-
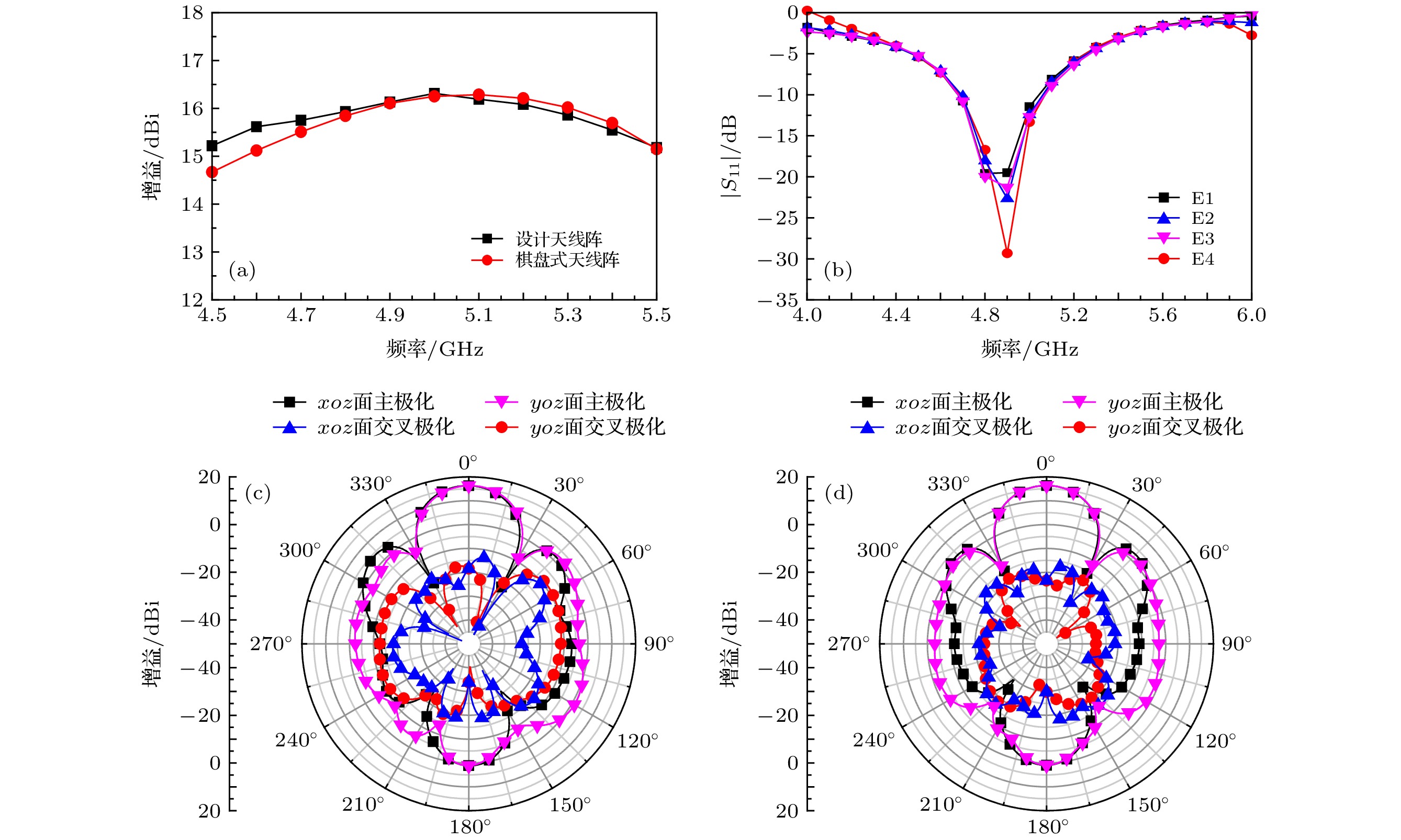
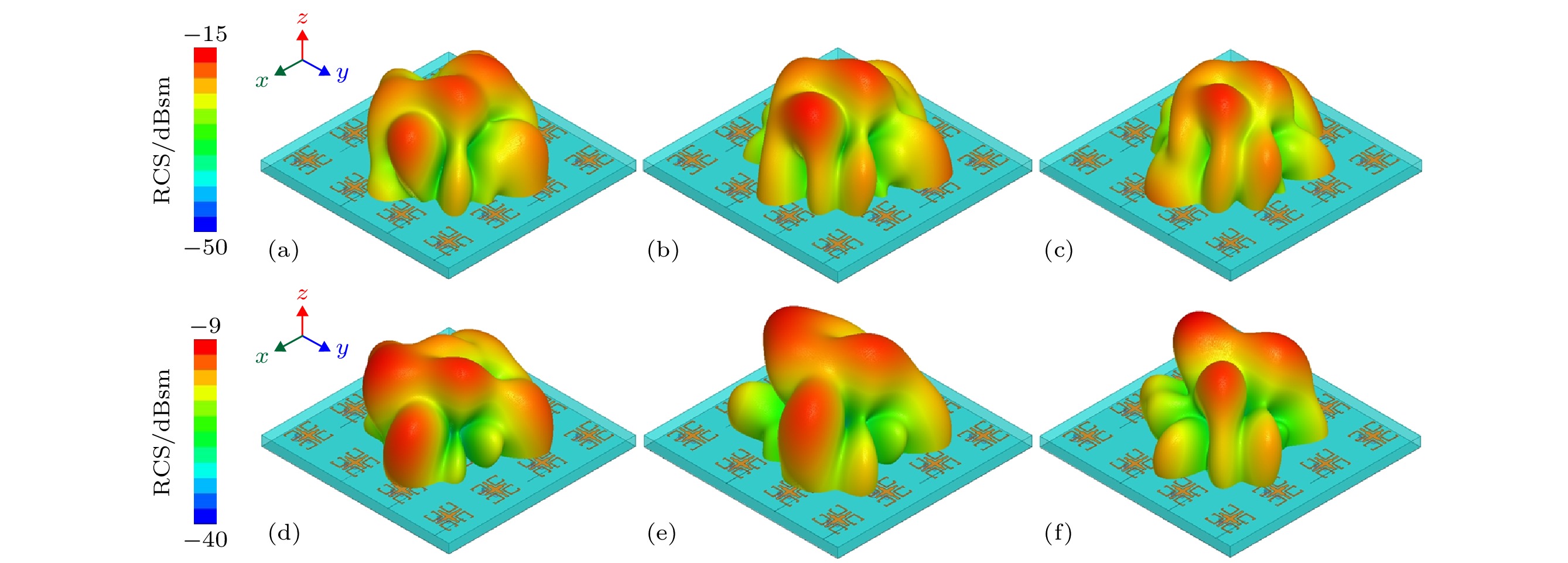
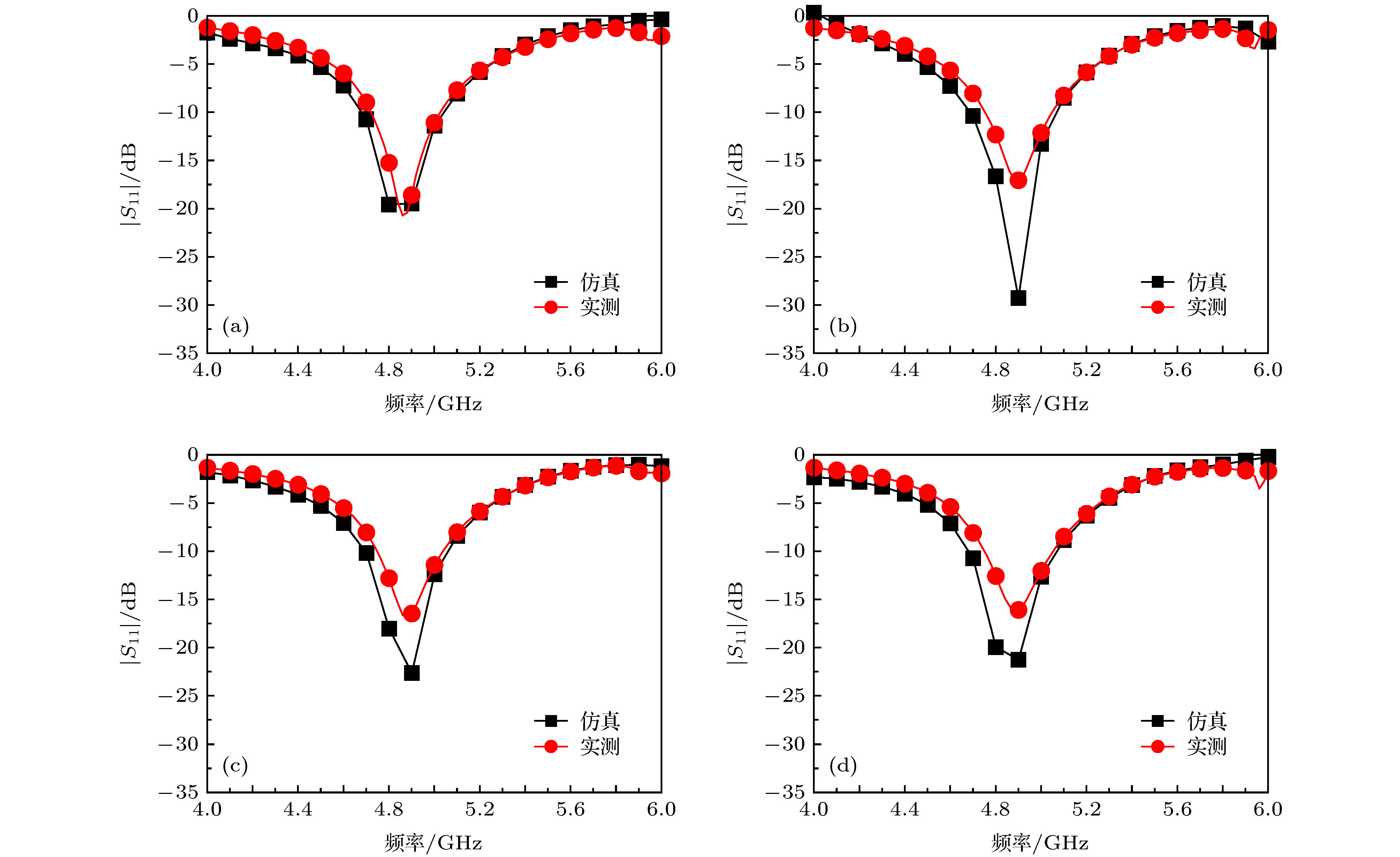
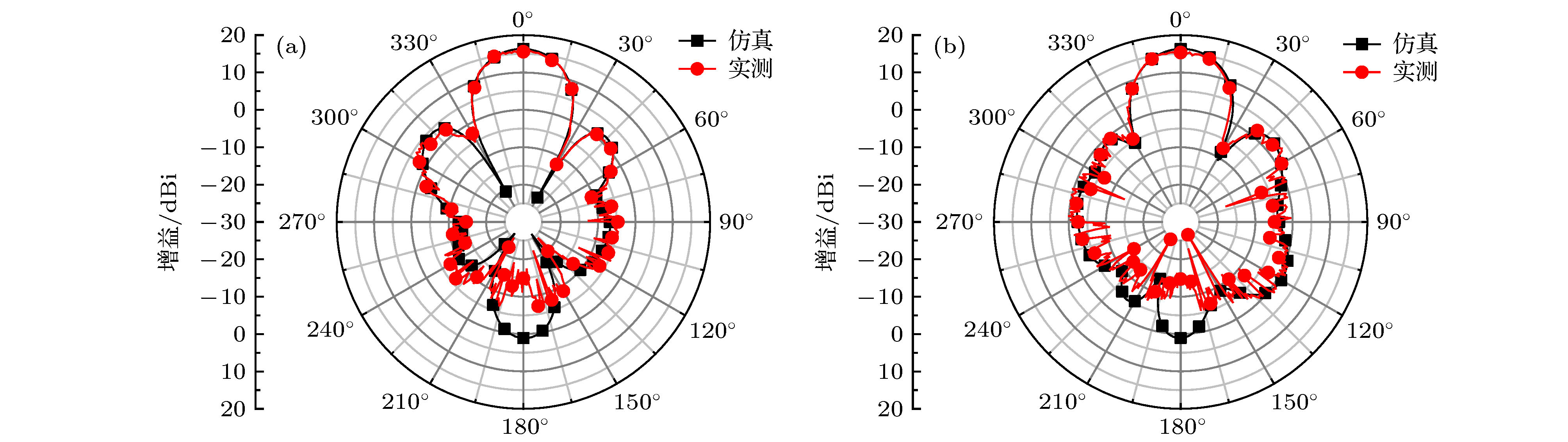
An aperiodic metasurface antenna array with low radar cross section (RCS) is designed. The upper patches of the two antenna elements have the same shape and are placed at an orthogonal position, which can effectively reduce the workload of simulating the reflection characteristics of the patch. As antenna elements, they have identical operational band and polarization mode, and as metasurfaces, they can form an effective phase difference of 180° ± 37°. The RCS of the array is reduced mainly by phase cancellation under the x polarization and by absorption under the y polarization. According to the coding metamaterial theory, the two elements can be coded aperiodically by using the programming software. Regarding element A and element B as “0” and “1”, respectively, the coding matrix can be solved by a genetic algorithm. Element A and element B are arranged according to positions “0” and “1” to obtain a proposed array. The scattering field of proposed array is diffusive, and the peak RCS is effectively reduced. In order to highlight the characteristics of the proposed array, the chessboard-type array is designed for comparison. The simulation results show that the radiation performance of proposed array is good. Comparing with the metal board of the same size, the 6 dB reduction bandwidth of the monostatic RCS is 4.8-7.4 GHz (relative bandwidth is 42.6%) under the x polarization and 4.6-7.8 GHz (relative bandwidth is 51.6%) under the y polarization. Comparing with the chessboard type array, the scattering energy distribution of the designed antenna array is very uniform and the peak RCS in space reduces obviously. When a 4.8 GHz electromagnetic wave is incident with different incident angles and polarization modes, the scattering field is diffusive. Compared with other similar arrays, the proposed array has advantages of simple design process and even scattering field. The experimental results are in good agreement with the simulation results. This work makes full use of the scattering characteristics of the antenna element itself to solve the problem that the array antenna possesses both good radiation characteristics and low scattering characteristics at the same time, and improves the design process of the antenna patch. This design method has certain universality and reference significance for designing the low RCS antenna array.
-
Keywords:
- low radar cross section /
- patch antenna array /
- diffusion
[1] 李文强, 曹祥玉, 高军, 赵一, 杨欢欢, 刘涛 2015 64 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W Q, Cao X Y, Gao J, Zhao Y, Yang H H, Liu T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Son X T, Ikmo P 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li G H, Zhai H Q, Li L, Liang C H, Yu R D, Liu S 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yoon J H, Yoon Y J, Lee W, So J 2012 Electron. Lett. 48 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Deng T W, Li Z W, Chen Z N 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 5886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Saptarshi G, Kumar V S 2018 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 60 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan M B, Qu S B, Wang J F, Zhang J Q, Zhang A X, Xia S, Wang W J 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bai Y, Zhao L, Ju D Q 2015 Opt. Express 23 8670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Agarwal M, Behera A K, Meshram M K 2016 Electron. Lett. 52 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ren J Y, Gong S X, Jiang W 2018 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu X B, Zhang J S, Li W, Lu R, Zhu S T, Xu Z, Zhang A X 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 1028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang L B, Zhou P H, Lu H P, Zhang L 2016 Opt. Mater. 6 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 于惠存, 曹祥玉, 高军, 杨欢欢, 韩江枫, 朱学文, 李桐 2018 67 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu H C, Cao X Y, Gao J, Yang H H, Han J F, Zhu X W, Li T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang J M, Yan L, Li L P, Zhang T, Li H H, Wang Q M, Hao Y N, Lei M, Bi K 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li Y F, Zhang J Q, Qu S B, Wang J F, Chen H Y, Xu Z, Zhang A X 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 221110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang X P, Wan L L, Chen T N, Song A L, Du X W 2016 AIP Adv. 6 065320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sharma A, Gangwar D, Kanaujia B K, Dwari S 2018 AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 91 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X, Gao J, Cao X Y, Zhao Y, Li S J 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Su J X, Kong C Y, Li Z R, Yin H C, Yang Y Q 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zheng Y J, Cao X Y, Gao J, Yang H H, Zhou Y L, Liu T 2017 Opt. Express 25 30001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 兰俊祥, 曹祥玉, 高军, 韩江枫, 刘涛, 丛丽丽, 王思铭 2019 68 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lan J X, Cao X Y, Gao J, Han J F, Liu T, Cong L L, Wang S M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y, Jia Y T, Zhang W B, Wang Y Z, Gong S X, Liao G S 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 6199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 不同参数对两单元性能的影响 (a) l2对单元A反射相位的影响; (b) l2对单元A反射幅度的影响; (c) l2对两单元|S11|的影响; (d) l6对单元A反射相位的影响; (e) l6对单元A反射幅度的影响; (f) l6对两单元|S11|的影响
Figure 2. Effects of l2 and l6: Effects of l2 on (a) reflection phase of element A, (b) reflection magnitude of element A, and (c) |S11| of element A and B; effects of l6 on (d) reflection phase of element A, (e) reflection magnitude of element A, and (f) |S11| of element A and B.
图 3 不同参数对单元B性能的影响 (a) lp2对反射相位的影响; (b) lp2对反射幅度的影响; (c) lp2对|S11|的影响; (d) ls对反射相位的影响; (e) ls对反射幅度的影响; (f) ls对|S11|的影响
Figure 3. Effects of lp2 and ls on element B: Effects of lp2 on (a) reflection phase, (b) reflection magnitude, and (c) |S11|; effects of ls on (d) reflection phase, (e) reflection magnitude, and (f) |S11|.
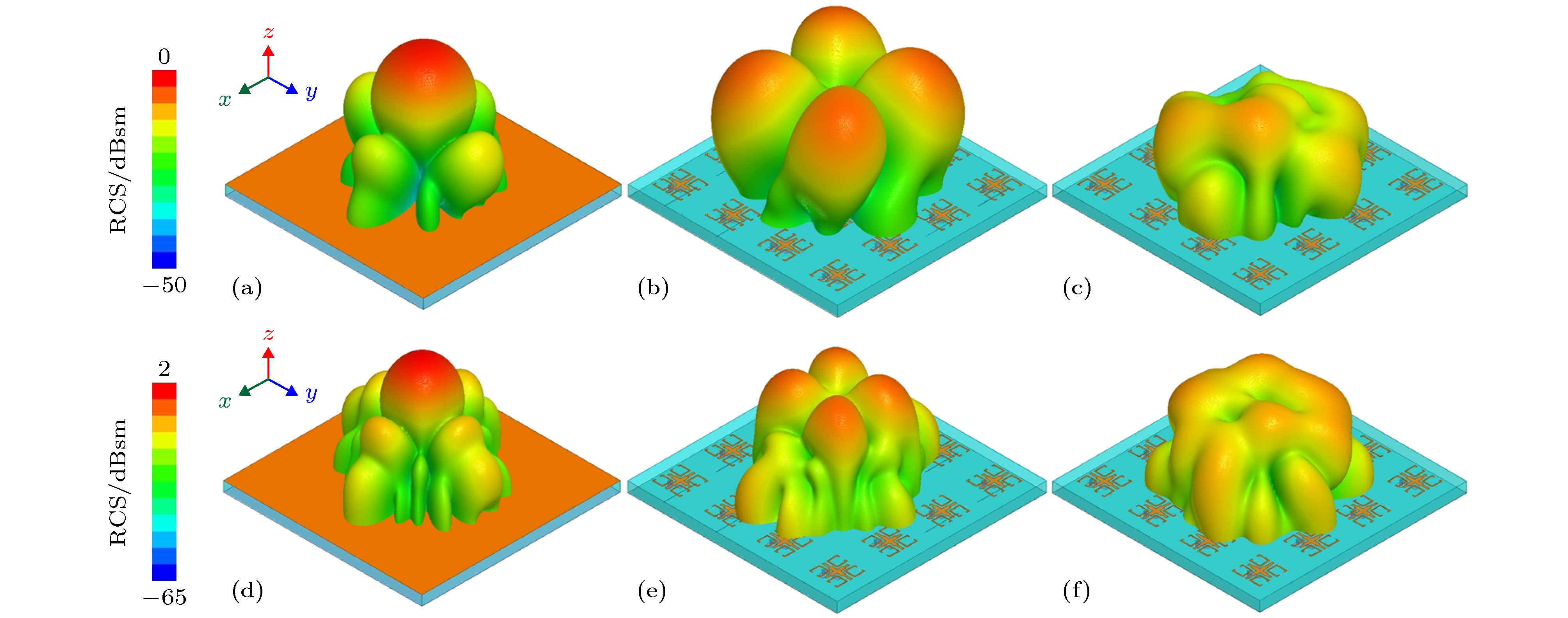
图 10 垂直入射时三维散射场分布 (a) 5 GHz时金属板散射场分布; (b) 5 GHz时棋盘式天线阵散射场分布; (c) 5 GHz时设计天线阵散射场分布; (d) 6.4 GHz时金属板散射场分布; (e) 6.4 GHz时棋盘式天线阵散射场分布; (f) 6.4 GHz时设计天线阵散射场分布
Figure 10. Three-dimensional scattering field for normal incidence: (a) Metal board, (b) chessboard type array and (c) proposed array at 5 GHz; (d) metal board, (e) chessboard type array and (f) proposed array at 6.4 GHz.
表 1 几种超表面天线阵列性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of other metasurface antenna arrays.
-
[1] 李文强, 曹祥玉, 高军, 赵一, 杨欢欢, 刘涛 2015 64 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W Q, Cao X Y, Gao J, Zhao Y, Yang H H, Liu T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Son X T, Ikmo P 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li G H, Zhai H Q, Li L, Liang C H, Yu R D, Liu S 2015 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yoon J H, Yoon Y J, Lee W, So J 2012 Electron. Lett. 48 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Deng T W, Li Z W, Chen Z N 2017 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 5886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Saptarshi G, Kumar V S 2018 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 60 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan M B, Qu S B, Wang J F, Zhang J Q, Zhang A X, Xia S, Wang W J 2014 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bai Y, Zhao L, Ju D Q 2015 Opt. Express 23 8670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Agarwal M, Behera A K, Meshram M K 2016 Electron. Lett. 52 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ren J Y, Gong S X, Jiang W 2018 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu X B, Zhang J S, Li W, Lu R, Zhu S T, Xu Z, Zhang A X 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 1028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang L B, Zhou P H, Lu H P, Zhang L 2016 Opt. Mater. 6 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 于惠存, 曹祥玉, 高军, 杨欢欢, 韩江枫, 朱学文, 李桐 2018 67 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu H C, Cao X Y, Gao J, Yang H H, Han J F, Zhu X W, Li T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang J M, Yan L, Li L P, Zhang T, Li H H, Wang Q M, Hao Y N, Lei M, Bi K 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li Y F, Zhang J Q, Qu S B, Wang J F, Chen H Y, Xu Z, Zhang A X 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 221110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang X P, Wan L L, Chen T N, Song A L, Du X W 2016 AIP Adv. 6 065320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sharma A, Gangwar D, Kanaujia B K, Dwari S 2018 AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 91 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X, Gao J, Cao X Y, Zhao Y, Li S J 2017 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Su J X, Kong C Y, Li Z R, Yin H C, Yang Y Q 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zheng Y J, Cao X Y, Gao J, Yang H H, Zhou Y L, Liu T 2017 Opt. Express 25 30001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 兰俊祥, 曹祥玉, 高军, 韩江枫, 刘涛, 丛丽丽, 王思铭 2019 68 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lan J X, Cao X Y, Gao J, Han J F, Liu T, Cong L L, Wang S M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y, Jia Y T, Zhang W B, Wang Y Z, Gong S X, Liao G S 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 6199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9788
- PDF Downloads: 240
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: