-
Central outflow’s collimation by magnetic field is an important theoretical mechanism for explaining the astrophysical objects’ morphology formation, and its credibility has been tested in many laser plasma experiments in a dimensionless manner. This article introduces integrated simulation and experiment work based on the present laboratory magnetically collimated jet framework, to explore how non-ideal terms’ strength including radiative cooling and magnetic diffusion from different targets can affect the outflow shape. The interaction between outflow from a target with low atomic number and external field satisfies the ideal magneto-hydrodynamic conditions, and the outflow shape results in diamagnetic cavity and jet; on the other hand, a heavy element target brings strong magnetic diffusion that destroys the collimation structure, together with the stagnation of outflow introduced by radiative cooling, and outflow shape results in weakly collimated hemisphere near the target and a detached magnetized density clump. The detailed dimensionless analysis shows that the large-scale dissipation of jets in young stellar objects can possibly be an analog of the laboratory jet’s magnetic diffusion breakup, also similar structures like the loosely collimated lobes and bright ansaes in planetary nebula can be observed in highly diffusive laboratory outflows. This article shows for the first time that a series of non-relativistic astronomical outflows’ dynamic behaviors can be explained by the non-ideal magneto-hydrodynamic evolution of laboratory plasmas.
[1] Bally J 2016 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 54 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Balick B, Frank A 2002 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 40 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Blandford R, Payne D 1982 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 199 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Spruit H, Foglizzo T, Stehle R 1997 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 288 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] García-Segura G 1997 Astrophys. J. Lett. 489 L189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] García-Segura G, Taam R E, Ricker P M 2020 arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.06073
[7] Blondin J M, Fryxell B A, Konigl A 1990 Astrophys. J. 360 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fendt C, Čemeljić M 2002 Astron. Astrophys. 395 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Remington B A, Arnett D, et al. 1999 Science 284 1488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Drake R 1999 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 104 14505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Takabe H 2001 Prog. Theor. Phys. Supp. 143 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lebedev S, Chittenden J, Beg F, et al. 2002 Astrophys. J. 564 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Albertazzi B, Ciardi A, Nakatsutsumi M, et al. 2014 Science 346 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Behera N, Singh R, Kumar A 2015 Phys. Lett. A 379 2215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramsey J P, Clarke D A 2019 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 484 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fryxell B, Olson K, Ricker P, Timmes F, Zingale M, Lamb D, MacNeice P, Rosner R, Truran J, Tufo H 2000 Astrophys. J. Suppl. S. 131 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Braginskii S 1965 Rev. Plasma Phys. 1 205
[18] Heltemes T, Moses G 2012 Comput. Phys. Commun. 183 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Eidmann K 1994 Laser Part. Beams 12 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fabbro R, Max C, Fabre E 1985 Phys. Fluids 28 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Huba J D 2006 Nrl plasma formulary. Tech. rep. Naval Research Lab Washington DC Plasma Physic Div.
[22] Ryutov D, Drake R, Kane J, Liang E, Remington B, Wood-Vasey W 1999 Astrophys. J. 518 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ryutov D, Drake R, Remington B 2000 Astrophys. J. Suppl. S. 127 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lee C F, Li Z Y, Codella C, Ho P T, Podio L, Hirano N, Shang H, Turner N J, Zhang Q 2018 Astrophys. J. 856 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Le Gouellec V J, Hull C L, Maury A J, et al. 2019 Astrophys. J. 885 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Witt A N, Vijh U P, Hobbs L, Aufdenberg J P, Thorburn J A, York D G 2009 Astrophys. J. 693 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Vlemmings W 2013 Proc. Int. Astron. Union 9 389
[28] Sahai R, Vlemmings W, Gledhill T, et al. 2017 Astrophys. J. Lett. 835 L13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shakura N I, Sunyaev R A 1973 Astron. Astrophys. 24 337
[30] Frank A, Gardiner T A, Delemarter G, Lery T, Betti R 1999 Astrophys. J. 524 947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
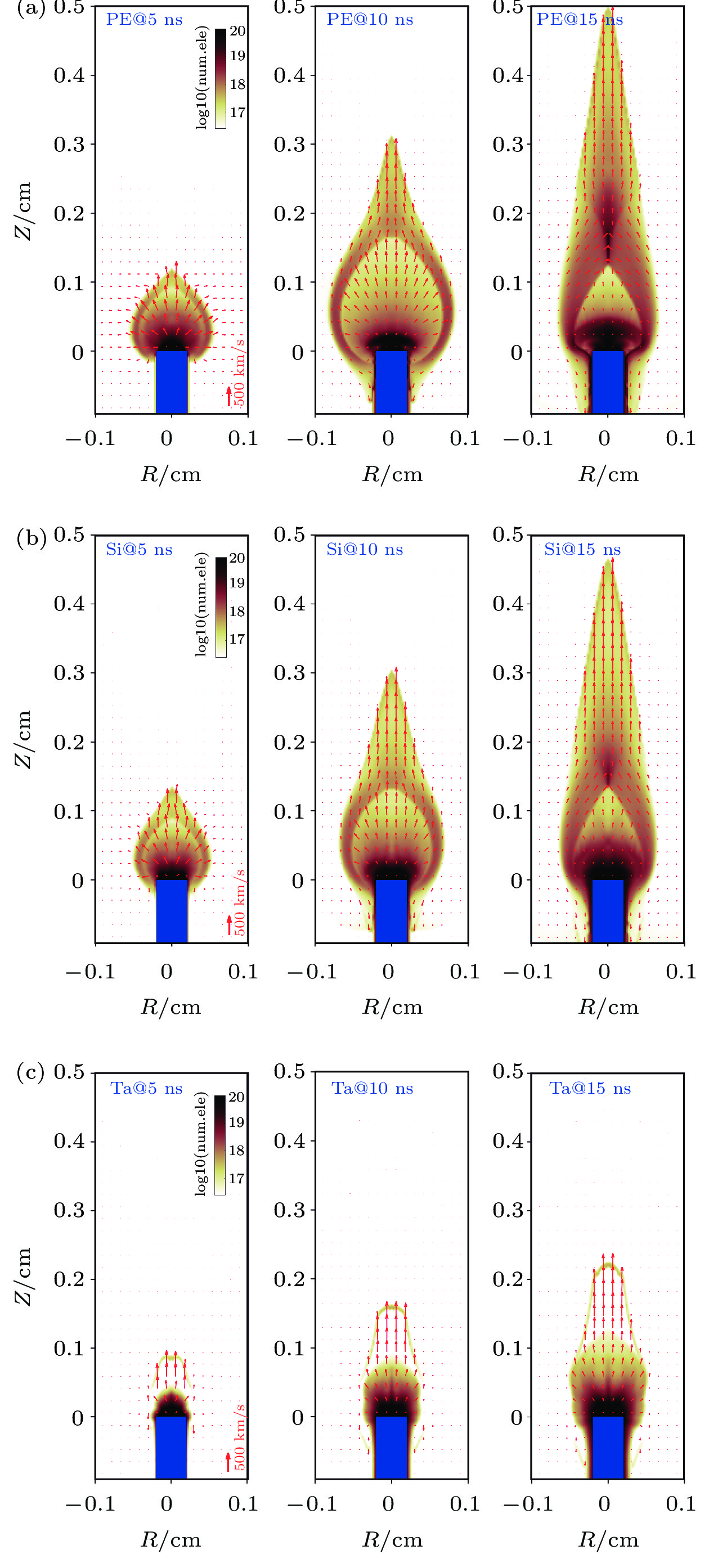
图 1 激光打击固体靶产生等离子体在8 T磁场中的电子密度时间演化, 按三列分别为相对激光上升沿延时5 ns、10 ns、15 ns. 使用的靶材料有(a) PE碳氢靶; (b) Si硅靶; (c) Ta钽靶. 激光沿R = 0轴由上至下入射, 聚焦于柱形靶水平端面中心R = 0, Z = 0处. 初始磁场方向与激光平行, 并均匀充满计算域
Figure 1. Electron density evolution of laser-ablated solid target plasma embedded in 8 Tesla of external magnetic field, three rows correspond to 5 ns, 10 ns, 15 ns delay from laser rising edge respectively. Solid target materials are (a) Polyethylene target; (b) silicon target; (c) tantalum target. Laser incident along R = 0 axis from top to the bottom, focus at the center of the flat end surface of target cylinder where R = 0 and Z = 0. Initial field is parallel to the laser direction, and uniformly distributed across the domain.
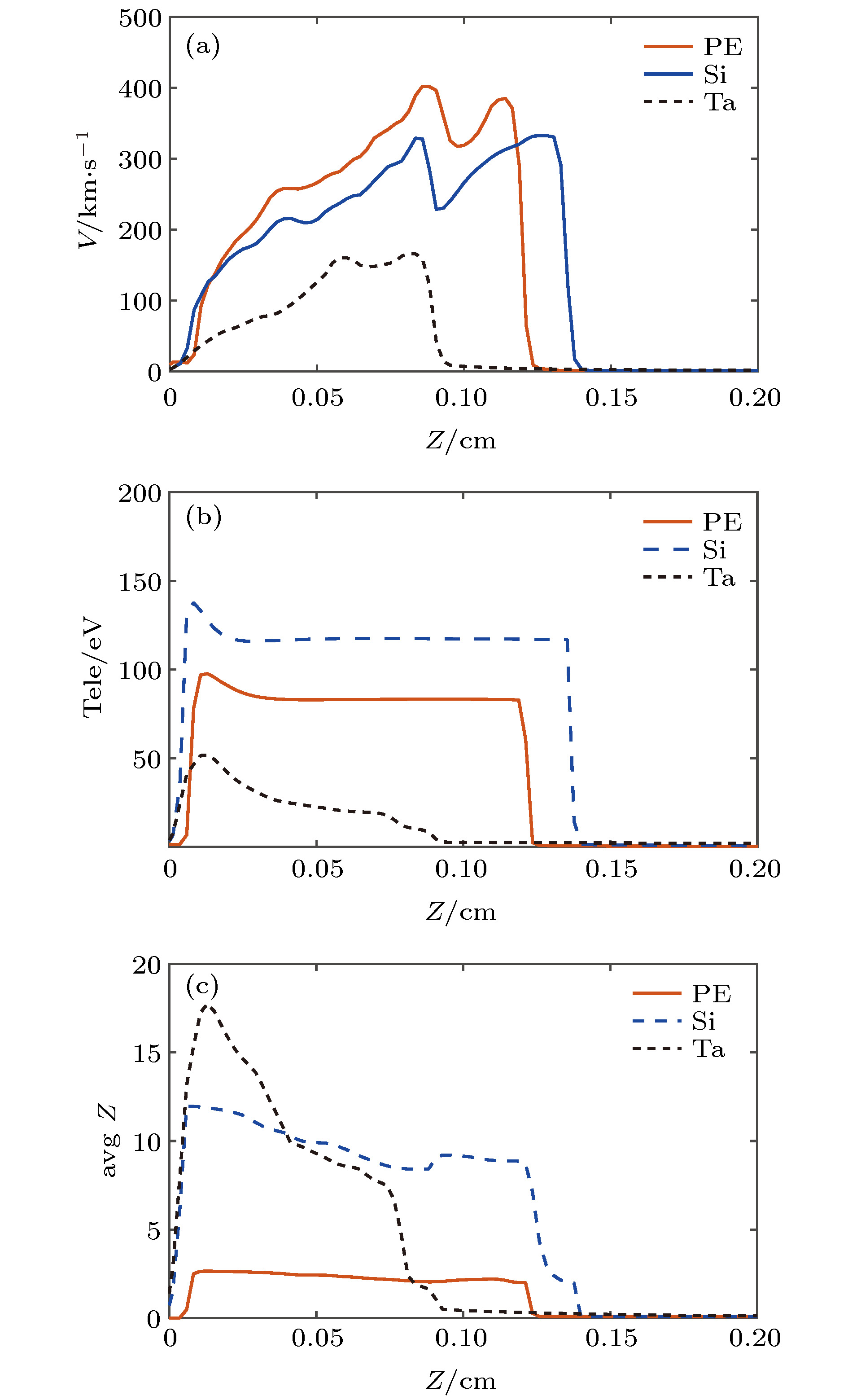
图 4 等离子体外流在5 ns延迟时刻, 对称轴上的纵向流速(+Z为正方向)、电子温度、平均电离度数值, 单幅图含碳氢、硅、钽靶结果
Figure 4. Line-out plot of plasma poloidal velocity (positive value along +Z direction), electron density and average ionization along outflow symmetry axis at 5 ns delay, individual values from CH, silicon and tantalum are included.
图 5 计算域内10 ns时的洛伦兹力(左半伪彩, 数值为负表示指向腔内)、磁力线状态(左半流线)、辐射能量密度(右半伪彩). 靶材依次为(a)碳氢靶; (b)硅靶; (c)钽靶. 虚线标识的是靶等离子体的边界
Figure 5. The Lorentz force (pseudocolor image on the left half, negative value indicates force pointing towards inside of the cavity), magnetic field lines (streamlines on the left half) and radiation energy density (pseudocolor image on the right half) status inside the simulation domain at 10 ns. Target materials are (a) Polyethylene; (b) silicon; (c) tantalum respectively. Dashed lines indicate the boundary of target materials.
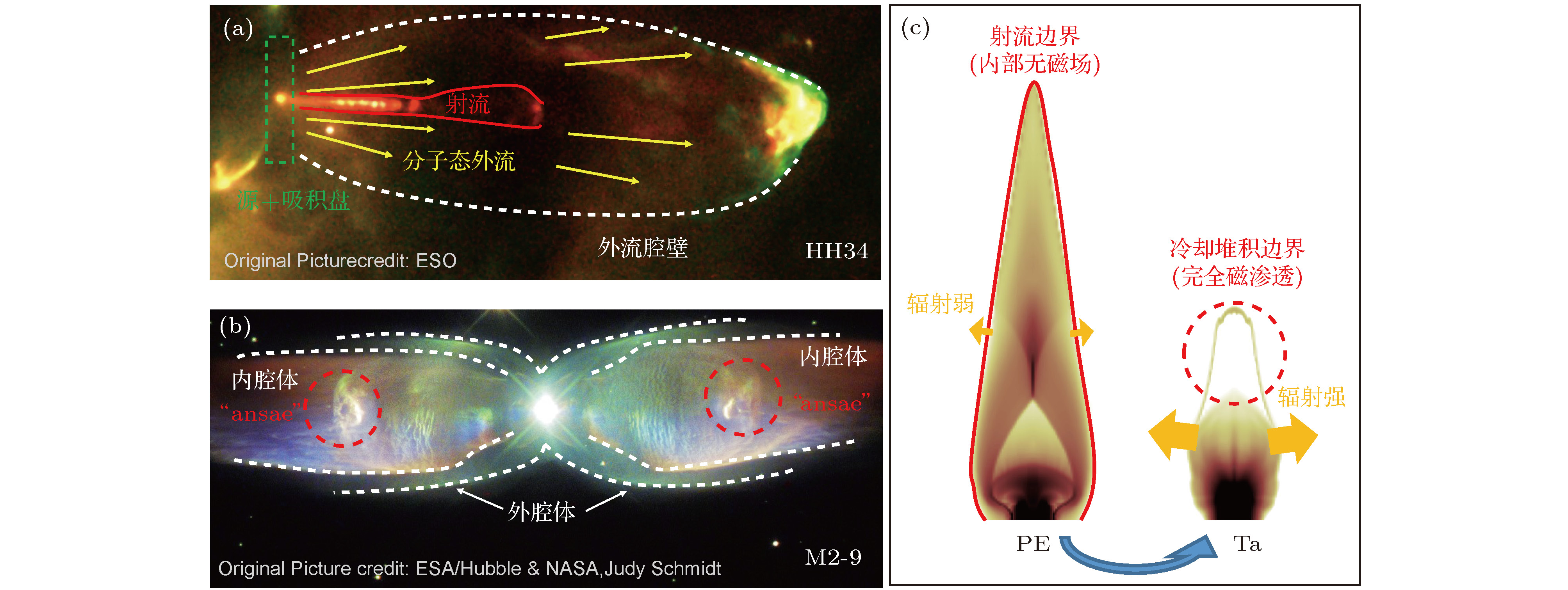
图 6 (a)典型原恒星系统HH34的射电观测图像, 大角度外流包裹着准直射流, 射流从核心星近区发出, 延伸至2.0 × 104 au距离消散(原图版权归属于ESO, 本文作者添加注释); (b)拥有点对称双极化腔体的行星状星云M2-9, 内侧椭球腔顶部有增强的发光结构“ansaes”(原图版权归属于ESA/Hubble & NASA, Judy Schmidt, 本文作者添加注释); (c)实验室等离子体从抗磁射流到磁化密度堆积的转变, 部分结构与天体形态有相似性
Figure 6. (a) Radio observation of a classical young stellar object HH34, the collimated jet is embedded inside a wide-angle outflow component, the jet originated from the inner region near the central star and extend 2.0 × 104 au of distance before termination (original image by ESO, annotated by author of this article); (b) planetary nebula M2-9 possesses a pair of point-symmetry bi-polar lobe cavities, with bright “ansaes” at the inside tips of the elliptical cavity shells (original image by ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt, annotated by author of this article); (c) laboratory plasma transformation from diamagnetic jet to magnetized density clump, structures show similarity with astrophysical objects.
表 1 实验室等离子体与相关天体外流动力学参数及无量纲参数对比
Table 1. Dynamics and dimensionless parameters comparison between laboratory plasma and related astronomical outflows
参数名称 碳氢靶 硅靶 钽靶 YSO PN 空间尺度/cm 0.1 0.1 0.1 特征流速/km·s–1 300 250 100 100 500 磁场强度/Gauss 8.0 × 104 8.0 × 104 8.0 × 104 0.01 0.01 离子密度/cm–3 2.0 × 1017 5.0 × 1016 3.0 × 1017 106 106 温度/eV 120 80 20 0.03 0.01 离子拉莫尔半径Li/cm 0.01 0.006 0.005 1.8 × 103 1.0 × 103 电子碰撞时间τe/s 1.0 × 10–10 6.0 × 10–10 1.0 × 10–12 1.6 × 10–4 3.7 × 10–5 特征冷却时间τcool/s 1.6 × 10–6 2.8 × 10–7 9.0 × 10–9 — — 冷却强度/C 470 70 0.9 ~1 $ \ll 1 $ 磁雷诺数Rm 100 12 0.4 2.2 44 Peclet数Pe 0.15 0.96 122 1.0 × 1011 6.9 × 1014 -
[1] Bally J 2016 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 54 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Balick B, Frank A 2002 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 40 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Blandford R, Payne D 1982 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 199 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Spruit H, Foglizzo T, Stehle R 1997 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 288 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] García-Segura G 1997 Astrophys. J. Lett. 489 L189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] García-Segura G, Taam R E, Ricker P M 2020 arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.06073
[7] Blondin J M, Fryxell B A, Konigl A 1990 Astrophys. J. 360 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fendt C, Čemeljić M 2002 Astron. Astrophys. 395 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Remington B A, Arnett D, et al. 1999 Science 284 1488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Drake R 1999 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 104 14505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Takabe H 2001 Prog. Theor. Phys. Supp. 143 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lebedev S, Chittenden J, Beg F, et al. 2002 Astrophys. J. 564 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Albertazzi B, Ciardi A, Nakatsutsumi M, et al. 2014 Science 346 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Behera N, Singh R, Kumar A 2015 Phys. Lett. A 379 2215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramsey J P, Clarke D A 2019 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 484 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fryxell B, Olson K, Ricker P, Timmes F, Zingale M, Lamb D, MacNeice P, Rosner R, Truran J, Tufo H 2000 Astrophys. J. Suppl. S. 131 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Braginskii S 1965 Rev. Plasma Phys. 1 205
[18] Heltemes T, Moses G 2012 Comput. Phys. Commun. 183 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Eidmann K 1994 Laser Part. Beams 12 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fabbro R, Max C, Fabre E 1985 Phys. Fluids 28 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Huba J D 2006 Nrl plasma formulary. Tech. rep. Naval Research Lab Washington DC Plasma Physic Div.
[22] Ryutov D, Drake R, Kane J, Liang E, Remington B, Wood-Vasey W 1999 Astrophys. J. 518 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ryutov D, Drake R, Remington B 2000 Astrophys. J. Suppl. S. 127 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lee C F, Li Z Y, Codella C, Ho P T, Podio L, Hirano N, Shang H, Turner N J, Zhang Q 2018 Astrophys. J. 856 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Le Gouellec V J, Hull C L, Maury A J, et al. 2019 Astrophys. J. 885 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Witt A N, Vijh U P, Hobbs L, Aufdenberg J P, Thorburn J A, York D G 2009 Astrophys. J. 693 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Vlemmings W 2013 Proc. Int. Astron. Union 9 389
[28] Sahai R, Vlemmings W, Gledhill T, et al. 2017 Astrophys. J. Lett. 835 L13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shakura N I, Sunyaev R A 1973 Astron. Astrophys. 24 337
[30] Frank A, Gardiner T A, Delemarter G, Lery T, Betti R 1999 Astrophys. J. 524 947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7982
- PDF Downloads: 75
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: