-
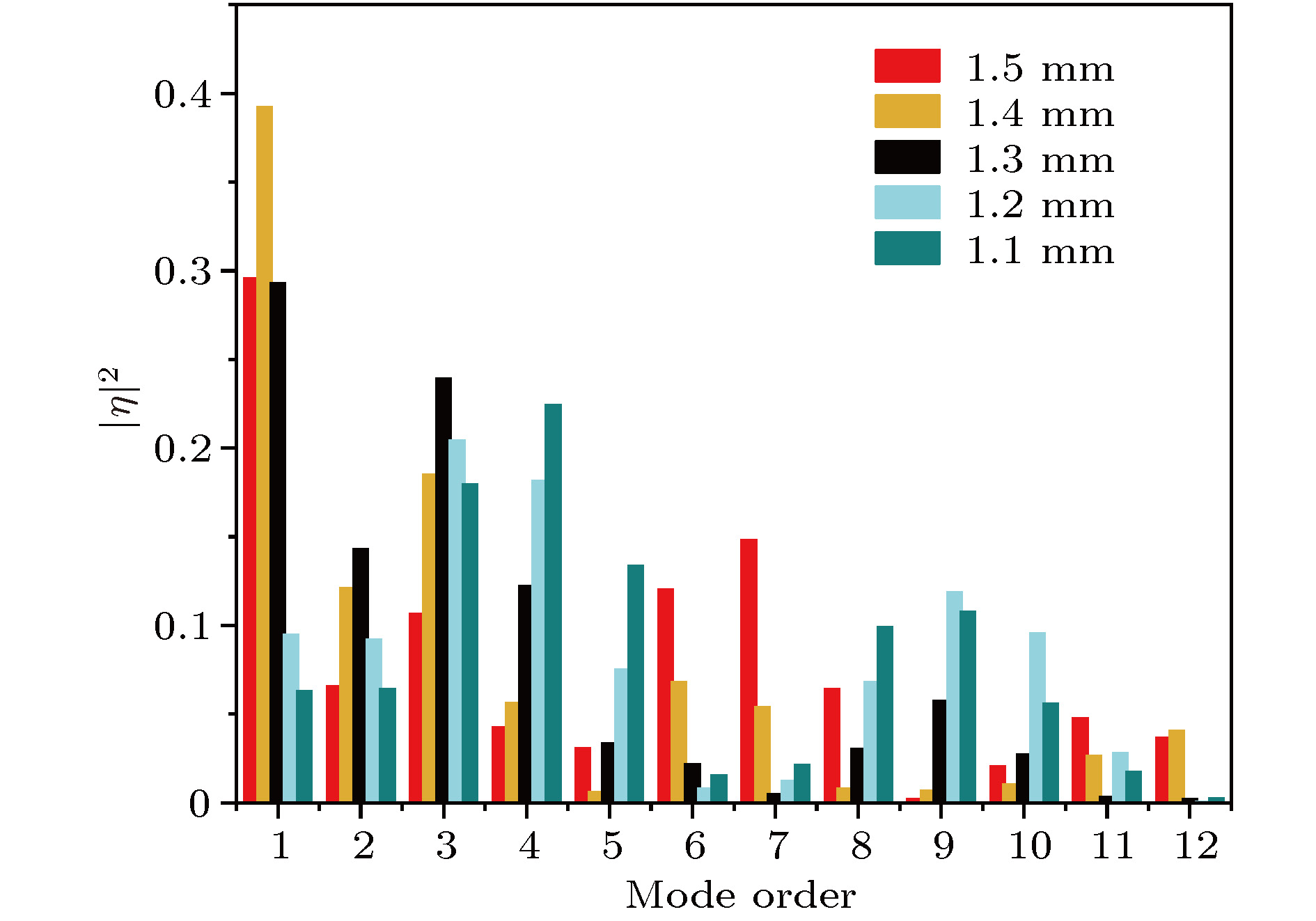
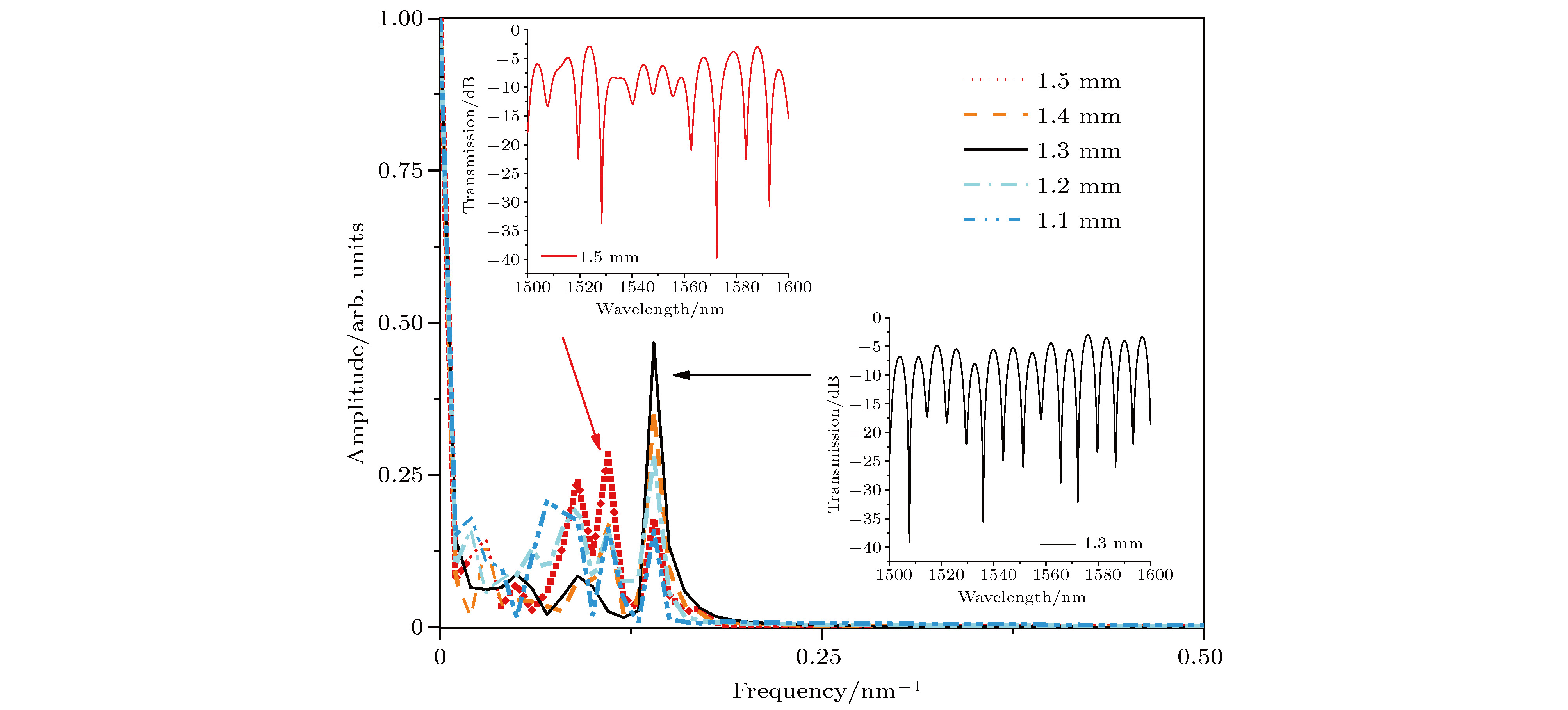
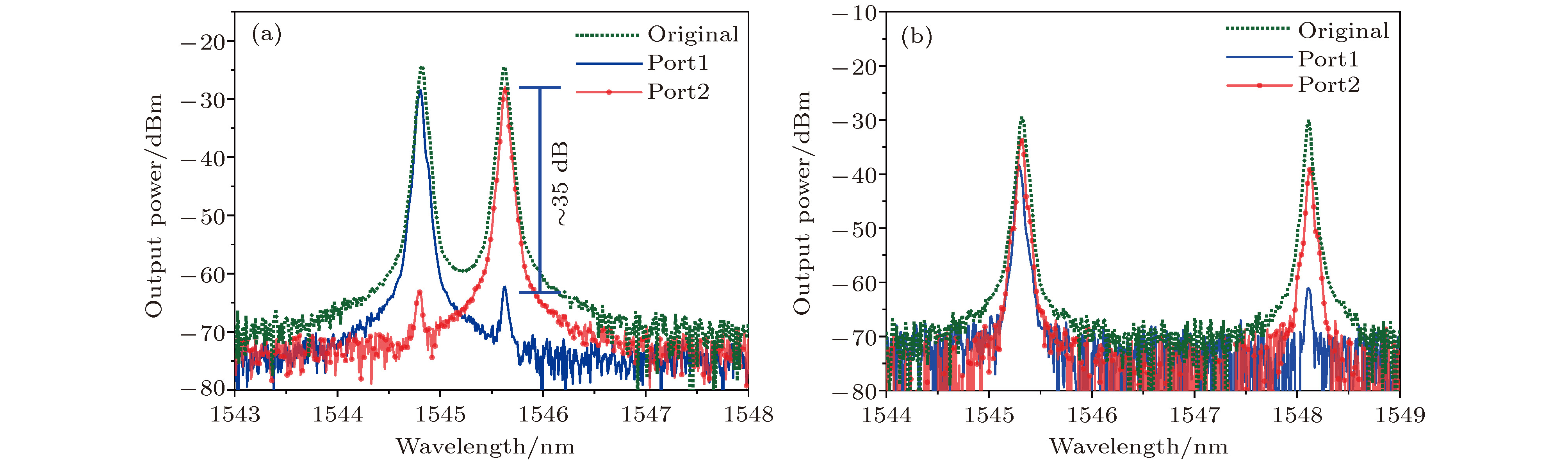
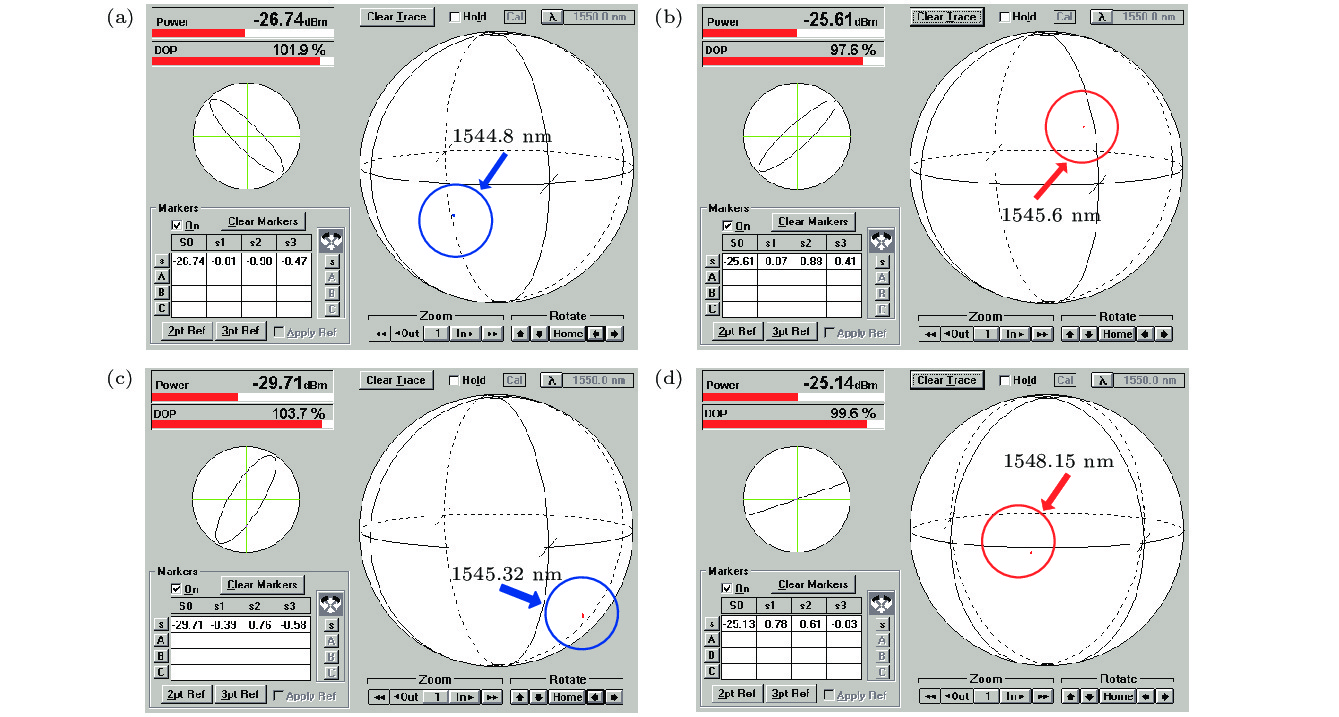
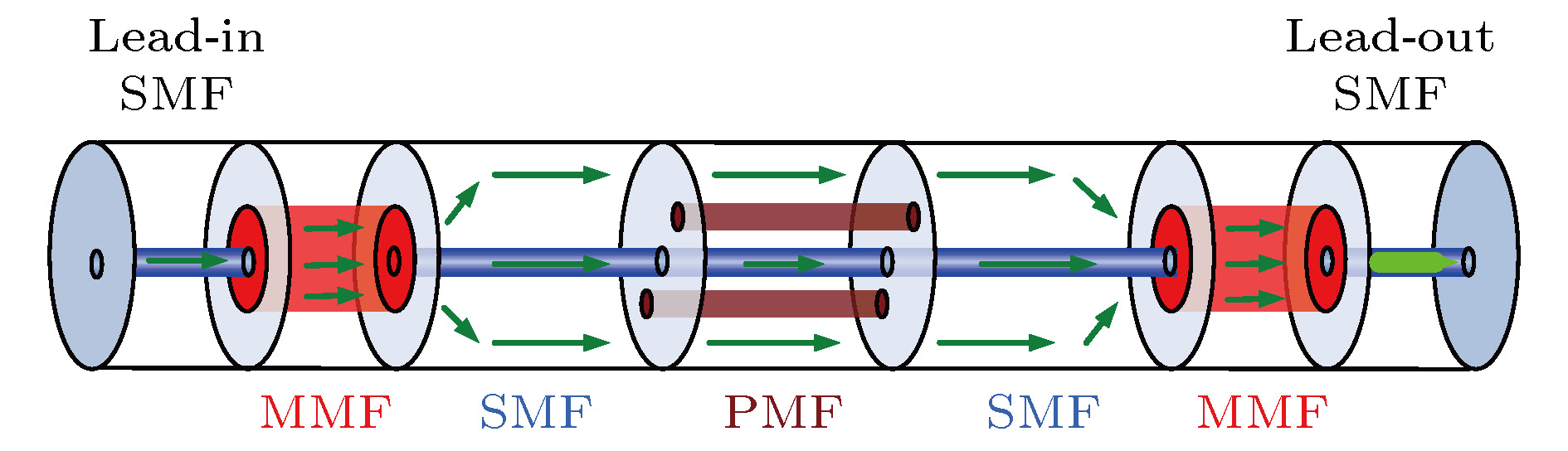
报道了一种具有全光纤结构的双波长掺铒光纤激光器, 该激光器的核心器件为一款新型的多模-单模-多模光纤干涉滤波器. 该滤波器通过一段偏振保持光纤引入偏振依赖相位差, 因而其干涉滤波效果具有良好的偏振依赖特性. 入射抽运功率为50 mW时, 系统输出激光波长为1544.82 与1545.61 nm, 波长间隔0.8 nm, 双波长激光边模抑制比均大于45 dB, 输出峰值功率差小于1 dB, 功率波动在0.7 dB以内. 通过调整腔内的偏振控制器, 可实现双波长间隔的连续可调谐输出, 波长间隔的调谐范围为0—3 nm. 输出信号的偏振态测试结果显示, 系统保持精准的单偏振输出, 并且在不同的调谐条件下, 双波长激光表现出不同的偏振特性, 当双波长激光的偏振状态相互正交时, 系统的偏振消光比达到35 dB, 整体调谐过程表现出良好的偏振稳定度.A continuously spacing-tunable dual-wavelength erbium-doped all-fiber laser is proposed and experimentally demonstrated in this paper. The key component of the laser is a novel polarization-maintained multimode-single-mode-multimode fiber interference filter, which is composed of two single-mode-multimode-single-mode fiber mode converters with a polarization-maintaining fiber sandwiched between them. As the polarization-maintaining fiber gives rise to a polarization-dependent phase difference, the fiber filter shows good polarization-dependent characteristics in interference filtering. Based on the mode interference and polarization control, the good wavelength tuning results are obtained in experiment. An optimized length of 1.3 mm for multimode fiber and 1.5 mm for polarization-maintaining fiber are adopted based on the theoretical and experimental analysis. When the phase difference between the lasing in the fast axial direction and that in the slow axial direction is
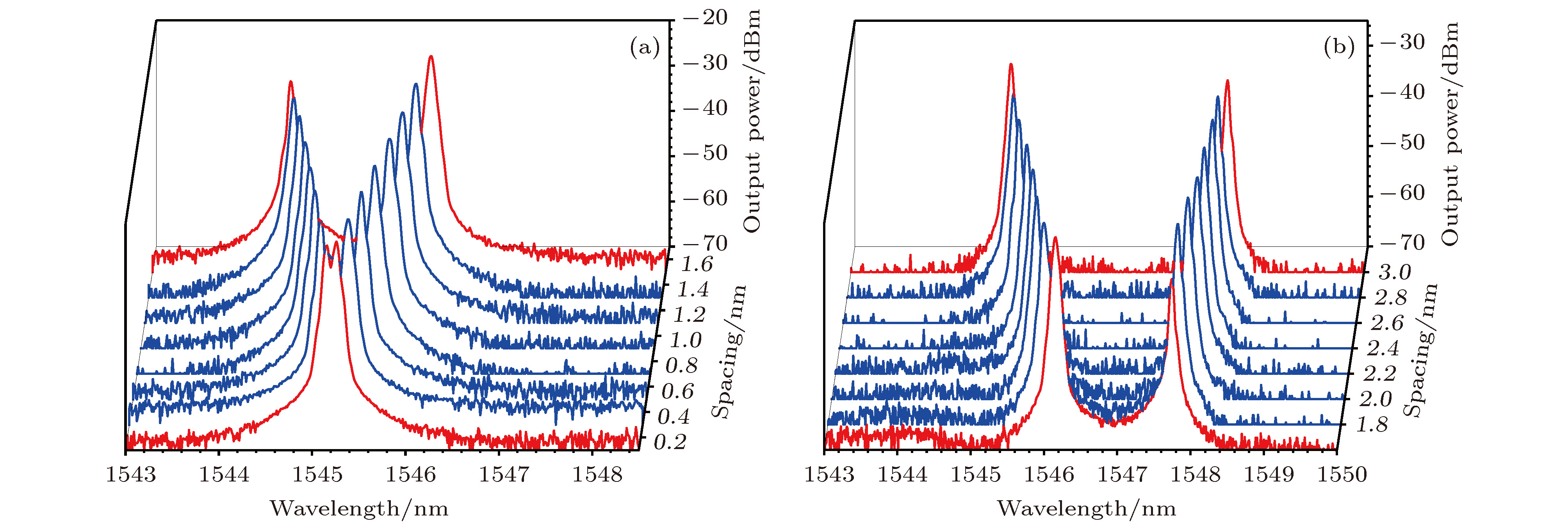
$ {\text{π}}$ , the peaks and valleys in the transmission spectrum of the fiber filter correspond exactly to the two orthogonal polarization states. In the test, when the pump power is 50 mW, a high-quality dual-wavelength lasing output (at 1544.82 nm and 1545.61 nm) is observed to have side-mode suppression ratio better than 45 dB, the wavelength spacing of 0.8 nm, the peak power difference of less than 1 dB, and the output keeps stable with a small power fluctuation less than 0.7 dB. By adjusting the polarization controller in the ring cavity, two different dual-wavelength outputs can be obtained, which are corresponding to tuning Ⅰ and tuning Ⅱ. In tuning Ⅰ, a dual-wavelength lasing output in a wavelength spacing tuning range of 0−1.2 nm can be obtained within 1 dB peak power difference, correspondingly, 0−1.6 nm tuning range within 10 dB peak power difference. In tuning Ⅱ, with continuously adjusting the polarization controller, the short wavelength signal of the dual-wavelength output stops resonating, and simultaneously another wavelength signal near 1547.8 nm is excited, the switching is continuous and the system remains dual-wavelength output. In tuning Ⅱ, a maximum tuning range of 1.6−3 nm is obtained. In both of tuning Ⅰ and tuning Ⅱ, a 0−3 nm continuously spacing-tunable dual-wavelength output is obtained, all of which keep stable single-polarization operation. The test results show that the polarization state of the dual-wavelength lasing varies with tuning; a maximum polarization extinction ratio of 35 dB is obtained as the two wavelengths are orthogonally polarized.-
Keywords:
- fiber laser /
- multimode-interference fiber filter /
- dual-wavelength /
- continuously tunable
[1] 刘江, 刘晨, 师红星, 王璞 2016 65 194209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Liu C, Shi H X, Wang P 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 194209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 窦志远, 田金荣, 李克轩, 于振华, 胡梦婷, 霍明超, 宋晏蓉 2015 64 064206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou Z Y, Tian J R, Li K X, Yu Z H, Hu M T, Huo M C, Song Y R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 064206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ahmad H, Muhammad F D, Chang H P, Thambiratnam K 2014 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 20 0902308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu T, Zhang B M, Shi L L, Huang S H, Deng M, Liu J G, Li X 2016 Opt. Express 24 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li Q, Feng S C, Peng W J, Liu P, Feng T, Tan S Y, Yan F P 2012 Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 54 2074
[6] Li Z, Zhou J, He B, Liu H K, Liu C, Wei Y R, Dong J X, Lou Q H 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 冯新焕, 刘艳格, 董孝义 2007 中国激光 34 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng X H, Liu Y G, Dong X Y 2007 Chin. J. Las. 34 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ibarra-Escamilla B, Durán-Sánchez M, Álvarez-Tamayo R I, Posada-Ramírez B, Kuzin E A, Das S, Dhar A, Pal M, Paul M C, Kir’yanov A V 2019 Laser Phys. 29 015102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yin B, Feng S C, Bai Y L, Liu Z B, Liang L J, Liu S, Jian S S 2014 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 26 1227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han J H 2010 Optik 121 2266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Feng T, Ding D L, Zhao Z W, Su H X, Yan F P, Yao X S 2016 Laser Phys. Lett. 13 105104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Feng T, Ding D L, Zhao Z W, Su H X, Yan F P, Yao X S 2016 Opt. Express 24 19760
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Feng T, Yan F P, Liu S, Bai Y, Peng W J, Tan S Y 2014 Laser Phys. Lett. 11 125106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] He X Y, Wang D N, Liao C R 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 842
[15] He X Y, Fang X, Liao C R, Wang D N, Sun J Q 2009 Opt. Express 17 21773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pan S L, Yao J P 2009 Opt. Express 17 5414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jasim A A, Ahmad H 2017 Opt. Laser Technol. 97 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang F, Xu E M, Dong J J, Zhang X L 2011 Opt. Commun. 284 2337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yeh C H, Chow C W, Shih F Y, Wang C H, Wu Y F, Chi S 2009 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 21 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Feng T, Yan F P, Liu S, Peng W J, Tan S Y, Bai Y L, Bai Y 2014 Laser Phys. 24 085101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Choi B K, ParkI G, Byun J H, Kim N, Han S P, Park K H, Seo J K, Lee H K, Jeon M Y 2013 Laser Phys. Lett. 10 125105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kim R K, Chu S H, Han Y G 2012 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 24 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Villanueva G E, Pérez-Millán P, Palací J, Cruz J L, Andrés M V, Martí J 2010 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 22 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liu J, Shen D Y, Huang H T, Zhao T, Zhang X Q, Fan D Y 2014 Appl. Phys. Express 7 032702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yan N, Han X F, Chang P F, Huang L G, Gao F, Yu X Y, Zhang W D, Zhang Z, Zhang G Q, Xu J J 2017 Opt. Express 25 27609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 刘江, 刘晨, 师红星, 王璞 2016 65 194209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J, Liu C, Shi H X, Wang P 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 194209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 窦志远, 田金荣, 李克轩, 于振华, 胡梦婷, 霍明超, 宋晏蓉 2015 64 064206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou Z Y, Tian J R, Li K X, Yu Z H, Hu M T, Huo M C, Song Y R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 064206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ahmad H, Muhammad F D, Chang H P, Thambiratnam K 2014 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 20 0902308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu T, Zhang B M, Shi L L, Huang S H, Deng M, Liu J G, Li X 2016 Opt. Express 24 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li Q, Feng S C, Peng W J, Liu P, Feng T, Tan S Y, Yan F P 2012 Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 54 2074
[6] Li Z, Zhou J, He B, Liu H K, Liu C, Wei Y R, Dong J X, Lou Q H 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 冯新焕, 刘艳格, 董孝义 2007 中国激光 34 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng X H, Liu Y G, Dong X Y 2007 Chin. J. Las. 34 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ibarra-Escamilla B, Durán-Sánchez M, Álvarez-Tamayo R I, Posada-Ramírez B, Kuzin E A, Das S, Dhar A, Pal M, Paul M C, Kir’yanov A V 2019 Laser Phys. 29 015102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yin B, Feng S C, Bai Y L, Liu Z B, Liang L J, Liu S, Jian S S 2014 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 26 1227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han J H 2010 Optik 121 2266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Feng T, Ding D L, Zhao Z W, Su H X, Yan F P, Yao X S 2016 Laser Phys. Lett. 13 105104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Feng T, Ding D L, Zhao Z W, Su H X, Yan F P, Yao X S 2016 Opt. Express 24 19760
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Feng T, Yan F P, Liu S, Bai Y, Peng W J, Tan S Y 2014 Laser Phys. Lett. 11 125106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] He X Y, Wang D N, Liao C R 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 842
[15] He X Y, Fang X, Liao C R, Wang D N, Sun J Q 2009 Opt. Express 17 21773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pan S L, Yao J P 2009 Opt. Express 17 5414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jasim A A, Ahmad H 2017 Opt. Laser Technol. 97 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang F, Xu E M, Dong J J, Zhang X L 2011 Opt. Commun. 284 2337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yeh C H, Chow C W, Shih F Y, Wang C H, Wu Y F, Chi S 2009 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 21 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Feng T, Yan F P, Liu S, Peng W J, Tan S Y, Bai Y L, Bai Y 2014 Laser Phys. 24 085101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Choi B K, ParkI G, Byun J H, Kim N, Han S P, Park K H, Seo J K, Lee H K, Jeon M Y 2013 Laser Phys. Lett. 10 125105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kim R K, Chu S H, Han Y G 2012 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 24 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Villanueva G E, Pérez-Millán P, Palací J, Cruz J L, Andrés M V, Martí J 2010 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 22 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liu J, Shen D Y, Huang H T, Zhao T, Zhang X Q, Fan D Y 2014 Appl. Phys. Express 7 032702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yan N, Han X F, Chang P F, Huang L G, Gao F, Yu X Y, Zhang W D, Zhang Z, Zhang G Q, Xu J J 2017 Opt. Express 25 27609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13508
- PDF下载量: 112
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: