-
Compared with those materials with superior magneto-optical properties, such as YIG, Ce:YIG and Ba3Tb(PO4)3, pure terbium gallium garnet (TGG) crystal has comparative low Verdet constant and cannot meet the requirements of some high-power devices. Doping Pr3+ ions in TGG crystal can remarkably enhance its magneto-optical properties and expand its application scope, but there are still lack of systematic theoretical calculations to clarify this phenomenon. Based on the quantum theory, this paper presents the influence of doping Pr3+ ions on the magneto-optical performance and the corresponding quantitative calculation results. Firstly, taking various effects on Tb3+ ions and Pr3+ ions in the crystal into consideration, the Hamiltonian is modeled and discussed in detail. The secular equations are solved by applying the perturbation method, and then the energy level shifts and wave functions of the Tb3+ ions and Pr3+ ions are worked out, where the spin-orbit coupling, crystal field, effective field and super-exchange interaction between the two types of ions are considered. Furthermore, the transition dipole moments of Tb3+ ions and Pr3+ ions from the 4f ground state to higher level 5d, together with the distribution probability at each energy level and the average magnetic moment, are resolved. Finally, the Verdet constants and magnetic susceptibilities of pure TGG crystal and Pr:TGG crystal are calculated and compared with each other. Moreover, the relationship between the Verdet constant of Pr:TGG crystal and the Pr3+-doping amount is derived. The results show that the Faraday rotation angle caused by Pr3+ ions is larger than that of Tb3+ ions, meanwhile, the strong super-exchange between Tb3+ ions and Pr3+ ions causes further splitting of the 4f energy level, resulting in a significant increasement of the Verdet constant of the Pr:TGG crystal, which reaches 313.4 rad/m·T, 191.2 rad/m·T and 60.4 rad/m·T at the wavelengths of 532 nm, 632.8 nm and 1064 nm, respectively. In addition, doping Pr3+ ions inside the crystal improves the internal effective magnetic moment, which can reach 9.92 μB at 10 K. At the same time, the magnetic susceptibility increases, while the temperature interdependency decreases. The linear relationship between the reciprocal of magnetic susceptibility and temperature reduces from 4.41/K to 3.92/K. The Verdet constant of the Pr:TGG crystal is linear with the amount of Pr3+ ions doping. When the contents of Tb3+ ions and Pr3+ ions inside the crystal are equal, the maximum value is reached, which is about 2913.4 rad/m·T. The calculation results in this paper are in good agreement with the existing experimental data. -
Keywords:
- Faraday rotation /
- quantum theory /
- Verdet constant /
- magnetic susceptibility
[1] Tian Y, Tan B Z, Yang J, Zhang Y, Gu S H 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 063302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kaminskii A A, Eichler H J, Reiche P, Uecker R 2005 Laser Phys. Lett. 2 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang F, Tian Y, Yi Z, Gu S H 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 094206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 李长胜 2015 64 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yasuhara R, Tokita S, Kawanaka J, Kawashima T 2007 Opt. Express 15 11264
[6] Yasuhara R, Furuse H 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 1751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yasuhara R, Tokita S, Kawanaka J 2007 Rev. Laser Eng. 35 806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘琳, 俞育德 1985 人工晶体学报 1 27
Liu L, Yu Y D 1985 J. Synth. Cryst. 1 27
[9] Chani V I, Takeda H, Fukuda T 1999 J. Alloy. Compd. 60 212
[10] 陈建斌, 林羽, 李国辉, 陈建珊, 滕硕, 姚元根 2014 人工晶体学报 43 8
Chen J B, Lin Y, Li G H, Chen J S, Teng S, Yao Y G 2014 J. Synth. Cryst. 43 8
[11] 徐嘉林, 董玮利, 彭海益, 刘旺, 金维召, 林海, 李春 2015 长春理工大学学报 3 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu J L, Dong W L, Peng H Y, Liu W, Jin W Z, Lin H, Li C 2015 J. Changchun Univ. Technol. 3 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 龙勇, 徐扬, 石自彬, 丁雨憧, 王佳, 付昌禄 2015 压电与声光 37 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Long Y, Xu Y, Shi Z B, Ding Y T, Wang J, Fu C L 2015 Piezoelectric and Sound and Light 37 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 裴广庆, 张艳, 柳祝平 2015 人工晶体学报 44 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei G Q, Zhang Y, Liu Z P 2015 J. Synth. Cryst. 44 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 龙勇, 石自彬, 丁雨憧 2016 压电与声光 38 433
Long Y, Shi Z B, Ding Y D 2016 Piezoelectr. Acoustoopt. 38 433
[15] Chen Z, Hang Y, Yang L, Wang J, Wang X Y, Zhang P X, Hong J Q, Shi C J, Wang Y Q 2015 Mater. Lett. 145 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen Z, Yang L, Wang X Y, Hang Y 2016 Opt. Mater. 62 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhu N F, Li Y X, Yu X F 2008 Mater. Lett. 62 2355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sugar J 1965 JOSA 55 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 杨翠红 2004 硕士学位论文(扬州: 扬州大学)
Yang C H 2004 M. S. Thesis (Yangzhou: Yangzhou University) (in Chinese)
[20] Suits J 1972 IEEE Trans. Magn. 8 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shen Y R 1964 Phys. Rev. B 133 A511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 蔡伟, 邢俊辉, 杨志勇 2017 66 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai W, Xing J H, Yang Z Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Villaverde A B, Donatti D A, Bozinis D G 1978 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 11 L495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kiyoshi S 2010 Crystal Growth & Design 10 3466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Löw U, Zvyagin S, Ozerov M, Schaufuss U, Kataev V, Wolf B, Lüthi B 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 作用于Tb3+, Pr3+离子的晶场参数(cm–1)
Table 1. Crystal field parameters acting on Tb3+ and Pr3+ ions (cm–1).
能级 ${B_{2,0}}$ ${B_{2,2}}$ ${B_{4,0}}$ ${B_{4,2}}$ ${B_{4,4}}$ ${B_{6,0}}$ ${B_{6,2}}$ ${B_{6,4}}$ ${B_{6,6}}$ Tb3+ 4f –129.9 271.2 –2558.8 296.2 1121.6 682.3 –157.2 1048 –4.7 5d –3063 1180 –139845 72999 5412 Pr3+ 4f –334 144 –2630 252 1126 932 –207 1622 –199 5d –4162 2150 –128877 79630 8425 表 2 晶场及自旋轨道作用下的能级位移(cm–1)
Table 2. Energy level shift under the action of crystal field and spin orbit (cm–1).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Tb3+ Ea1 41.6 49.7 84.9 89.2 267.5 272 303.2 310.5 Eb1 –863.2 –336.4 –56.3 784.6 1446.7 1996.2 Pr3+ Ea1 –7.4 –8.9 55 452.8 512.4 549.9 567.1 722.4 Eb1 –1767.6 –542.9 1115.9 1198.2 2349.5 表 3 有效场作用下的能级分裂(cm–1)
Table 3. Energy level splitting under the action of effective field (cm–1).
1 2 3 4 Tb3+ (± 2.342$\mp\; 0.9516 \nu \chi $) (± 0.463$\mp\; 0.1422 \nu \chi $) (± 0.897$\mp\; 0.3641 \nu \chi $) (± 1.499$\mp \;0.6561 \nu \chi $) Pr3+ (± 1.641$\mp \;0.8244 \nu \chi $) (± 0.423$\mp\; 0.0893 \nu \chi $) (± 3.302$\mp\; 0.1176 \nu \chi $) 表 4 超交换作用下的能级位移(cm–1)
Table 4. Energy level shift under the action of super-exchange interaction (cm–1).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Tb3+ Ea3 –201.3 –152.3 –96.4 –3.2 82.4 141 168.3 210 Eb2 –499.1 –112.7 78.8 236.7 774.1 1135.8 Pr3+ Ea3 –262.1 –194.3 –32.4 56.9 61.5 176.5 211.7 387.9 Eb2 –844.1 –10.3 743.5 882.4 1178.3 表 5 不同波长下的维尔德常数V (
${\rm{rad/m}} \cdot {\rm{T}}$ )Table 5. Verdet constant at different wavelengths (
${\rm{rad/m}} \cdot {\rm{T}}$ ).表 6 不同Pr3+离子含量(y)下的维尔德常数V(
${\rm{rad/m}} \cdot {\rm{T}}$ )Table 6. Verdet constant under different Pr3+ ions content (
${\rm{rad/m}} \cdot {\rm{T}}$ ).λ/nm
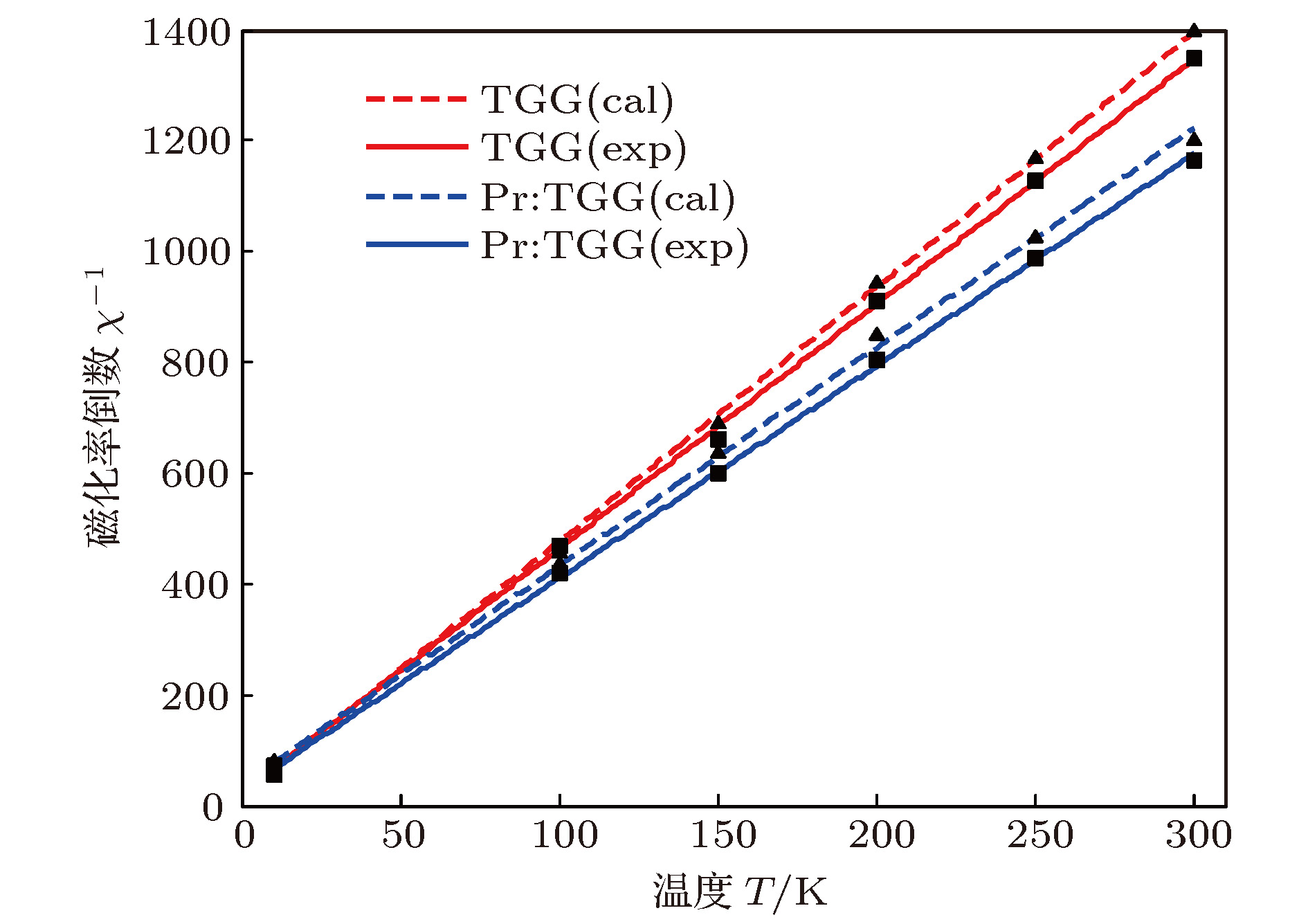
y0 0.073 1 1.5 2 2.927 3 532 179.4 312.5 2002.1 2913.4 2021.4 367.9 237.7 632.8 122.2 190.2 1099.8 1588.6 1112.9 231 161.5 1064 31.8 59.7 432.1 632.3 438 77.8 49.4 表 7 不同温度下磁化率的倒数1/χ
Table 7. Inverse magnetic susceptibility at different temperatures.
-
[1] Tian Y, Tan B Z, Yang J, Zhang Y, Gu S H 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 063302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kaminskii A A, Eichler H J, Reiche P, Uecker R 2005 Laser Phys. Lett. 2 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang F, Tian Y, Yi Z, Gu S H 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 094206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 李长胜 2015 64 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yasuhara R, Tokita S, Kawanaka J, Kawashima T 2007 Opt. Express 15 11264
[6] Yasuhara R, Furuse H 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 1751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yasuhara R, Tokita S, Kawanaka J 2007 Rev. Laser Eng. 35 806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘琳, 俞育德 1985 人工晶体学报 1 27
Liu L, Yu Y D 1985 J. Synth. Cryst. 1 27
[9] Chani V I, Takeda H, Fukuda T 1999 J. Alloy. Compd. 60 212
[10] 陈建斌, 林羽, 李国辉, 陈建珊, 滕硕, 姚元根 2014 人工晶体学报 43 8
Chen J B, Lin Y, Li G H, Chen J S, Teng S, Yao Y G 2014 J. Synth. Cryst. 43 8
[11] 徐嘉林, 董玮利, 彭海益, 刘旺, 金维召, 林海, 李春 2015 长春理工大学学报 3 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu J L, Dong W L, Peng H Y, Liu W, Jin W Z, Lin H, Li C 2015 J. Changchun Univ. Technol. 3 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 龙勇, 徐扬, 石自彬, 丁雨憧, 王佳, 付昌禄 2015 压电与声光 37 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Long Y, Xu Y, Shi Z B, Ding Y T, Wang J, Fu C L 2015 Piezoelectric and Sound and Light 37 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 裴广庆, 张艳, 柳祝平 2015 人工晶体学报 44 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei G Q, Zhang Y, Liu Z P 2015 J. Synth. Cryst. 44 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 龙勇, 石自彬, 丁雨憧 2016 压电与声光 38 433
Long Y, Shi Z B, Ding Y D 2016 Piezoelectr. Acoustoopt. 38 433
[15] Chen Z, Hang Y, Yang L, Wang J, Wang X Y, Zhang P X, Hong J Q, Shi C J, Wang Y Q 2015 Mater. Lett. 145 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen Z, Yang L, Wang X Y, Hang Y 2016 Opt. Mater. 62 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhu N F, Li Y X, Yu X F 2008 Mater. Lett. 62 2355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sugar J 1965 JOSA 55 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 杨翠红 2004 硕士学位论文(扬州: 扬州大学)
Yang C H 2004 M. S. Thesis (Yangzhou: Yangzhou University) (in Chinese)
[20] Suits J 1972 IEEE Trans. Magn. 8 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shen Y R 1964 Phys. Rev. B 133 A511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 蔡伟, 邢俊辉, 杨志勇 2017 66 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai W, Xing J H, Yang Z Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Villaverde A B, Donatti D A, Bozinis D G 1978 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 11 L495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kiyoshi S 2010 Crystal Growth & Design 10 3466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Löw U, Zvyagin S, Ozerov M, Schaufuss U, Kataev V, Wolf B, Lüthi B 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 16647
- PDF Downloads: 92
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: