-
Charge exchange, or electron capture, between highly charged ions and atoms and molecules has been considered as one of important mechanisms controlling soft X-ray emissions in many astrophysical objects and environments. However, to model charge exchange soft X-ray emission, astrophysicists commonly use principal quantum number n and angular momentum quantum numberl resolved state-selective capture cross section data, which are usually obtained by empirical and semi-classical theory calculations. The accuracy of the theoretical model is the key to constructing an accurate X-ray spectrum. With a newly-built cold target recoil ion momentum spectroscopy apparatus, we perform a series of precise state-selective cross section measurements on Ne8+ ions’ single electron capture with He targets, with the projectile energy ranging from 1.4 to 20 keV/u. The experimentally measured Q value spectrum shows that the process of electron captured to state of Ne7+ with n = 4 is the main reaction channel, and that with n = 3 and 5 are the small reaction channels. Using Gaussian curve to fit the area of each channel on the Q value spectrum and normalizing the area of all channels, we obtain the n-resolved relative state-selective cross section. By comparing the measured relative cross sections with the results calculated by the multichannel Landau-Zener method and molecular Coulomb over-barrier model, significant difference among the strengths of small reaction channels is found. Specifically, the multichannel Landau-Zener method overestimates the contribution of n = 2 channel and n = 3 channel, and underestimates the contribution of n = 5 channel. The molecular Coulomb over-barrier model overestimates the contribution of n = 5 channel and underestimates the contribution of n = 3 channel. The significant difference between the theoretical model calculation and experimental measurement is due to the limitations of semiclassical theoretical method and classical theoretical method. Furthermore, with l distribution models commonly used in the astrophysical literature, including the statistical model, separable model, Landau-Zener-I model, Landau-Zener-II model and even model, we calculate the soft X-ray emissions in the charge exchange between 1.6 and 2.4 keV/u Ne8+ and He. It is found that the calculated intensities of X-ray spectra significantly deviate from the existing measurements, and only the separable model can partly match the laboratory simulated solar wind charge exchange X-ray measurement. Furthermore, we find that the intensity of the charge exchange X-ray emission spectrum measured experimentally is dependent on the collision energy, while the emission spectrum calculated based on the model seems to be unchanged with the increase of the collision energy. These results indicate that if the classical and semi-classical models are applied to the astrophysical plasma for studying diffusive soft X-ray background, the obtained parameters of the astrophysical plasma will be inaccurate.
-
Keywords:
- reaction microscopes /
- charge exchange /
- state selective capture /
- soft X-ray
[1] Dörner R, Mergel V, Jagutzki O, Spielberger L, Ullrich J, Möshammer R 2000 Phys. Rep. 330 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fischer D, Gudmundsson M, Berenyi Z, Haag N 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 012714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hayakawa S 1960 Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 12 110
[5] Joseph S, Gary S 1969 Phys. Rev. Lett. 23 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pravdo S H, Boldt E A 1975 Astrophys. J. 200 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lisse C M, Dennerl K, Englhauser J 1996 Science 274 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cravens T E 1997 Geophys. Res. Lett. 24 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Beiersdorfer P, Boyce K R, Brown G V 2003 Science 300 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cravens T E 2000 Astrophys. J. 532 L153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Koutroumpa D, Lallement R, Raymond J C, Kharchenko V 2014 Astrophys. J. 696 1517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hasan A, Eissa F, Ali R, Schultz D, Stancil P 2001 Astrophys. J. 560 L201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Seredyuk B, McCullough R W, Gilbody H B 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 022710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bodewits D, Hoekstra R 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 032703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Machacek J R, Mahapatra D P, Schultz D R 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 052708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ali R, Beiersdorfer P, Harris C L, Neill A 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 012711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Betancourt-Martinez G L, Beiersdorfer P, Brown G V 2018 Astrophys. J. 868 L17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang R T, Wulf D, McCammon D 2019 AIP Conf. Proc. 2160 070004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Defay X, Morgan K, McCammon D 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 052702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fogle M, Wu lf D, Morgan K, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 042705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Beiersdorfer P, Bitter M, Marion M, Olson R E 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 032725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lepson J K, Beiersdorfer P, Bitter M, Roquemore A L, Kaita R 2017 AIP Conf. Proc. 1811 190008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hell N, Brown G V, Wilms J 2016 Astrophys. J. 830 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ma X, Liu H P, Sun L T 2009 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 163 012104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu X L, Ma X W, Li J Y 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 460 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma X, Zhang R T, Zhang S F, Z hu, X L, Feng W T 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bliman S, Cornille M, Langereis A 1997 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68 1080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bonnet J J, Fleury A, Bonnefoy M 1985 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 18 L23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Roncin P, Barat M, Laurent H 1986 Eur. Phys. Lett. 2 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Folkmann F, Eisum N, Ciric D, Drentje A 1989 J. Phys. 50 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Langereis A, Nordgren J, Bruch R 1997 Phys. Scr. T73 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fischer D, Feuerstein B, DuBois R 2002 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 35 1369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Abdallah M A, Wolff W, Wolf H E 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Otranto S, Olson, R E, Beiersdorfer P 2006 Phys. Rev. A 73 022723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Niehaus A 1986 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 19 2925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lyons D, Cumbee R S, Stancil P C 2017 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 232 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Kahn S M, Sunyaev R A, von Ballmoos P 2019 State-of-the-Art Reviews on Energetic Ion-Atom and Ion-Molecule Collisions (Vol. 2) (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) p33
[38] Cumbee R S, Liu L, Lyons D 2016 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 458 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Smith R K, Foster A R, Edgar R J, Brickhouse N S 2014 Astrophys. J. 787 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Abdallah M A, Wolff W, Wolf H E 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 4373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
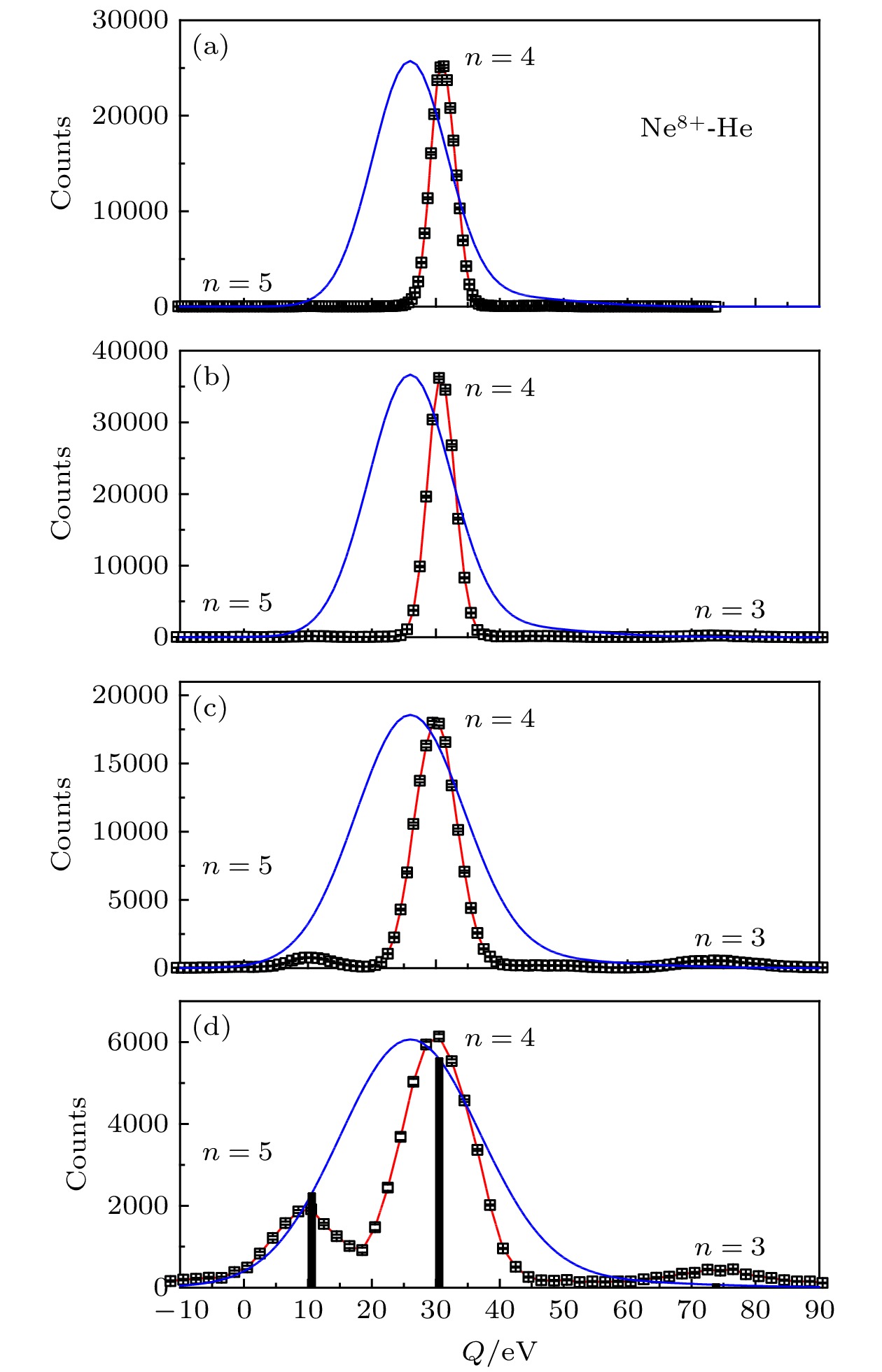
图 2 不同入射炮弹能量下Ne8+-He单电子俘获的Q值谱 (a) 1.6 keV/u; (b) 2.4 keV/u; (c) 7.2 keV/u; (d) 20 keV/u. 黑色空心方块和红色实线是实验测量的结果, 蓝色实线为归一到实验测量峰值的MCBM计算的反应窗. 图(d) 中的黑色粗线与MCBM计算的反应窗的交点反映了MCBM计算的态选择截面的大小
Figure 2. Measured Q spectrum of single electron capture between Ne8+ and He with different incident projectile energies: (a) 1.6 keV/u; (b) 2.4 keV/u; (c) 7.2 keV/u; (d) 20.0 keV/u. The black hollow square and the red solid line are the results of the experimental measurement, and the blue solid line is the response window calculated by MCBM normalized to the peak of the experimental measurement. The heavy black thread in panel (d) represents the intensity of state selected cross sections for MCBM calculations
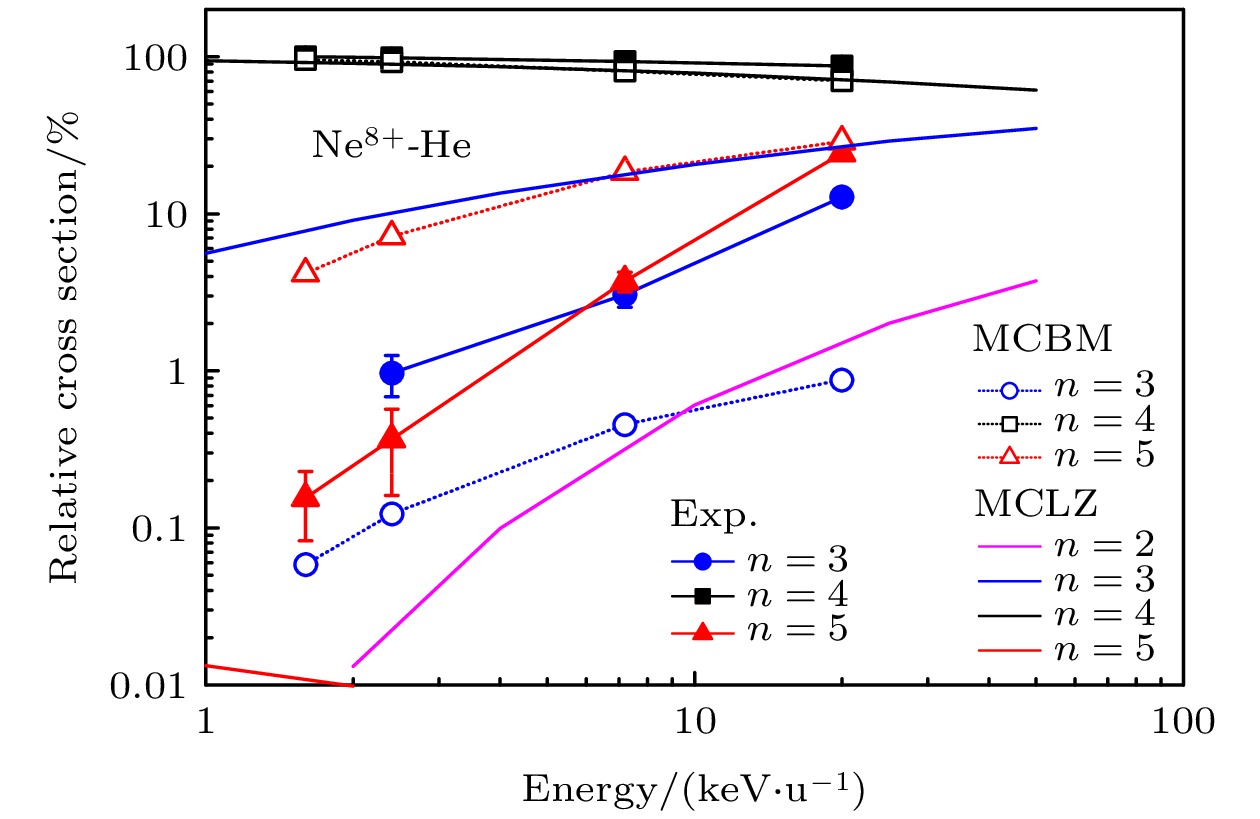
图 3 Ne8+-He单电子俘获的相对态选择截面, 实心点和实线是实验测量的结果, 空心点和点线是MCBM计算的结果, 不同的颜色与形状代表不同的俘获通道, 实线是MCLZ计算的结果
Figure 3. Ne8+-He single electron capture relative state selection cross section, the solid shape and solid line is the result of experimental measurement, the hollow shape and dot line is the result of MCBM calculation, different colors and shapes represent different capture channels, and the solid line is the result of MCLZ calculation
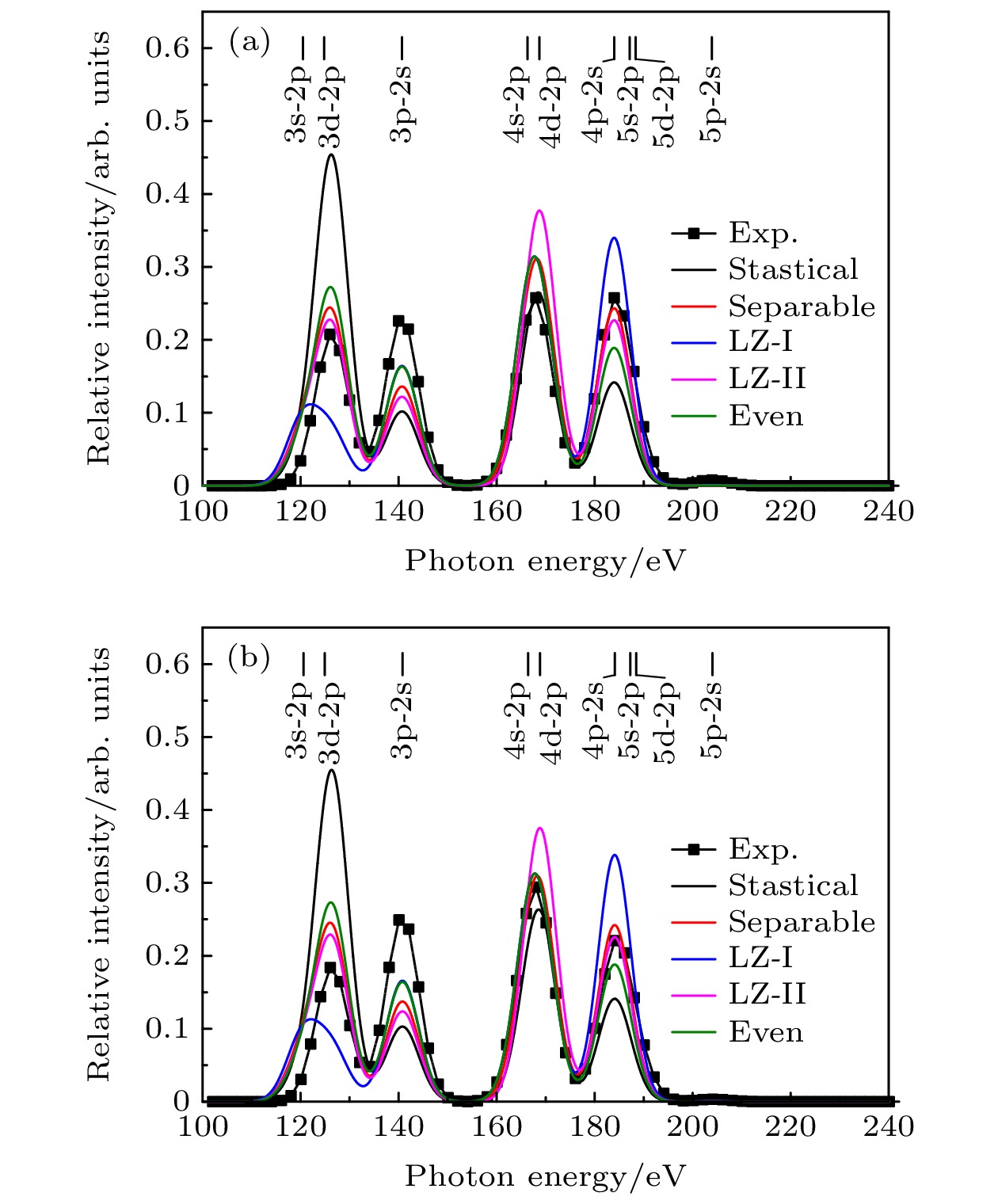
图 4 1.6和2.4 keV/u的Ne8+-He俘获电子后的归一化
$ {\rm{Ne}}^{7+*}$ 发射谱 (a) 1.6 keV/u; (b) 2.4 keV/u. 黑色、红色、蓝色、品红、绿色实线分别代表Statistical, Separable, Landau-Zenner-I, Landau-Zenner-II, 以及Even模型计算的结果, 黑色实心点代表Zhang等[18]测量的结果, 半高全宽是7.9 eVFigure 4. Normalized
$ {\rm{Ne}}^{7+*}$ emission spectrum after electron capture of Ne8+-He at 1.6 and 2.4 keV/u: (a) 1.6 keV/u; (b) 2.4 keV/u. The black, red, blue, magenta, and green solid lines represent the results calculated by the Statistical, Separable, Landau-Zenner-I, Landau-Zenner-II, and Even models, respectively. The black solid points represent the results measured by Zhang 2019, the full width at half maximum is 7.9 eV. -
[1] Dörner R, Mergel V, Jagutzki O, Spielberger L, Ullrich J, Möshammer R 2000 Phys. Rep. 330 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fischer D, Gudmundsson M, Berenyi Z, Haag N 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 012714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hayakawa S 1960 Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 12 110
[5] Joseph S, Gary S 1969 Phys. Rev. Lett. 23 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pravdo S H, Boldt E A 1975 Astrophys. J. 200 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lisse C M, Dennerl K, Englhauser J 1996 Science 274 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cravens T E 1997 Geophys. Res. Lett. 24 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Beiersdorfer P, Boyce K R, Brown G V 2003 Science 300 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cravens T E 2000 Astrophys. J. 532 L153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Koutroumpa D, Lallement R, Raymond J C, Kharchenko V 2014 Astrophys. J. 696 1517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hasan A, Eissa F, Ali R, Schultz D, Stancil P 2001 Astrophys. J. 560 L201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Seredyuk B, McCullough R W, Gilbody H B 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 022710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bodewits D, Hoekstra R 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 032703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Machacek J R, Mahapatra D P, Schultz D R 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 052708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ali R, Beiersdorfer P, Harris C L, Neill A 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 012711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Betancourt-Martinez G L, Beiersdorfer P, Brown G V 2018 Astrophys. J. 868 L17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang R T, Wulf D, McCammon D 2019 AIP Conf. Proc. 2160 070004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Defay X, Morgan K, McCammon D 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 052702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fogle M, Wu lf D, Morgan K, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 042705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Beiersdorfer P, Bitter M, Marion M, Olson R E 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 032725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lepson J K, Beiersdorfer P, Bitter M, Roquemore A L, Kaita R 2017 AIP Conf. Proc. 1811 190008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hell N, Brown G V, Wilms J 2016 Astrophys. J. 830 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ma X, Liu H P, Sun L T 2009 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 163 012104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu X L, Ma X W, Li J Y 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 460 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma X, Zhang R T, Zhang S F, Z hu, X L, Feng W T 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bliman S, Cornille M, Langereis A 1997 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68 1080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bonnet J J, Fleury A, Bonnefoy M 1985 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 18 L23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Roncin P, Barat M, Laurent H 1986 Eur. Phys. Lett. 2 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Folkmann F, Eisum N, Ciric D, Drentje A 1989 J. Phys. 50 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Langereis A, Nordgren J, Bruch R 1997 Phys. Scr. T73 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fischer D, Feuerstein B, DuBois R 2002 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 35 1369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Abdallah M A, Wolff W, Wolf H E 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Otranto S, Olson, R E, Beiersdorfer P 2006 Phys. Rev. A 73 022723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Niehaus A 1986 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 19 2925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lyons D, Cumbee R S, Stancil P C 2017 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 232 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Kahn S M, Sunyaev R A, von Ballmoos P 2019 State-of-the-Art Reviews on Energetic Ion-Atom and Ion-Molecule Collisions (Vol. 2) (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) p33
[38] Cumbee R S, Liu L, Lyons D 2016 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 458 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Smith R K, Foster A R, Edgar R J, Brickhouse N S 2014 Astrophys. J. 787 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Abdallah M A, Wolff W, Wolf H E 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 4373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7711
- PDF Downloads: 137
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: