-
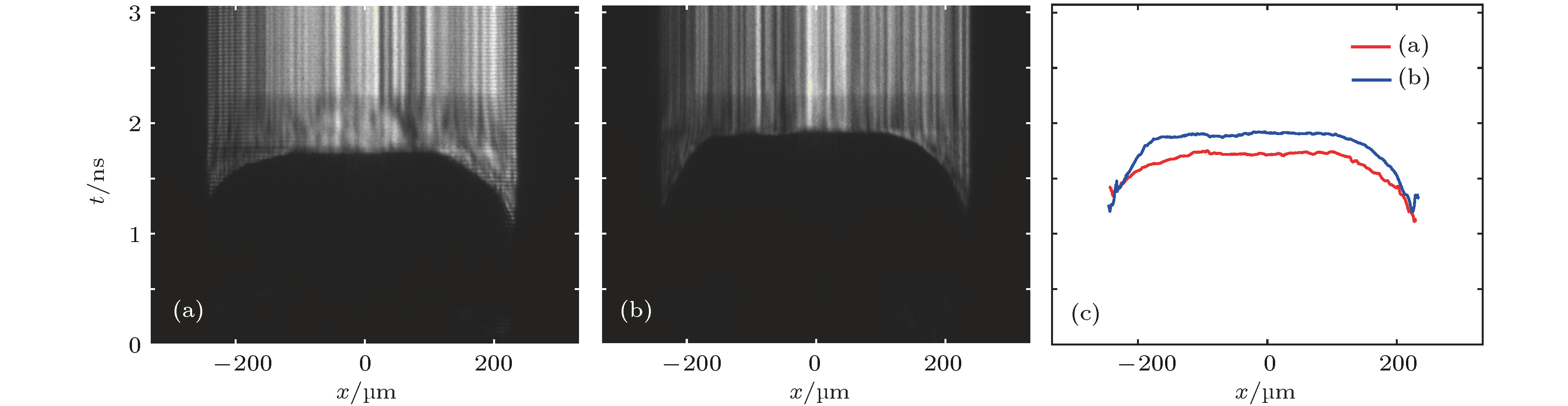
The experimental study of laser-driven material state equation puts forward extremely high requirements for the uniformity and stability of the target spot intensity distribution, and these two characteristics greatly determine the accuracy and repeatability of the experimental results. In this paper, a beam smoothing scheme combining diffraction-weakened lens array (LA) with induced spatial incoherent (ISI) technique based on low-coherence laser is proposed to solve the problems, that is, the uniformity and stability of the target spot intensity distribution in the material state equation experiments driven with narrow-band coherent laser. The super-Gaussian soft aperture used in our scheme can improve the intensity fluctuation caused by the hard-edge diffraction of the lens elements, and the temporal smoothing technique, ISI, can reduce the interference effect between the lens array elements. The speckle patterns of target spot, which are caused by interference between beamlets and determine the high nonuniformity, will randomly reconstruct after each coherent time. The high-frequency components are further smoothed by the time-average effect. In broadband high-power laser devices, ISI can be combined with LA by making the lens elements with different thickness values. This scheme can enhance the focal spot uniformity and improve the tolerance of the system to the wavefront phase distortion. The influence of wavefront phase distortion on target surface uniformity and stability are analyzed. The simulation results show that this smoothing scheme significantly reduces the target spot nonuniformity, improves the tolerance of random wavefront phase distortion, and presents a uniform and stable target spot intensity distribution. The nonuniformity of target spot will be reduced to about 10% after 10 ps, and about 3% after 100 ps. In addition, statistical analysis shows that the peak-to-valley value and the nonuniformity of the target spot intensity distribution are strongly correlated with the gradient of root-mean-square of the wavefront phase distortion. Using this method, the tolerance range of the wavefront phase distortion can be given according to the requirements of the experiments, which has reference value for designing and optimizing the laser driver parameters in the state equation experiment.
-
Keywords:
- beam smoothing /
- high-power laser driver /
- lens array /
- introduced
[1] Lin Y, Kessler T, Lawrence G 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kato Y, Mima K, Miyanaga N, Arinaga S, Kitagawa Y, Nakatsuka M, Yamanaka C 1984 Phys. Rev. Lett. 53 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Deng X M, Liang X C, Chen Z Z, Yu W Y, Ma R Y 1986 Appl. Opt. 25 3377
[4] 江秀娟, 李菁辉, 朱俭, 林尊琪 2015 64 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X J, Li J H, Zhu J, Lin Z Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 周冰洁, 钟哲强, 张彬 2012 61 214002
Zhou B J, Zhong Z Q, Zhang B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 214002
[6] Skupsky S, Short R, Kessler T, Craxton R, Letzring S, Soures J 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 66 3456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Skupsky S, Craxton R, Skupsky S, Craxton R S 1999 Phys. Plasmas 6 2157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Miyaji G, Miyanaga N, Urushihara S, Suzuki K, Matsuoka S, Nakatsuka M 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Obenschain S, Grun J, Herbst M, Kearney K, Manka C, McLean E, Mostovych A, Stamper A, Whitlock R, Bodner S, Gardner J, Lehmberg R 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 56 2807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Obenschain S, BodnerS, Colombant D, Gerber K, Lehmberg R, McLean E, Mostovych A, Pronko M, Pawley C, Schmitt A, Sethian J, Serlin V, Stamper J, Sullivan C 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 5
[11] Rothenberg J 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 3654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y C, Wang F, Zhang Y, Huang X X, Hu D X, Zheng W G, Zhu R H, Deng X W 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 5850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weng X F, Li T F, Zhong Z Q, Zhang B 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haynam C, Wegner P, Auerbach J, Bowers M, Dixit S, Erbert G, Heestand G, Henesian M, Hermann M, Jancaitis K, Manes K, Marshall C, Mehta N, Menapace J, Moses E, Murray J, Nostrand M, Orth C, Patterson R, Sacks R, Shaw M, Spaeth M, Sutton S, Williams W, Widmayer C, White R, Yang S, Wonterghem B 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang X J, Li J H, Li H G, Li Y, Lin Z Q 2011 Appl. Opt. 50 5213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 江秀娟, 李菁辉, 李华刚, 周申蕾, 李扬, 林尊琪 2012 61 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X J, Li J H, Li H G, Zhou S L, Li Y, Lin Z Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou S L, Lin Z Q, Jiang X J 2007 Opt. Commun. 272 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 陈泽尊, 向春, 邓锡铭 1985 中国激光 13 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Z Z, Xiang C, Deng X M 1985 Chin. J. Las. 13 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Regan S, Marozas J, Kelly J, Boehly T, Donaldson W, Jaanimagi P, Keck R, Kessler T, Meyerhofer D, Seka W 2000 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17 1483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
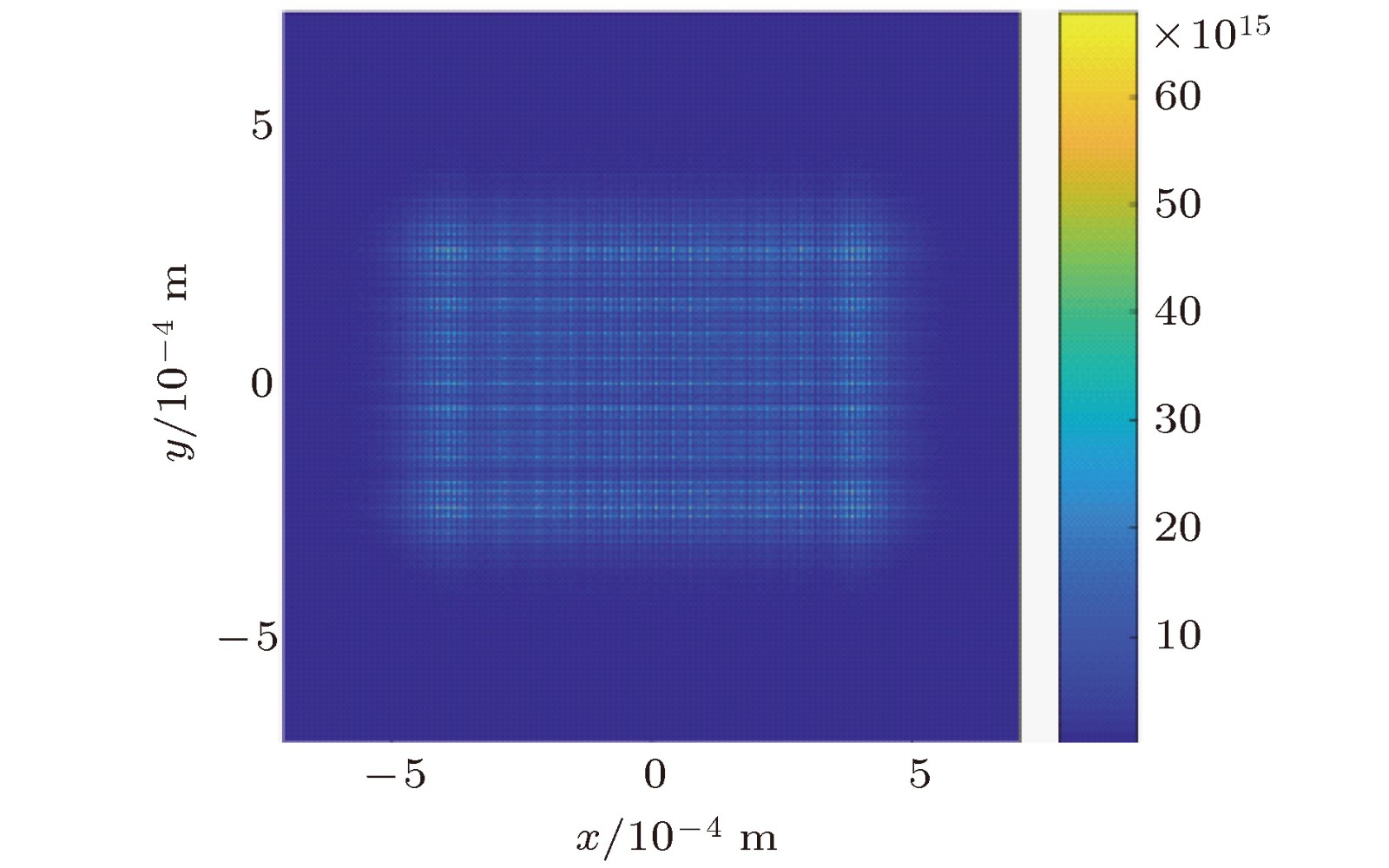
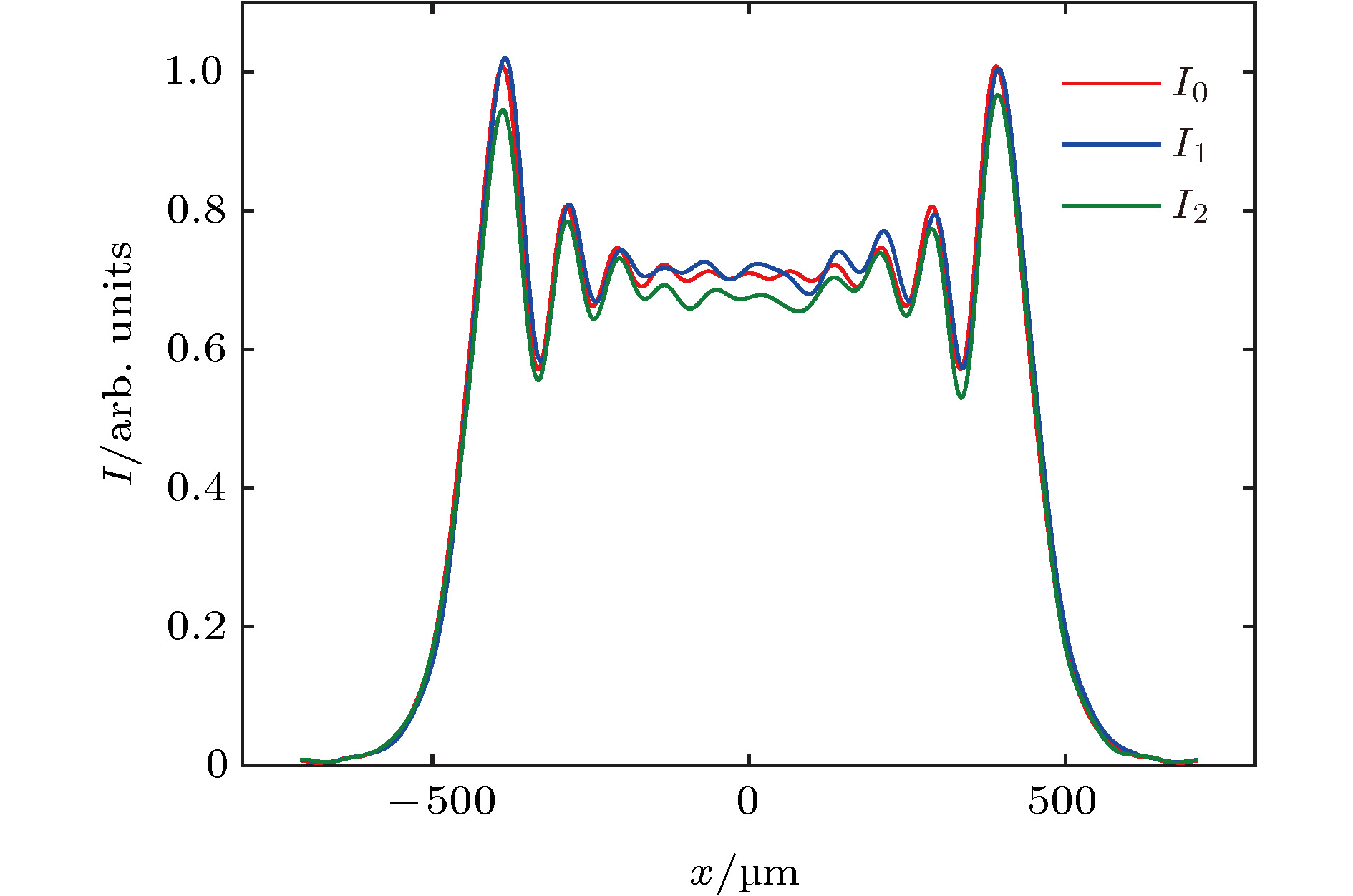
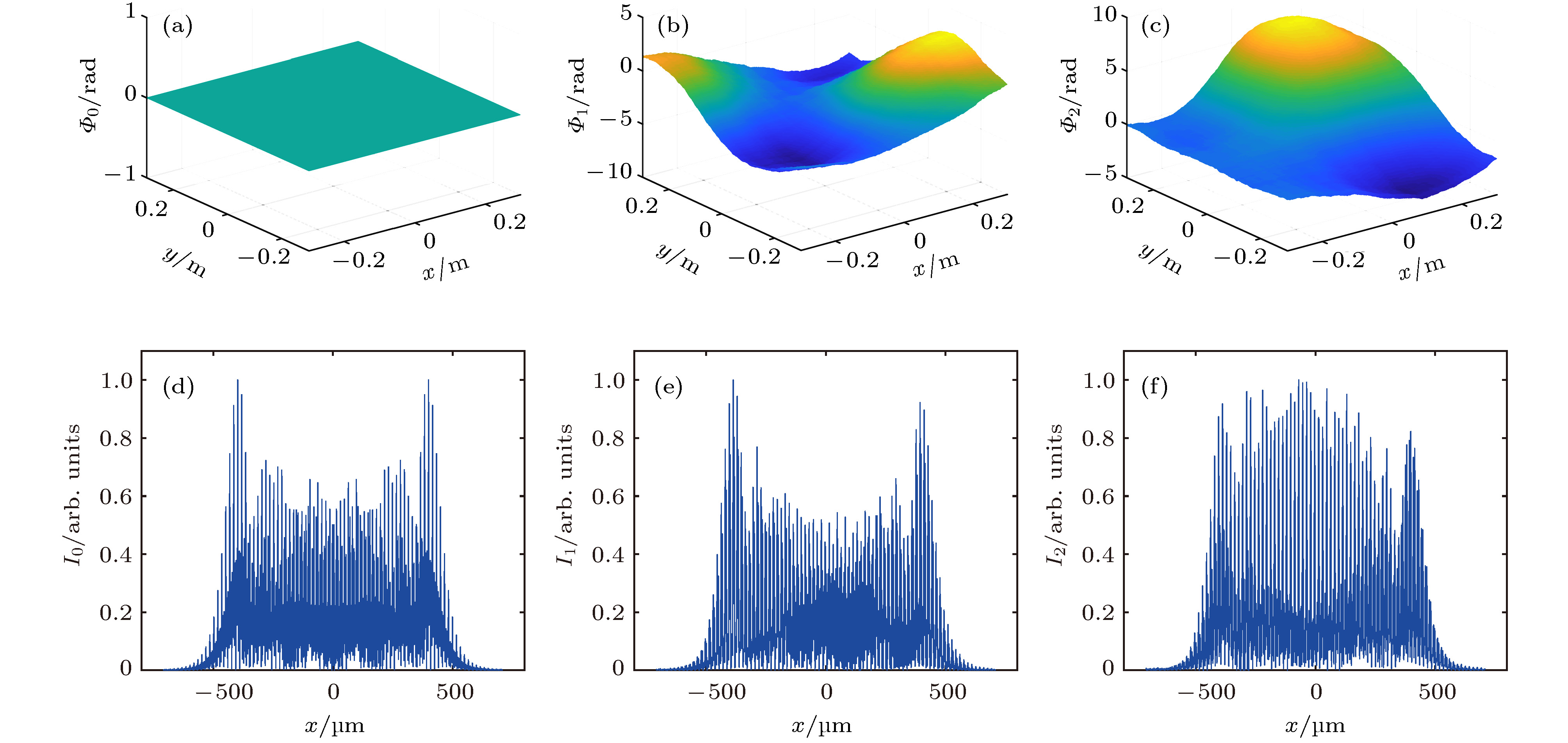
图 4 波前畸变造成的焦斑分布不均匀性及差异性 上排为波前相位理想分布及波前畸变, 下排为对应的焦斑强度分布
Figure 4. The nonuniformity and difference of the focal spot distributions caused by wavefront distortion. The upper row is the ideal distribution of the wavefront phase and the wavefront distortion, and the lower row is the focal spot intensity distribution, respectively.
表 1 不同波前相位畸变, 焦斑不均匀度随匀滑时间的变化
Table 1. The nonuniformity of target at different smoothing time with different wavefront distortion.
T($\tau $) 1 10 100 1000 Inf $ \sigma ({\phi _0})$ 0.9716 0.3423 0.0956 0.0303 0.0060 $ \sigma ({\phi _1})$ 1.0267 0.3209 0.1012 0.0332 0.0118 $ \sigma ({\phi _2})$ 0.9374 0.3042 0.0989 0.0345 0.0158 -
[1] Lin Y, Kessler T, Lawrence G 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 1703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kato Y, Mima K, Miyanaga N, Arinaga S, Kitagawa Y, Nakatsuka M, Yamanaka C 1984 Phys. Rev. Lett. 53 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Deng X M, Liang X C, Chen Z Z, Yu W Y, Ma R Y 1986 Appl. Opt. 25 3377
[4] 江秀娟, 李菁辉, 朱俭, 林尊琪 2015 64 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X J, Li J H, Zhu J, Lin Z Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 周冰洁, 钟哲强, 张彬 2012 61 214002
Zhou B J, Zhong Z Q, Zhang B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 214002
[6] Skupsky S, Short R, Kessler T, Craxton R, Letzring S, Soures J 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 66 3456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Skupsky S, Craxton R, Skupsky S, Craxton R S 1999 Phys. Plasmas 6 2157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Miyaji G, Miyanaga N, Urushihara S, Suzuki K, Matsuoka S, Nakatsuka M 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Obenschain S, Grun J, Herbst M, Kearney K, Manka C, McLean E, Mostovych A, Stamper A, Whitlock R, Bodner S, Gardner J, Lehmberg R 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 56 2807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Obenschain S, BodnerS, Colombant D, Gerber K, Lehmberg R, McLean E, Mostovych A, Pronko M, Pawley C, Schmitt A, Sethian J, Serlin V, Stamper J, Sullivan C 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 5
[11] Rothenberg J 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 3654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y C, Wang F, Zhang Y, Huang X X, Hu D X, Zheng W G, Zhu R H, Deng X W 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhong Z Q, Hou P C, Zhang B 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 5850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weng X F, Li T F, Zhong Z Q, Zhang B 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haynam C, Wegner P, Auerbach J, Bowers M, Dixit S, Erbert G, Heestand G, Henesian M, Hermann M, Jancaitis K, Manes K, Marshall C, Mehta N, Menapace J, Moses E, Murray J, Nostrand M, Orth C, Patterson R, Sacks R, Shaw M, Spaeth M, Sutton S, Williams W, Widmayer C, White R, Yang S, Wonterghem B 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang X J, Li J H, Li H G, Li Y, Lin Z Q 2011 Appl. Opt. 50 5213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 江秀娟, 李菁辉, 李华刚, 周申蕾, 李扬, 林尊琪 2012 61 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang X J, Li J H, Li H G, Zhou S L, Li Y, Lin Z Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 124202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou S L, Lin Z Q, Jiang X J 2007 Opt. Commun. 272 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 陈泽尊, 向春, 邓锡铭 1985 中国激光 13 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Z Z, Xiang C, Deng X M 1985 Chin. J. Las. 13 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Regan S, Marozas J, Kelly J, Boehly T, Donaldson W, Jaanimagi P, Keck R, Kessler T, Meyerhofer D, Seka W 2000 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17 1483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14768
- PDF Downloads: 105
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: