-
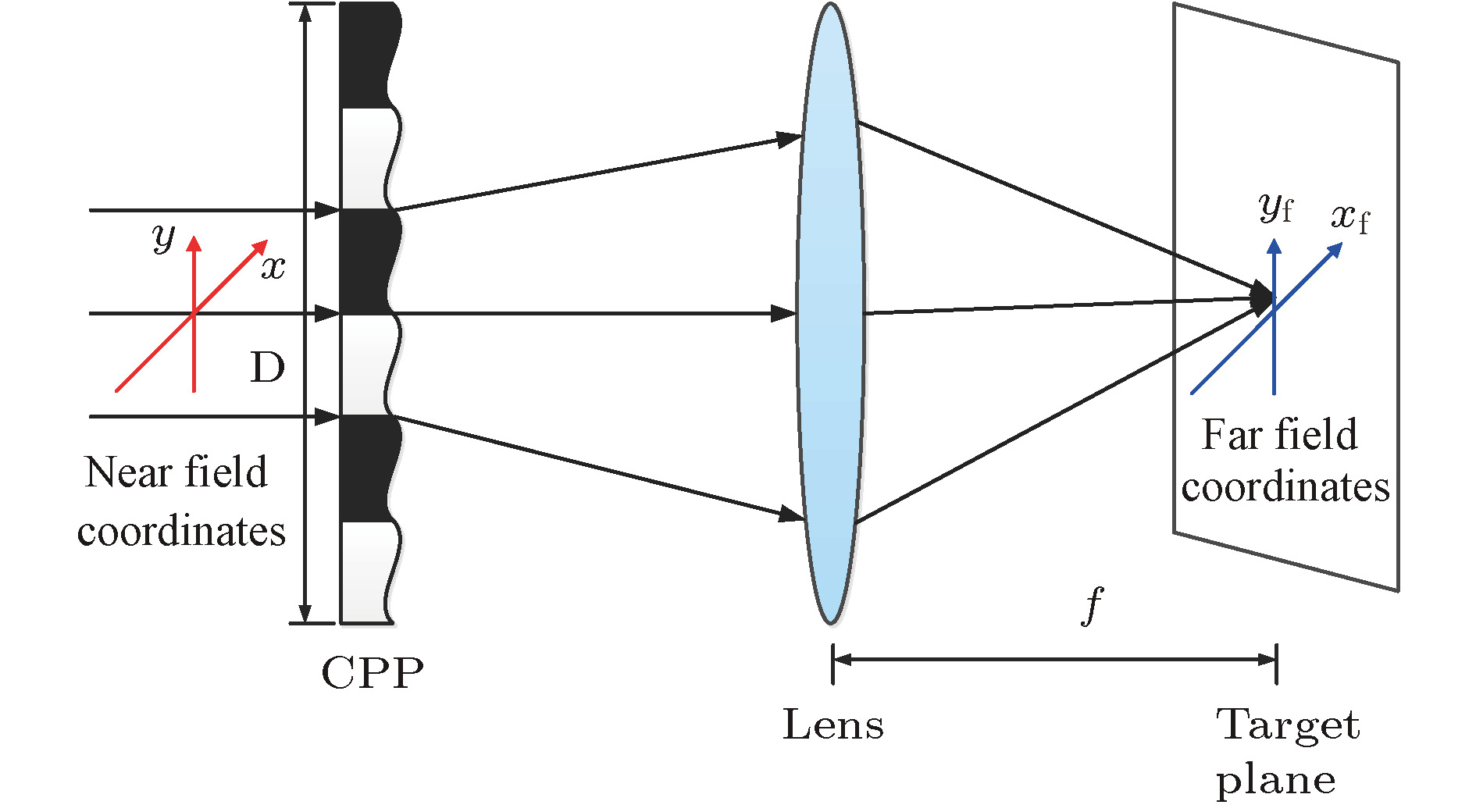
In the laser-driven inertial confinement fusion facilities, the irradiation uniformity of the laser beams on the target is a key factor affecting the effective compression of the target. At present, a variety of beam-smoothing techniques have been developed to control the spatiotemporal characteristics of the focal spots. However, many optical components involved in optical transmission links and complex transmission transformations often lead to complex optical transmission. Moreover, when using the diffraction optical method to analyze the shape and characteristics of the focal spots, a lot of data are needed to be processed and calculated, resulting in large calculation and low computational efficiency. It is urgent to find a new and fast method to describe the statistical properties of the focal spots. In addition, in the beam-smoothing technique, since the phase distribution of the continuous phase plate is obtained by multiple iterations of random numbers, although the details of focal spots obtained by different continuous phase plates are not the same, they all have similar statistical properties. Therefore, the modulation of the laser beam by the continuous phase plate can be regarded as the transmission process of the laser beam through a random surface. Although the intensities of the speckle within the focal spot at different locations have the strong randomness, and the random distributions of the target speckles obtained by different beam-smoothing methods are different, the overall distribution satisfies a certain statistical law. In this paper, the light-field properties of the focal spot are described by the statistical characterization method. The circular complex Gaussian random variables are used to directly describe the statistical properties of the target surface light field, and the far-field focal spots obtained by the diffractive optical method and those by the statistical characterization method are compared with each other and analyzed based on the typical focal spot evaluation parameters. The results show that the instantaneous properties of the focal spots obtained by the diffractive optical method and those obtained by the statistical characterization method are basically identical, but their time-integrated far-field focal spots are different. The correlation coefficient can be further used to describe the time-varying properties of the far-field focal spots. Compared with the diffractive optical method, in the numerical calculation process, the statistical characterization method of light field properties can directly obtain the analytical expression of the statistical distribution of the light field according to the statistical properties of the continuous phase plate surface shape. Secondly, this method can avoid the numerical calculation process from near field to far field. Last but not least, there is no need to perform data processing on each point of the light field, which makes things simple and effective and does not require large-scale data storage and processing.
-
Keywords:
- statistical optics /
- inertial confinement fusion /
- beam smoothing /
- focal spot
[1] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, Glendinning S C, Glenzer S H, Haan S W, Kauffman R L, Landen O L, Suter L J 2004 Phys. Plasmas 11 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Regan S P, Marozas J A, Kelly J H, Boehly T R, Donaldson W R, Jaanimagi P A, Keck R L, Kessler T J, Meyerhofer D D, Seka W, Skupsky S, Smalyuk V A 2000 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17
1483  Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang C L, Yan H, Wang J, Zhang R Z 2013 Opt. Express 21 11171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lin Y, Kessler T J, Lawrence G N 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李平, 王伟, 赵润昌, 耿远超, 贾怀庭, 粟敬钦 2014 63 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P, Wang W, Zhao R C, Geng Y C, Jia H T, Su J Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Garnier J, Videau L, Gouedard C, Migus A 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 14 1928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Garnier J, Videau L 2001 Phys. Plasmas 8 4914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le Cain A, Riazuelo G, Sajer J M 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 082711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Le Cain A, Riazuelo G, Sajer J M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 102704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 林中校, 张蓉竹, 杨春林, 许乔 2010 强激光与粒子束 22 2634
Lin Z X, Zhang R Z, Yang C L, Xu Q 2010 High Power Laser and Partical Beams 22 2634
[11] Marozas J A 2007 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 24 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kline J L, Glenzer S H, Olson R E, Suter L J, Widmann K, Callahan D A, Dixit S N, Thomas C A, Hinkel D E, Williams E A, Moore A S, Celeste J, Dewald, E, Hsing W W, Warrick A, Atherton J, Azevedo S, Beeler R, Berger R, Conder A, Divol L, Haynam C A, Kalantar D H, Kauffman R, Kyrala G A, Kilkenny J, Liebman J, Le Pape S, Larson D, Meezan N B, Michel P, Moody J, Rosen M D, Schneider M B, Van Wonterghem B, Wallace R J, Young B K, Landen O L, MacGowan B J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 085003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张锐 2013 博士学位论文(合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhang R 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[14] Skupsky S, Short R W, Kessler T, Craxton R S, Letzring S, Soures J M 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 66 3456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 钟哲强, 侯鹏程, 张彬 2016 65 094207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 5850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Haynam C A, Wegner P J, Auerbach J M, et al. 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rothenberg J E 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 14 1664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李俊昌 2008 计算物理 25 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J C 2008 Chinese Journal of Computational Physics 25 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 吕晨, 张蓉竹 2014 63 164203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü C, Zhang R Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 164203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 温圣林, 唐才学, 张远航, 颜浩, 侯晶, 罗子健 2015 中国激光 42 0908001
Wen S L, Tang C X, Zhang Y H, Yan H, Hou J, Luo Z J 2015 Chinese Journal of Lasers 42 0908001
[22] 冯友君, 林中校, 张蓉竹 2011 60 104202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y J, Lin Z X, Zhang R Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 104202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 杨春林 2018 67 085201
Yang C L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 085201
[24] Joseph W G 2009 Speckle Phenomena in Optics (Beijing: Science Press) pp62−71
[25] 李腾飞, 侯鹏程, 张彬 2016 光学学报 36 1114002
Li T F, Hou P C, Zhang B 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 1114002
-
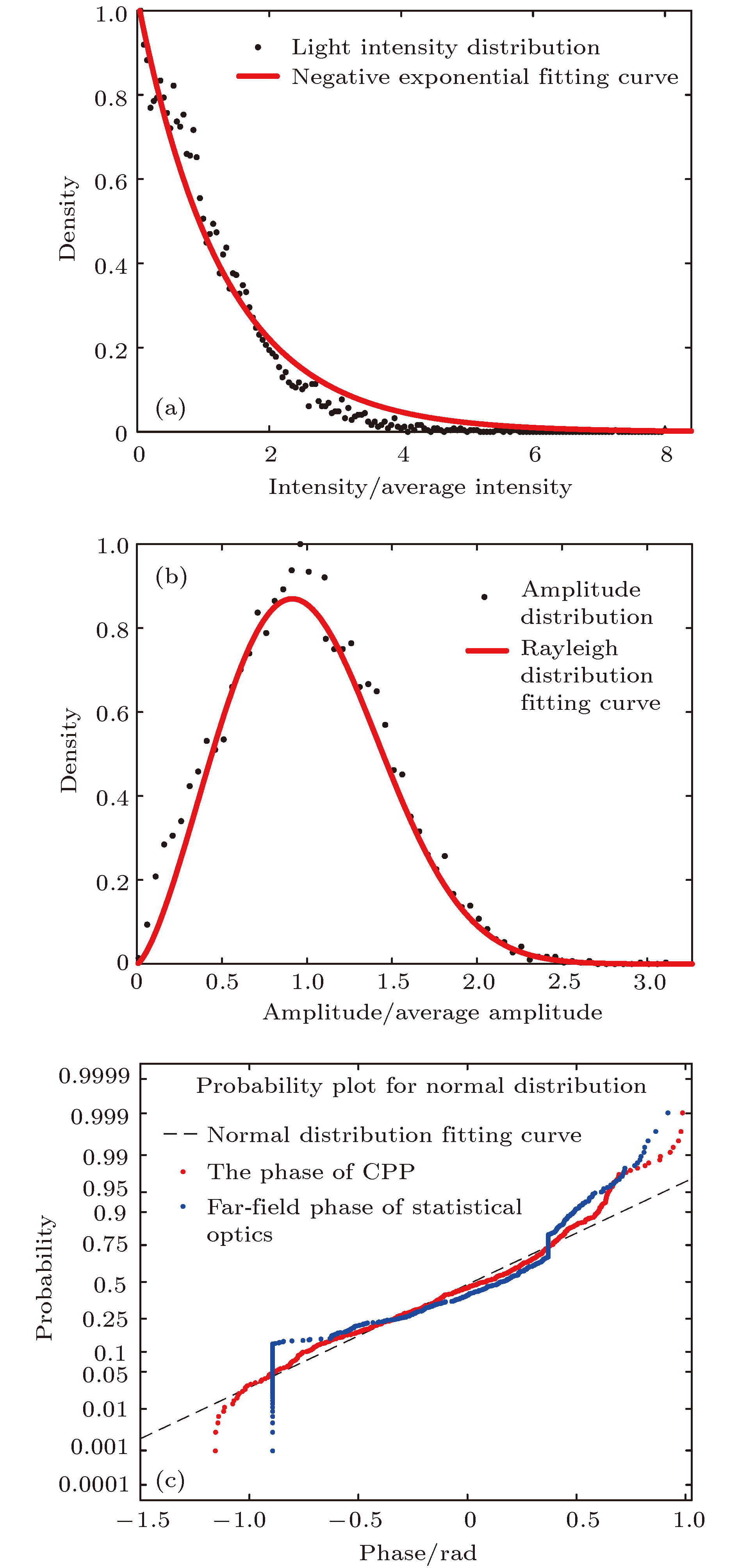
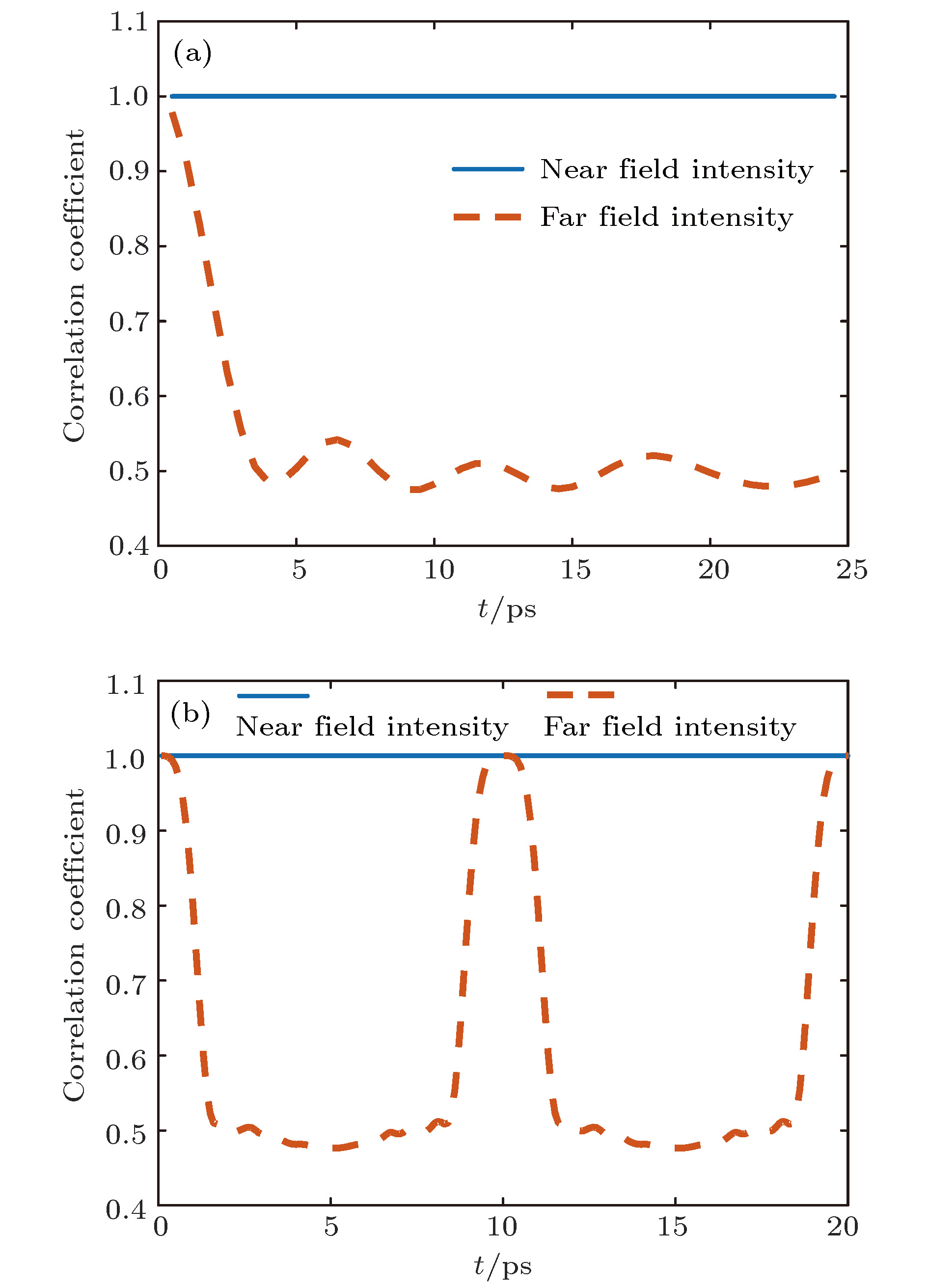
图 4 激光束经过CPP整形后靶面光强和位相统计特征 (a) CPP整形后的靶面光强分布; (b) CPP整形后的靶面振幅分布; (c) CPP位相与远场位相统计分布
Figure 4. The statistical characteristics of the laser beam's intensity and phase of the target plane after CPP's shaping: (a) Intensity distribution of the target plane after CPP's reshaping; (b) amplitude distribution of the target plane after CPP's shaping; (c) statistical distribution of CPP's phase and far field phase.
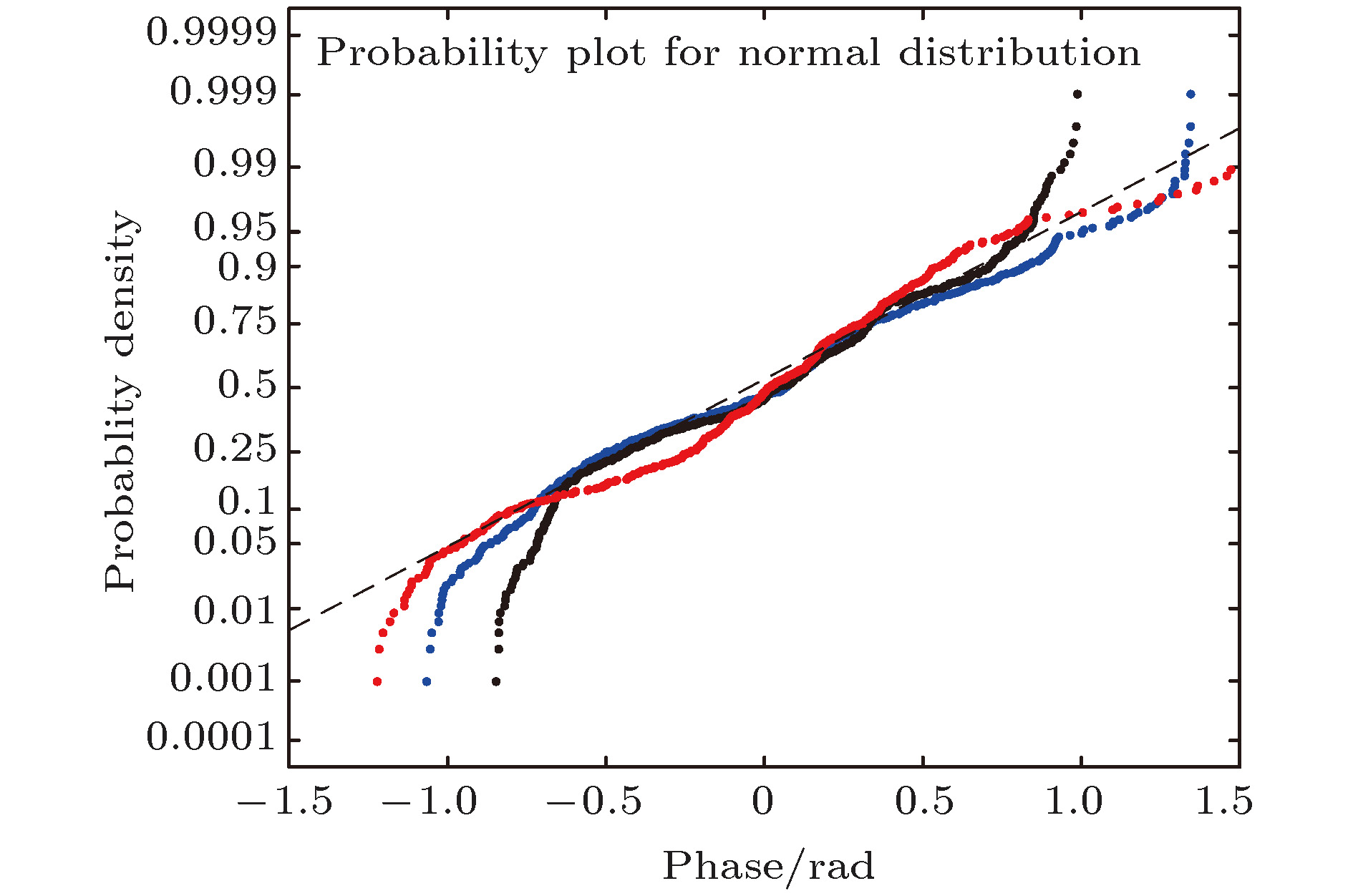
图 5 数值求解与的瞬时远场光强特性比较 (a)瞬时焦斑光强FOPAI对比; (b)数值求解远场位相与解析求解远场位相统计特性
Figure 5. Comparison of characteristics of instantaneous far-field intensity solved by numerical analysis and that Solved by analytical solution: (a) FOPAI's comparison instantaneous focal spot intensity; (b) statistical characteristics of numerical solution far-field phase and analytical solution far-field phase.
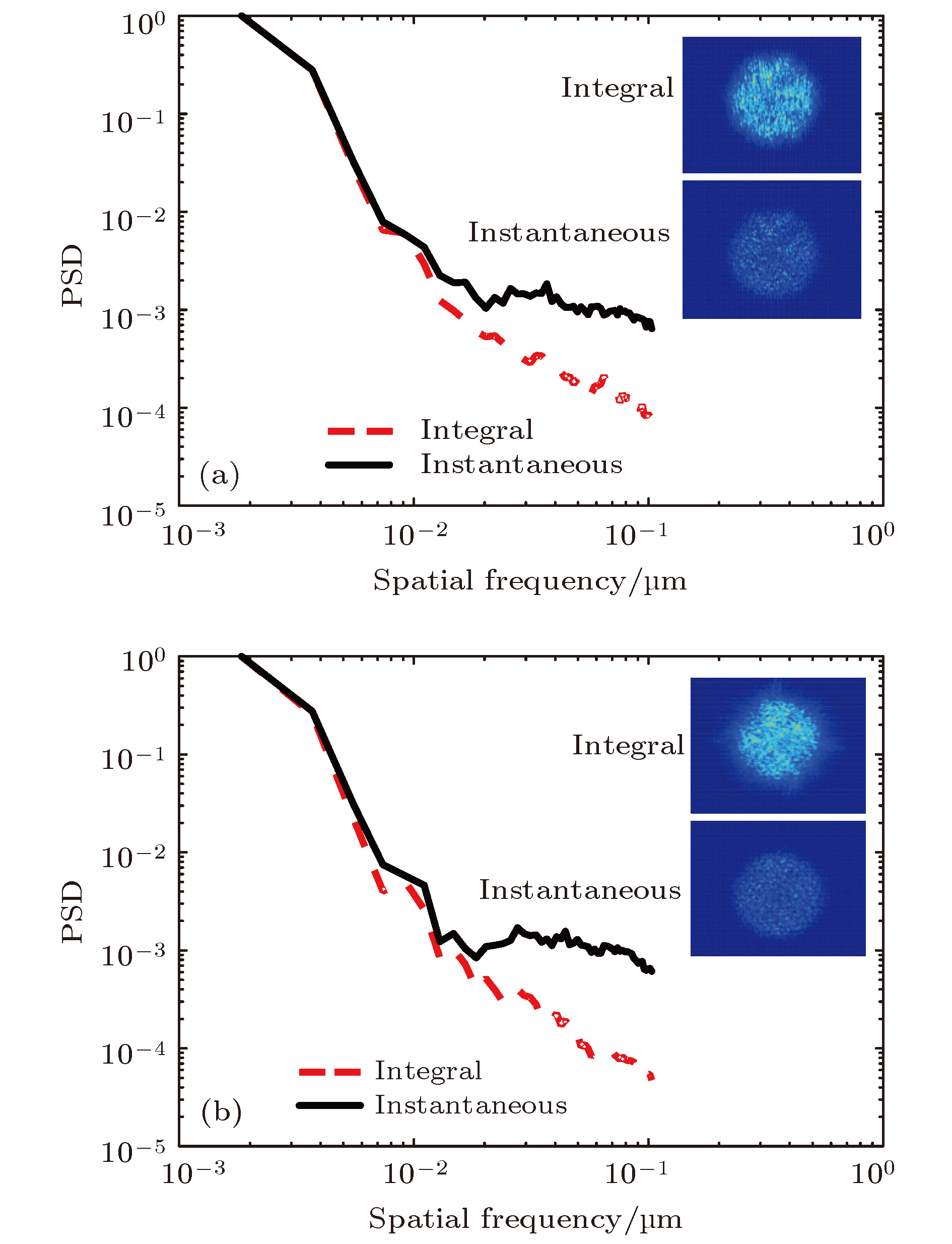
图 6 不同束匀滑方案下瞬时与积分焦斑的统计特性 (a) 1D-SSD+CPP瞬时、积分焦斑及其PSD; (b) RS+CPP瞬时、积分焦斑及其PSD
Figure 6. Statistical characteristics of instantaneous and integral focal spots obtained by different beam smoothing schemes: (a) Instantaneous, integral focal spots and their PSD of 1D-SSD+CPP; (b) instantaneous, integral focal spots and their PSD of RS+CPP.
表 1 瞬时与积分焦斑的PSD积分与光通量对比度的统计关系
Table 1. Statistical relationship between PSD integral and luminous flux contrast of instantaneous and integral focal spots.
Statistics PSD integral square value
of instantaneousInstantaneous luminous
flux contrastPSD integral square value
of time integralIntegrated luminous
flux contrastCPP 1.069 1.094 — — Statistical optical 0.979 0.987 — — SSD+CPP 1.079 1.093 1.067 0.514 RS+CPP 1.077 1.090 1.056 0.478 -
[1] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, Glendinning S C, Glenzer S H, Haan S W, Kauffman R L, Landen O L, Suter L J 2004 Phys. Plasmas 11 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Regan S P, Marozas J A, Kelly J H, Boehly T R, Donaldson W R, Jaanimagi P A, Keck R L, Kessler T J, Meyerhofer D D, Seka W, Skupsky S, Smalyuk V A 2000 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17
1483  Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang C L, Yan H, Wang J, Zhang R Z 2013 Opt. Express 21 11171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lin Y, Kessler T J, Lawrence G N 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李平, 王伟, 赵润昌, 耿远超, 贾怀庭, 粟敬钦 2014 63 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li P, Wang W, Zhao R C, Geng Y C, Jia H T, Su J Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Garnier J, Videau L, Gouedard C, Migus A 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 14 1928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Garnier J, Videau L 2001 Phys. Plasmas 8 4914
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le Cain A, Riazuelo G, Sajer J M 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 082711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Le Cain A, Riazuelo G, Sajer J M 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 102704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 林中校, 张蓉竹, 杨春林, 许乔 2010 强激光与粒子束 22 2634
Lin Z X, Zhang R Z, Yang C L, Xu Q 2010 High Power Laser and Partical Beams 22 2634
[11] Marozas J A 2007 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 24 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kline J L, Glenzer S H, Olson R E, Suter L J, Widmann K, Callahan D A, Dixit S N, Thomas C A, Hinkel D E, Williams E A, Moore A S, Celeste J, Dewald, E, Hsing W W, Warrick A, Atherton J, Azevedo S, Beeler R, Berger R, Conder A, Divol L, Haynam C A, Kalantar D H, Kauffman R, Kyrala G A, Kilkenny J, Liebman J, Le Pape S, Larson D, Meezan N B, Michel P, Moody J, Rosen M D, Schneider M B, Van Wonterghem B, Wallace R J, Young B K, Landen O L, MacGowan B J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 085003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张锐 2013 博士学位论文(合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhang R 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[14] Skupsky S, Short R W, Kessler T, Craxton R S, Letzring S, Soures J M 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 66 3456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 钟哲强, 侯鹏程, 张彬 2016 65 094207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 5850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Haynam C A, Wegner P J, Auerbach J M, et al. 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rothenberg J E 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 14 1664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李俊昌 2008 计算物理 25 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J C 2008 Chinese Journal of Computational Physics 25 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 吕晨, 张蓉竹 2014 63 164203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü C, Zhang R Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 164203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 温圣林, 唐才学, 张远航, 颜浩, 侯晶, 罗子健 2015 中国激光 42 0908001
Wen S L, Tang C X, Zhang Y H, Yan H, Hou J, Luo Z J 2015 Chinese Journal of Lasers 42 0908001
[22] 冯友君, 林中校, 张蓉竹 2011 60 104202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y J, Lin Z X, Zhang R Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 104202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 杨春林 2018 67 085201
Yang C L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 085201
[24] Joseph W G 2009 Speckle Phenomena in Optics (Beijing: Science Press) pp62−71
[25] 李腾飞, 侯鹏程, 张彬 2016 光学学报 36 1114002
Li T F, Hou P C, Zhang B 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 1114002
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12343
- PDF Downloads: 67
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: