-
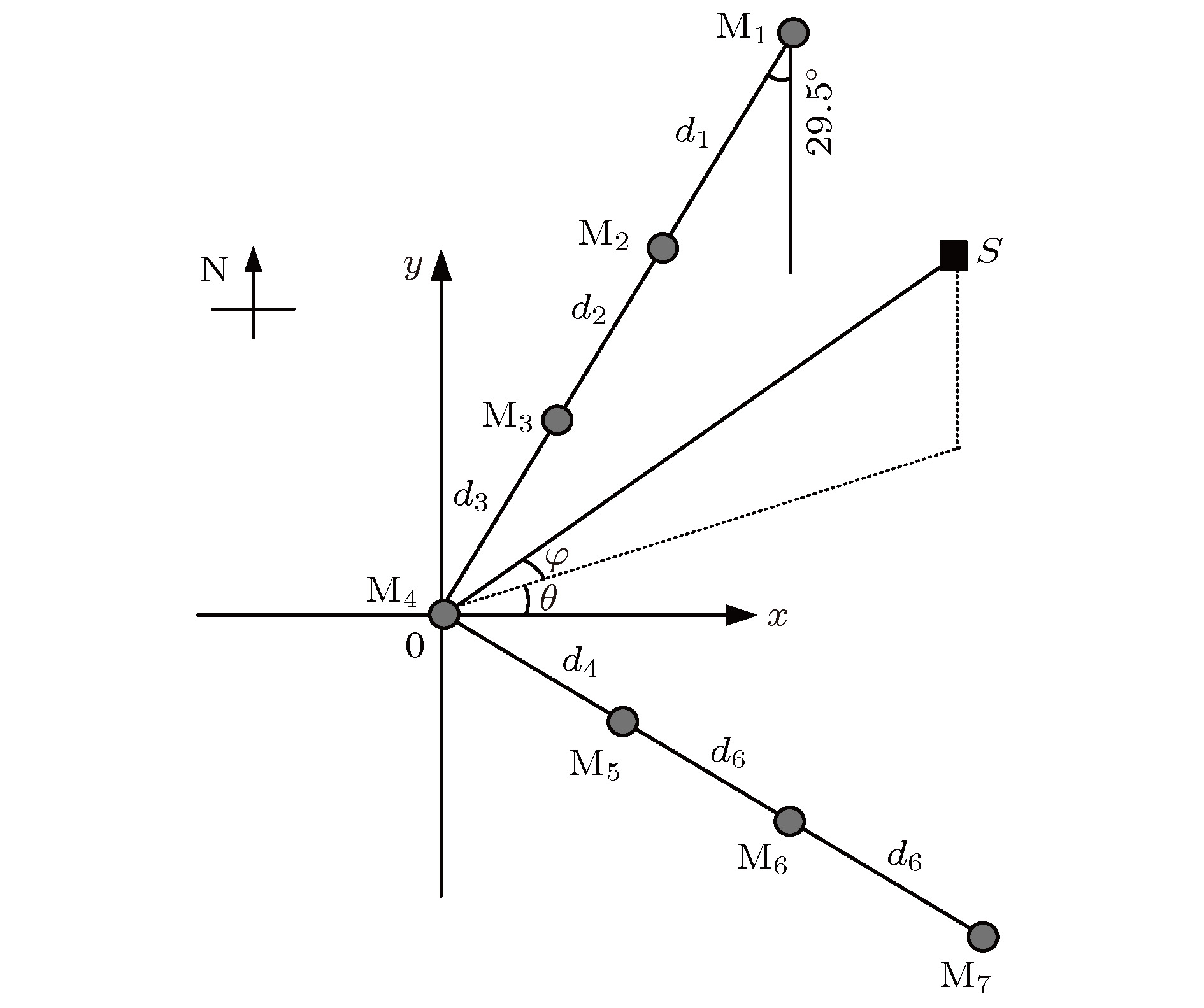
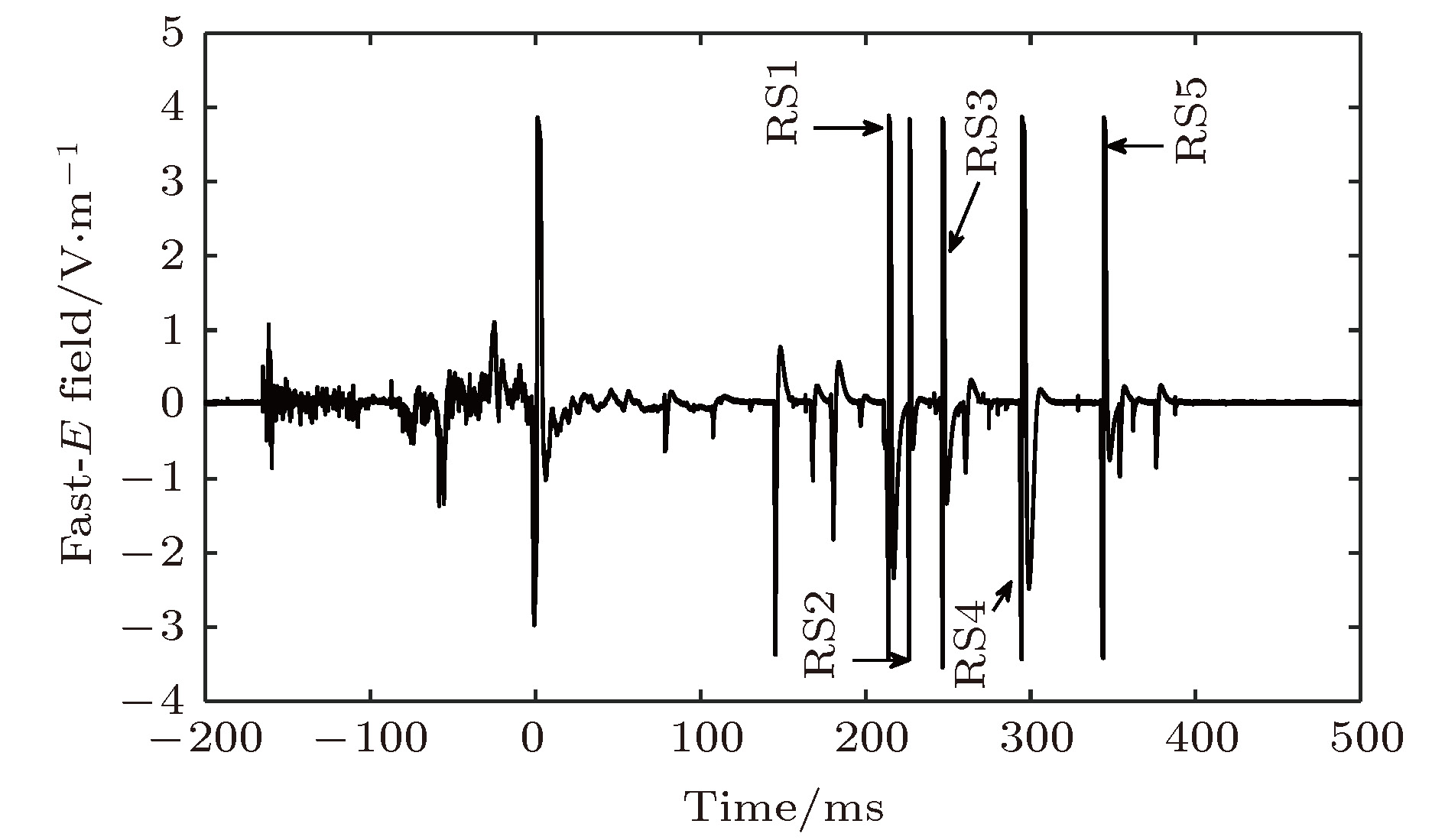
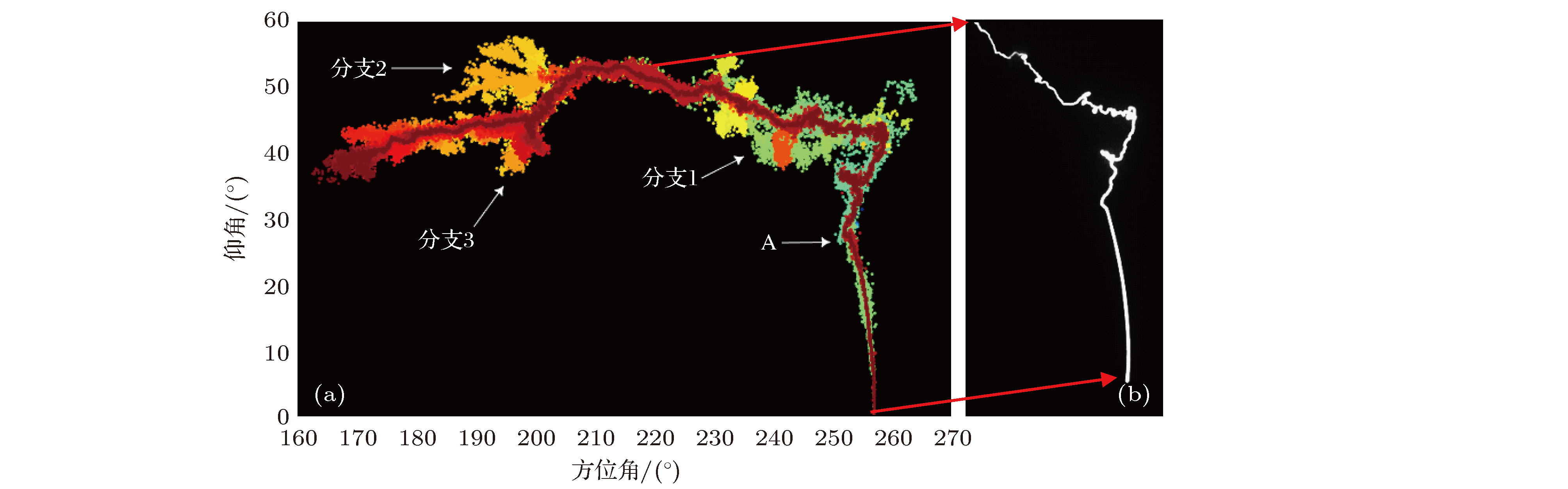
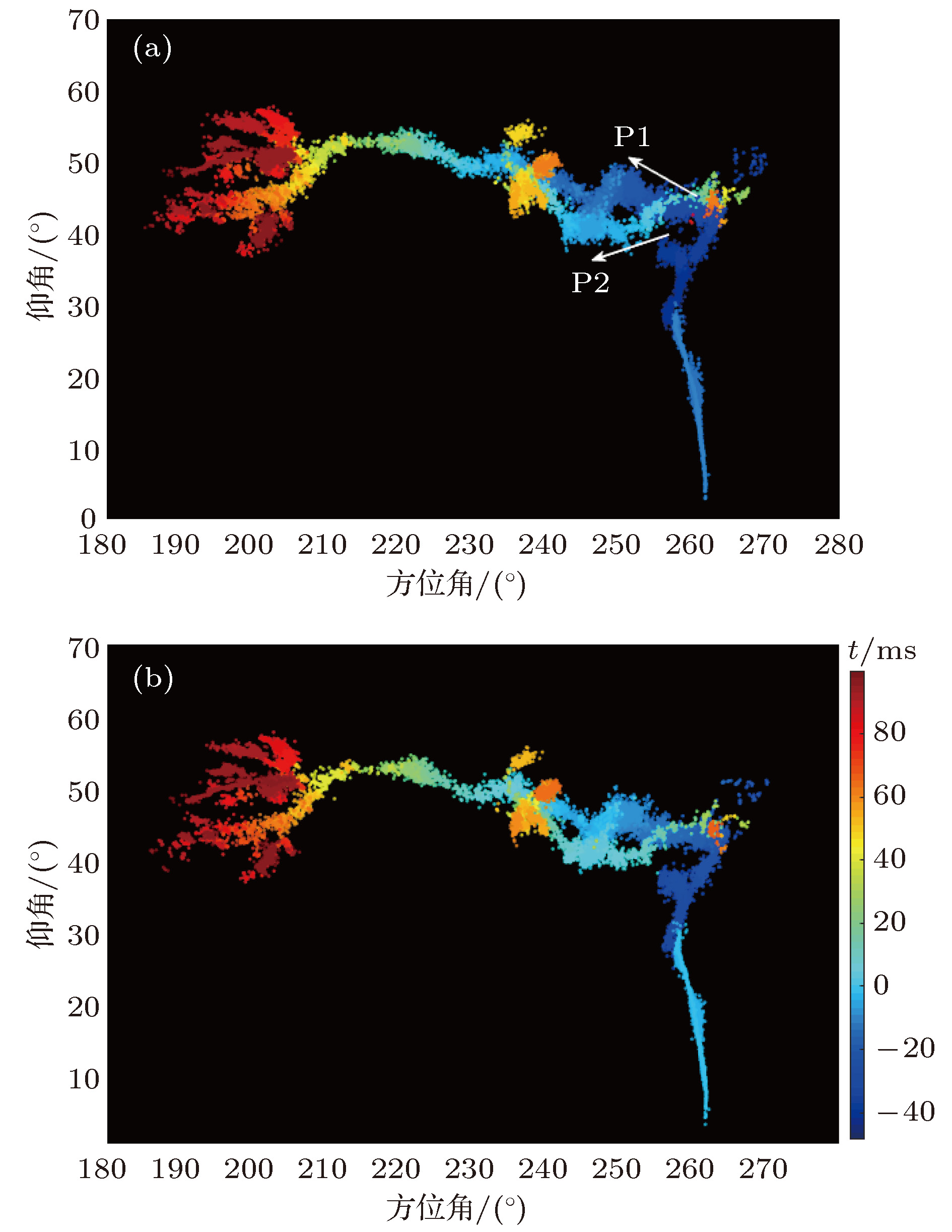
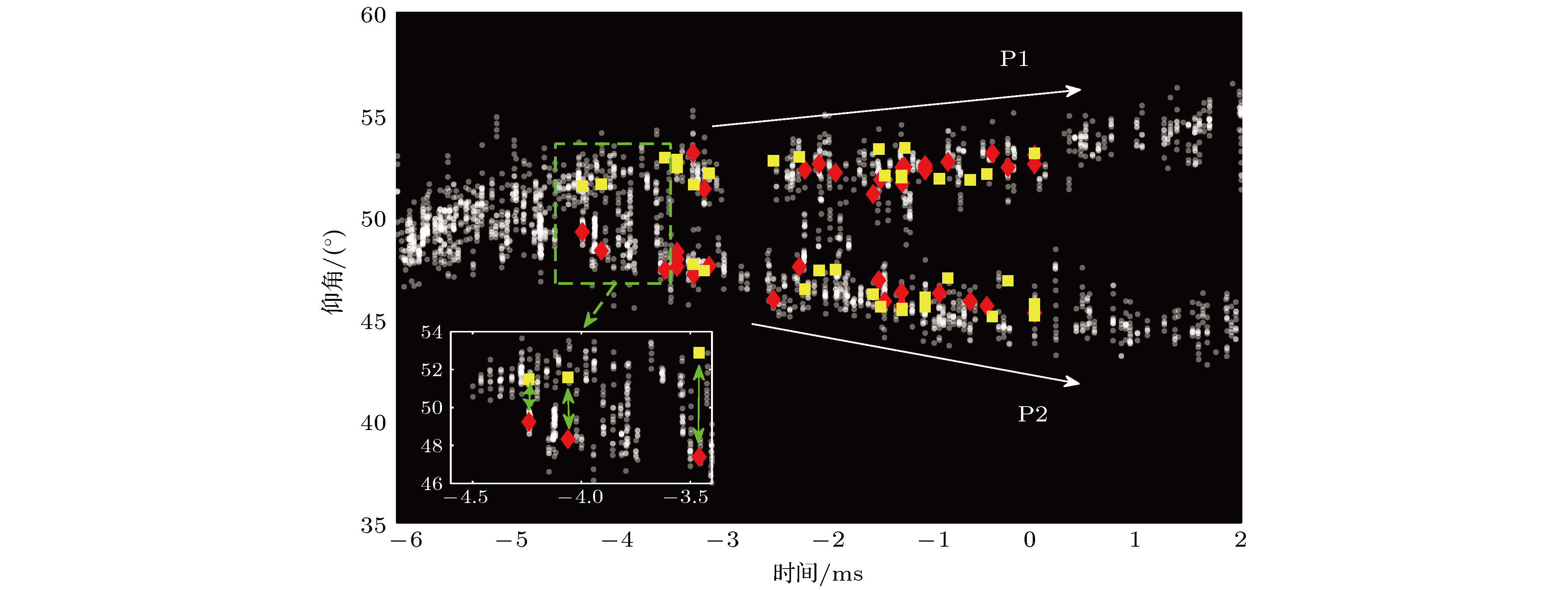
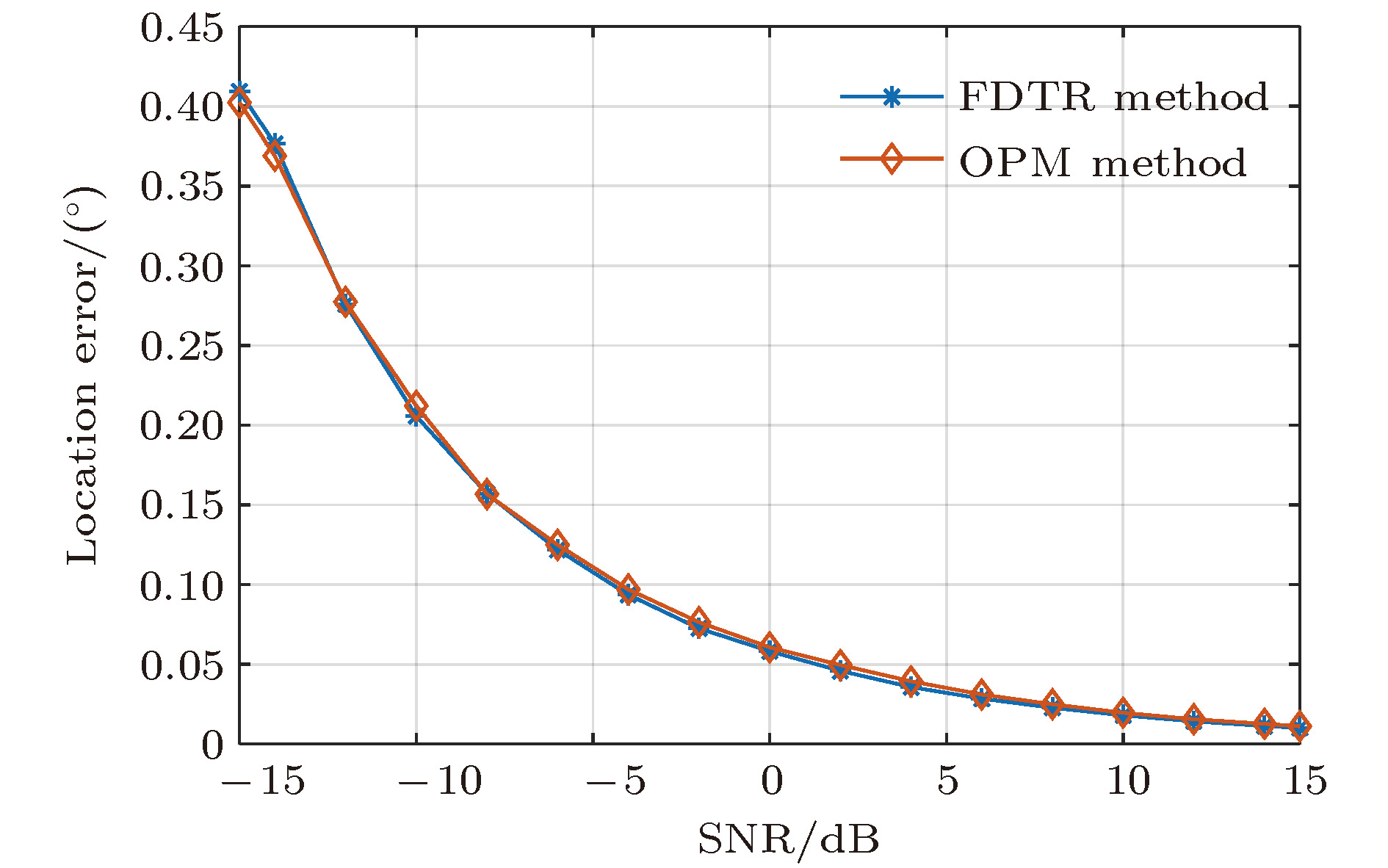
Broadband very-high frequency (VHF) localization of lightning radiation sources provides an important means for understanding lightning discharge characteristics and the corresponding physical mechanisms. In order to improve the ability to locate weak radiation sources, the orthogonal propagator method (OPM) is proposed to map the space-time evolution process of lightning discharge channels based on the theory of spatial spectrum estimation. In the method, the linear decomposition of the covariance matrix is used to form the orthogonal propagator, and the spatial spectrum is constructed according to orthogonality of subspaces. Then, the location of lightning radiation sources is determined by searching for the maximum of the spatial spectrum. For broadband VHF signals, the non-coherent subspace method is used to average the effective frequency points in bandwidth to reduce noise interference. Based on a multiple-antenna radiation continuous observation system (MARCOS), locating performance of the method is analyzed by numerical simulation. The method is verified by parameters such as locating error, half-peak width of the spatial spectrum, and angular resolution. Compared with the results from the time reversal technique(FDTR), the location error and recognition probability under a low signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the proposed OPM algorithm are similar to those of FDTR algorithm, but the angular resolution for two radiation sources of OPM algorithm is better than that of FDTR algorithm. Finally, the proposed method is used to map the spatial and temporal development of a classical triggered lightning discharge channels in the summer of 2017. The results show that the proposed method can clearly depict the basic structure of lightning discharge channels with high spatial and temporal resolution. For the upward positive leader of the triggered lightning, the OPM algorithm can locate more radiation sources with a better structure than the FDTR algorithm. It implies that the proposed OPM algorithm is better for locating weak radiation sources than the FDTR algorithm. Meanwhile, the OPM algorithm has better performance for resolving two radiation sources in the same window than the FDTR algorithm. As a result, the proposed OPM method is of great significance for improving the application value of broadband VHF arrays in the study of locating weak radiation sources and lightning initiation mechanisms.
-
Keywords:
- very high frequency /
- propagator method /
- localization of radiation sources /
- triggered-lightning
[1] Shao X M, Holden D N, Rhodes C T 1996 Geophys. Res. Lett. 23 1917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dong W, Liu X, Yu Y, Zhang Y 2001 Chin. Sci. Bull. 46 1561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shao X M, Blaine W, Dingus B, Smith D, Ho C, Caffrey M, Graham P, Haynes B, Bowers G, Rassoul H 2018 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 123 1
[4] Lyu F, Cummer S A, Qin Z, Chen M 2019 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 124 2994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shao X M, Krehbiel P R, Thomas R J, Rison W 1995 J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 100 2749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shao X M, Krehbiel P R 1996 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 101 26641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ushio T O, Kawasaki Z I, Ohta Y, Matsuura K 1997 Geophys. Res. Lett. 24 2769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 董万胜, 刘欣生, 张义军 2001 科学通报 46 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong W S, Liu X S, Zhang Y J 2001 Chin. Sci. Bull. 46 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 邱实, 杨波, 董万胜, 高太长 2009 气象科学 29 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiu S, Yang B, Dong W S, Gao T C 2009 J. Meteorol. Sci. 29 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sun Z, Qie X, Liu M, Cao D, Wang D 2013 Atmosph. Res. 129-130 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stock M G, Akita M, Krehbiel P R, Rison W, Edens H E, Kawasaki Z, Stanley M A 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 11 9
[12] Kasemir H W 1960 J. Geophys. Res. 65 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mazur V 2002 C. R. Phys. 3 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 苟学强, 张义军, 李亚珺, 陈明理 2018 67 205201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gou X Q, Zhang Y J, Li Y J, Chen M L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 205201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mazur V, Ruhnke L H, Warner T A, Orville R E 2013 J. Electrostat. 71 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang T, Shi Q, Shi L H, Li Y 2017 IEEE Trans. Electromag. Compatibility 59 1949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang T, Shi L, Qiu S, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Duan Y, Liu B 2018 IEEE Access 6 26558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Marcos S, Benidir M 1990 Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing, on IEEE International Conference France, Albuquerque, New Mexico,USA, 3-6 April 1990
[19] Marcos S, Marsal A, Benidir M 1994 Proceedings of ICASSP '94. IEEEInternational Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Adelaide, Australia, 19-22 April,1994.
[20] 王永良, 陈辉, 彭应宁, 万群 2004 空间谱估计理论与算法 (北京: 清华大学出版社)
Wang Y L, Chen H, Peng Y N, Wan Q 2004 Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithms (Beijing: Peking University Press) pp18–30 (in Chinese)
[21] 张小飞, 汪飞, 徐大专 2010 阵列信号处理的理论和应用 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Zhang X F, Wang F, Xu D Z 2010 Theory and Application of Array Signal Processing (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp118–119 (in Chinese)
[22] Ester M, Kriegel H P, Sander J, Xu X Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining Portland, USA, August 02-04,1996 pp226–231
-
表 1 低信噪比条件下两种算法的识别概率的比较
Table 1. Comparison of recognition probabilities of two algorithms under low SNR.
SNR –15 dB –14 dB 宽带OPM定位算法 65.22% 98.76% 宽带FDTR定位算法 65.23% 98.68% 表 2 不同入射角度时两种方法的最小可分辨角度
Table 2. Minimum distinguishable angles of two methods at different incident angles.
入射角度(θ, φ) (30°,30°) (120°,60°) (220°,45°) (320°,80°) 宽带OPM
定位方法3° 3° 12° 3° 宽带FDTR
定位方法5° 13° 16° 8° -
[1] Shao X M, Holden D N, Rhodes C T 1996 Geophys. Res. Lett. 23 1917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dong W, Liu X, Yu Y, Zhang Y 2001 Chin. Sci. Bull. 46 1561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shao X M, Blaine W, Dingus B, Smith D, Ho C, Caffrey M, Graham P, Haynes B, Bowers G, Rassoul H 2018 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 123 1
[4] Lyu F, Cummer S A, Qin Z, Chen M 2019 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 124 2994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shao X M, Krehbiel P R, Thomas R J, Rison W 1995 J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 100 2749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shao X M, Krehbiel P R 1996 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 101 26641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ushio T O, Kawasaki Z I, Ohta Y, Matsuura K 1997 Geophys. Res. Lett. 24 2769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 董万胜, 刘欣生, 张义军 2001 科学通报 46 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong W S, Liu X S, Zhang Y J 2001 Chin. Sci. Bull. 46 427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 邱实, 杨波, 董万胜, 高太长 2009 气象科学 29 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiu S, Yang B, Dong W S, Gao T C 2009 J. Meteorol. Sci. 29 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sun Z, Qie X, Liu M, Cao D, Wang D 2013 Atmosph. Res. 129-130 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stock M G, Akita M, Krehbiel P R, Rison W, Edens H E, Kawasaki Z, Stanley M A 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 11 9
[12] Kasemir H W 1960 J. Geophys. Res. 65 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Mazur V 2002 C. R. Phys. 3 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 苟学强, 张义军, 李亚珺, 陈明理 2018 67 205201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gou X Q, Zhang Y J, Li Y J, Chen M L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 205201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mazur V, Ruhnke L H, Warner T A, Orville R E 2013 J. Electrostat. 71 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang T, Shi Q, Shi L H, Li Y 2017 IEEE Trans. Electromag. Compatibility 59 1949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang T, Shi L, Qiu S, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Duan Y, Liu B 2018 IEEE Access 6 26558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Marcos S, Benidir M 1990 Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing, on IEEE International Conference France, Albuquerque, New Mexico,USA, 3-6 April 1990
[19] Marcos S, Marsal A, Benidir M 1994 Proceedings of ICASSP '94. IEEEInternational Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Adelaide, Australia, 19-22 April,1994.
[20] 王永良, 陈辉, 彭应宁, 万群 2004 空间谱估计理论与算法 (北京: 清华大学出版社)
Wang Y L, Chen H, Peng Y N, Wan Q 2004 Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithms (Beijing: Peking University Press) pp18–30 (in Chinese)
[21] 张小飞, 汪飞, 徐大专 2010 阵列信号处理的理论和应用 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Zhang X F, Wang F, Xu D Z 2010 Theory and Application of Array Signal Processing (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp118–119 (in Chinese)
[22] Ester M, Kriegel H P, Sander J, Xu X Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining Portland, USA, August 02-04,1996 pp226–231
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12945
- PDF Downloads: 70
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: