-
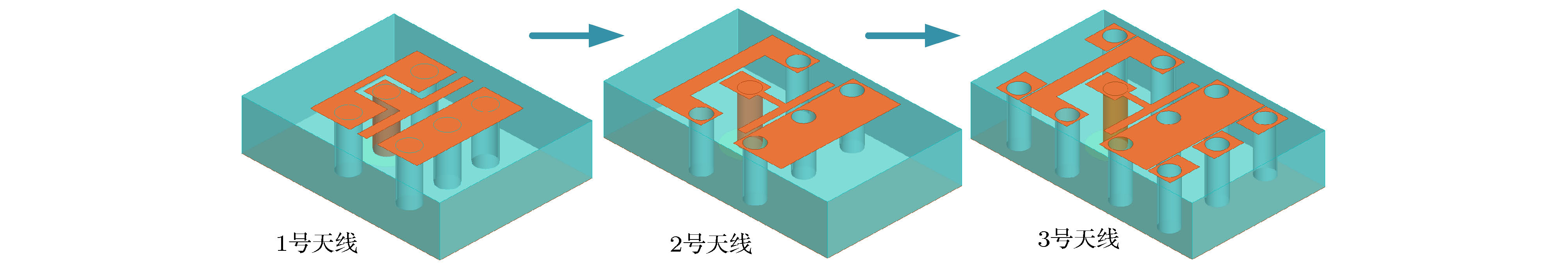
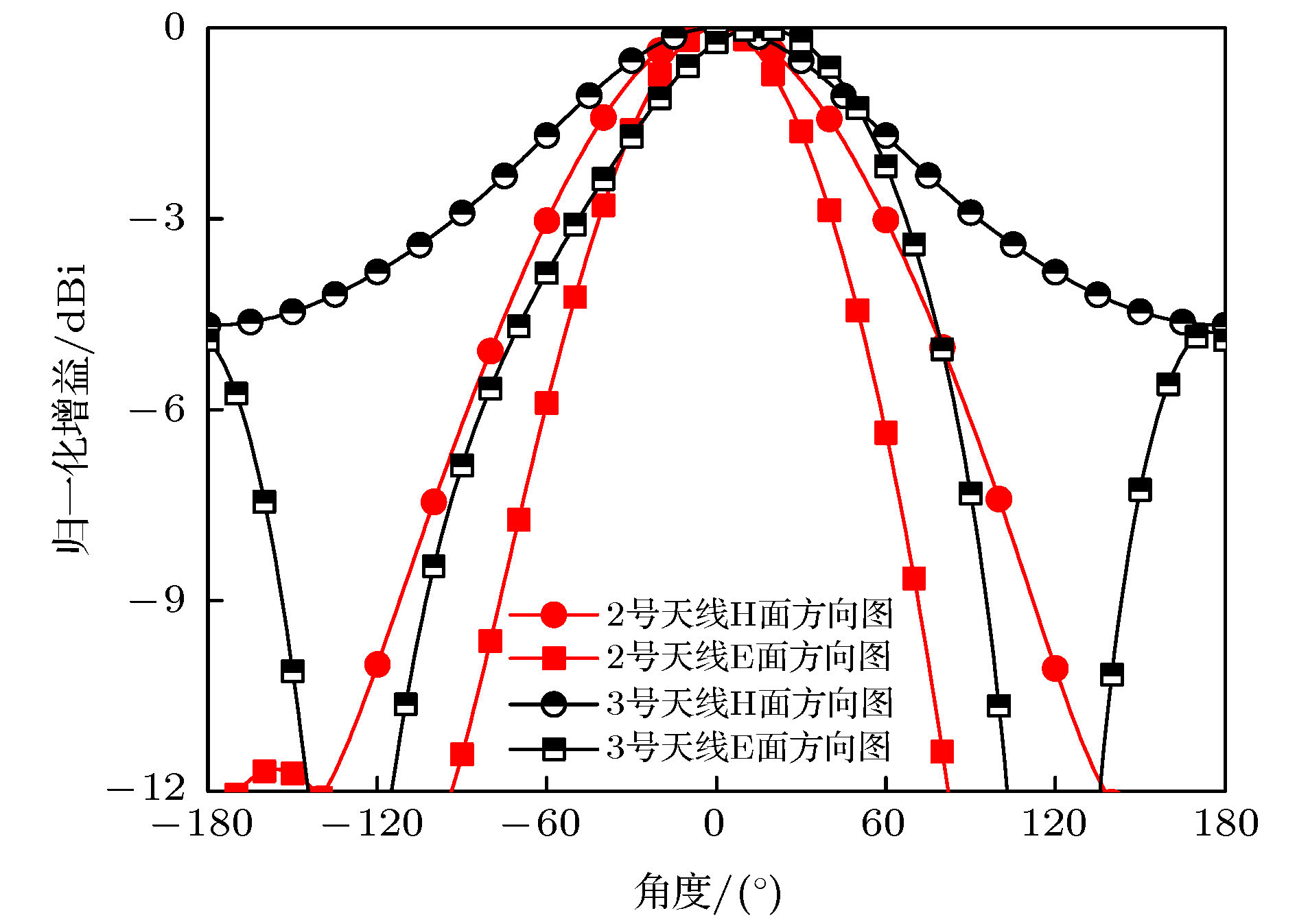
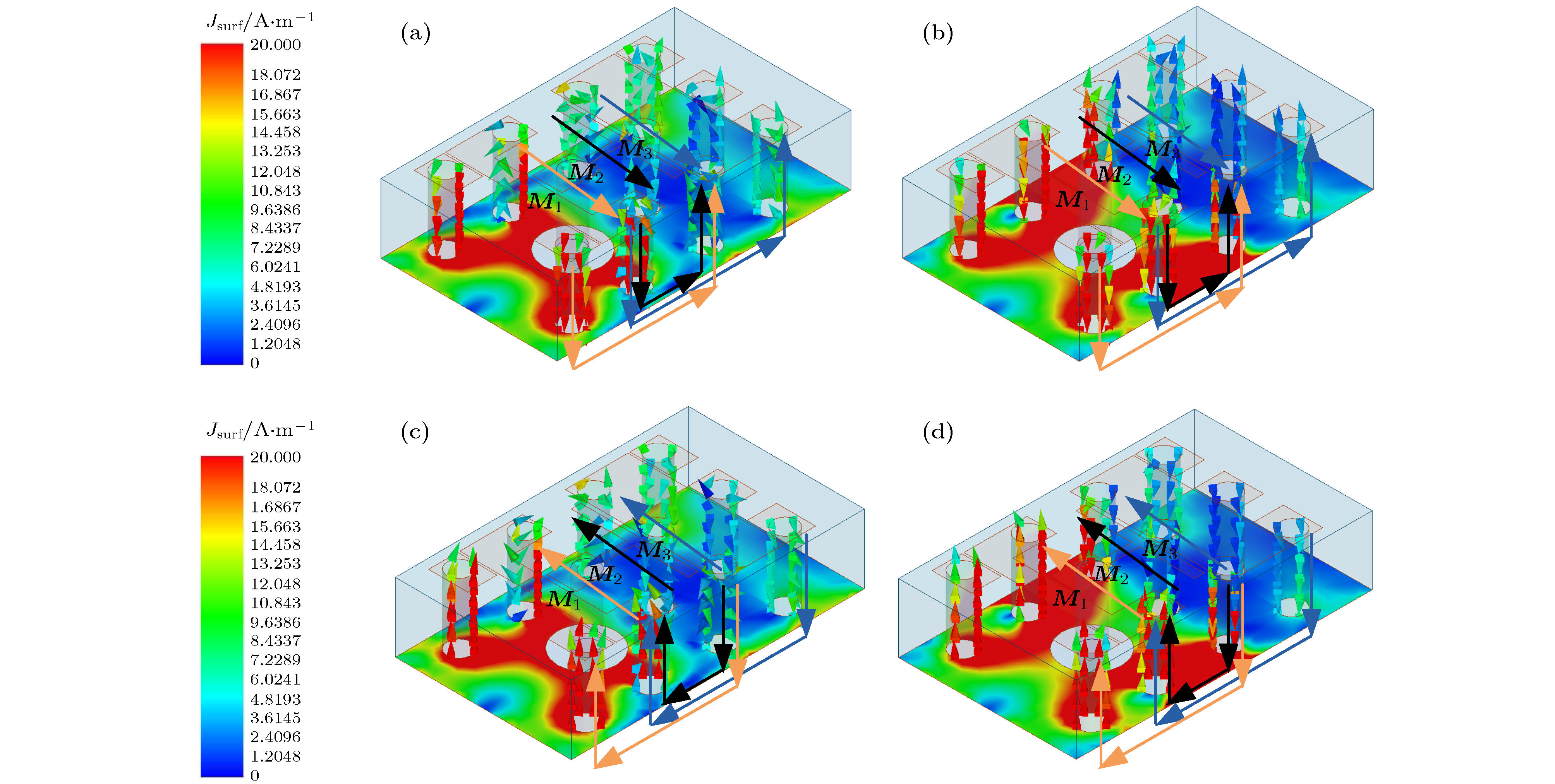
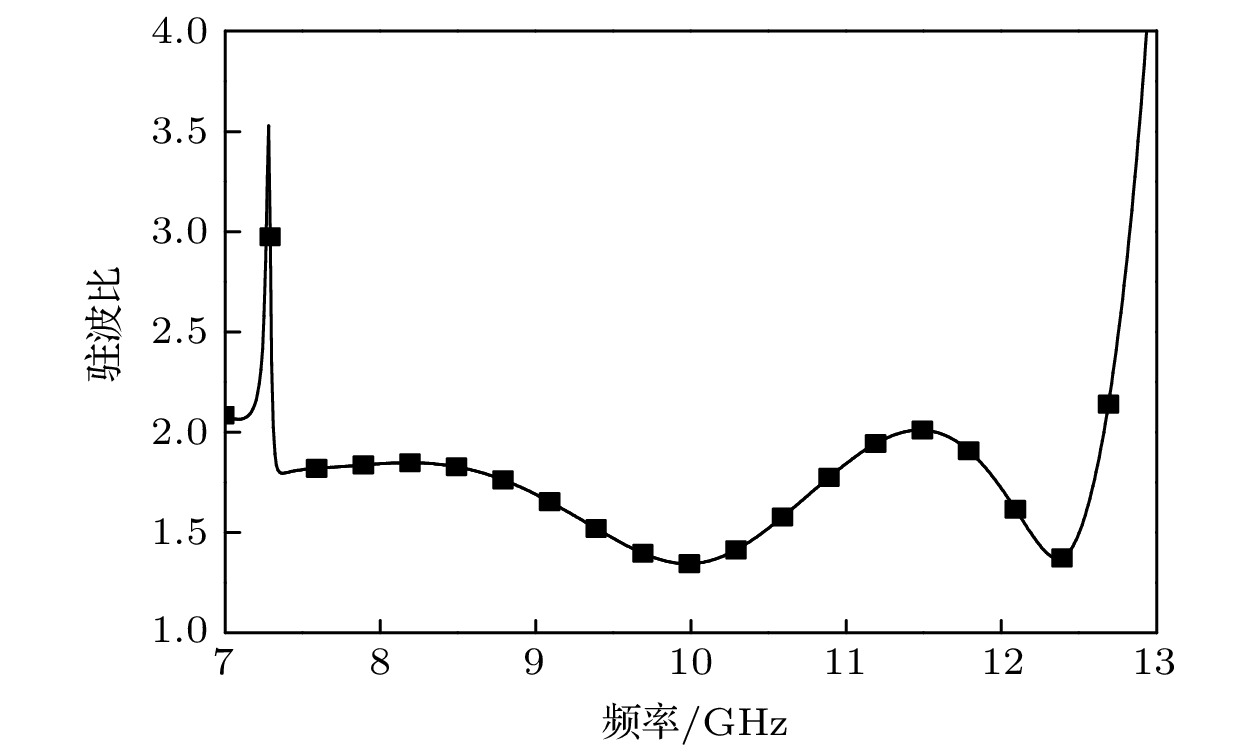
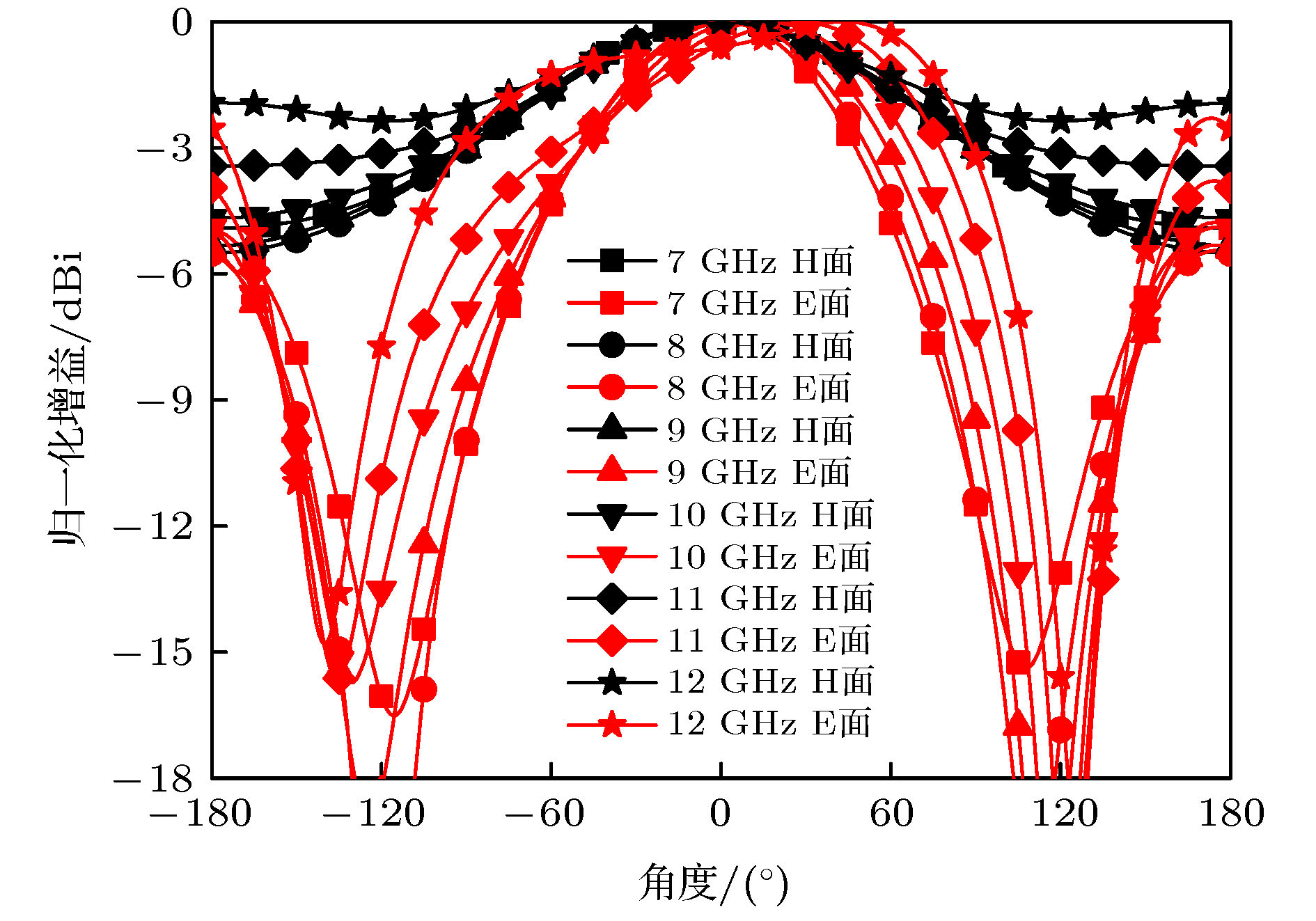
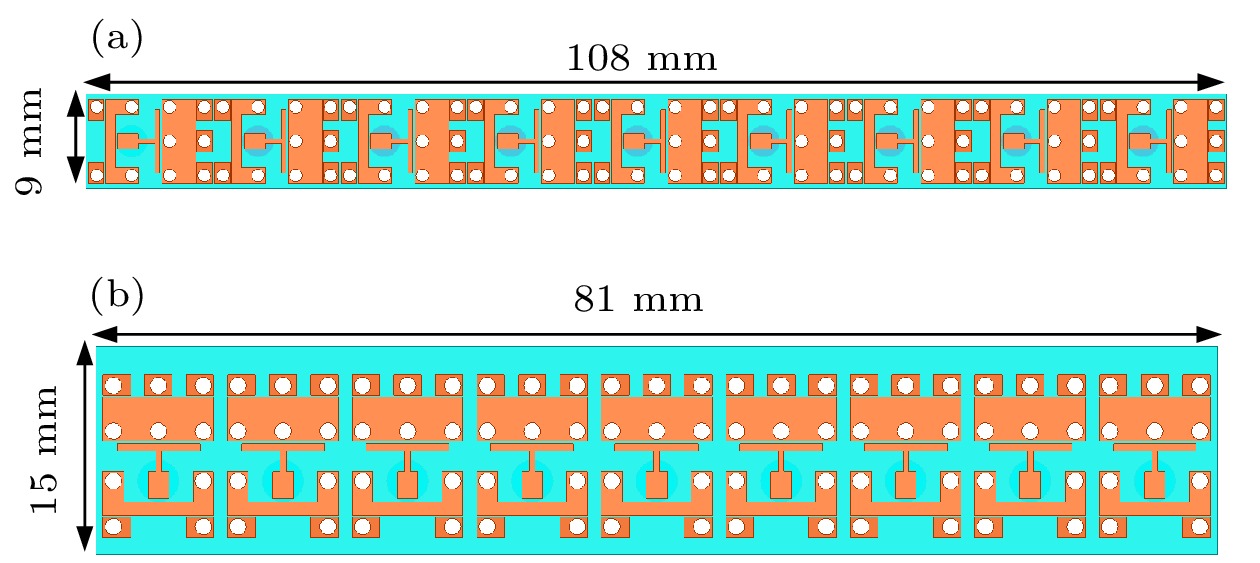
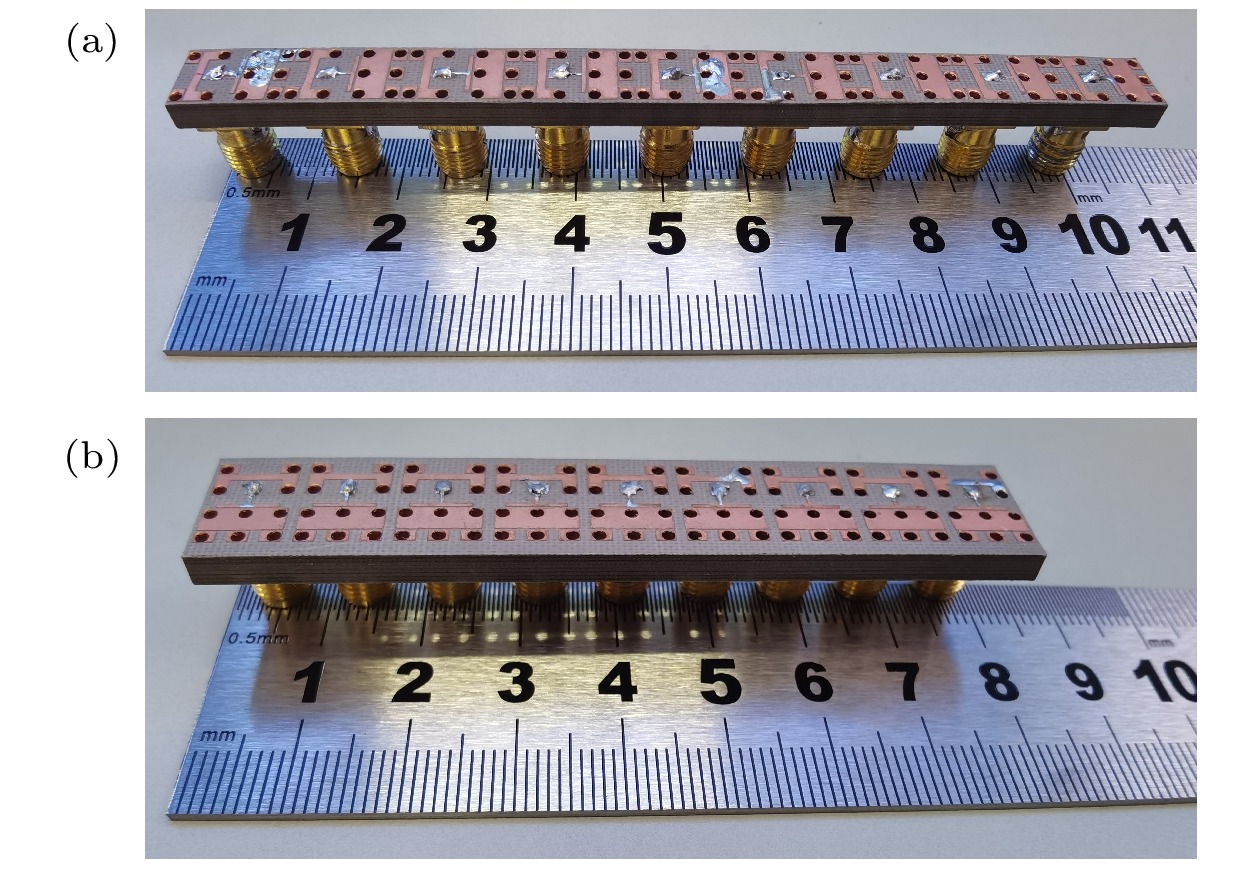
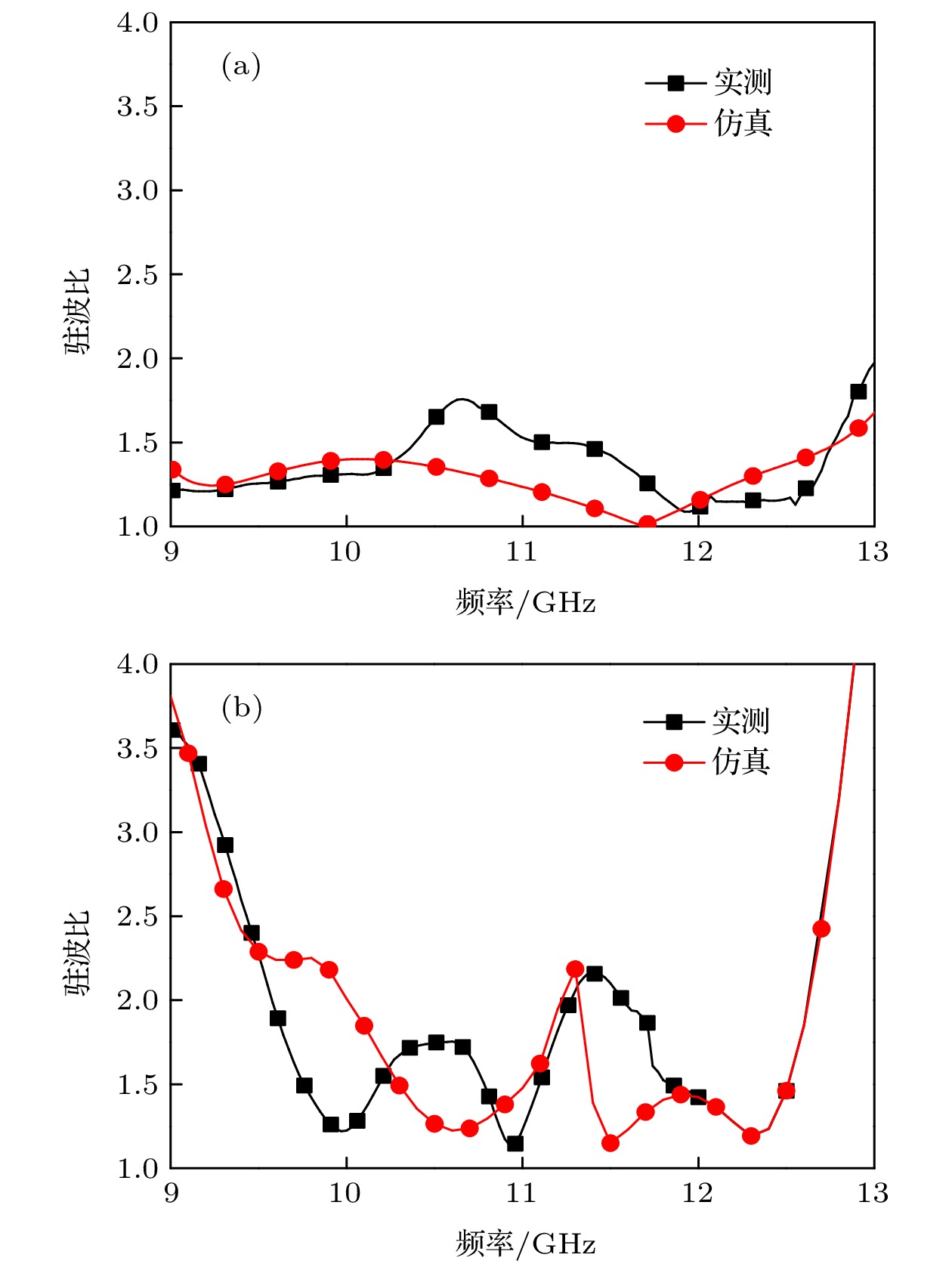
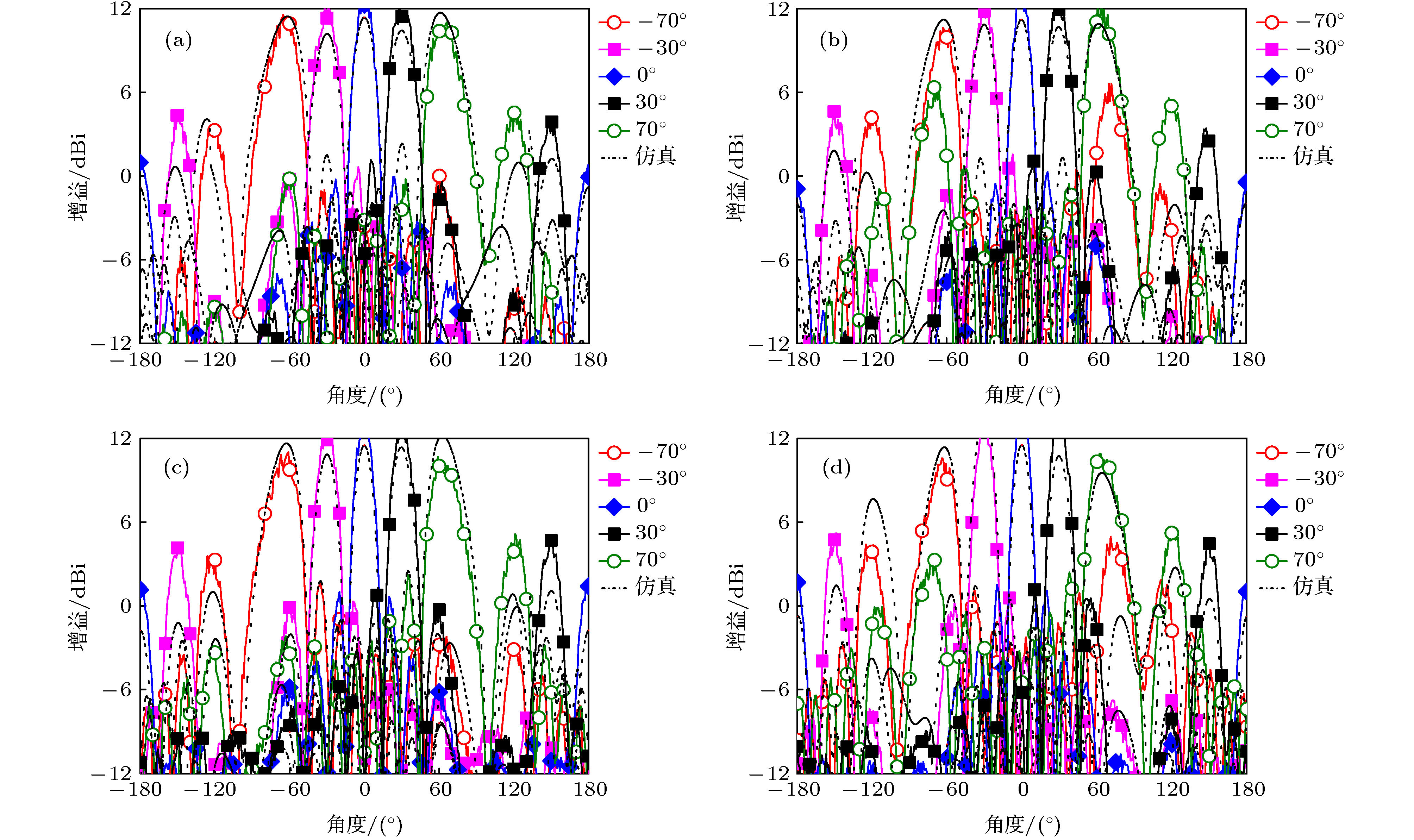
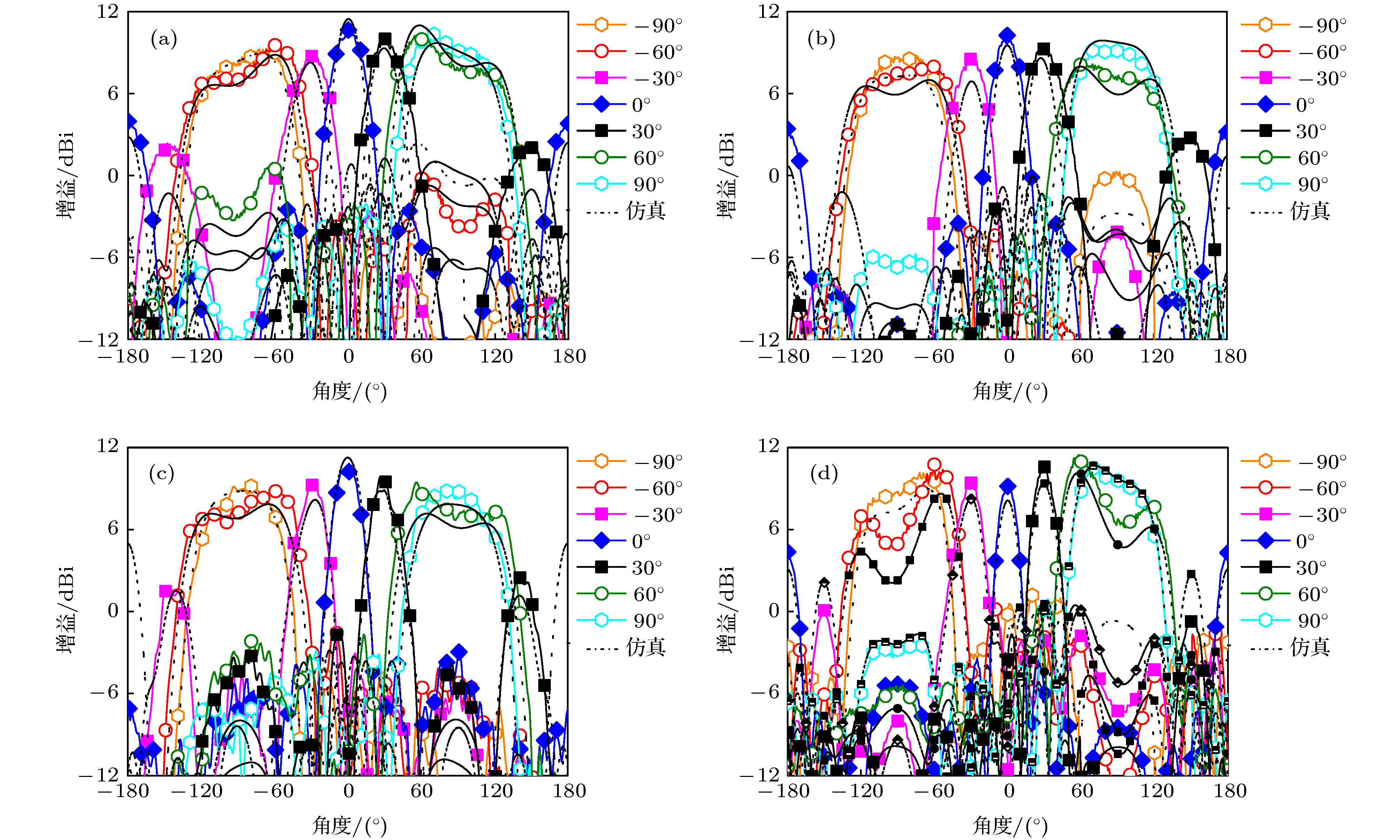
Microstrip phased array has aroused interest of many researchers because of its beam agility. However, a big problem for typical microstrip array is that its main beam can only scan from about –50° to 50°, with a gain loss of 4-5 dB. Meanwhile, the relatively narrow operating bandwidth of microstrip antenna is also a problem in application. These flaws have dramatically limited its applications and spawned many studies on phased array with wide-angle scanning capability. Several methods have been proposed to broaden the scanning coverage of phased array, such as utilizing pattern-reconfigurable antenna as an element of array, taking wide-beam antenna as the element of array, and adopt metasurface as the top cladding of array. However, most of existing researches mainly focus on achieving wide-angle scanning performance within a relatively narrow bandwidth. A phased array that possesses wide-angle scanning capability at both main planes within a relatively wide bandwidth is highly desirable. In this paper, a wide-beam magnetoelectric (ME) dipole antenna is proposed. It consists of an ME dipole antenna in the form of microstrip patch and a pair of magnetic dipoles. Metallic through holes integrated with patches and ground are utilized to form magnetic currents. Extra magnetic dipoles are added to broaden the 3-dB beam-width. The simulated results reveal that the 3-dB beam-width of the proposed antenna is greater than 107° in the E-plane (9 GHz–12 GHz) and 178° in the H-plane (7 GHz–12 GHz) respectively. The impedance bandwidth of the proposed antenna is 53.26% from 7.3 GHz to 12.6 GHz (VWSR < 2). Based on the proposed antenna element, two linear phased arrays are fabricated and measured. To test the wide-angle scanning capability of the arrays, each antenna element is simply fed with alternating currents with identical amplitude and linearly increasing phases. The measured results reveal that the wide-angle scanning capability of H-plane array and E-plane array can be obtained from 9 GHz to 12 GHz. The scanning beam of the H-plane array can cover the range from -90° to 90°. The scanning beam of the E-plane array can cover the range from –70° to 70°. The impedance bandwidth of the central antenna is 27.03% for the H-plane array from 9.6 GHz to 12.6 GHz (active VWSR < 2.5) and 36.36% for the E-plane array from 9 GHz to 13 GHz (active VWSR < 2) respectively. Hence, the proposed method can be used as a reference for designing a wide-beam antenna and wide-angle scanning phased array and the designed phased arrays can be applied to X-band radar systems.
-
Keywords:
- wide beam /
- wide-angle scanning /
- magnetoelectric(ME) dipole antenna /
- phased array
[1] 张祖稷, 金林, 束咸荣 2005 雷达天线技术 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第221页
Zhang Z J, Jin L, Shu X R 2007 Radar Antenna Technology (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) p221 (in Chinese)
[2] Bai Y Y, Xiao S Q, Wang B Z, Ding Z F 2010 J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 31 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bai Y Y, Xiao S Q, Tang M C, Ding Z F 2011 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59 4071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding X, Wang B Z, He G Q 2013 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61 5319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xiao S Q, Zheng C R, Li M, Xiong J 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cheng Y F, Ding X, Shao W, Yu M X, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 16 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding X, Cheng Y F, Shao W, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 4548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ge L, Luk K M 2015 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 14 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ge L, Luk K M 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shi Y, Cai Y, Yang J, Li L 2019 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 18 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin G 2007 Radar Sci. Technol. 5 157
[12] Wang R, Wang B Z, Hu C, Ding X 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 3908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang R, Wang B Z, Ding X, Yang X S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 2729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu C M, Xiao S Q, Tu H L, Ding Z F 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 1151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cheng Y F, Ding X, Shao W, Yu M X, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 16 876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang G W, Li J Y, Wei D J, Xu R 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang G W, Li J Y, Yang J J, Zhou S G 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 6724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yang G W, Chen Q Q, Li J Y, Zhou S G, Xing Z J 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 71897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chattopadhyay S 2009 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 57 3325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang H H, Li T, Xu L M, Cao X Y, Gao J, Tian J H, Yang H N, Sun D 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 152715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lü Y H, Ding X, Wang B Z, Anagnostou D E 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 1402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Luk K M, Wong H 2006 Int. J. Microw. Opt. Technol. 1 35
[23] Ng K B, Wong H, So K K, Chan C H, Luk K M 2012 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60 3129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li Y J, Luk K M 2014 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 62 1830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lai J, Feng B, Zeng Q 2019 IEEE 6th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility Nanjing, China November 1–4, 2019 p1
[26] Feng B T, Zhu C, Cheng J C, Sim C Y D 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 43346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 郑贵 2016 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Zheng G 2016 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[28] 王茂泽 2014 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Wang M Z 2014 M. S. Thesis (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[29] 徐志 2008 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Xu Z 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[30] Smolders A B 1996 Proceedings of International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology Boston, MA, USA, October 15–18, 1996 p87
[31] Kedar A, Beenamole K S 2011 Prog. Electro. Res. B 27 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
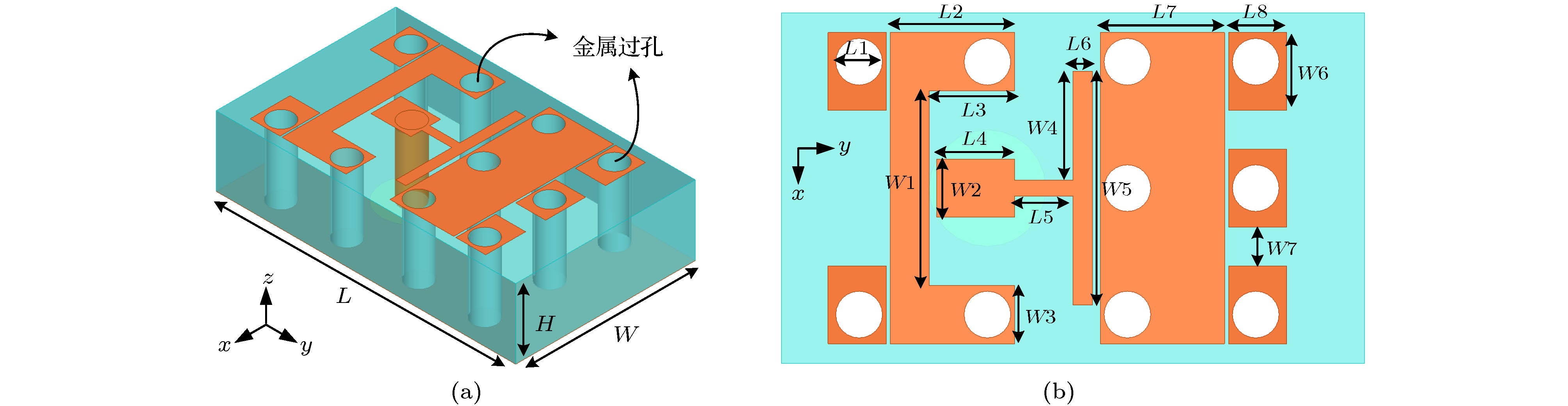
表 1 宽波束天线单元参数
Table 1. Parameters of the wide-beam antenna.
天线参数 L W H L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8 W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 参数值/mm 15 9 3.5 0.6 3.2 2.2 2 1.5 0.5 3.2 1.5 5 1.5 1.5 2.8 6 2 1 表 2 天线单元3-dB波束宽度
Table 2. 3-dB beam-width of the antenna.
频率/GHz E面3-dB波束宽度/(°) H面3-dB波束宽度/(°) 7 97 180.4 8 101.1 178.2 9 107 178.4 10 115.8 185.2 11 135.5 220.9 12 180.6 360 表 3 2号天线与3号天线增益对比
Table 3. Comparison between Ant.2 and Ant.3.
频率/GHz 参考天线增益/dBi 本文天线增益-/dBi 9 5.91 4.19 10 5.98 3.91 11 5.84 3.59 12 5.43 2.87 表 4 已报道宽波束磁电偶极子天线与本文天线特性对比
Table 4. Comparison between the reported and proposed magneto-electric dipole antenna.
文献 相对阻抗带宽/% 工作频带/GHz 增益/dBi 剖面/λ E面波束宽度/(°) H面波束宽度/(°) [16] 34.6 3.1—4.4 — 0.21 174 112 [17] 81.1 3.3—7.8 3.65 ± 1.65 0.27 215 (5.5 GHz)
106 (7.5 GHz)186 (5.5 GHz)
83 (7.5 GHz)[24] 41 2.42—3.7 6.3 0.45 75 120 [25] 63 2.76—5.3 5 0.15 129.1 (3.4 GHz)
151.6 (4.9 GHz)100.4 (3.4 GHz)
94.2 (4.9 GHz)[26] 22.6
19.63.25—4.08
4.29—5.226.9 ± 0.3
5.4 ± 0.70.27
0.2391 (3.5 GHz)
168 (4.9 GHz)
83 (3.5 GHz)
74 (4.9 GHz)83 (3.5 GHz)
162 (4.9 GHz)
90 (3.5 GHz)
133 (4.9 GHz)本文 53.26 7.3—12.6 3.53 ± 0.66 0.116 >97 >178.2 表 5 已报道X波段相控阵与本文相控阵天线特性对比
Table 5. Comparison between the reported and proposed X-band phased arrays.
-
[1] 张祖稷, 金林, 束咸荣 2005 雷达天线技术 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第221页
Zhang Z J, Jin L, Shu X R 2007 Radar Antenna Technology (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) p221 (in Chinese)
[2] Bai Y Y, Xiao S Q, Wang B Z, Ding Z F 2010 J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 31 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bai Y Y, Xiao S Q, Tang M C, Ding Z F 2011 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59 4071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding X, Wang B Z, He G Q 2013 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61 5319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xiao S Q, Zheng C R, Li M, Xiong J 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cheng Y F, Ding X, Shao W, Yu M X, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 16 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding X, Cheng Y F, Shao W, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 4548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ge L, Luk K M 2015 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 14 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ge L, Luk K M 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shi Y, Cai Y, Yang J, Li L 2019 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 18 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lin G 2007 Radar Sci. Technol. 5 157
[12] Wang R, Wang B Z, Hu C, Ding X 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 3908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang R, Wang B Z, Ding X, Yang X S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 2729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liu C M, Xiao S Q, Tu H L, Ding Z F 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 1151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cheng Y F, Ding X, Shao W, Yu M X, Wang B Z 2017 IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. 16 876
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang G W, Li J Y, Wei D J, Xu R 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang G W, Li J Y, Yang J J, Zhou S G 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 6724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yang G W, Chen Q Q, Li J Y, Zhou S G, Xing Z J 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 71897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chattopadhyay S 2009 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 57 3325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang H H, Li T, Xu L M, Cao X Y, Gao J, Tian J H, Yang H N, Sun D 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 152715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lü Y H, Ding X, Wang B Z, Anagnostou D E 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 1402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Luk K M, Wong H 2006 Int. J. Microw. Opt. Technol. 1 35
[23] Ng K B, Wong H, So K K, Chan C H, Luk K M 2012 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60 3129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li Y J, Luk K M 2014 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 62 1830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lai J, Feng B, Zeng Q 2019 IEEE 6th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility Nanjing, China November 1–4, 2019 p1
[26] Feng B T, Zhu C, Cheng J C, Sim C Y D 2019 IEEE Acc. 7 43346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 郑贵 2016 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Zheng G 2016 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[28] 王茂泽 2014 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Wang M Z 2014 M. S. Thesis (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[29] 徐志 2008 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Xu Z 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[30] Smolders A B 1996 Proceedings of International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology Boston, MA, USA, October 15–18, 1996 p87
[31] Kedar A, Beenamole K S 2011 Prog. Electro. Res. B 27 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 13068
- PDF Downloads: 285
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: