益辉, 谭云 2012 61 156601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Yin Y H, Tan Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 156601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 尹益辉, 刘远东, 陈长安, 谭云 2016 中国科学 技术科学 46 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin Y H, Liu Y D, Chen C A, Tan Y 2016 Sci. Sin. Tech. 46 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu P P, Zhan Q, Fu Z Y, Wei Y P, Wang Y M, Wang F M, Ohnuki S, Wan F R 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 649 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krsjak V, Degmova J, Sojak S, Slugen V 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 499 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Taverna D, Kociak M, Stéphan O, Fabre A, Finot E, Décamps B, Colliex C 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 035301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fréchard S, Walls M, Kociak M, Chevalier J P, Henry J, Gorse D 2009 J. Nucl. Mater. 393 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Trinkaus H 1983 Radiat. Eff. 78 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 郭立平, 罗凤凤, 于雁霞 2017 核材料辐照位错环 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第174−200页
Guo L P, Luo F F, Yu Y X 2017 Dislocation Loops in Irradiated Nuclear Materials (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp174−200
[15] Wolfer W G 1988 Philos. Mag. A 58 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Y, Yin Y, Zhao F, Deng K, Feng J, Li J, Yan G 2019 Steel Res. Int. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Deng H Q, Hu W Y, Gao F, Heinisch H L, Hu S Y, Li Y L, Kurtz R J 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 442 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gao C, Tian D, Li M, Qian D 2018 Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. with Mater. Atoms 418 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang B L, Wang J, Hou Q 2011 Chin. Phys. B 20 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hetherly J, Martinez E, Nastasi M, Caro A 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 419 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Caro A, Hetherly J, Stukowski A, Caro M, Martinez E, Srivilliputhur S, Zepeda-Ruiz L, Nastasi M 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 418 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xie H, Gao N, Xu K, Lu G H, Yu T, Yin F 2017 Acta Mater. 141 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Caskey G R 1985 Fusion Technol. 8 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Edmondson P D, Parish C M, Zhang Y, Hallén A, Miller M K 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 434 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang F, Wang X, Wierschke J B, Wang L 2015 Scr. Mater. 109 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Plimpton S 1995 J. Comput. Phys. 117 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 梁力, 谈效华, 向伟, 王远, 程焰林, 马明旺 2015 64 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L, Tan X H, Xiang W, Wang Y, Cheng Y L, Ma M W 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ackland G J, Mendelev M I, Srolovitz D J, Han S, Barashev A V 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 S2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Aziz R A, Janzen A R, Moldover M R 1995 Phys.Rev.Lett 74 1586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gao F, Deng H, Heinisch H L, Kurtz R J 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 418 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo S H, Zhu B E, Liu W C, Pan Z Y, Wang Y X 2009 Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. with Mater. Atoms 267 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Thompson A P, Plimpton S J, Mattson W 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 154107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rycroft, Chris H 2009 Chaos 19 41111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Mills R L, Liebenberg D H, Bronson J C 1980 Phys. Rev. B 21 5137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Stukowski A 2010 Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18 15012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Stukowski A, Bulatov V V, Arsenlis A 2012 Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 20 85007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Evans J H 1978 J. Nucl. Mater. 76–77 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Martienssen W, Warlimont H 2005 Handbook of Condensed Matter and Materials Data (New York: Springer Berlin Heidelberg) pp132−134
[39] Wolfer W G 1989 Philos. Mag. A 59 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Iwakiri H 2000 J. Nucl. Mater. 283-287 1134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Donnelly S E 1985 Radiat. Eff. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Trinkaus H 1989 Scr. Metall. 23 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
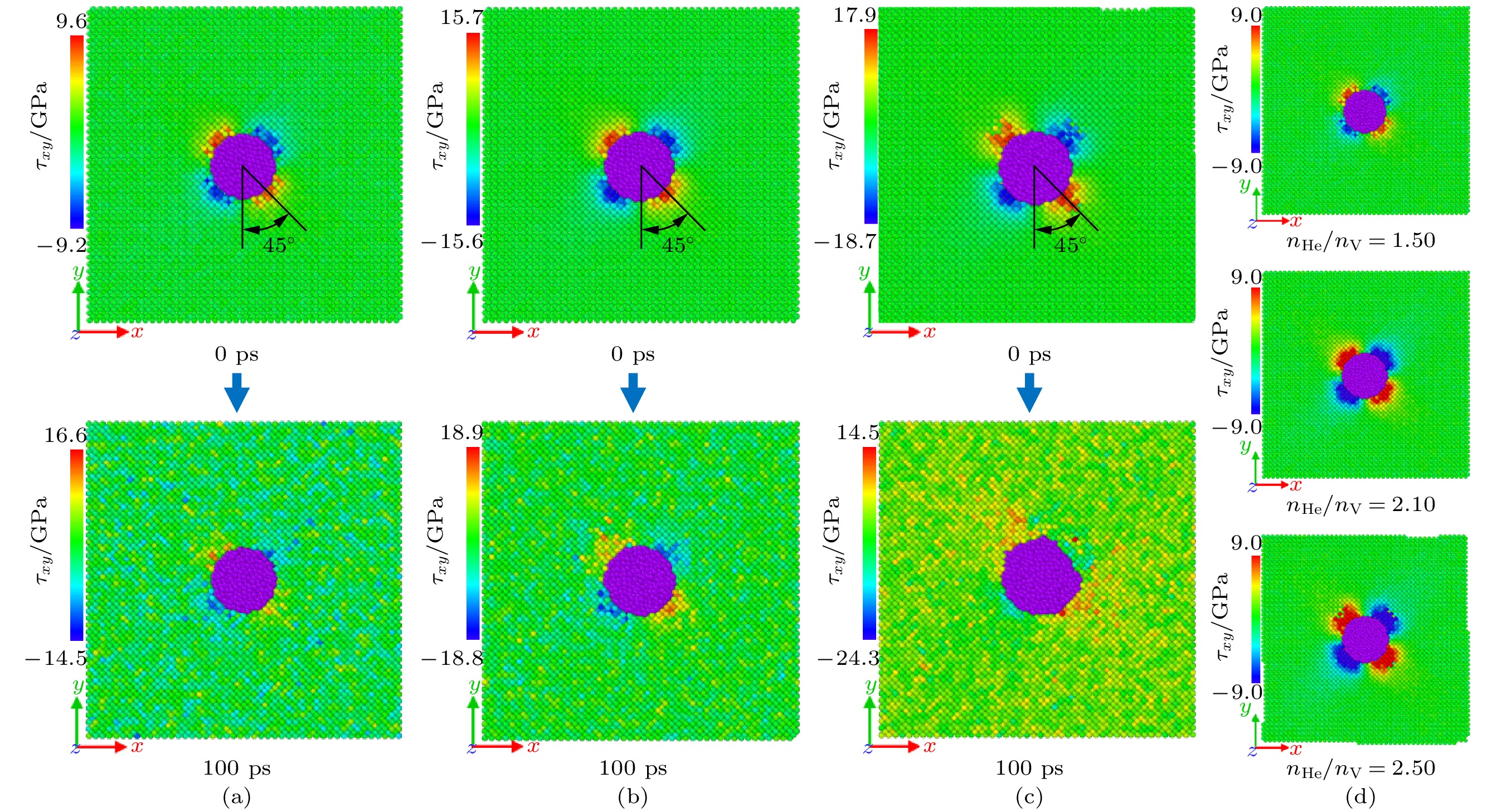
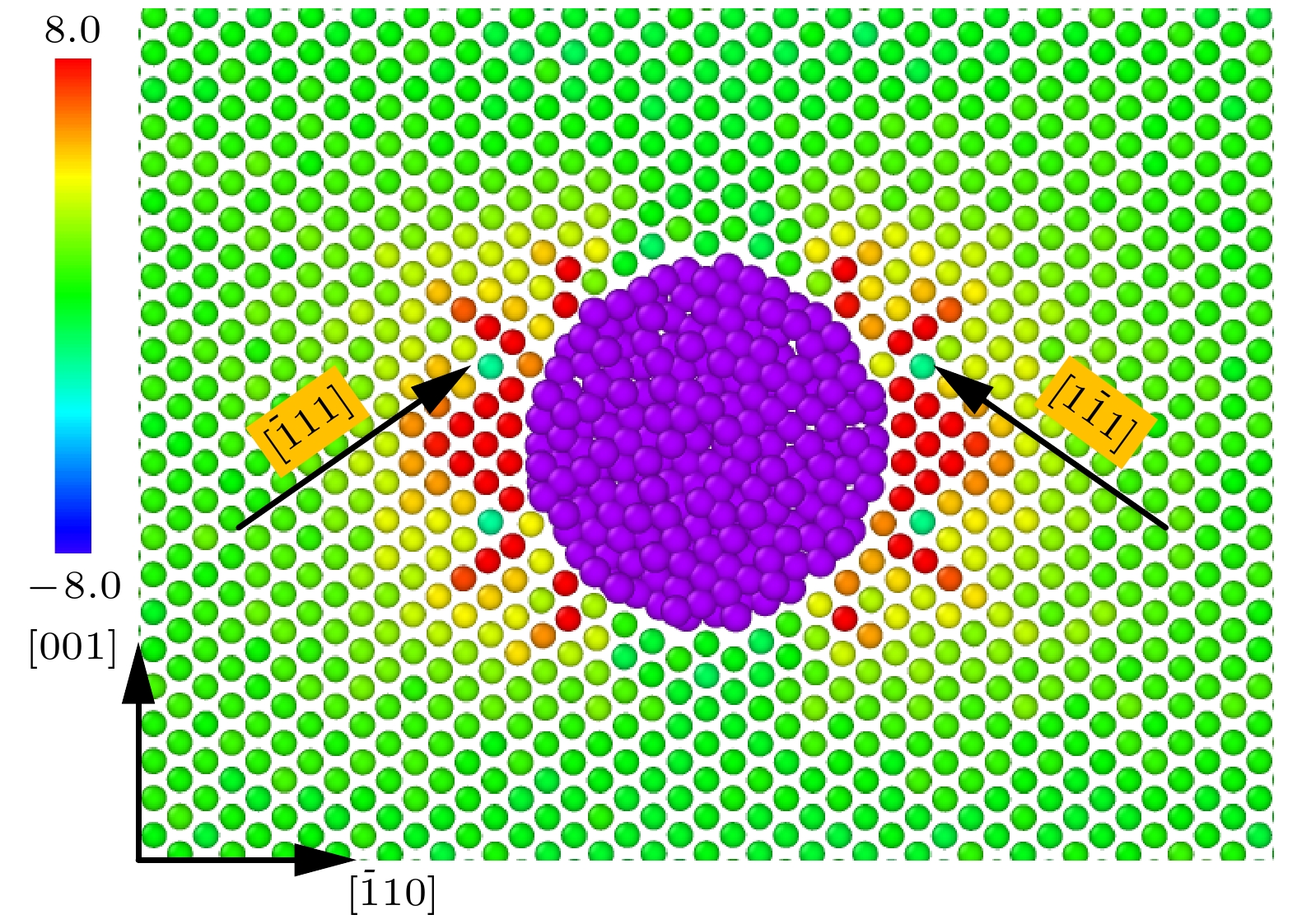
图 5 氦泡周围Fe原子阵列的剪应力分布 (a) nHe/nV = 1.50; (b) nHe/nV = 2.10; (c) nHe/nV = 2.50; (d) 上下限相同时0 ps处的原子应力分布
Figure 5. Shear stress distribution of Fe atom array around helium bubble: (a) nHe/nV = 1.50; (b) nHe/nV = 2.10; (c) nHe/nV = 2.50; (d) atomic stress distribution at 0 ps with the same upper and lower limit.
图 6 初始半径为1.31 nm, nHe/nV = 2.10时氦泡冲出的位错环在xy平面投影 (a) 88 ps; (b) 92 ps; (c) 100 ps; (d)删除图6(c)中Fe原子后带缺陷网格的位错图
Figure 6. Projection of dislocation loops produced by helium bubbles in xy plane, when initial radius of helium bubble is 1.31 nm, nHe/nV = 2.10: (a) 88 ps; (b) 92 ps; (c) 100 ps; (d) a dislocation picture with a defect mesh after removing the Fe atoms in Fig. 6(c).
-
[1] 王佩璇, 宋家树 2002 材料中的氦及氚渗透 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第1−52页
Wang P X, Song J S 2002 Helium and Permeation of Tritium in Materials (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp1−52
[2] Trinkaus H, Singh B N 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Barnes R S 1965 Nature 206 1307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang Z J, Allen F I, Shan Z W, Hosemann P 2016 Acta Mater. 121 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 彭述明, 王和义 2015 氚化学与工艺学 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第1−51页
Peng S M, Wang H Y 2015 Tritium Chemistry and Technology (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp1−51
[6] 刘远东, 尹益辉, 谭云, 孙颖, 梅军 2011 中国科学 技术科学 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Yin Y H, Tan Y, Sun Y, Mei J 2011 Sci. China Tech. Sci. 54 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘远东, 尹益辉, 谭云 2012 61 156601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y D, Yin Y H, Tan Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 156601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 尹益辉, 刘远东, 陈长安, 谭云 2016 中国科学 技术科学 46 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin Y H, Liu Y D, Chen C A, Tan Y 2016 Sci. Sin. Tech. 46 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu P P, Zhan Q, Fu Z Y, Wei Y P, Wang Y M, Wang F M, Ohnuki S, Wan F R 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 649 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krsjak V, Degmova J, Sojak S, Slugen V 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 499 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Taverna D, Kociak M, Stéphan O, Fabre A, Finot E, Décamps B, Colliex C 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 035301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fréchard S, Walls M, Kociak M, Chevalier J P, Henry J, Gorse D 2009 J. Nucl. Mater. 393 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Trinkaus H 1983 Radiat. Eff. 78 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 郭立平, 罗凤凤, 于雁霞 2017 核材料辐照位错环 (第1版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第174−200页
Guo L P, Luo F F, Yu Y X 2017 Dislocation Loops in Irradiated Nuclear Materials (1st Ed.) (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) pp174−200
[15] Wolfer W G 1988 Philos. Mag. A 58 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Y, Yin Y, Zhao F, Deng K, Feng J, Li J, Yan G 2019 Steel Res. Int. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Deng H Q, Hu W Y, Gao F, Heinisch H L, Hu S Y, Li Y L, Kurtz R J 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 442 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gao C, Tian D, Li M, Qian D 2018 Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. with Mater. Atoms 418 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang B L, Wang J, Hou Q 2011 Chin. Phys. B 20 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hetherly J, Martinez E, Nastasi M, Caro A 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 419 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Caro A, Hetherly J, Stukowski A, Caro M, Martinez E, Srivilliputhur S, Zepeda-Ruiz L, Nastasi M 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 418 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xie H, Gao N, Xu K, Lu G H, Yu T, Yin F 2017 Acta Mater. 141 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Caskey G R 1985 Fusion Technol. 8 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Edmondson P D, Parish C M, Zhang Y, Hallén A, Miller M K 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 434 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang F, Wang X, Wierschke J B, Wang L 2015 Scr. Mater. 109 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Plimpton S 1995 J. Comput. Phys. 117 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 梁力, 谈效华, 向伟, 王远, 程焰林, 马明旺 2015 64 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang L, Tan X H, Xiang W, Wang Y, Cheng Y L, Ma M W 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 046103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ackland G J, Mendelev M I, Srolovitz D J, Han S, Barashev A V 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 S2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Aziz R A, Janzen A R, Moldover M R 1995 Phys.Rev.Lett 74 1586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gao F, Deng H, Heinisch H L, Kurtz R J 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 418 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo S H, Zhu B E, Liu W C, Pan Z Y, Wang Y X 2009 Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. with Mater. Atoms 267 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Thompson A P, Plimpton S J, Mattson W 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 154107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rycroft, Chris H 2009 Chaos 19 41111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Mills R L, Liebenberg D H, Bronson J C 1980 Phys. Rev. B 21 5137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Stukowski A 2010 Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18 15012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Stukowski A, Bulatov V V, Arsenlis A 2012 Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 20 85007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Evans J H 1978 J. Nucl. Mater. 76–77 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Martienssen W, Warlimont H 2005 Handbook of Condensed Matter and Materials Data (New York: Springer Berlin Heidelberg) pp132−134
[39] Wolfer W G 1989 Philos. Mag. A 59 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Iwakiri H 2000 J. Nucl. Mater. 283-287 1134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Donnelly S E 1985 Radiat. Eff. 90 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Trinkaus H 1989 Scr. Metall. 23 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8753
- PDF Downloads: 119
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: