-
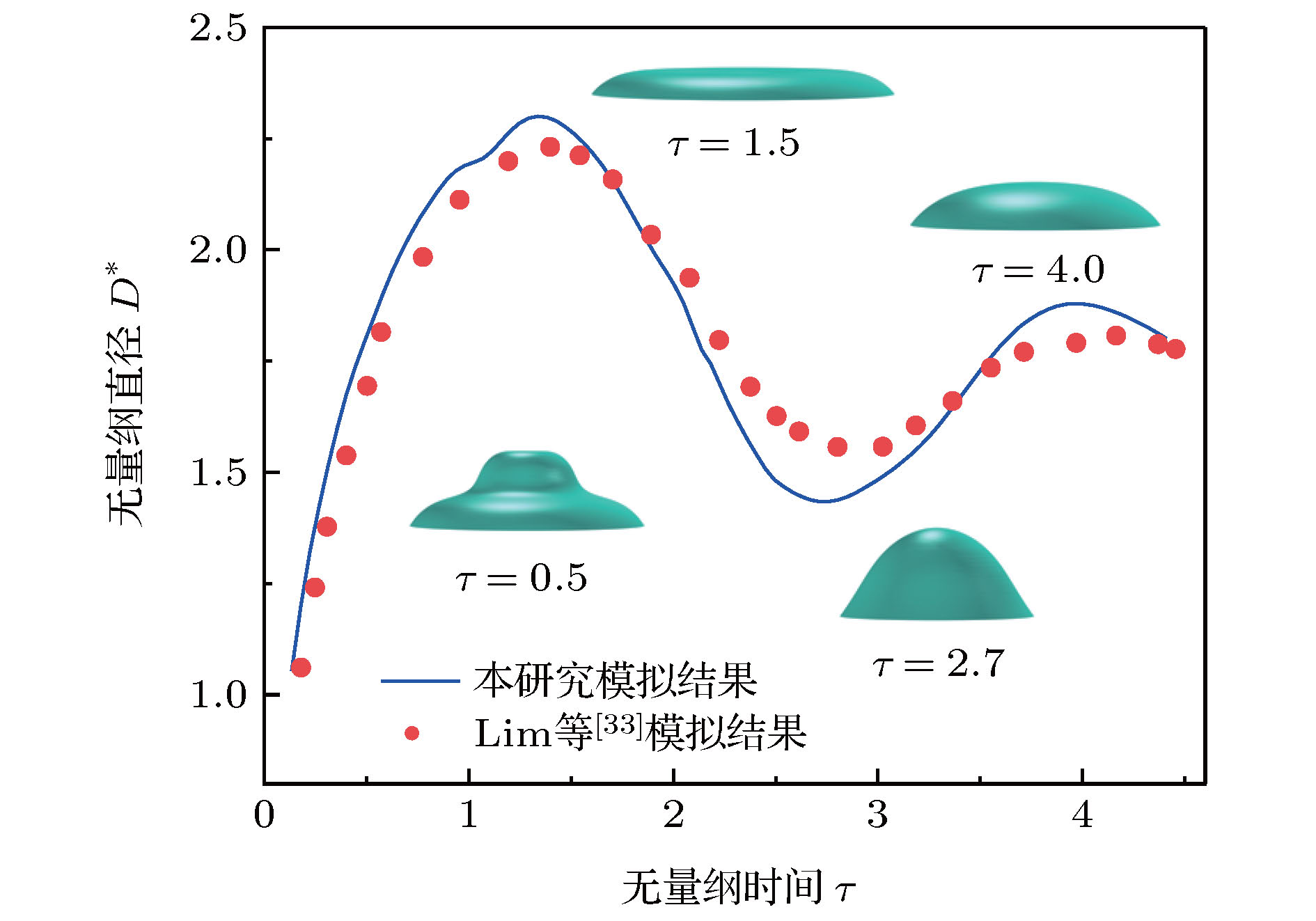
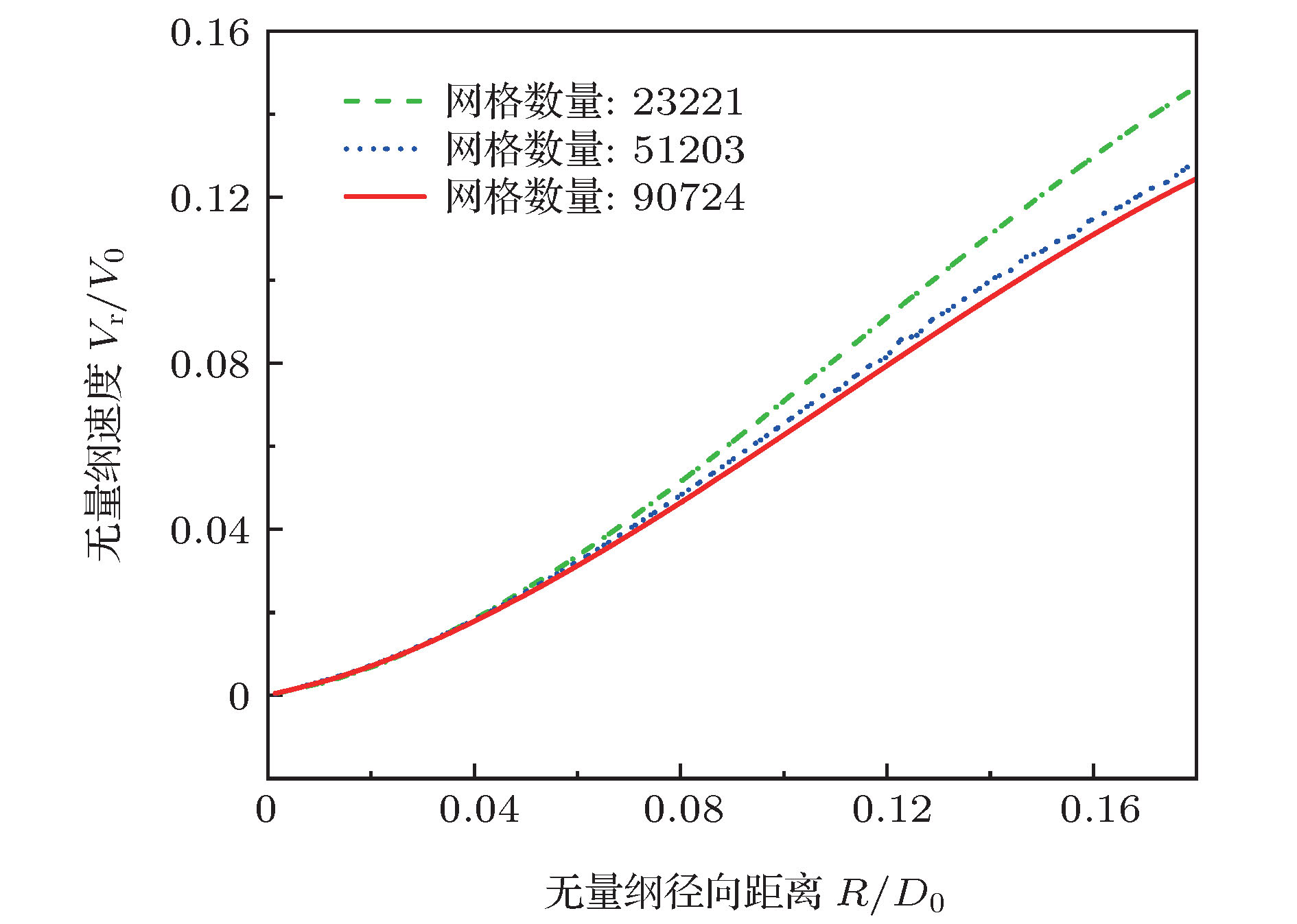
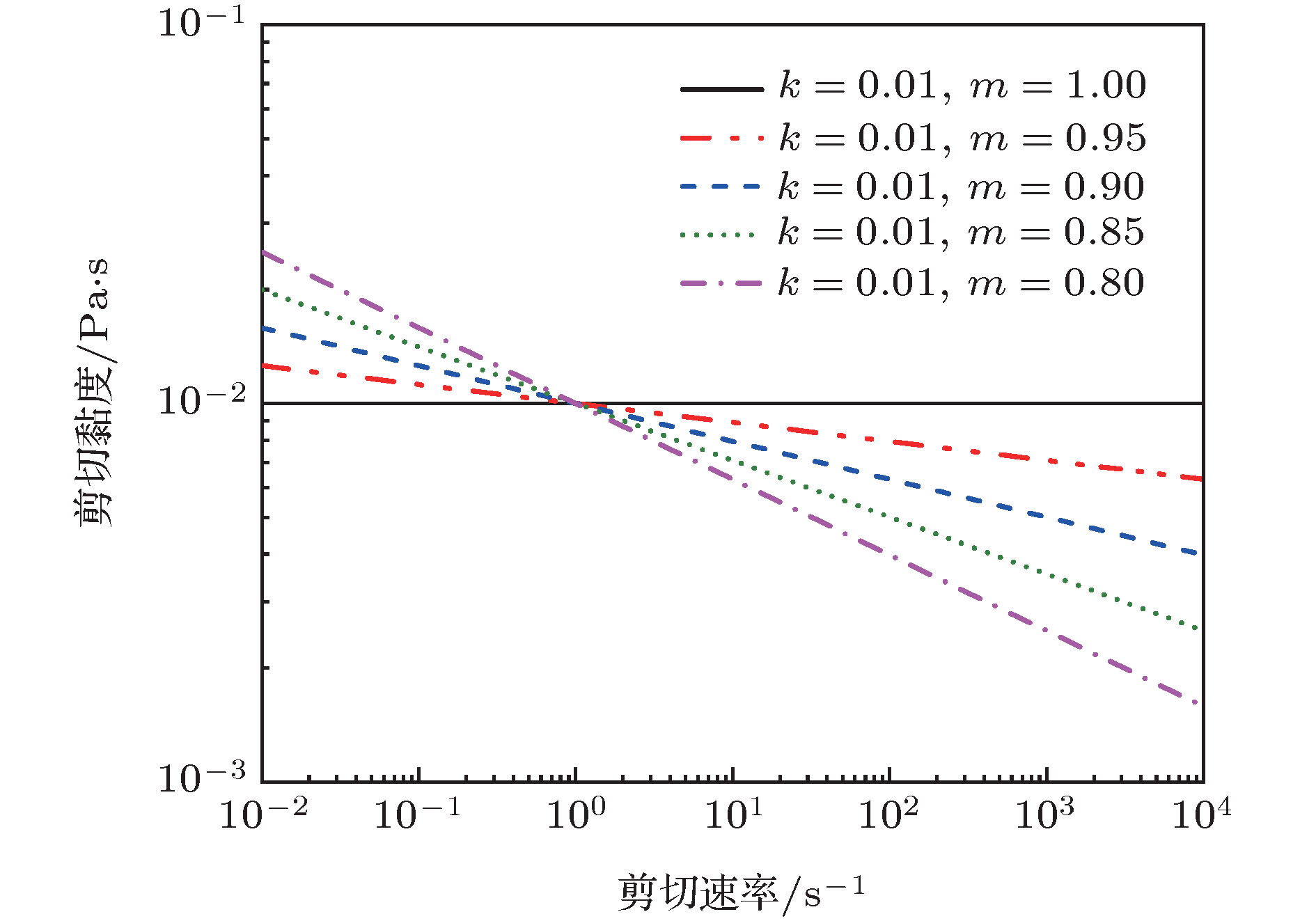
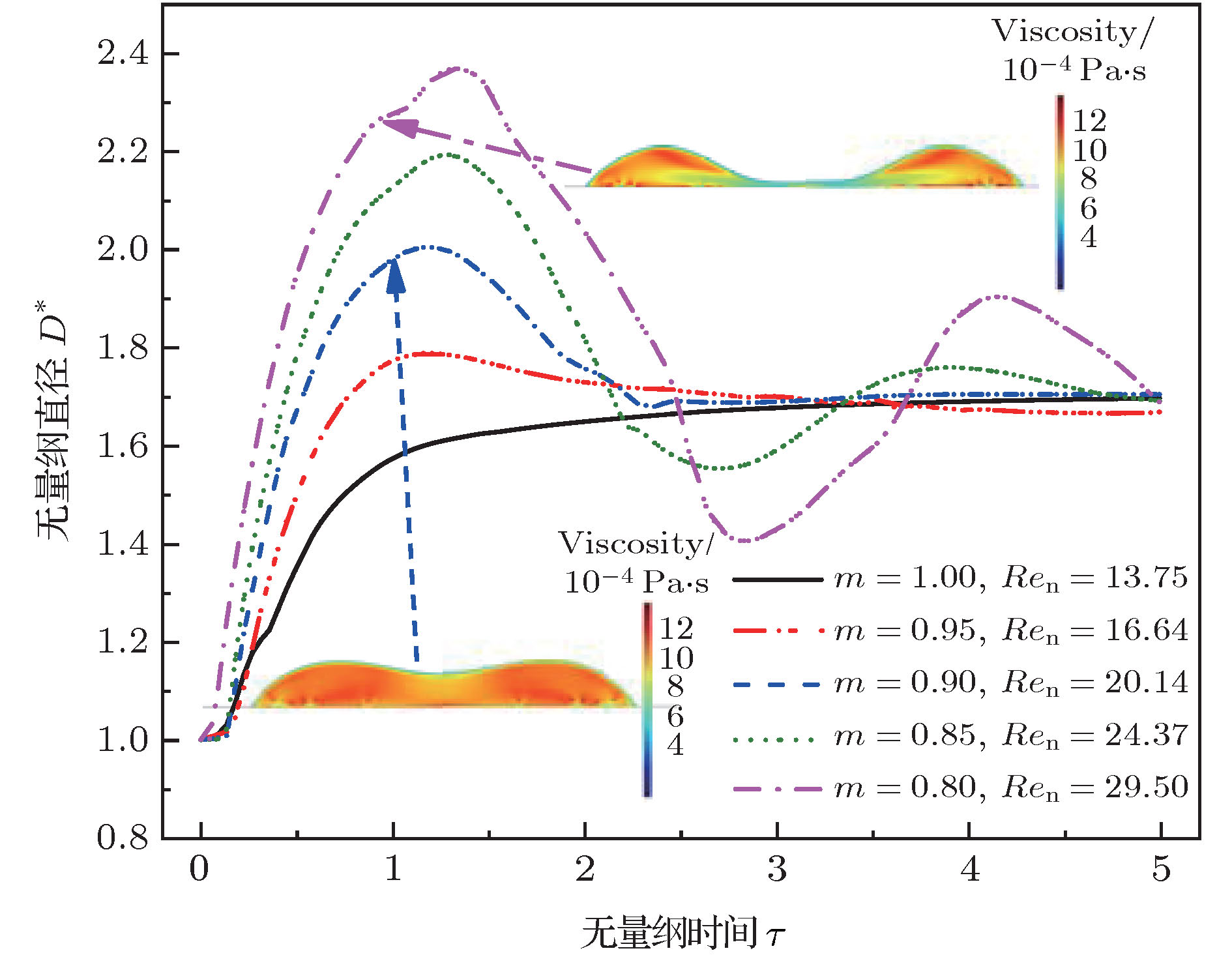
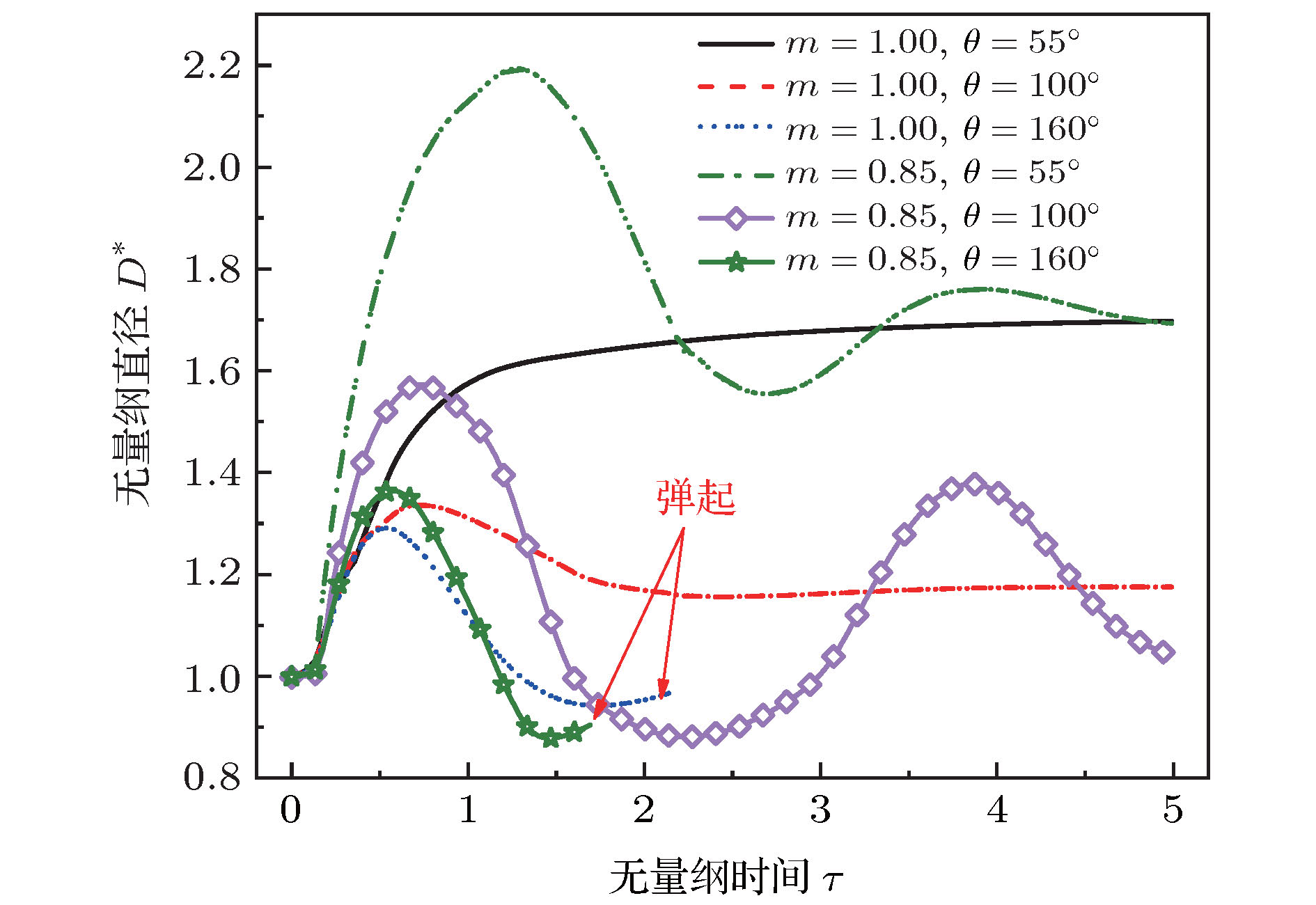
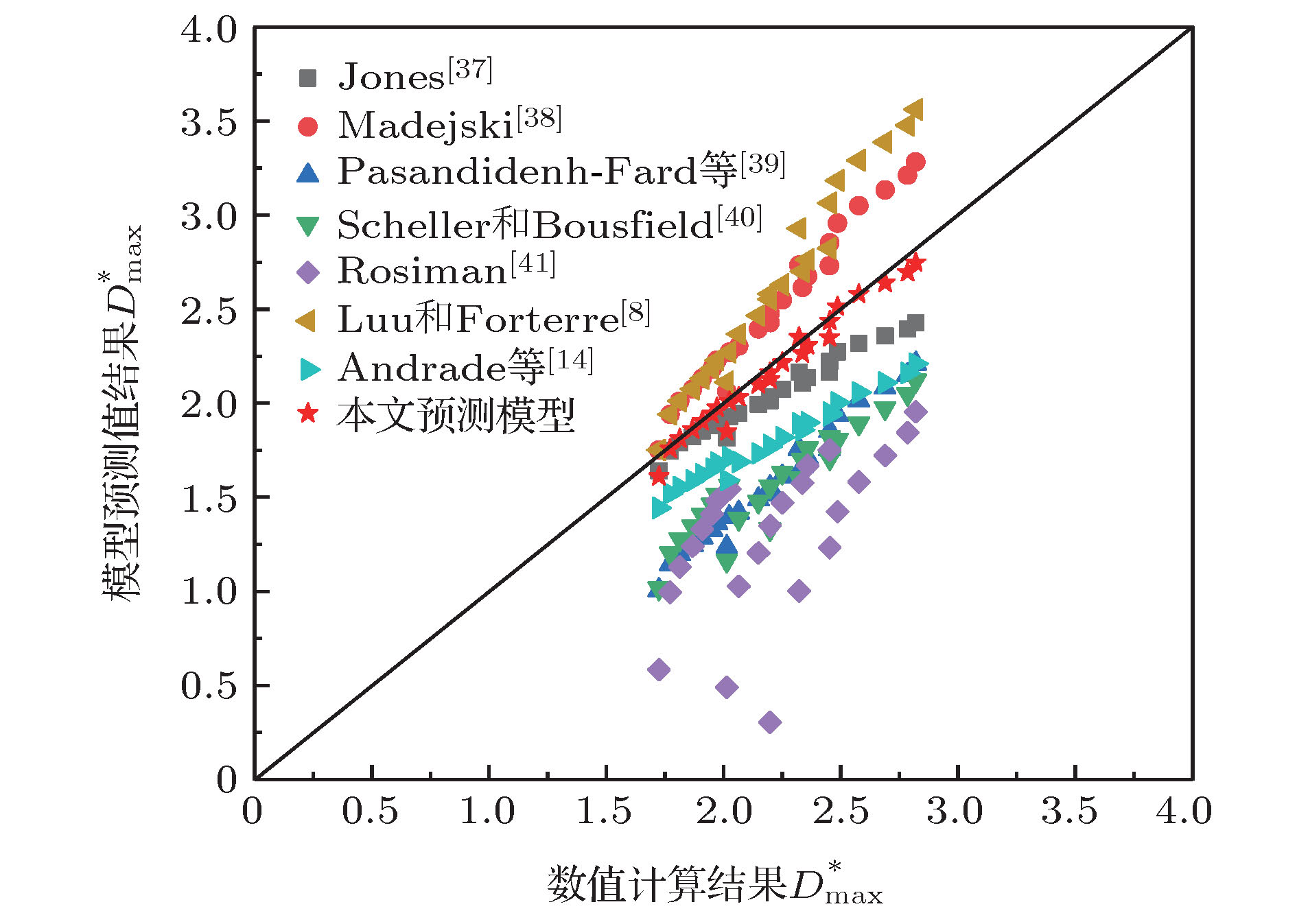
Controlling impact dynamics of droplets on solid surfaces is a significant problem in a variety of applications, such as inkjet printing, spray cooling and coating and so on. Most of fluids used in industries always contain various kinds of additives such as surfactants, polymers and particles. Therefore, these fluids exhibit non-Newtonian behaviors, for instance, yield-stress, viscoelastic, shear-thickening and shear-thinning. The impact dynamics of Newtonian droplets on solid surfaces has been extensively investigated. However, the number of researches about fluids with non-Newtonian properties is comparatively very small. In this work, we employ the finite element scheme coupled with level set method to simulate the impact process of droplets on solid surfaces. The numerical simulation models the presence of shear-thinning viscosity by using the truncated power-law rheological model. We first conduct a mesh convergence study and verify the numerical model. The simulation results are found to be in good agreement with experimental data in the literature. By performing extensive numerical simulations and varying the rheological parameters and surface wettabilities, the influences of these parameters on the impact dynamics are evaluated, and the dominant effects that govern the spreading and receding process are determined. The simulation results show that for the case of droplet impacting on surface with contact angle θ = 55°, the spreading is stronger with power-law index decreasing as evidenced by larger shape deformation and faster interface moving speed. As power-law index decreases, we expect the maximum dimensionless diameter to increase and the minimum dimensionless height to decrease during inertial spreading. For the case of droplet with lower power-law index (m = 0.85 and 0.80), which indicates lower viscous dissipation during impact, the dimensionless parameters have significant differences. After first receding, the impacting droplet is not balanced any more and it starts to spread again until its kinetic energy is completely damped by fluid viscous dissipation. For the case of droplet (m = 0.80) impacting on surface, the center breakage can be observed during droplet spreading, which results from the effect of strong shear-thinning property. When a shear-thinning droplet impacts on a surface with contact angle θ = 100°, the oscillation behavior can be observed and the oscillation amplitude increases as power law index decreases. Bouncing phenomenon can be observed when a droplet impacts on surface with contact angle θ = 160°, regardless of rheological property. Finally, we propose an empirical model to predict the maximum dimensionless diameter of shear-thinning droplet impacting on the surface with contact angle θ = 55° as a function of non-Newtonian Reynolds number Ren.
-
Keywords:
- non-Newtonian fluid /
- droplet impact /
- finite element method /
- level-set method /
- spreading dynamics
[1] Rioboo R, Tropea C, Marengo M 2001 Atomization Sprays 11 155
[2] 荣松, 沈世全, 王天友, 车志钊 2019 68 154701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rong S, Shen S Q, Wang T Y, Che Z Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 154701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 杨亚晶, 梅晨曦, 章旭东, 魏衍举, 刘圣华 2019 68 156101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y J, Mei C X, Zhang X D, Wei Y J, Liu S H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 156101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yarin A L 2006 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Josserand C, Thoroddsen S T 2016 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48 365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jung S, Hoath S D, Hutchings I M 2013 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 14 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Huh H K, Jung S, Seo K W, Lee S J 2015 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 18 1221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Luu L H, Forterre Y 2009 J. Fluid Mech. 632 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Saïdi A, Martin C, Magnin A 2010 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 165 596
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Boyer F, Sandoval-Nava E, Snoeijer J H, Dijksman J F, Lohse D 2016 Phys. Rev. Fluids 1 013901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] German G, Bertola V 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 375111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] An S M, Lee S Y 2012 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 38 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] An S M, Lee S Y 2012 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 37 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Andrade R, Skurtys O, Osorio F 2015 J. Food Eng. 157 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Laan N, de Bruin K G, Bartolo D, Josserand C, Bonn D 2014 Phys. Rev. Appl. 2 044018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 刘海龙, 沈学峰, 王睿, 曹宇, 王军锋 2018 力学学报 50 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H L, Shen X F, Wang R, Cao Y, Wang J F 2018 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 50 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hou T Y, Lowengrub J S, Shelley M J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tryggvason G, Bunner B, Esmaeeli A, Juric D, Al-Rawahi N, Tauber W, Han J, Nas S, Jan Y-J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yue P, Feng J J, Liu C, Shen J 2004 J. Fluid Mech. 515 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hirt C W, Nichols B D 1981 J. Comput. Phys. 39 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ding H, Spelt P D M 2007 Phys. Rev. E 75 046708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gunstensen A K, Rothman D H, Zaleski S, Zanetti G 1991 Phys. Rev. A 43 4320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Olsson E, Kreiss G 2005 J. Comput. Phys. 210 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 郑志伟, 李大树, 仇性启, 崔运静 2017 66 014704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z W, Li D S, Qiu X Q, Cui Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李玉杰, 黄军杰, 肖旭斌 2018 67 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Huang J J, Xiao X B 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高亚军, 姜汉桥, 李俊键, 赵玉云, 胡锦川, 常元昊 2017 66 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y J, Jiang H J, Li J J, Zhao Y Y, Hu J C, Chang Y H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 韩丁丁, 刘浩然, 刘难生, 丁航 2018 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 48 094705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han D D, Liu H R, Liu N S, Ding H 2018 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 48 094705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kim E, Baek J 2012 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 173–174 62
[29] Wang Y, Do-Quang M, Amberg G 2017 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 243 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu H L, Um M K, Hwang W R 2015 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 224 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bashir S, Rees J M, Zimmerman W B 2014 Int. J. Multiph. Flow 60 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Chang Q, Zhang M, Bai F, Wu J, Xia Z, Jiao K, Du Q 2013 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 198 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lim C Y, Lam Y C 2014 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 17 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Lindner A, Bonn D, Meunier J 2000 Phys. Fluids 12 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Q, Qian T Z, Wang X P 2016 Phys. Fluids 28 022103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhang L, Ku T, Cheng X, Song Y, Zhang D 2018 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 22 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jones H 1971 J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 4 1657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Madejski J 1976 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 19 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Pasandideh-Fard M, Qiao Y M, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J 1996 Phys. Fluids 8 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Scheller B L, Bousfield D W 1995 AIChE J. 41 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Roisman I V 2009 Phys. Fluids 21 052104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 数值模拟参数设置
Table 1. Symbols and constants in numerical simulation
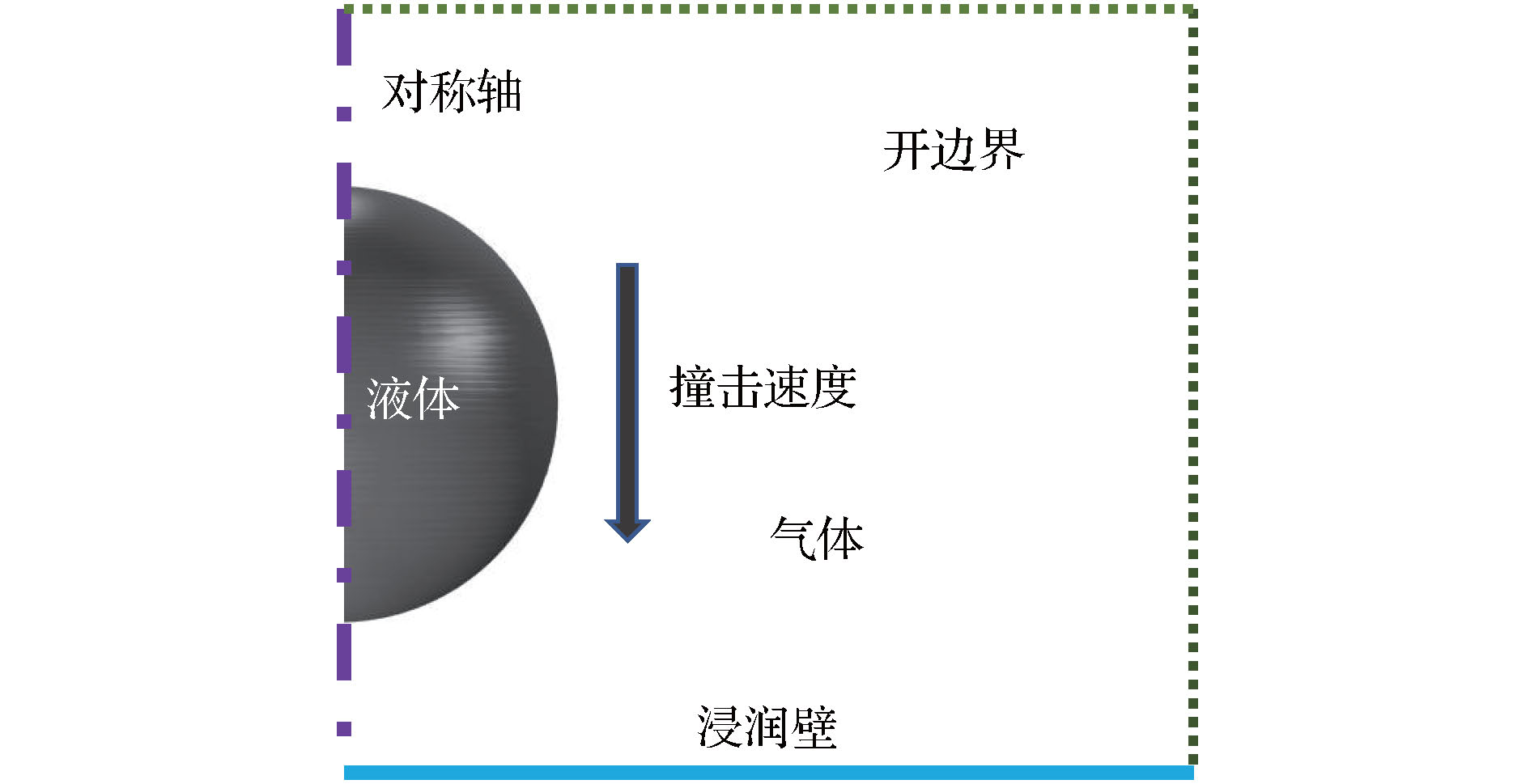
参数 符号/单位 数值 重新初始化参数 $\gamma /{\rm{m}} \cdot {{\rm{s}}^{ - 1}}$ 1 界面厚度 $\varepsilon /\text{μm}$ $5 \times {10^{ - 2}}$ 气体密度 ${\rho _1}/{\rm{kg}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - {\rm{3}}}}$ 1.2 气体黏度 ${\eta _1}{\rm{/Pa}} \cdot {\rm{s}}$ $2 \times {10^{ - 5}}$ 液体密度 ${\rho _2}/{\rm{kg}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - {\rm{3}}}}$ 1000 液体黏度 ${\eta _2}{\rm{/Pa}} \cdot {\rm{s}}$ $8.9 \times {10^{ - 4}}$ 温度 T/℃ 25 液滴初始直径 ${D_0}/{\text{μ} m }$ 55 液滴撞击速度 uz$/{\rm{m}} \cdot {{\rm{s}}^{ - 1}}$ 2.45 接触角 $\theta /{(^ \circ })$ 55 气液界面张力 $\sigma /{\rm{mN}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - 1}}$ 72.8 表 2 最大无量纲直径预测模型
Table 2. Prediction models of maximum dimensionless factor.
模型出处 方程 均方根误差 Jones[37] $D_{\max }^* = {({\rm{4/3} }Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/4})^{1/2} }$ 0.20 Madejski[38] $D_{\max }^* = Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/5}$ 0.31 Pasandideh-Fard等[39] $D_{\max }^* = 0.5 Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/4}$ 0.64 Scheller和Bousfield[40] $D_{\max }^* = 0.61{(R{e_{\rm{n}}}W{e^{1{\rm{/}}2}}{\rm{)}}^{0.166}}$ 0.65 Roisman[41] $D_{\max }^* = 0.87 Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/5} - {\rm{0} }{\rm{.40} }Re_{\rm{n} }^{2/5}W{e^{ - 1/2} }$ 0.97 Luu和Forterre[8] $D_{\max }^* = Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/(2 m + 3)}$ 0.44 Andrade等[14] $D_{\max }^* = 1.28 + 0.071 W{e^{1/4} }Re_{\rm{n} } ^{1/4}$ 0.43 本文预测模型 $D_{\max }^* = Re_{\rm{n} } ^{0.17} = {\left[ {\rho D_0^mV_0^{2 - m}/k} \right]^{0.17} }$ 0.06 -
[1] Rioboo R, Tropea C, Marengo M 2001 Atomization Sprays 11 155
[2] 荣松, 沈世全, 王天友, 车志钊 2019 68 154701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rong S, Shen S Q, Wang T Y, Che Z Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 154701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 杨亚晶, 梅晨曦, 章旭东, 魏衍举, 刘圣华 2019 68 156101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y J, Mei C X, Zhang X D, Wei Y J, Liu S H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 156101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yarin A L 2006 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Josserand C, Thoroddsen S T 2016 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48 365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jung S, Hoath S D, Hutchings I M 2013 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 14 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Huh H K, Jung S, Seo K W, Lee S J 2015 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 18 1221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Luu L H, Forterre Y 2009 J. Fluid Mech. 632 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Saïdi A, Martin C, Magnin A 2010 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 165 596
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Boyer F, Sandoval-Nava E, Snoeijer J H, Dijksman J F, Lohse D 2016 Phys. Rev. Fluids 1 013901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] German G, Bertola V 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 375111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] An S M, Lee S Y 2012 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 38 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] An S M, Lee S Y 2012 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 37 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Andrade R, Skurtys O, Osorio F 2015 J. Food Eng. 157 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Laan N, de Bruin K G, Bartolo D, Josserand C, Bonn D 2014 Phys. Rev. Appl. 2 044018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 刘海龙, 沈学峰, 王睿, 曹宇, 王军锋 2018 力学学报 50 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H L, Shen X F, Wang R, Cao Y, Wang J F 2018 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 50 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hou T Y, Lowengrub J S, Shelley M J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tryggvason G, Bunner B, Esmaeeli A, Juric D, Al-Rawahi N, Tauber W, Han J, Nas S, Jan Y-J 2001 J. Comput. Phys. 169 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yue P, Feng J J, Liu C, Shen J 2004 J. Fluid Mech. 515 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hirt C W, Nichols B D 1981 J. Comput. Phys. 39 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ding H, Spelt P D M 2007 Phys. Rev. E 75 046708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gunstensen A K, Rothman D H, Zaleski S, Zanetti G 1991 Phys. Rev. A 43 4320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Olsson E, Kreiss G 2005 J. Comput. Phys. 210 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 郑志伟, 李大树, 仇性启, 崔运静 2017 66 014704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z W, Li D S, Qiu X Q, Cui Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李玉杰, 黄军杰, 肖旭斌 2018 67 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y J, Huang J J, Xiao X B 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 184701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高亚军, 姜汉桥, 李俊键, 赵玉云, 胡锦川, 常元昊 2017 66 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y J, Jiang H J, Li J J, Zhao Y Y, Hu J C, Chang Y H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 韩丁丁, 刘浩然, 刘难生, 丁航 2018 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 48 094705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han D D, Liu H R, Liu N S, Ding H 2018 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 48 094705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kim E, Baek J 2012 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 173–174 62
[29] Wang Y, Do-Quang M, Amberg G 2017 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 243 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu H L, Um M K, Hwang W R 2015 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 224 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bashir S, Rees J M, Zimmerman W B 2014 Int. J. Multiph. Flow 60 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Chang Q, Zhang M, Bai F, Wu J, Xia Z, Jiao K, Du Q 2013 J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 198 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lim C Y, Lam Y C 2014 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 17 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Lindner A, Bonn D, Meunier J 2000 Phys. Fluids 12 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Q, Qian T Z, Wang X P 2016 Phys. Fluids 28 022103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhang L, Ku T, Cheng X, Song Y, Zhang D 2018 Microfluid. Nanofluidics 22 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jones H 1971 J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 4 1657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Madejski J 1976 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 19 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Pasandideh-Fard M, Qiao Y M, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J 1996 Phys. Fluids 8 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Scheller B L, Bousfield D W 1995 AIChE J. 41 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Roisman I V 2009 Phys. Fluids 21 052104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12254
- PDF Downloads: 212
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: