-
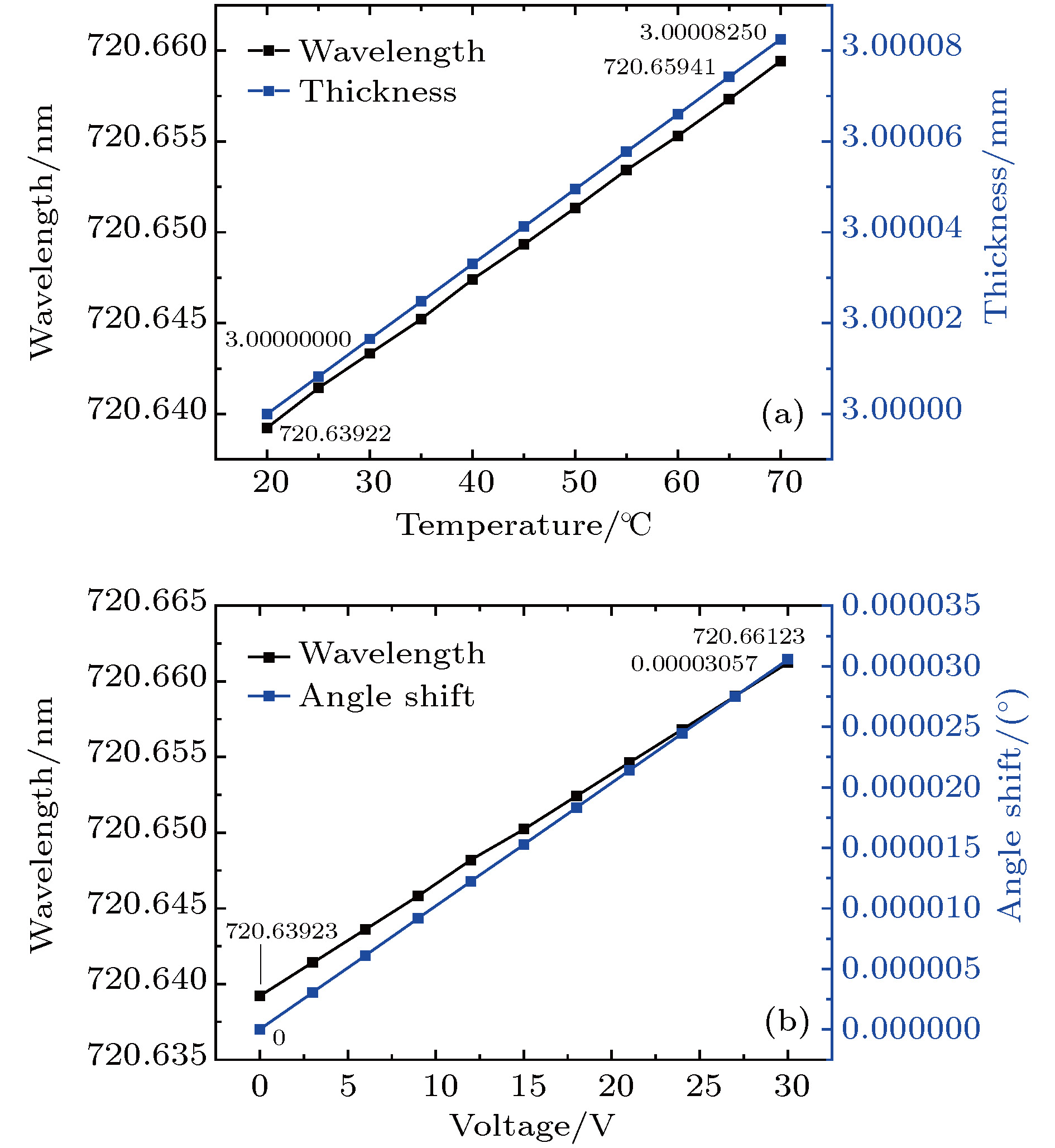
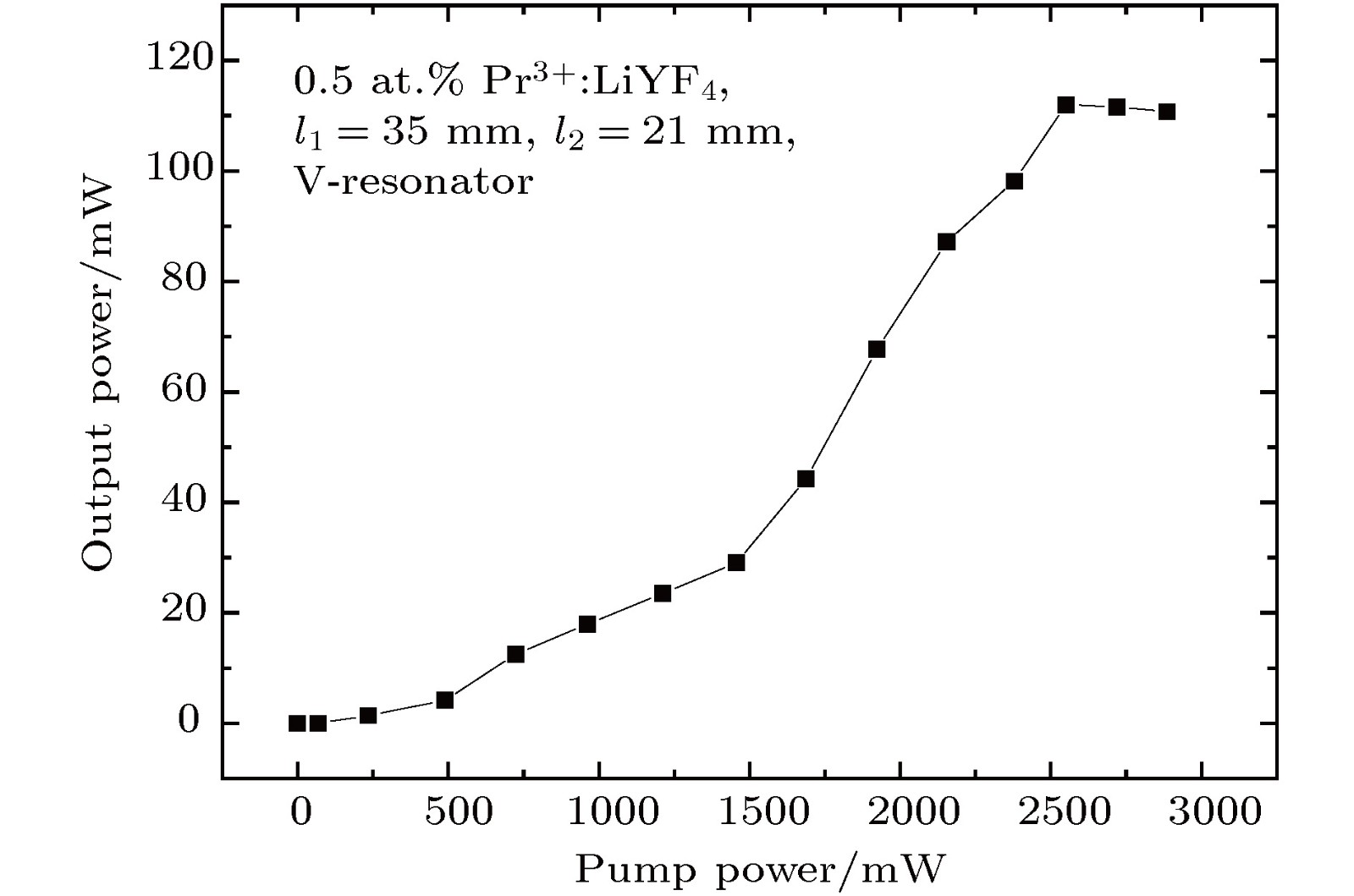
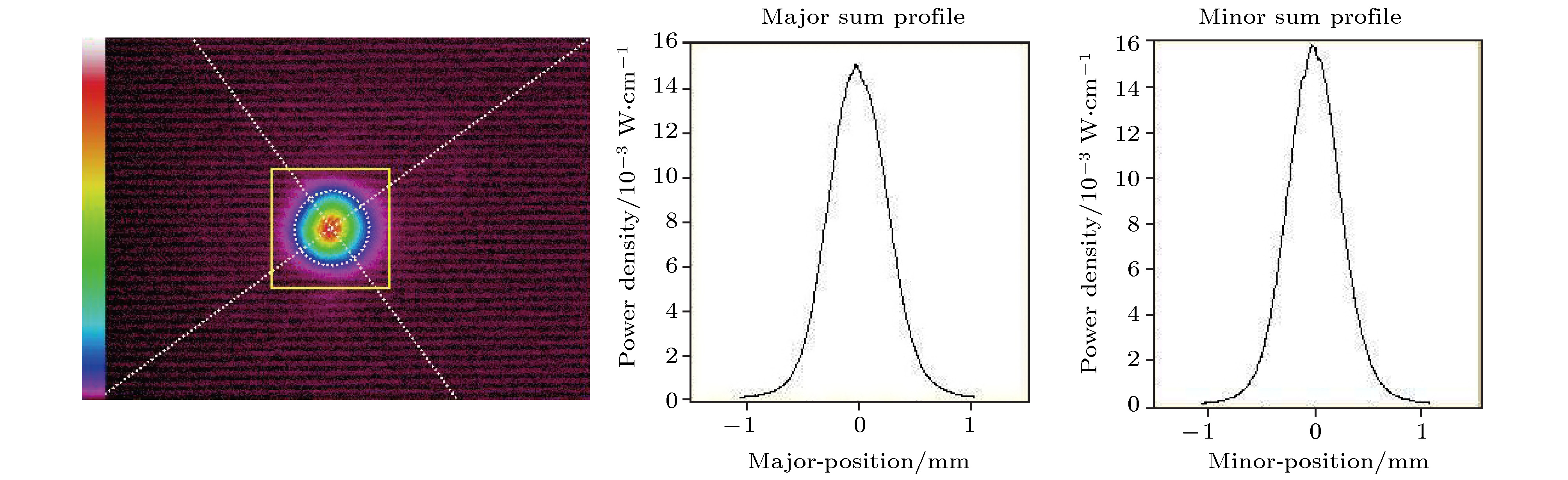
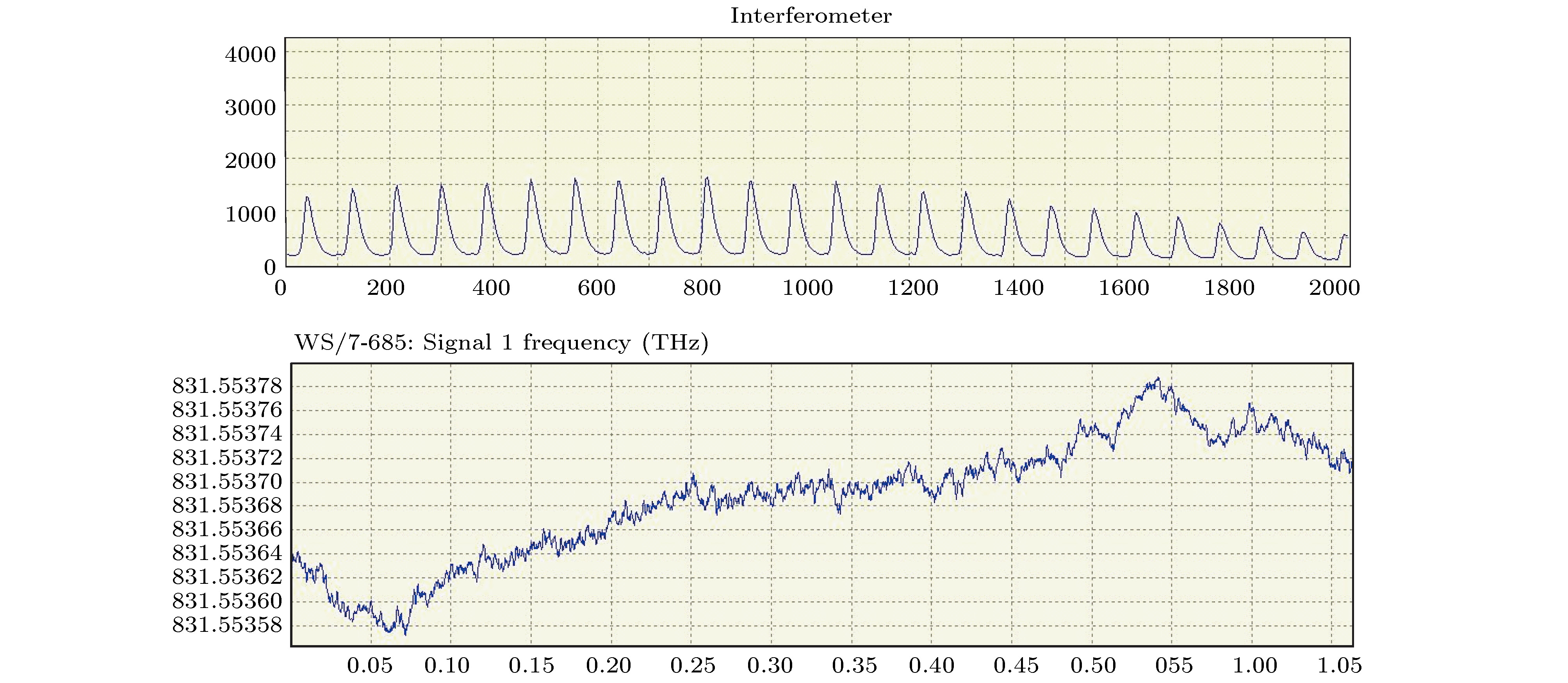
In recent years, all-solid-state ultraviolet lasers have had widely potential applications in the fields of spectroscopy, biological analysis, precision manufacturing, optical data storage, high-resolution printing, medicine and lithography. The good monochrome of all-solid-state ultraviolet laser can improve the accuracy of spectral absorption measurement when used to detect specific proteins and reduce the laser spot diameter when used for high density data storage or acousto-optic deflector. In this paper, a combined dual-wavelength laser diode (LD) beam end-pumped single longitudinal mode Pr3+:LiYF4 all-solid-state UV laser at 360 nm is presented. A V-folded cavity structure is used in the laser, which consists of a reflective volume Bragg grating (RBG) and a Fabry-Perot (F-P) etalon. The RBG is used as a wavelength selection and resonator reflector to narrow the width of spectral line. The F-P etalon is hybrid in the cavity, serving as a narrow-band filter, to achieve the single longitudinal mode. The lithium triborate crystal with critical type-I phase matching at room temperature is used for implementing the second-harmonic generation of the fundamental 720 nm laser and obtaining an efficient and compact ultraviolet laser at 360 nm. The optical resonator is simulated and analyzed by MATLAB software. Two experiments are conducted to compare the accuracy of central wavelength tuning by changing the temperature of F-P etalon and the angle of F-P etalon. The result shows that the change temperature of F-P etalon can achieve 0.165 pm/℃, showing that it is a better method. The structure of the laser is simplified and the anti-interference capability is improved in this way. It is different from mode competition method and the stability of single longitudinal mode laser output is increased. When the output power of LD at 444 nm is 1200 mW and that of LD at 469 nm is 1400 mW, a single longitudinal mode CW UV laser at 360 nm with output power as high as 112 mW is achieved. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is 4.3%, and the longitudinal linewidth of laser is 30 MHz. The measurements show that the edge suppression ratio is greater than 60 dB, the stability of root mean square (RMS) of output power in 4 h is better than 0.5%, the frequency shift in 1h is better than 220 MHz, and amplitude noise is less than 0.5%.
-
Keywords:
- Pr3+:LiYF4 crystal /
- single longitudinal mode /
- reflective volume Bragg grating /
- dual-wavelength
[1] Chen M, Wang Z C, Wang B S, Yang F, Zhang G C, Zhang S J, Zhang F F, Zhang X W, Zong N, Wang Z M, Bo Y, Peng Q J, Cui D F, Wu Y C, Xu Z Y 2016 J. Lumin. 172 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 毛叶飞, 张恒利, 徐浏, 邓波, 桑思晗, 何京良, 邢冀川, 辛建国, 江毅 2015 64 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao Y F, Zhang H L, Xu L, Deng B, Sang S H, He J L, Xing J C, Xin J G, Jiang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mao Y F, Zhang H L, Sang S H, Zhang X, Yu X L, Xing J C, Xin J G, Jiang Y 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 094201-1
[4] Cai Z P, Qu B, Cheng Y J, Luo S Y, Xu B, Xu H Y, Luo Z Q, Camy P, Doualan J L, Moncorgé R 2014 Opt. Express 22 31722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Camy P, Xu B, Doualan J L, Moncorgé R 2011 Advanced Solid-State Photonics Istanbul, Turkey, February 13−16, 2011 pATuB10
[6] Luo S Y, Yan X G, Xu B, Xiao L P, Xu H, Cai Z P, Weng J 2018 Opt. Commun. 406 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘哲 2013 博士学位论文 (福建: 厦门大学)
Liu Z 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Fujian: Xiamen University) (in Chinese)
[8] Akbari R, Major A 2013 Laser Phys. 23 035401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ostroumov V, Seelert W, Hunziker L, Ihli C, Richter A, Heumann E, Huber G 2007 Solid State Lasers XVI: Technology and Devices San Jose, USA, January 22−25, 2007 p645103-1
[10] Zhang C M, Yu W X, Zhang C G, Yao Y, Zhu P F, Song P, Bai L 2015 Opt. Spectrosc. 118 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tu X, Wu X, Li M, Liu L Y, Xu L 2012 Opt. Express 20 19996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 谢仕永, 张小富, 杨程亮, 乐小云, 薄勇, 崔大复, 许祖彦 2016 65 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie S Y, Zhang X F, Yang C L, Le X Y, Bo Y, Cui D F, Xu Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] George J, Oak S M, Singh B P 2010 Opt. Laser Technol. 42 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yao B, Jing W, Dai T, Ju Y, Wang Y 2017 Opt. Express 25 27671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nunez P M, Wetter N U, Zondy J J, Cruz F C 2013 Laser Phys. 23 025801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li J, Yang S, Zhao C, Zhang H, Xie W 2010 Opt. Express 18 12161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dai T Y, Wu J, Ju L, Zhang Z G, Xu L W, Yao B Q, Wang Y Z 2016 Infrared Phys. Technol. 77 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Qian L M, Ren D M, Zhao W J, Liu Y Y, Qu Y C, Bai Y, Chen Z L 2012 Laser Phys. 22 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shie N C, Hsieh W F, Shy J T 2011 Opt. Express 19 21109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 白扬博, 向望华, 祖鹏, 张贵忠 2012 61 214208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y B, Xiang W H, Zu P, Zhang G Z 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 214208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qu B, Xu B, Luo S, Cheng Y, Xu H, Cai Z, Camy P, Doualan J, Moncorgé R 2015 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 27 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xu B, Liu Z, Xu H, Cai Z, Zeng C, Huang S, Yan Y, Wang F, Camy P, Doualan J L, Braud A, Moncorgé R 2013 Opt. Commun. 305 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo S, Yan X, Cui Q, Xu B, Xu H, Cai Z 2016 Opt. Commun. 380 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fibrich M, Šulc J, Jelínková H 2016 Solid State Lasers XXV: Technology and Devices San Francisco, United States, February 15−18, 2016 p97261E-1
[25] Fibrich M, Jelínková H, Šulc J, Nejezchleb K, Škoda V 2010 Solid State Lasers XIX: Technology and Devices San Francisco, United States, February 15−18, 2010 p757828-1
[26] Gün T, Metz P, Huber G 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 92
[27] Metz P W, Reichert F, Moglia F, Müller S, Marzahl D T, Kränkel C, Huber G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu Z, Cai Z P, Huang S L, Zeng C H, Meng Z Y, Bu Y K, Luo Z Q, Xu B, Xu H Y, Ye C C, Stareki F, Camy P, Moncorgé R 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
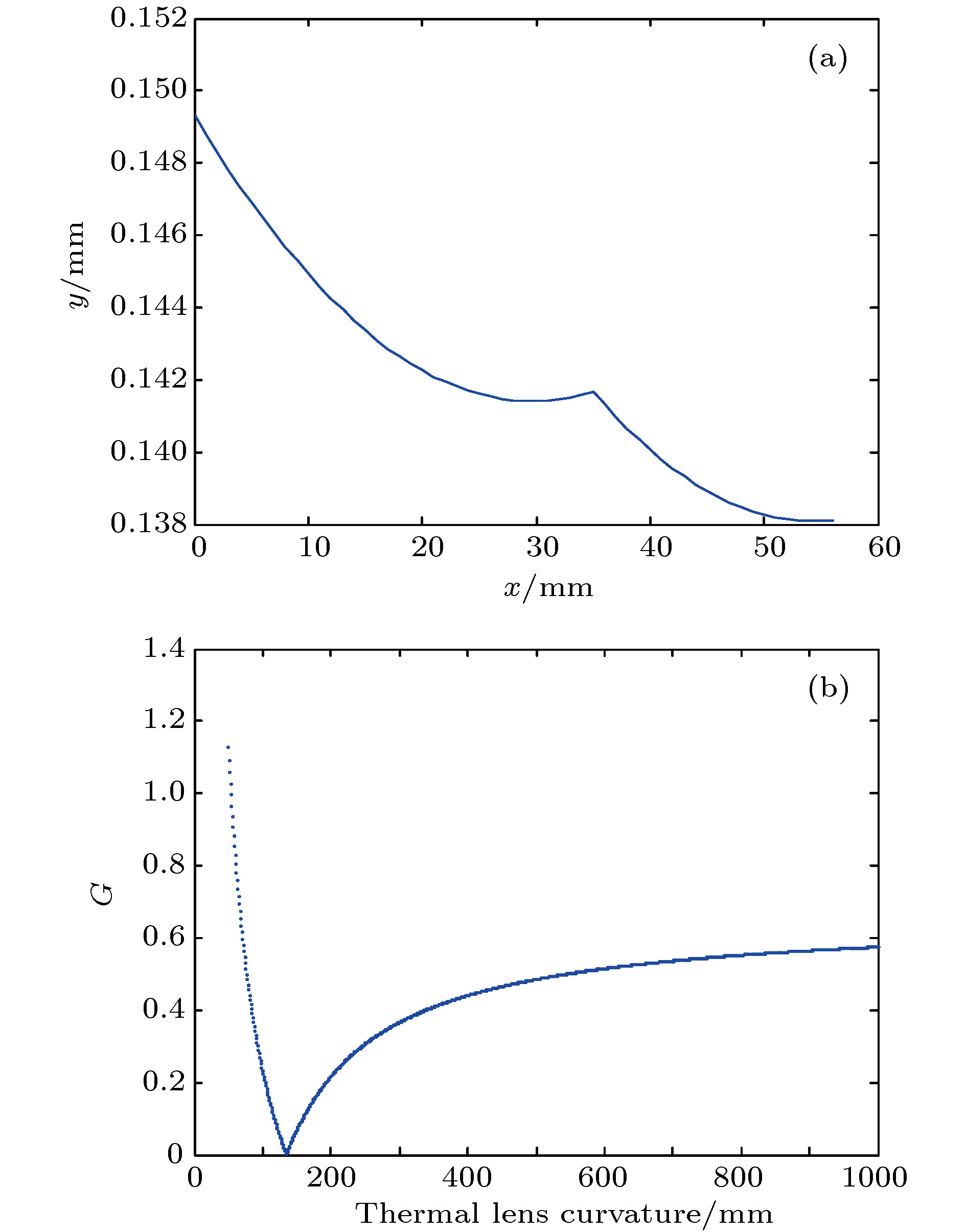
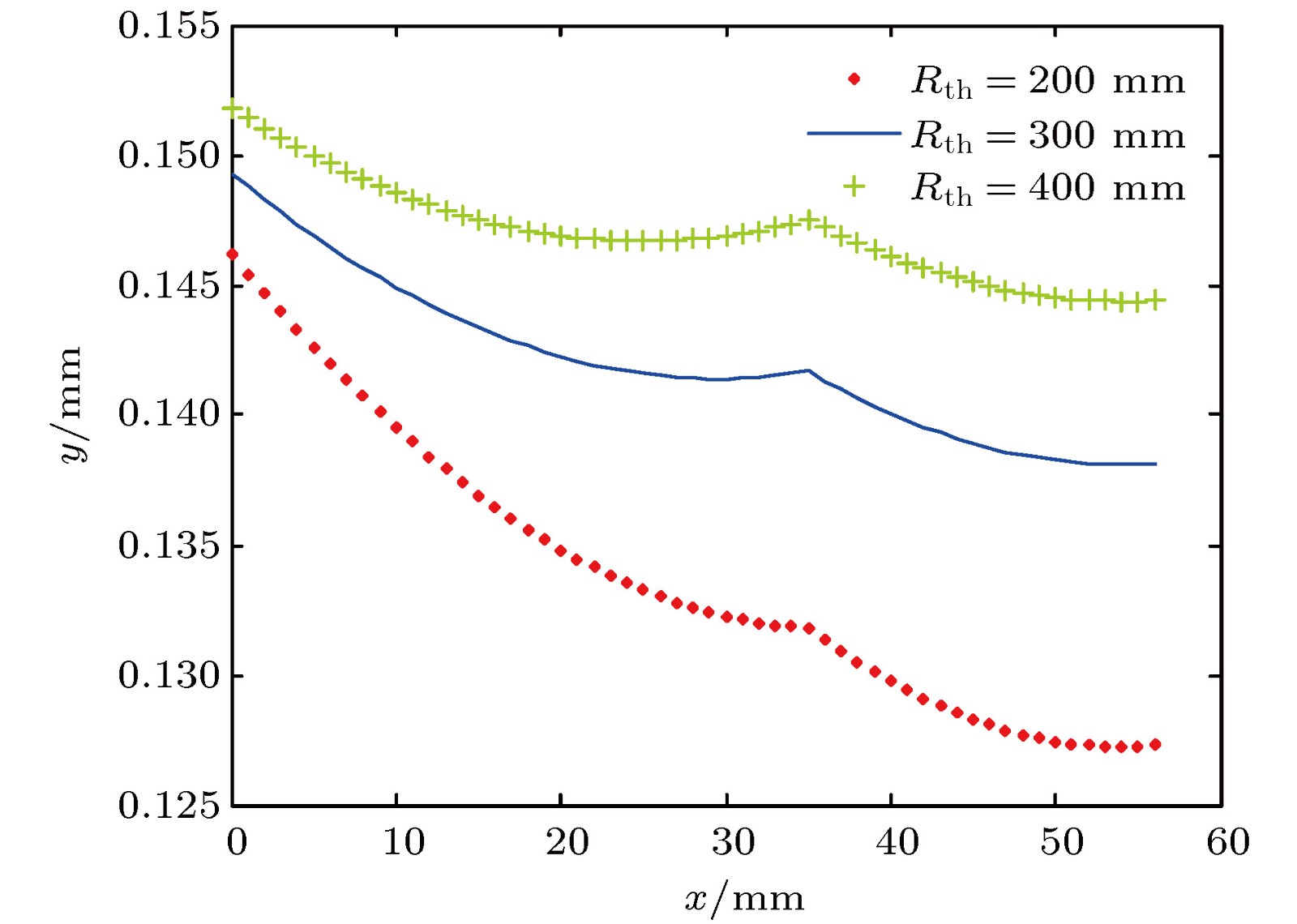
图 5 谐振腔稳定性分析 (a) 晶体热焦距Rth取300 mm时, 腔内两个束腰半径模拟图; (b) 谐振腔稳定参数G随热焦距Rth的变化
Figure 5. Stability analysis of optical resonator: (a) Simulation ofbeam waist radii inside Pr3+:LiYF4 and LBO in the resonant cavity when the thermal focal length is 300 mm; (b) the variation curve of the stability parameter G of the resonator with the thermal focal length of the crystal.
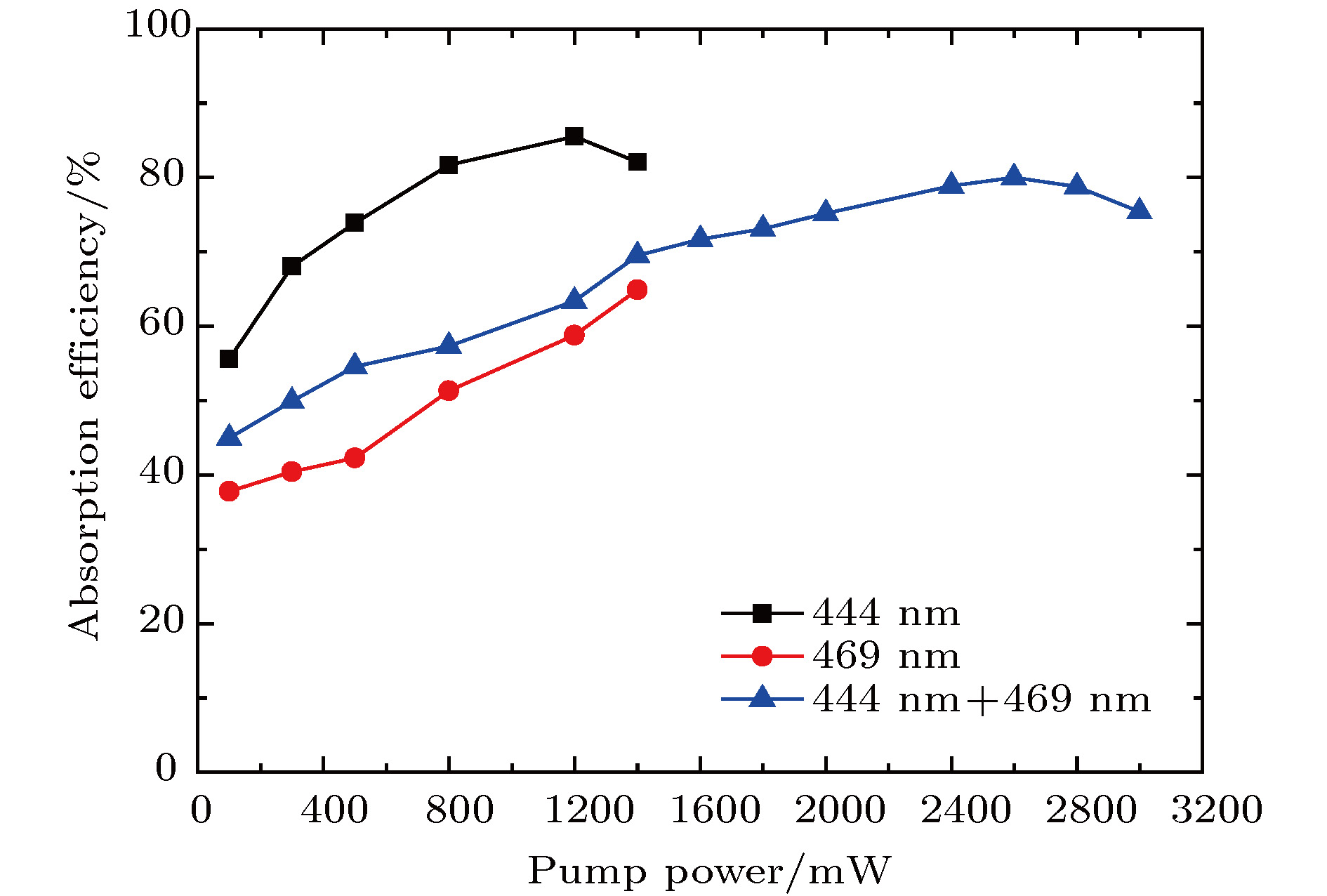
表 1 Pr3+:LiYF4晶体蓝光波段峰值吸收截面(室温)
Table 1. Peak absorption cross section of blue light in Pr3+:LiYF4 crystal (room temperature).
Peak wavelength $\lambda $/nm Absorption cross section ${\sigma _{\rm{a}}}$/10-20 cm2 Polarization Corresponding transition Line width/nm 444 9.0 ${\text{π}}$ 3H4→3P2 1.8 469 6.5 ${\text{π}}$ 3H4→3P1+1I6 0.9 479 21.7 ${\text{π}}$ 3H4→3P0 0.5 -
[1] Chen M, Wang Z C, Wang B S, Yang F, Zhang G C, Zhang S J, Zhang F F, Zhang X W, Zong N, Wang Z M, Bo Y, Peng Q J, Cui D F, Wu Y C, Xu Z Y 2016 J. Lumin. 172 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 毛叶飞, 张恒利, 徐浏, 邓波, 桑思晗, 何京良, 邢冀川, 辛建国, 江毅 2015 64 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao Y F, Zhang H L, Xu L, Deng B, Sang S H, He J L, Xing J C, Xin J G, Jiang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mao Y F, Zhang H L, Sang S H, Zhang X, Yu X L, Xing J C, Xin J G, Jiang Y 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 094201-1
[4] Cai Z P, Qu B, Cheng Y J, Luo S Y, Xu B, Xu H Y, Luo Z Q, Camy P, Doualan J L, Moncorgé R 2014 Opt. Express 22 31722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Camy P, Xu B, Doualan J L, Moncorgé R 2011 Advanced Solid-State Photonics Istanbul, Turkey, February 13−16, 2011 pATuB10
[6] Luo S Y, Yan X G, Xu B, Xiao L P, Xu H, Cai Z P, Weng J 2018 Opt. Commun. 406 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘哲 2013 博士学位论文 (福建: 厦门大学)
Liu Z 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Fujian: Xiamen University) (in Chinese)
[8] Akbari R, Major A 2013 Laser Phys. 23 035401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ostroumov V, Seelert W, Hunziker L, Ihli C, Richter A, Heumann E, Huber G 2007 Solid State Lasers XVI: Technology and Devices San Jose, USA, January 22−25, 2007 p645103-1
[10] Zhang C M, Yu W X, Zhang C G, Yao Y, Zhu P F, Song P, Bai L 2015 Opt. Spectrosc. 118 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tu X, Wu X, Li M, Liu L Y, Xu L 2012 Opt. Express 20 19996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 谢仕永, 张小富, 杨程亮, 乐小云, 薄勇, 崔大复, 许祖彦 2016 65 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie S Y, Zhang X F, Yang C L, Le X Y, Bo Y, Cui D F, Xu Z Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] George J, Oak S M, Singh B P 2010 Opt. Laser Technol. 42 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yao B, Jing W, Dai T, Ju Y, Wang Y 2017 Opt. Express 25 27671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nunez P M, Wetter N U, Zondy J J, Cruz F C 2013 Laser Phys. 23 025801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li J, Yang S, Zhao C, Zhang H, Xie W 2010 Opt. Express 18 12161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dai T Y, Wu J, Ju L, Zhang Z G, Xu L W, Yao B Q, Wang Y Z 2016 Infrared Phys. Technol. 77 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Qian L M, Ren D M, Zhao W J, Liu Y Y, Qu Y C, Bai Y, Chen Z L 2012 Laser Phys. 22 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shie N C, Hsieh W F, Shy J T 2011 Opt. Express 19 21109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 白扬博, 向望华, 祖鹏, 张贵忠 2012 61 214208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y B, Xiang W H, Zu P, Zhang G Z 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 214208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qu B, Xu B, Luo S, Cheng Y, Xu H, Cai Z, Camy P, Doualan J, Moncorgé R 2015 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 27 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xu B, Liu Z, Xu H, Cai Z, Zeng C, Huang S, Yan Y, Wang F, Camy P, Doualan J L, Braud A, Moncorgé R 2013 Opt. Commun. 305 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo S, Yan X, Cui Q, Xu B, Xu H, Cai Z 2016 Opt. Commun. 380 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fibrich M, Šulc J, Jelínková H 2016 Solid State Lasers XXV: Technology and Devices San Francisco, United States, February 15−18, 2016 p97261E-1
[25] Fibrich M, Jelínková H, Šulc J, Nejezchleb K, Škoda V 2010 Solid State Lasers XIX: Technology and Devices San Francisco, United States, February 15−18, 2010 p757828-1
[26] Gün T, Metz P, Huber G 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 92
[27] Metz P W, Reichert F, Moglia F, Müller S, Marzahl D T, Kränkel C, Huber G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu Z, Cai Z P, Huang S L, Zeng C H, Meng Z Y, Bu Y K, Luo Z Q, Xu B, Xu H Y, Ye C C, Stareki F, Camy P, Moncorgé R 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30 302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 17054
- PDF Downloads: 139
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: