-
高能粒子在等离子体中的能量沉积及其导致的电子离子能量分配对理解惯性约束聚变的点火和燃烧过程至关重要. 基于量子动理学的T矩阵扩展模型, 本文研究了宽广温度密度区间的能量沉积和电子能量分配因子. 相较于基于小角度散射的阻止本领模型, T矩阵扩展模型能考虑由大角度库仑散射及其累积过程带来的横向偏转效应. 首先研究了横向偏转效应对电子能量分配因子的影响, 然后计算了宽温度密度区间的电子能量分配因子, 基于这些数据的分析发展了适用于惯性约束聚变模拟的电子能量分配因子拟合表达式. 研究发现, 考虑横向偏转效应会给电子能量分配因子带来约27.5%的差异. 这一结论表明, 准确描述高能粒子能量沉积过程中的大角度库仑散射及其累积效应带来的横向偏转会影响惯性约束聚变点火和燃烧模拟的精确性.Energy deposition of high-energy ions and the resulting electron-ion energy partition in dense plasmas are of essential importance in understanding the hot-spot ignition and burning of inertial confinement fusion. In this work, the energy deposition and electron-ion energy partition of high-energy ions are studied in a wide range of temperatures and densities based on the improved T-matrix model. Compared with the stopping power model based on the assumption of small-angle scattering, the improved T-matrix model can consistently take into account the large-angle Coulomb scattering and the resulting transversal deflection of the high-energy ions. We investigate the influence of the effect of transversal deflection on the electron-ion energy partition and propose a fitting formula for the energy partition fraction to plasma electrons. This formula is applicable to inertial confinement fusion simulations. It is found that when the effect of transversal deflection is considered, the relative energy deposited into electrons in plasma is reduced by about 27.5% at most. This conclusion suggests that the transversal deflection of energetic ions, induced by the large-angle Coulomb scattering and its cumulative effect, ought to be considered in accurately simulating the hot-spot ignition and burning of the fuel in inertial confinement fusion.
-
Keywords:
- energy deposition /
- electron-ion energy partition /
- nonideal plasmas /
- inertial confinement fusion
[1] 江少恩, 丁永坤, 缪文勇, 刘慎业, 郑志坚, 张保汉, 张继彦, 黄天晅, 李三伟, 陈家斌, 蒋小华, 易荣清, 杨国洪, 杨家敏, 胡昕, 曹柱荣, 黄翼翔 2009 中国科学G辑: 物理学 力学 天文学 39 1571
Jiang S E, Ding Y K, Miu W Y, Liu S Y, Zheng Z J, Zhang B H, Zhang J Y, Huang T X, Li S W, Chen J B, Jiang X H, Yi R Q, Yang G H, Yang J M, Hu X, Cao Z R, Huang Y X 2009 Sci. Chin. Phys., Mech. Astron. 39 1571
[2] Hurricane O A, Patel P K, Betti R, Froula D H, Regan S P, Slutz S A, Gomez M R, Sweeney M A 2023 Rev. Mod. Phys. 95 025005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 朱少平, 罗民兴 2024 物理 53 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu S P, Luo M X 2024 Physics 53 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Atzeni S, Meyer-ter Vehn J 2004 The Physics of Inertial Fusion: Beam Plasma Interaction, Hydrodynamics, Hot Dense Matter (Vol. 125) (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[5] Betti R, Christopherson A, Spears B, Nora R, Bose A, Howard J, Woo K, Edwards M, Sanz J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 255003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Stanton L G, Murillo M S 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 082301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Wang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 076018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Eliezer S, Martínez-Val J M 1998 Laser Part. Beams 16 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Son S, Fisch N 2006 Phys. Lett. A 356 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Brown L S, Preston D L, Singleton Jr R L 2005 Phys. Rep. 410 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fraley G S, Linnebur E J, Mason R J, Morse R L 1974 Phys. Fluids 17 474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zylstra A, Hurricane O 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Butler S, Buckingham M 1962 Phys. Rev. 126 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li C K, Petrasso R D 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown L S, Preston D L, Singleton Jr R L 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 016406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] He B, Wang Z G, Wang J G 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 012704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang Y N, Wang Z G, Zhao Y T, He B 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zylstra A B, Rinderknecht H G, Frenje J A, Li C K, Petrasso R D 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 122703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bernstein D J, Baalrud S D, Daligault J 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 082705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Landau L, Lifshitz E 1977 Quantum Mechanics: Non-Relativistic Theory, Chapter XVII (Oxford: Pergamon Press
[21] Joachain C J 1975 Quantum Collision Theory, Chapter 4 (North-Holland Publishing Company
[22] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Wang J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 055005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zwicknagel G, Toepffer C, Reinhard P G 1999 Phys. Rep. 309 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bernstein D J, Baalrud S D 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 072705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Zou S, Wang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 106005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Long K, Tahir N 1986 Nucl. fusion 26 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gus’Kov S Y, Il’In D, Sherman V 2013 EPJ Web of Conferences 59 02018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
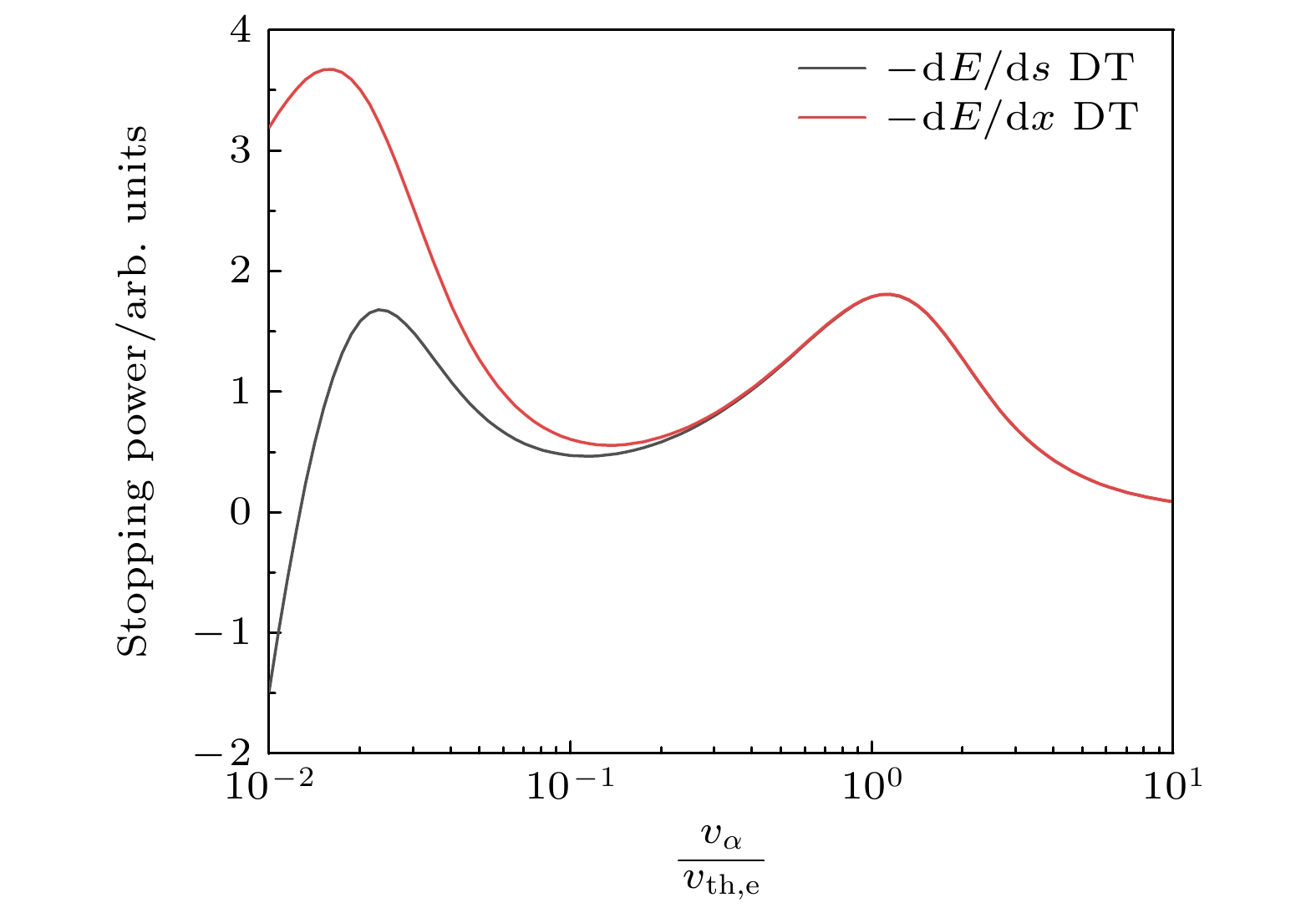
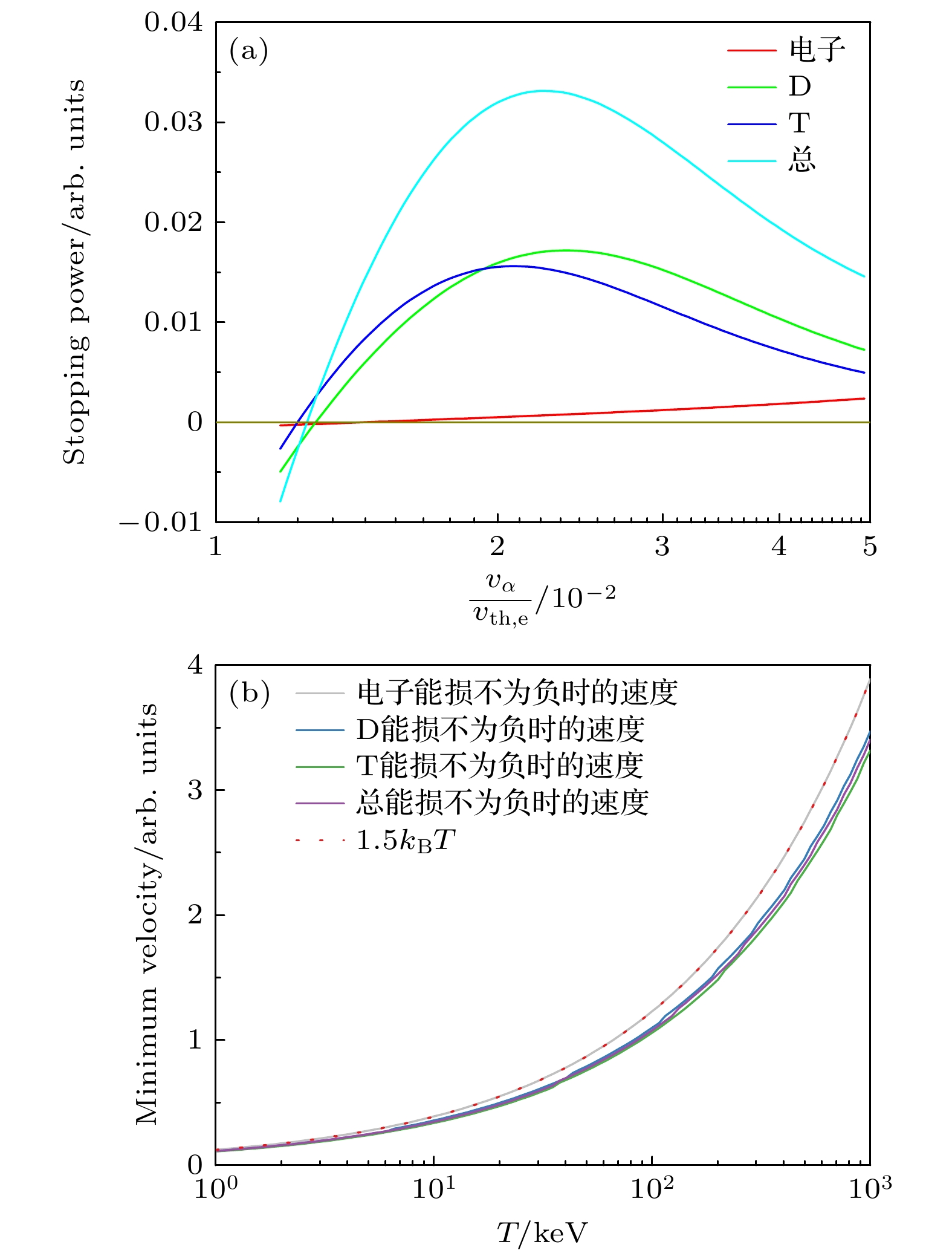
图 1 (a)温度为$ 200 \; \mathrm{keV} $和电子密度为$ 10^{25} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $的DT等离子体中, 不同类型的等离子体粒子对能量为$ E_0 = $$ 3.54 \; \mathrm{MeV} $的α粒子CSD阻止本领的贡献; (b)电子密度为$ 10^{25} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $的DT等离子体中, 不同阻止本领为0时α粒子的速度, 红色虚线对应能量为$ E_\mathrm{min} = 3 k_\mathrm{B} T / 2 $时α粒子的速度
Fig. 1. (a) Partial and total CSD stopping power of α particle with $ E_0 = 3.54 \; \mathrm{MeV} $ in a DT plasma with $ T = $$ 200 \; \mathrm{keV} $ and $ n_\mathrm{e} = 10^{25} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $; (b) the characteristic velocity of α particle for the case of partial and total stopping power equal to 0 in DT plasmas with $ n_\mathrm{e} = $$ 10^{25} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $. The red dash line represents the velocity of α particle when $ E_\alpha = E_\mathrm{min} = 3 k_\mathrm{B} T / 2 $.
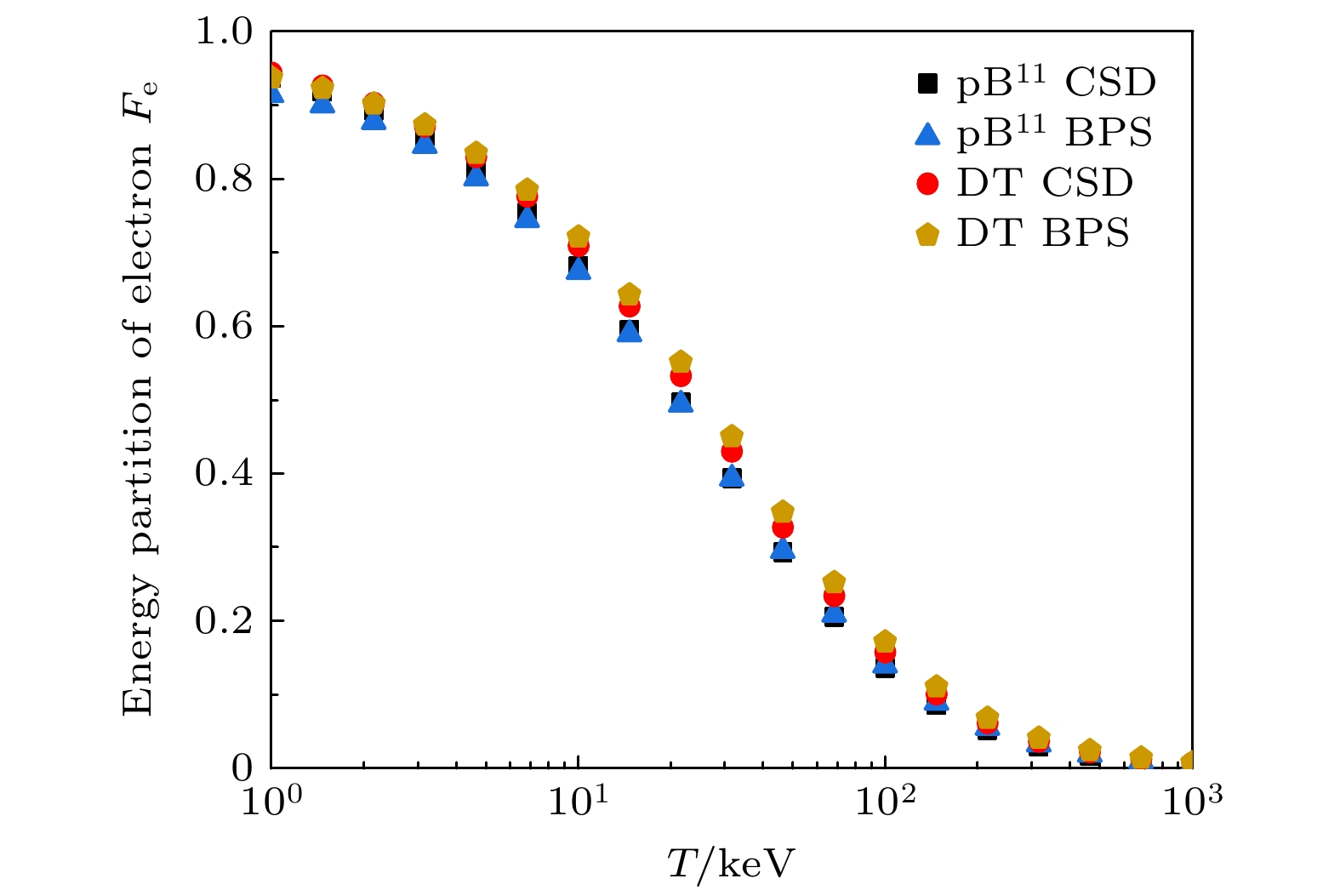
图 2 电子密度为$ 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $的DT与$ \mathrm{p}^{11}\mathrm{B} $等离子体中的电子能量分配因子. 方形和三角形符号分别对应$ \mathrm{p}^{11}\mathrm{B} $等离子体中CSD和BPS模型计算的结果, 而圆形和五边形分别对应DT等离子体中CSD和BPS模型计算的结果
Fig. 2. Energy partition of electrons in DT and $ \mathrm{p}^{11}\mathrm{B} $ plasmas at a fixed electron density $ 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $. The square and triangle symbols displays the predictions from CSD and BPS stopping power for $ \mathrm{p}^{11}\mathrm{B} $ plasmas, while the circles and pentagons correspond to CSD and BPS results for DT plasmas.
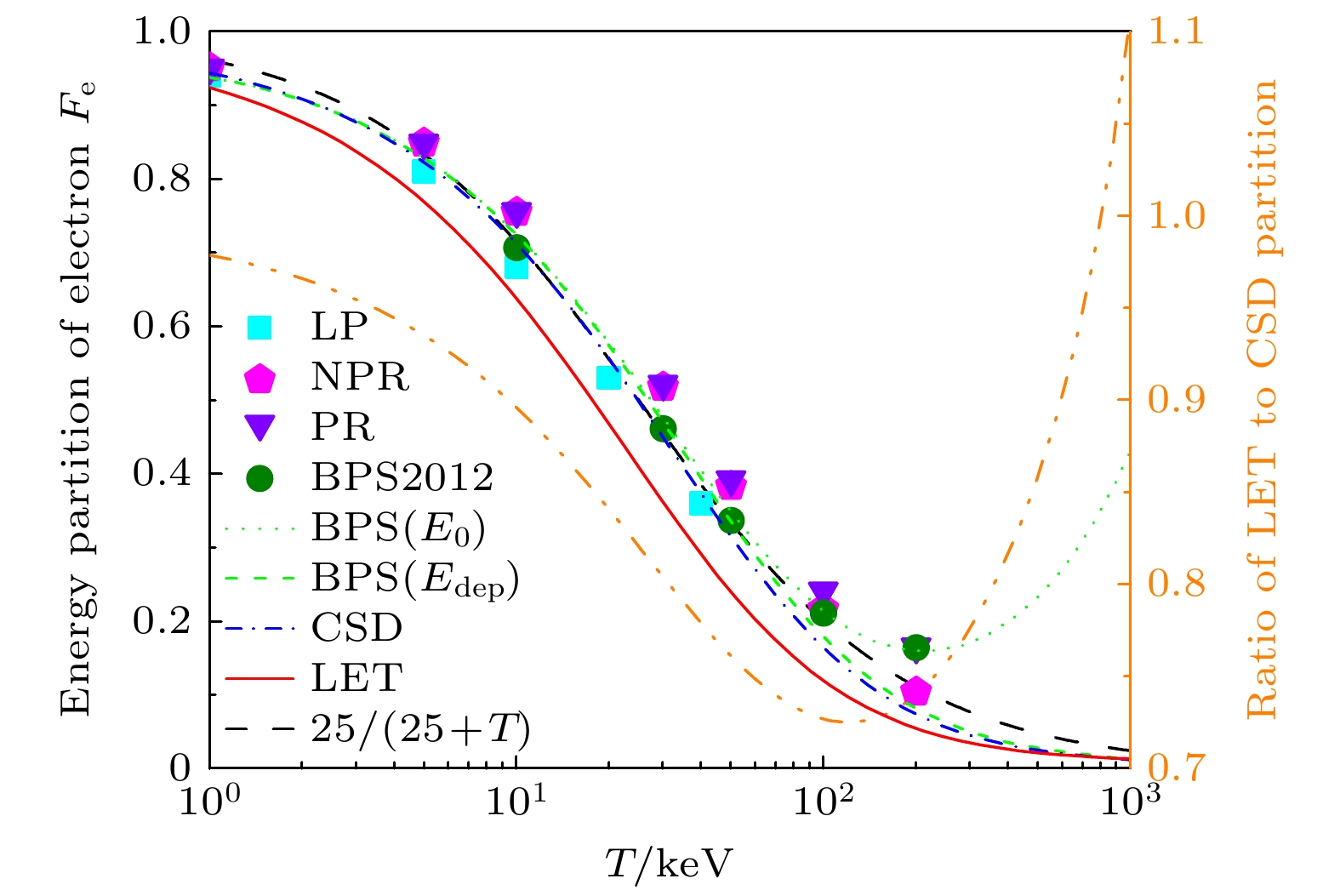
图 4 左轴: 电子密度为$ 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $的DT等离子体中, 电子能量分配因子$ F_\mathrm{e} $随温度的变化. 方形和圆形分别对应Li-Petrasso模型[14]和BPS模型[10]的结果, 而五角星和三角符号表示不考虑和考虑入射粒子反冲效应的结果[16]. BPS$ (E_0) $和BPS$ (E_\mathrm{dep}) $分别表示$ E_\mathrm{min} = 0, \; 3 k_\mathrm{B} T / 2 $对应的结果. CSD (蓝色点虚线)和LET (红色实线)之间的差异表征偏转效应的贡献. 黑色虚线对应方程(2)中取$ T_0 = 25 $的结果. 右轴: LET和CSD阻止本领对应的电子能量分配因子之间的比值
Fig. 4. Left axis: energy partition of electron $ F_\mathrm{e} $ in DT plasmas with $ n_\mathrm{e} = 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $ at different temperatures. Square and circle symbols denotes the results of Li-Petrasso[14] and BPS[10] models, while pentagram and triangle symbols represent the results without and with projectile recoil based on dielectric formalism of stopping power[16]. BPS$ (E_0) $ and BPS$ (E_\mathrm{dep}) $ are predictions with $ E_\mathrm{min} = $$ 0, \; 3 k_\mathrm{B} T / 2 $, respectively. The difference between LET (red solid line) and CSD (blue dotted-dash line) describes the influence of deflection effect. The black dash line displays the results calculated with $ T_0 = 25 $ in Eq. (2). Right axis: the ratio of energy partition $ F_\mathrm{e} $ from LET and CSD stopping power.
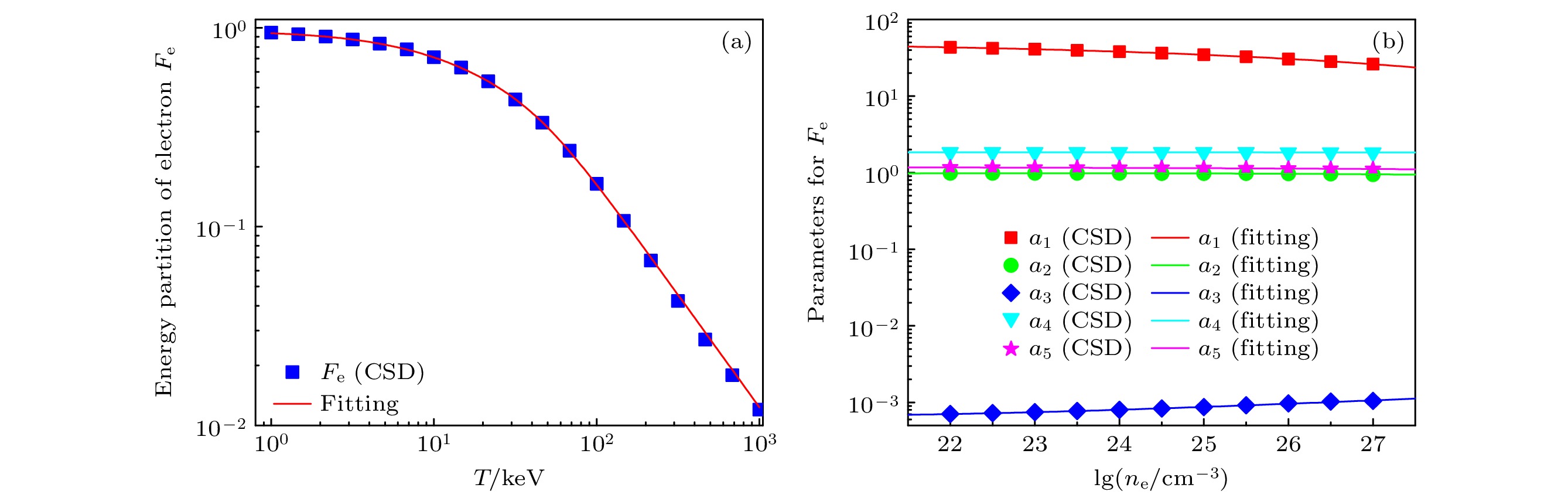
图 5 (a)电子密度为$ 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $的DT等离子体中, 基于CSD阻止本领计算的电子能量分配因子$ F_\mathrm{e} $及其拟合; (b) CSD模型中, 电子能量分配因子$ F_\mathrm{e} $拟合参数$ a_i $随密度的变化及其拟合
Fig. 5. (a) Fitting for energy partition of electron $ F_\mathrm{e} $ based on the CSD stopping power in a DT plasma with $ n_\mathrm{e} = 10^{26} \; \mathrm{cm^{-3}} $; (b) the corresponding fitting parameters $ a_i $ for the CSD $ F_\mathrm{e} $.
表 1 基于CSD和BPS阻止本领的电子能量分配因子$ F_\mathrm{e} $的拟合参数, 见方程(18)和方程(19). 其中符号$ x(y) $表示$ x\times 10^y $
Table 1. Fitting parameters in Eqs. (18) and (19) for $ F_\mathrm{e} $ based on CSD and BPS stopping power. The symbol $ x(y) $ means $ x\times 10^y $.
模型 CSD BPS $ b_i^0 $ $ b_i^1 $ $ b_i^2 $ $ b_i^0 $ $ b_i^1 $ $ b_i^2 $ $ a_1 $ $ -4.3914(1) $ $ 9.9935(0) $ $ -2.7411(-1) $ $ 1.4686(1) $ $ 5.0738(0) $ $ -1.6737(-1) $ $ a_2 $ $ -2.0193(-1) $ $ 1.0276(-1) $ $ -2.2237(-3) $ $ 3.2581(-1) $ $ 5.9071(-2) $ $ -1.3240(-3) $ $ a_3 $ $ 3.6309(-3) $ $ -2.9969(-4) $ $ 7.5755(-6) $ $ 8.6989(-4) $ $ -5.5310(-5) $ $ 2.1109(-6) $ $ a_4 $ $ 1.5664(0) $ $ 2.5995(-2) $ $ -5.9935(-4) $ $ 1.6985(0) $ $ 1.3887(-2) $ $ -3.4874(-4) $ $ a_5 $ $ 5.7808(-1) $ $ 5.6886(-2) $ $ -1.3692(-3) $ $ 1.0067(0) $ $ 1.9037(-2) $ $ -5.4891(-4) $ -
[1] 江少恩, 丁永坤, 缪文勇, 刘慎业, 郑志坚, 张保汉, 张继彦, 黄天晅, 李三伟, 陈家斌, 蒋小华, 易荣清, 杨国洪, 杨家敏, 胡昕, 曹柱荣, 黄翼翔 2009 中国科学G辑: 物理学 力学 天文学 39 1571
Jiang S E, Ding Y K, Miu W Y, Liu S Y, Zheng Z J, Zhang B H, Zhang J Y, Huang T X, Li S W, Chen J B, Jiang X H, Yi R Q, Yang G H, Yang J M, Hu X, Cao Z R, Huang Y X 2009 Sci. Chin. Phys., Mech. Astron. 39 1571
[2] Hurricane O A, Patel P K, Betti R, Froula D H, Regan S P, Slutz S A, Gomez M R, Sweeney M A 2023 Rev. Mod. Phys. 95 025005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 朱少平, 罗民兴 2024 物理 53 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu S P, Luo M X 2024 Physics 53 287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Atzeni S, Meyer-ter Vehn J 2004 The Physics of Inertial Fusion: Beam Plasma Interaction, Hydrodynamics, Hot Dense Matter (Vol. 125) (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[5] Betti R, Christopherson A, Spears B, Nora R, Bose A, Howard J, Woo K, Edwards M, Sanz J 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 255003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Stanton L G, Murillo M S 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 082301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Wang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 076018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Eliezer S, Martínez-Val J M 1998 Laser Part. Beams 16 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Son S, Fisch N 2006 Phys. Lett. A 356 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Brown L S, Preston D L, Singleton Jr R L 2005 Phys. Rep. 410 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fraley G S, Linnebur E J, Mason R J, Morse R L 1974 Phys. Fluids 17 474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zylstra A, Hurricane O 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Butler S, Buckingham M 1962 Phys. Rev. 126 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li C K, Petrasso R D 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown L S, Preston D L, Singleton Jr R L 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 016406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] He B, Wang Z G, Wang J G 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 012704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang Y N, Wang Z G, Zhao Y T, He B 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zylstra A B, Rinderknecht H G, Frenje J A, Li C K, Petrasso R D 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 122703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bernstein D J, Baalrud S D, Daligault J 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 082705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Landau L, Lifshitz E 1977 Quantum Mechanics: Non-Relativistic Theory, Chapter XVII (Oxford: Pergamon Press
[21] Joachain C J 1975 Quantum Collision Theory, Chapter 4 (North-Holland Publishing Company
[22] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Wang J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 055005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zwicknagel G, Toepffer C, Reinhard P G 1999 Phys. Rep. 309 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bernstein D J, Baalrud S D 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 072705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lin C, He B, Wu Y, Zou S, Wang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 106005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Long K, Tahir N 1986 Nucl. fusion 26 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gus’Kov S Y, Il’In D, Sherman V 2013 EPJ Web of Conferences 59 02018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1135
- PDF下载量: 75
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: