-
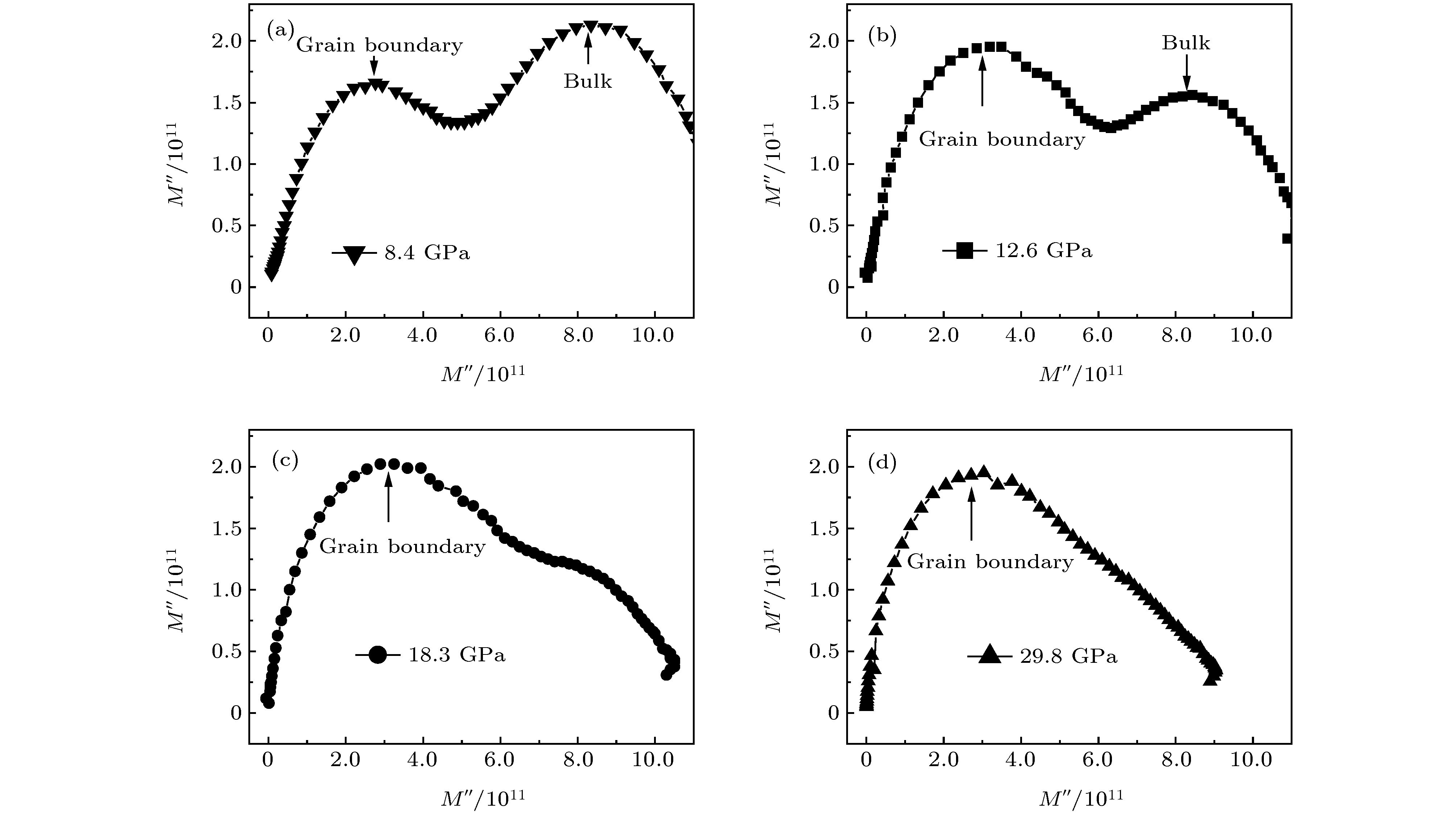
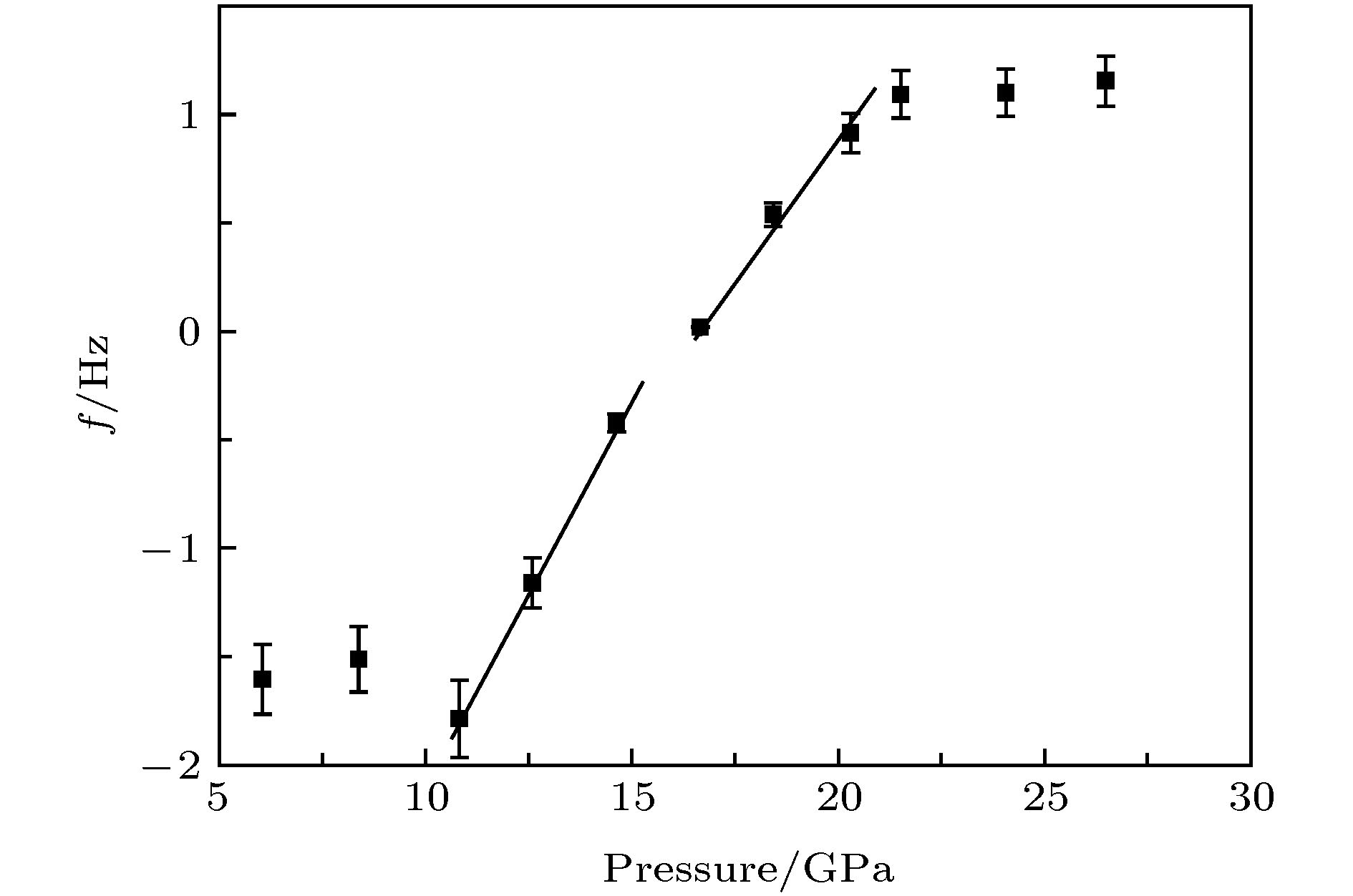
In this paper, the grain and grain boundary characteristics and mechanisms of phase transition (from wurtzite to zinc-blende to rock-salt phase structure) of ZnS nanocrystallines are investigated via in situ impedance measurement under pressure up to 29.8 GPa. It should be noted that there are two semiarcs can be found from the modulus plots of ZnS under different pressures. The semiarc in high frequency region represents the grain characteristic, and another one in low frequency region refers to the grain boundary characteristic. The former decreases gradually with pressure increasing and the latter shows an opposite trend. This fact indicates that the effect of grain characteristic becomes weaker and weaker, and the role of grain boundary characteristic is just on the contrary. The grain resistance and grain boundary resistance of ZnS nanocrystalline are also studied. In the low pressure region, both resistances increase with different increment rate with pressure increasing, which can be attributed to the enhanced ability of trap charge carriers due to the small size effect of nanoparticles. In addition, two discontinuous points (about 11 and 15 GPa) can be observed in both resistance curves, corresponding to the points of phase transition from wurtzite to zinc-blende to rock-salt phase structure. With pressure increasing, both resistances decrease gradually until 21 GPa, and this point corresponds to the end of transition from zinc-blende to rock-salt phase structure. Their consequent variations are different, grain boundary resistance gradually decreases with the pressure increasing, while the grain resistance is almost a constant. Additionally, the relaxation frequency, as an intrinsic characteristic, is not affected by the geometrical parameters. According to the linear relation between the grain boundary relaxation frequency and pressure in the pressure range of phase transformation, the mechanism of structure transition from wurtzite to zinc-blende to rock-salt phase structure is also discussed in detail. Based on the investigations, the in situ impedance spectroscopy can not only be used to accurately measure the grain and grain boundary characteristics, but also provide information for studying the phase transformation under pressure.
-
Keywords:
- high pressure /
- ZnS /
- impedance spectroscopy /
- phase transition
[1] Ding Z, Quinn B M, Haram S K, Pell L E, Korgel B A, Bard A J 2002 Science 296 1293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Stoica T, Sutter E, Meijers R J, Debnath R K, Calarco R, Luth H, Grutzmacher D 2008 Small 4 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bai F, Bian K, Huang X 2019 Chem. Rev. 119 7673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haase M, Alivisatos A P 1992 J. Phys. Chem. 96 6756
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cui X Y, Hu T J, Wang J S, Zhang J K, Zhao R, Li F F 2017 RSC Adv. 7 12098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ono S, Kikegawa T 2018 Phase Transitions 91 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Biering S, Schwerdtfeger P 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 137 034705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bilge M, Özdemir S, Kart H H 2008 Mater. Chem. Phys. 111 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Z, Guo Q 2009 J. Phys. Chem.C 113 4286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pan Y W, Qu S, Dong S, Cui Q L, Gao C X, Zou G T 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 14 10487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bi C, Pan L Q, Guo Z G, Zhao Y L, Huang M F, Xin J 2010 Mater. Lett. 64 1681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Han Y H, Gao C X, Ma Y Z, Liu C L, Peng G, Wu B J, Liu B, Hu T J, Cui X Y, Ren W B, Li Y, Su N N, Liu H W, Zou G T 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum 81 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王月, 张凤霞, 王春杰, 高春晓 2014 63 216401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang F X, Wang C J, Gao C X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 216401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 曹楚南, 张鉴清 2002 电化学阻抗谱导论 (典藏版1) (北京: 科学出版社) 第21页
Cao C N, Zhang J Q 2002 Introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p21 (in Chinese)
[15] Li J, Wang W 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 125325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maier J 1987 Solid State Ionics 23 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fleig J, Maier J 1998 J. Electrochem. Soc. 145 2081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fleig, J 2002 Solid State Ionics 150 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tolbert S H, Alivisatos A P 1994 Science 265 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tolbert S H, Alivisatos A P 1995 J. Chem. Phys. 102 4642
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tolbert S H, Herhold A B, Brus L E, Alivisatos A P 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 4384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H Z, Huang F, Gilbert B, Banfield J F 2003 J. Phys. Chem. B 107 13051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao M, Zheng W T, Li J C, Wen Z, Gu M X, Sun C Q 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 085427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kodiyalam S, Rajiv K K, Hideaki K, Aiichiro N, Fuyuki S, Vashishta P 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ye X, Sun D Y, Gong X G 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 094108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wickham J N, Herhold A B, Alivisators A P 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Goldstein A N, Echer C M, Alivisatos A P 1992 Science 256 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Brus L E, Harkless J A W, Stillinger F H 1996 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 4834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Macdonald J R 1987 Impedance Spectrum (New York: Wiley) pp13–14, 205
[30] Chen C C, Herhold A B, Johnson C S, Alivisatos A P 1997 Science 276 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang Z W, Daemen L L, Zhao Y S, Zha C S, Downs R T, Wang X, Wang Z L 2005 Nat. Mater. 4 922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gilbert B, Frazer B H, Zhang H, Huang F, Banfield J F, Haskel D, Lang J C, Srajer G, de Stasio G 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 245205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 (a) 金刚石对顶砧薄膜电极示意图: 1, Mo电极; 2, 裸露的金刚石砧面; 3, 沉积在金刚石砧面的Al2O3薄膜; 4, 沉积在Mo薄膜上的Al2O3薄膜; (b)金刚石对顶砧剖面示意图
Figure 2. (a) The configuration of a complete microcircuit on a diamond anvil: 1, the Mo electrodes; 2, the exposed diamond anvil; 3, the Al2O3 layer deposited on the diamond anvil; 4, the Al2O3 layer deposited on the Mo film; (b) the cross section of the designed diamond-anvil-cell.
-
[1] Ding Z, Quinn B M, Haram S K, Pell L E, Korgel B A, Bard A J 2002 Science 296 1293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Stoica T, Sutter E, Meijers R J, Debnath R K, Calarco R, Luth H, Grutzmacher D 2008 Small 4 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bai F, Bian K, Huang X 2019 Chem. Rev. 119 7673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haase M, Alivisatos A P 1992 J. Phys. Chem. 96 6756
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cui X Y, Hu T J, Wang J S, Zhang J K, Zhao R, Li F F 2017 RSC Adv. 7 12098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ono S, Kikegawa T 2018 Phase Transitions 91 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Biering S, Schwerdtfeger P 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 137 034705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bilge M, Özdemir S, Kart H H 2008 Mater. Chem. Phys. 111 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Z, Guo Q 2009 J. Phys. Chem.C 113 4286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pan Y W, Qu S, Dong S, Cui Q L, Gao C X, Zou G T 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 14 10487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bi C, Pan L Q, Guo Z G, Zhao Y L, Huang M F, Xin J 2010 Mater. Lett. 64 1681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Han Y H, Gao C X, Ma Y Z, Liu C L, Peng G, Wu B J, Liu B, Hu T J, Cui X Y, Ren W B, Li Y, Su N N, Liu H W, Zou G T 2010 Rev. Sci. Instrum 81 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王月, 张凤霞, 王春杰, 高春晓 2014 63 216401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang F X, Wang C J, Gao C X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 216401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 曹楚南, 张鉴清 2002 电化学阻抗谱导论 (典藏版1) (北京: 科学出版社) 第21页
Cao C N, Zhang J Q 2002 Introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p21 (in Chinese)
[15] Li J, Wang W 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 125325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maier J 1987 Solid State Ionics 23 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fleig J, Maier J 1998 J. Electrochem. Soc. 145 2081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fleig, J 2002 Solid State Ionics 150 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tolbert S H, Alivisatos A P 1994 Science 265 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tolbert S H, Alivisatos A P 1995 J. Chem. Phys. 102 4642
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tolbert S H, Herhold A B, Brus L E, Alivisatos A P 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 4384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H Z, Huang F, Gilbert B, Banfield J F 2003 J. Phys. Chem. B 107 13051
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao M, Zheng W T, Li J C, Wen Z, Gu M X, Sun C Q 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 085427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kodiyalam S, Rajiv K K, Hideaki K, Aiichiro N, Fuyuki S, Vashishta P 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ye X, Sun D Y, Gong X G 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 094108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wickham J N, Herhold A B, Alivisators A P 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Goldstein A N, Echer C M, Alivisatos A P 1992 Science 256 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Brus L E, Harkless J A W, Stillinger F H 1996 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 4834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Macdonald J R 1987 Impedance Spectrum (New York: Wiley) pp13–14, 205
[30] Chen C C, Herhold A B, Johnson C S, Alivisatos A P 1997 Science 276 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang Z W, Daemen L L, Zhao Y S, Zha C S, Downs R T, Wang X, Wang Z L 2005 Nat. Mater. 4 922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gilbert B, Frazer B H, Zhang H, Huang F, Banfield J F, Haskel D, Lang J C, Srajer G, de Stasio G 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 245205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14495
- PDF Downloads: 153
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: