-
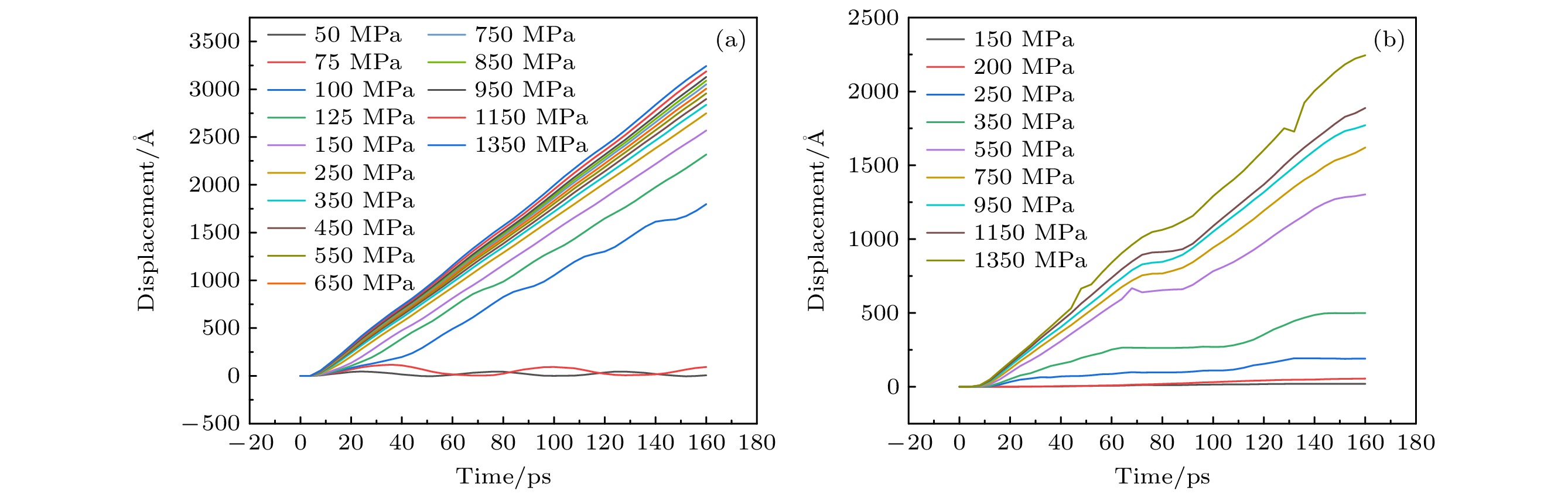
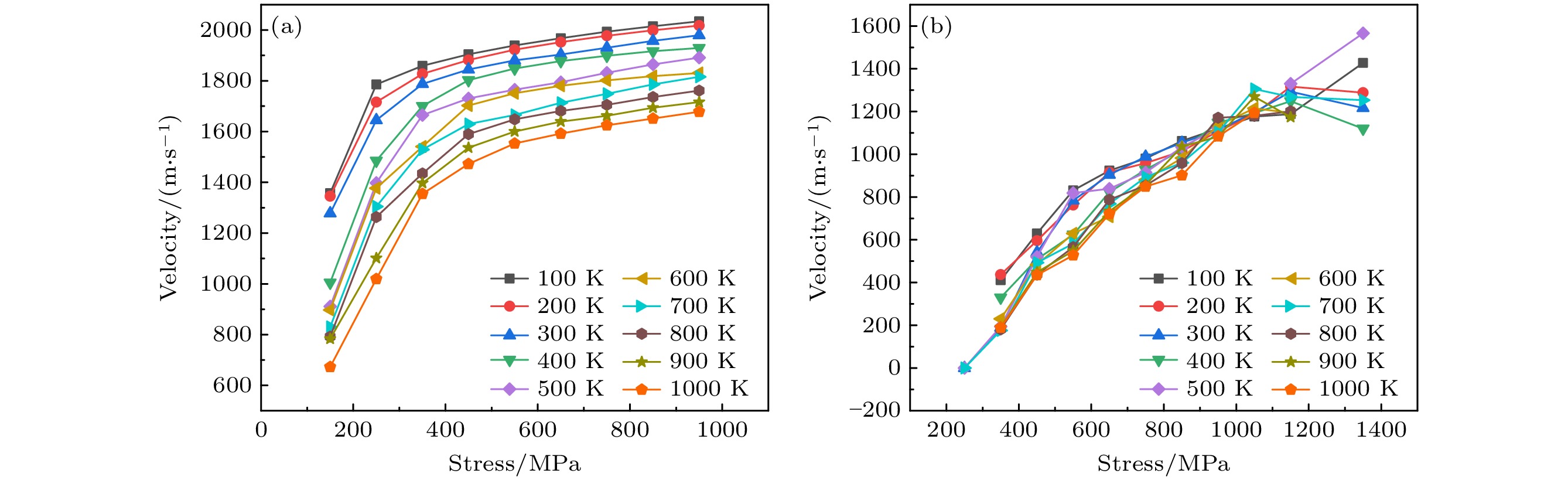
利用分子动力学对纯V和TiVTa等比合金中的刃位错运动以及刃位错与位错环之间的相互作用开展模拟研究. 结果表明, 纯V中控制刃位错运动的是声子拖拽机制; 而在TiVTa合金中, 由于存在显著的晶格畸变和局部化学波动, 声子拖拽机制和纳米段脱陷机制同时控制刃位错运动. 在纯V和TiVTa合金中加入不同尺寸的间隙$ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $环和$ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $环, 发现位错与环之间存在两种相互作用机制: 对于小尺寸位错环, 位错倾向于吸收位错环后继续运动; 对于大尺寸位错环, 位错倾向于切过位错环后继续运动. 位错环对位错的阻碍作用随着位错环尺寸的增加而增加、随着温度的升高而降低. $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $环由于极强的移动性, 对位错运动产生的阻碍作用低于$ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $环, 而这种差异在TiVTa合金中降低, 因为TiVTa合金中显著的晶格畸变降低了$ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $环的移动性.
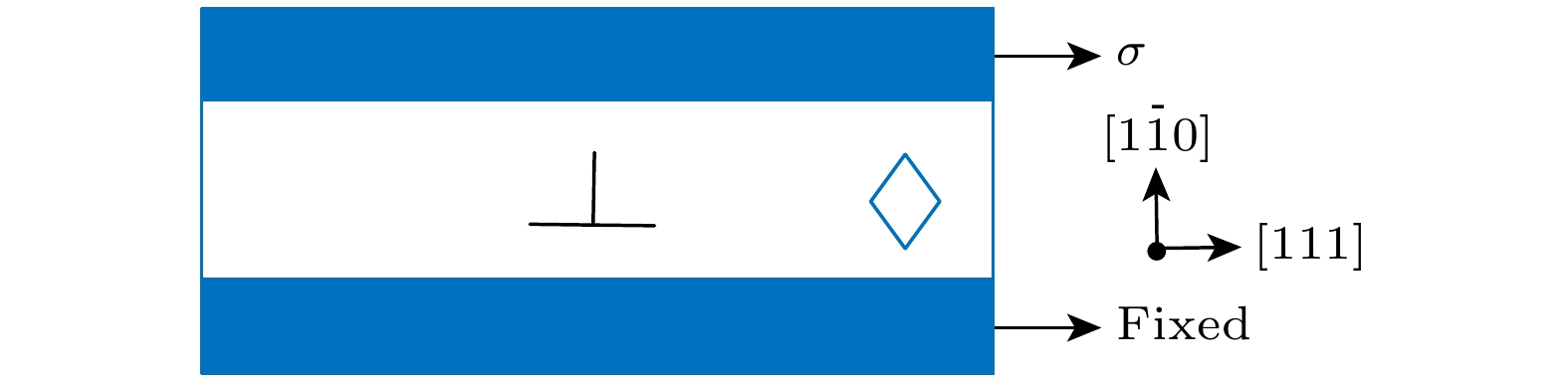
The motion of edge dislocations and the interaction between edge dislocations and dislocation loops in pure V and TiVTa alloy are simulated in this work, with the aim to reveal the influences of the existence of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ dislocation loops, which are dominant in pure V, and $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ dislocation loops, which are dominant in TiVTa alloy, on the irradiation properties of materials and the differences between the irradiation properties influenced by the two types of dislocation loops. The edge dislocations and $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops and $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops with different sizes are introduced into pure V and TiVTa alloy by using molecular dynamics simulation technology. The effects of loop type, loop size, and temperature on the interaction between edge dislocations and dislocation loops in pure V and TiVTa alloy are compared with each other and analyzed. The differences in interaction between dislocations and dislocation loops are summarized, and the reasons are revealed. The simulation results of edge dislocation motion reveal that the velocity of edge dislocations in the pure V decreases with temperature increasing, while the velocity of edge dislocations in the TiVTa alloy shows no significant relation to temperature. This is due to phonon-drag mechanism controlling the motion of edge dislocations in the pure V. In the TiVTa alloy, due to inevitable local chemical fluctuations, the phonon-drag mechanism and the nanoscale segment detrapping mechanism simultaneously control the motion of edge dislocations. The simulation results of the interaction between edge dislocations and dislocation loops show that there are two kinds of interaction mechanisms between dislocations and loops in pure V and TiVTa alloy: for small dislocation loops, dislocations tend to absorb the loops and continue to move; for large dislocation loops, dislocations tend to go through the loops and then move forward. With the size of dislocation loop increasing, the stress required for dislocations to detach from the dislocation loops also increases. With the increase of temperature, the stress required for dislocations to detach from the dislocation loops decreases. This is because the larger the size of the loops, the larger the contact area between dislocations and loops, and the greater the obstacle presented by the loops. With the increase in temperature, atomic vibrations are accelerated, and the hindrance of the loops is reduced. When comparing the interaction between $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops and $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops and dislocations, it is found that the hindrance of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops to dislocation movement is lower than that of $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops, and the difference in the hindrance to dislocation between $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops and $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops is more significant in pure V than what is observed in TiVTa alloy. This is because the mobility of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops is higher than that of $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops, the hindrance to dislocation motion of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops is lower than that of $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops. However, in the TiVTa alloy, significant lattice distortion reduces the mobility of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops. Therefore, the hindrance of $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loops in the TiVTa alloy is lower than that of $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loops, but the difference between them is reduced compared with what is observed in pure V. -
Keywords:
- molecular dynamics /
- TiVTa alloy /
- edge dislocation /
- dislocation loop
[1] Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsau C H, Chang S Y 2004 Adv. Eng. Mater. 6 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Senkov O N, Wilks G B, Scott J M, Miracle D B 2011 Intermetallics 19 698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Couzinié J P, Dirras G 2019 Mater. Charact. 147 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Fu A, Guo W M, Liu B, Cao Y K, Xu L Y, Fang Q H, Yang H, Liu Y 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 815 152466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yang C, Aoyagi K, Bian H K, Chiba A 2019 Mater. Lett. 254 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sadeghilaridjani M, Ayyagari A, Muskeri S, Hasannaeimi V, Salloom R, Chen W Y, Mukherjee S 2020 J. Nucl. Mater. 529 151955
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kareer A, Waite J C, Li B, Couet A, Armstrong D E J, Wilkinson A J 2019 J. Nucl. Mater. 526 151744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] El-Atwani O, Alvarado A, Unal K, Fensin S, Hinks J A, Greaves G, Baldwin J K S, Maloy S A, Martinez E 2021 Mater. Today Energy 19 100599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lu Y P, Huang H F, Gao X Z, Ren C L, Gao J, Zhang H Z, Zheng S J, Jin Q Q, Zhao Y H, Lu C Y, Wang T M, Li T J 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mei L, Zhang Q, Dou Y, Fu E G, Li L, Chen S, Dong Y, Guo X, He X, Yang W, Xue Y, Jin K 2023 Scr. Mater. 223 115070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] George E P, Raabe D, Ritchie R O 2019 Nat. Rev. Mater. 4 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen B, Li S Z, Zong H X, Ding X D, Sun J, Ma E 2020 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117 16199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lee C, Maresca F, Feng R, Chou Y, Ungar T, Widom M, An K, Poplawsky J D, Chou Y C, Liaw P K, Curtin W A 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yin X, Dou Y K, He X F, Jin K, Wang C L, Dong Y G, Wang C Y, Xue Y F, Yang W 2023 Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett. ) 36 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bacon D J, Osetsky Y N, Rong Z 2006 Philos. Mag. 86 3921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Marian J, Wirth B D, Schäublin R, Odette G R, Perlado J M 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rong Z, Osetsky Y N, Bacon D J 2005 Philos. Mag. 85 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nomoto A, Soneda N, Takahashi A, Ishino S 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 林盼栋, 聂君锋, 刘美丹 2022 清华大学学报 (自然科学版) 62 2029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin P D, Nie J F, Liu M D 2022 J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol. ) 62 2029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王瑾, 贺新福, 曹晗, 王东杰, 豆艳坤, 杨文 2021 原子能科学技术 55 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, He X F, Cao H, Wang D J, Dou Y K, Yang W 2021 At. Energy Sci. Technol. 55 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王瑾, 贺新福, 曹晗, 贾丽霞, 豆艳坤, 杨文 2021 70 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, He X F, Cao H, Jia L X, Dou Y K, Yang W 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu M S, Wang Z Q, Wang F, Setyawan W, Long X H, Liu Y, Dong L M, Gao N, Gao F, Wang X L 2023 Acta Mater. 245 118651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li J, Chen H T, Fang Q H, Jiang C, Liu Y, Liaw P K 2020 Int. J. Plast. 133 102819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dou Y K, Cao H, He X F, Gao J, Cao J L, Yang W 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 857 157556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Thompson A P, Aktulga H M, Berger R, Bolintineanu D S, Brown W M, Crozier P S, in't Veld P J, Kohlmeyer A, Moore S G, Nguyen T D, Shan R, Stevens M J, Tranchida J, Trott C, Plimpton S J 2022 Comput. Phys. Commun. 271 108171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Daw M S, Foiles S M, Baskes M I 1993 Mater. Sci. Rep. 9 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Stukowski A 2009 Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18 015012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Qiu R Y, Chen Y C, Liao X C, He X F, Yang W, Hu W Y, Deng H Q 2021 J. Nucl. Mater. 557 153231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chen B, Li S Z, Ding J, Ding X D, Sun J, Ma E 2023 Scr. Mater. 222 115048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma E 2020 Scr. Mater. 181 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang F L, Balbus G H, Xu S Z, Su Y Q, Shin J, Rottmann P F, Knipling K E, Stinville J C, Mills L H, Senkov O N, Beyerlein I J, Pollock T M, Gianola D S 2020 Science 370 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kubilay R E, Ghafarollahi A, Maresca F, Curtin W A 2021 npj Comput. Mater. 7 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bu Y Q, Wu Y, Lei Z F, Yuan X Y, Wu H H, Feng X B, Liu J B, Ding J, Lu Y, Wang H T, Lu Z P, Yang W 2021 Mater. Today 46 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
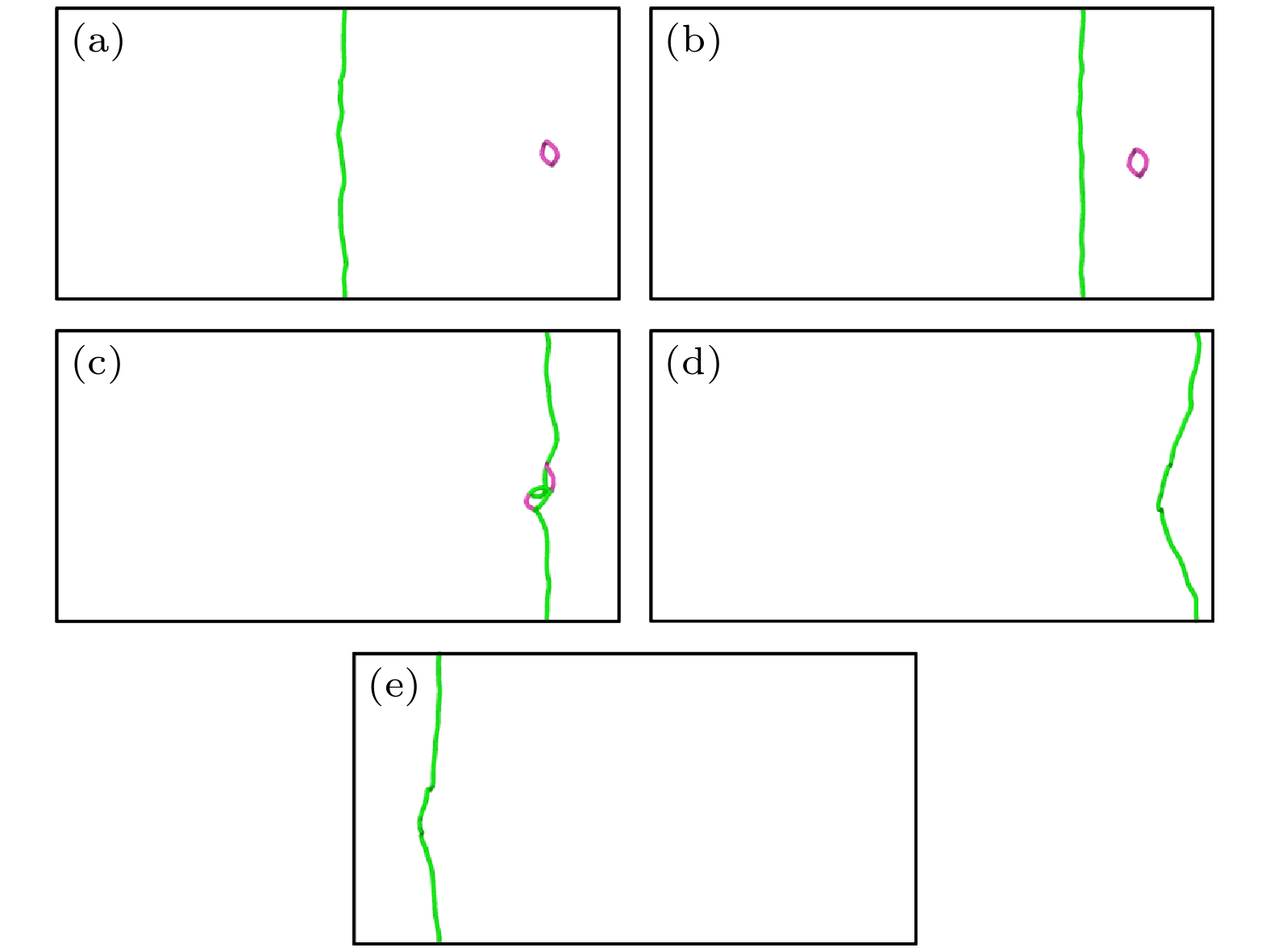
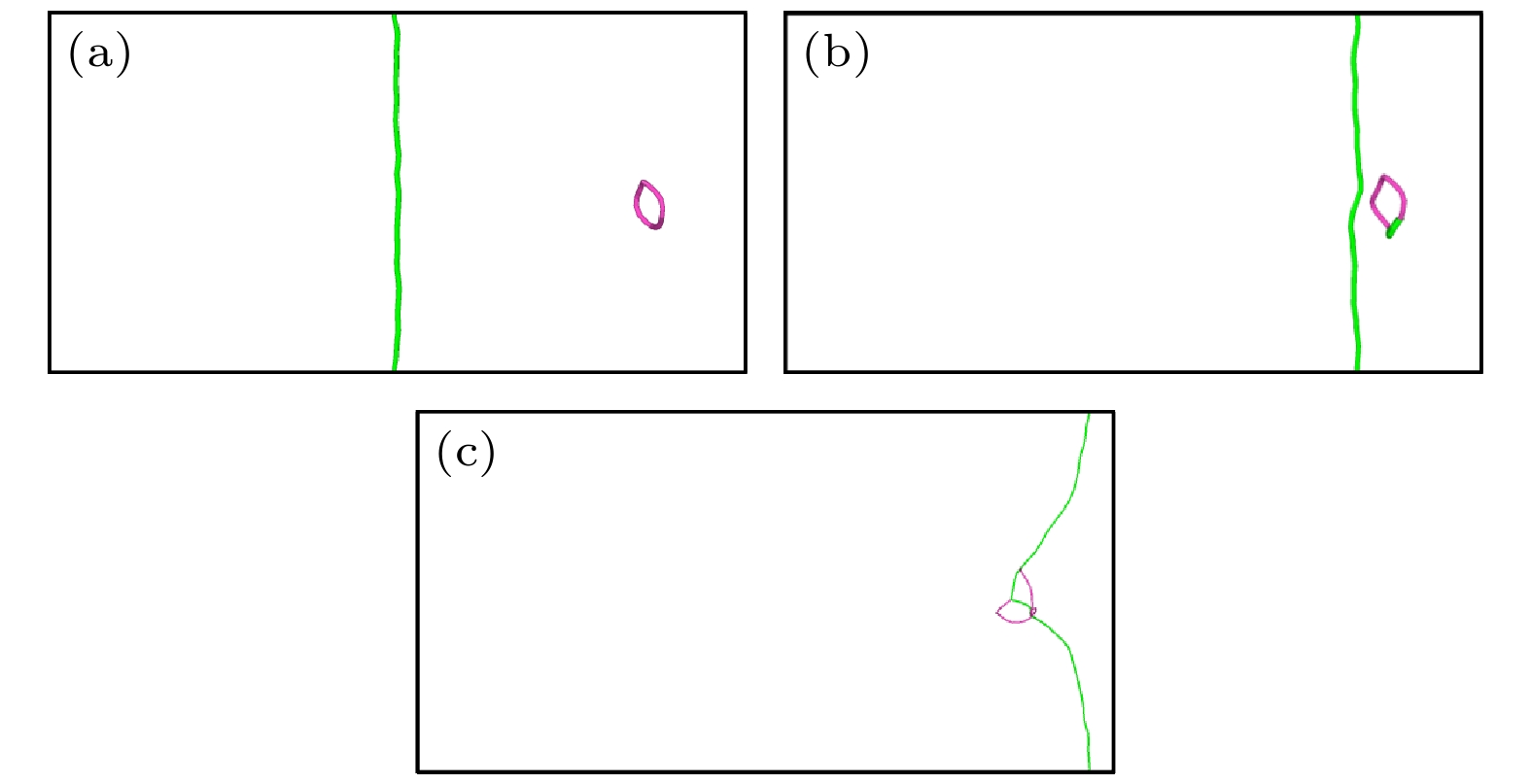
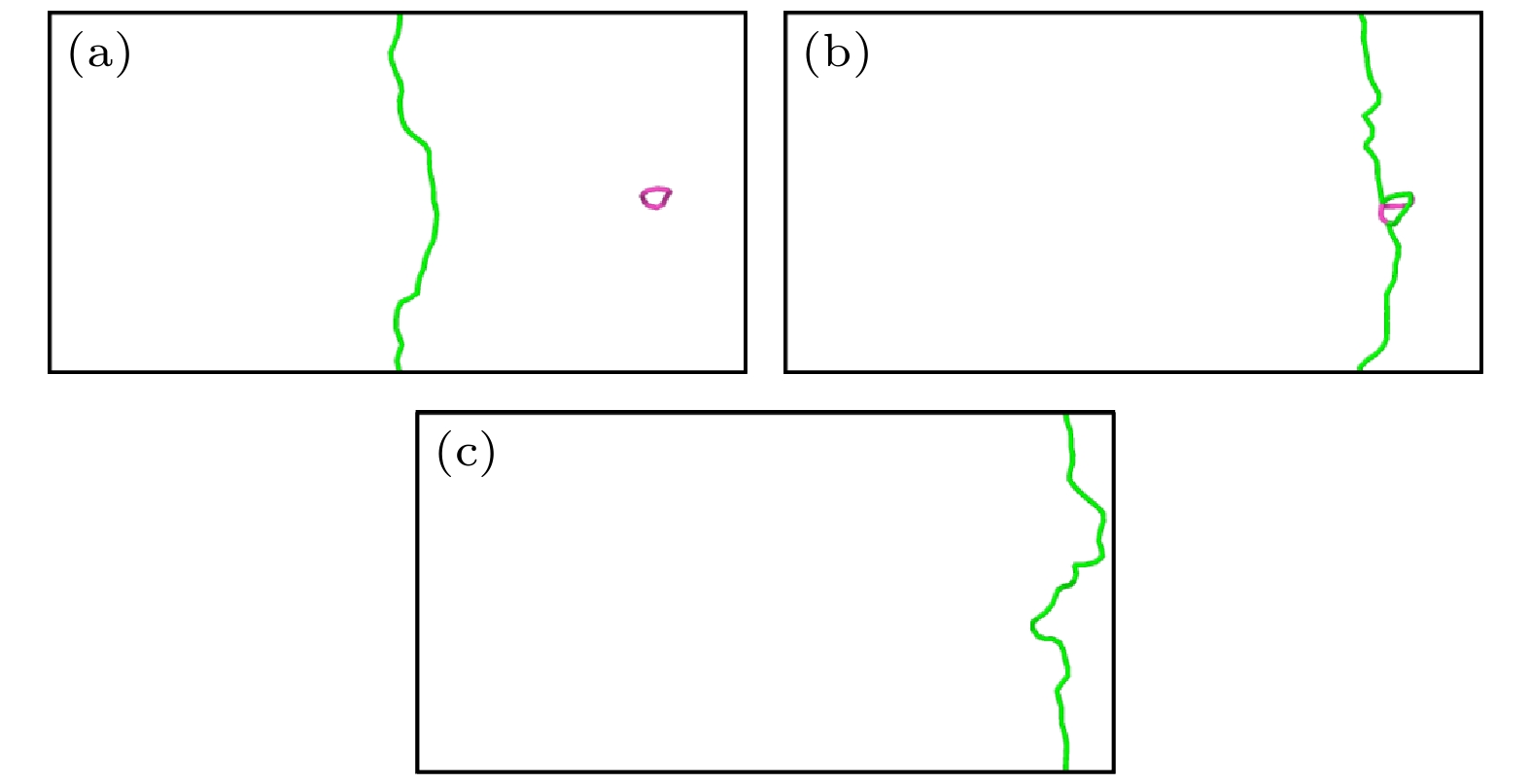
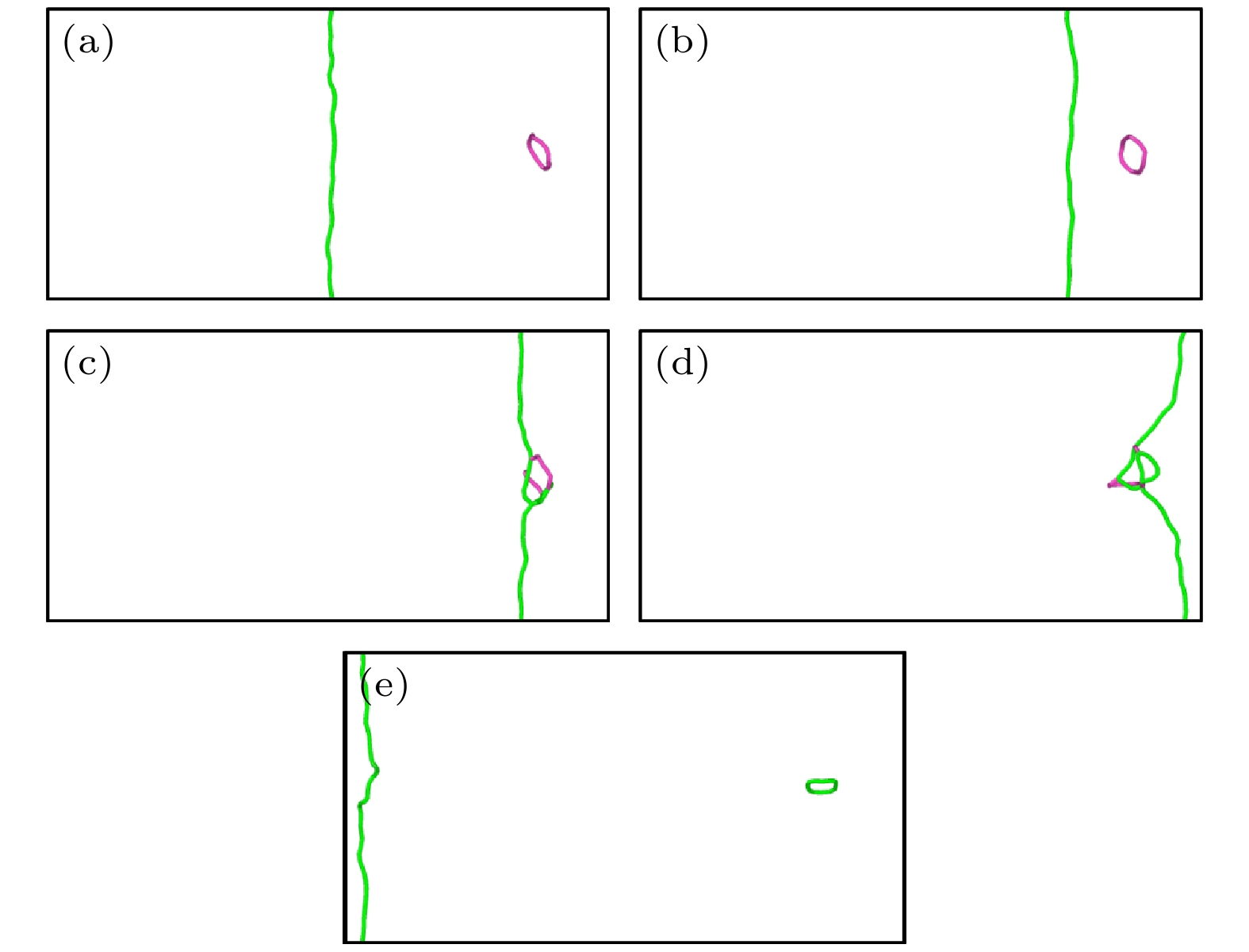
图 5 纯V中位错与间隙数为60的$ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $环在150 MPa下相互作用的可视化图像 (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 20 ps; (c) t = 24 ps; (d) t = 28 ps; (e) t = 36 ps
Fig. 5. Interaction between dislocation and $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loop with 60 self interstitial atoms at 150 MPa in pure V: (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 20 ps; (c) t = 24 ps; (d) t = 28 ps; (e) t = 36 ps.
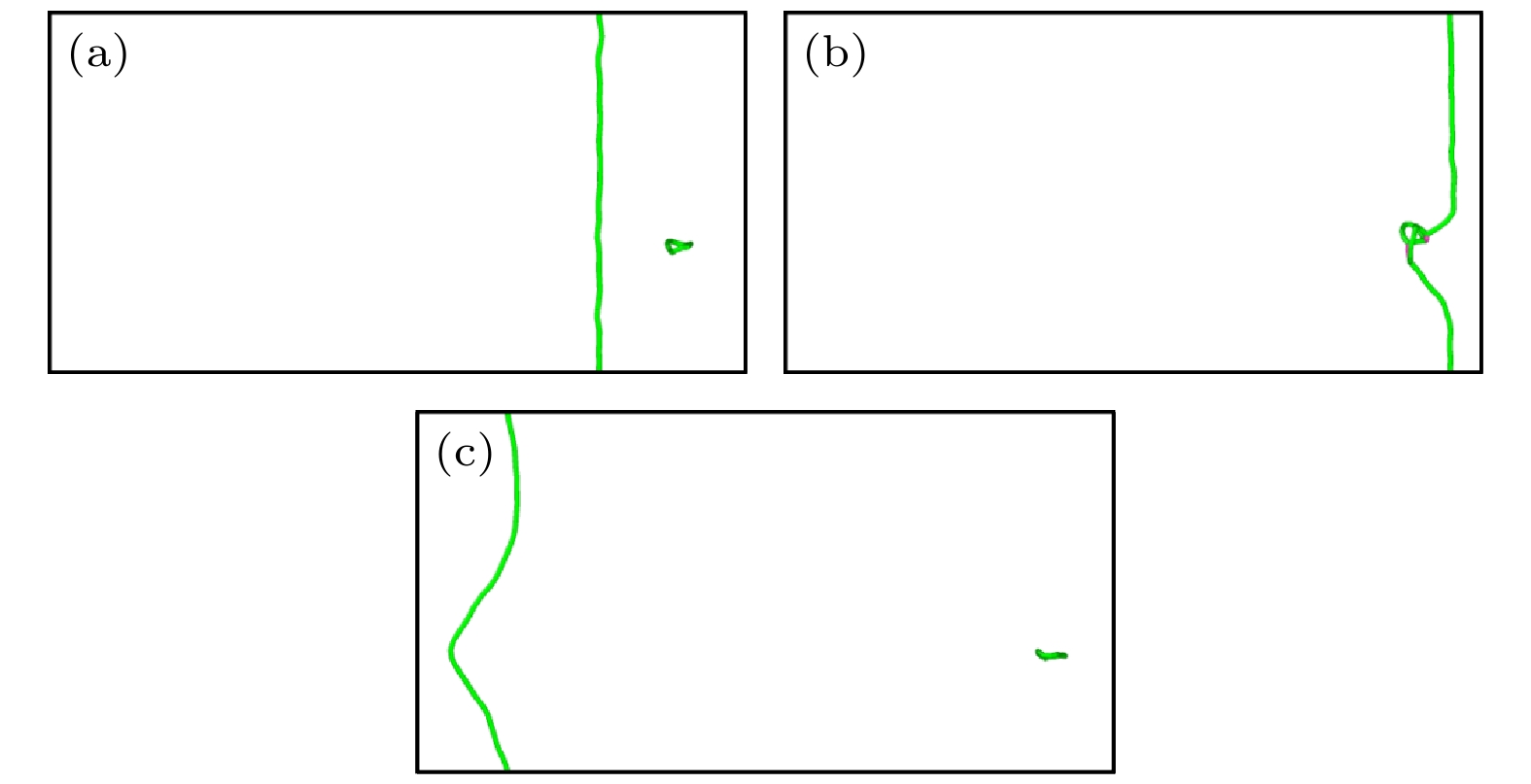
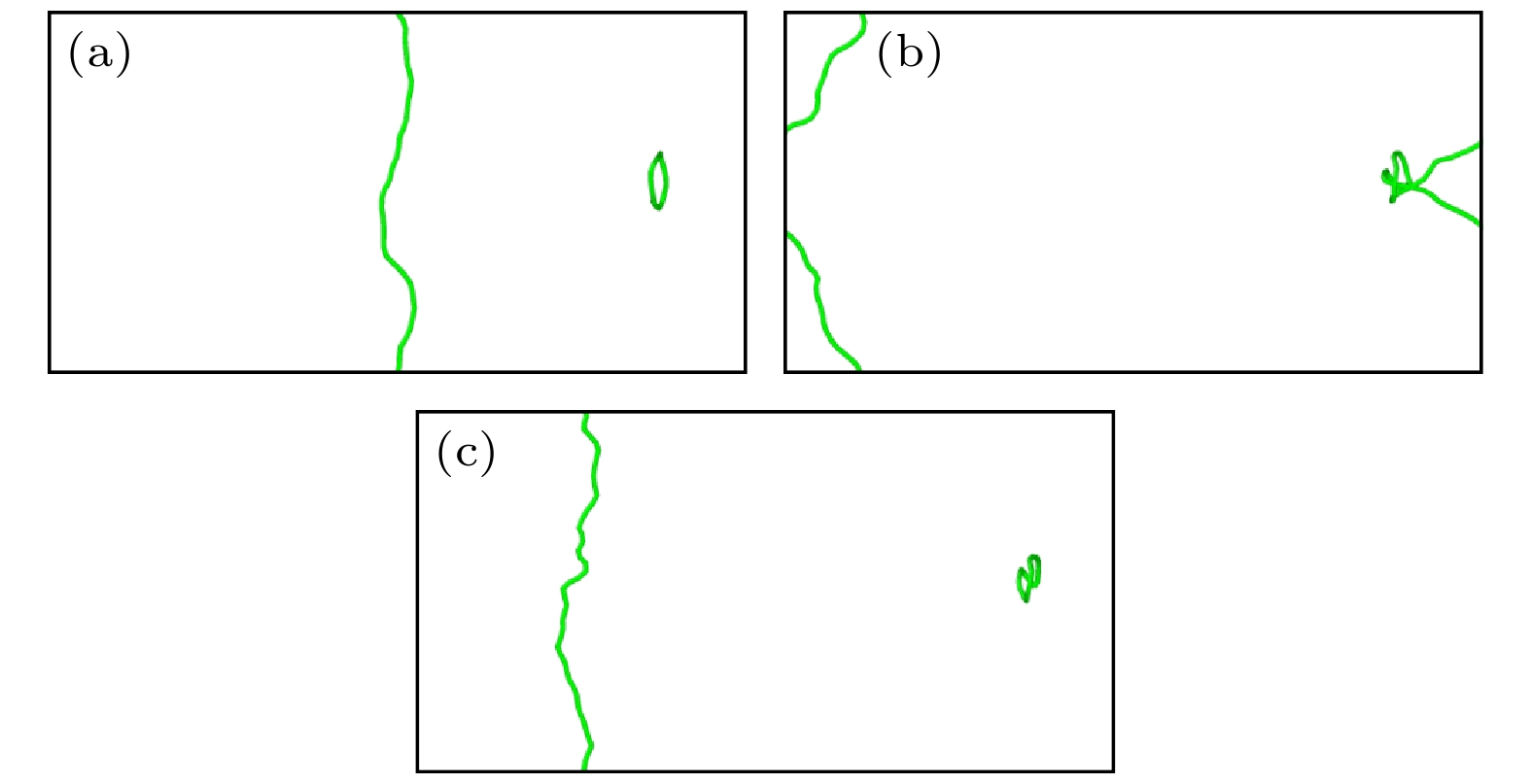
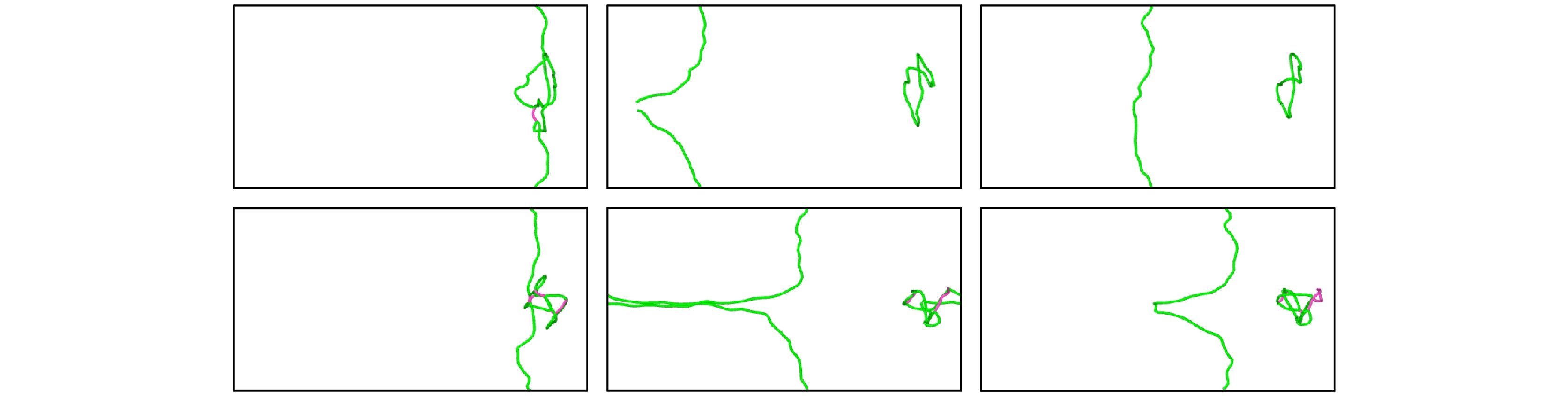
图 8 纯V中位错与间隙数为144的$ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $环的相互作用(a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 20 ps; (c) t = 22 ps; (d) t = 76 ps; (e) t = 118 ps; (f) t = 124 ps
Fig. 8. Interaction between dislocation and $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loop with 144 self interstitial atoms in pure V: (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 20 ps; (c) t = 22 ps; (d) t = 76 ps; (e) t = 118 ps; (f) t = 124 ps.
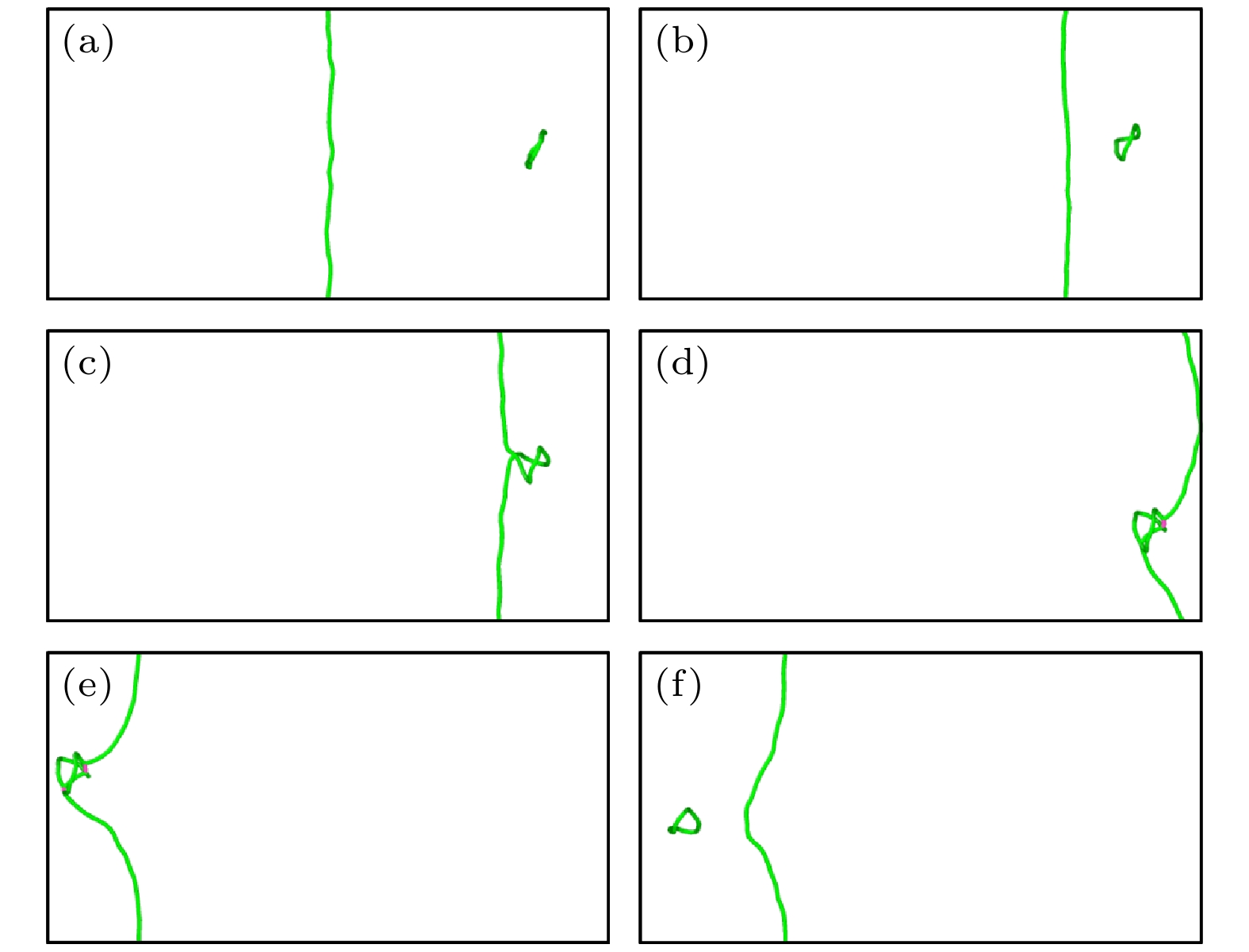
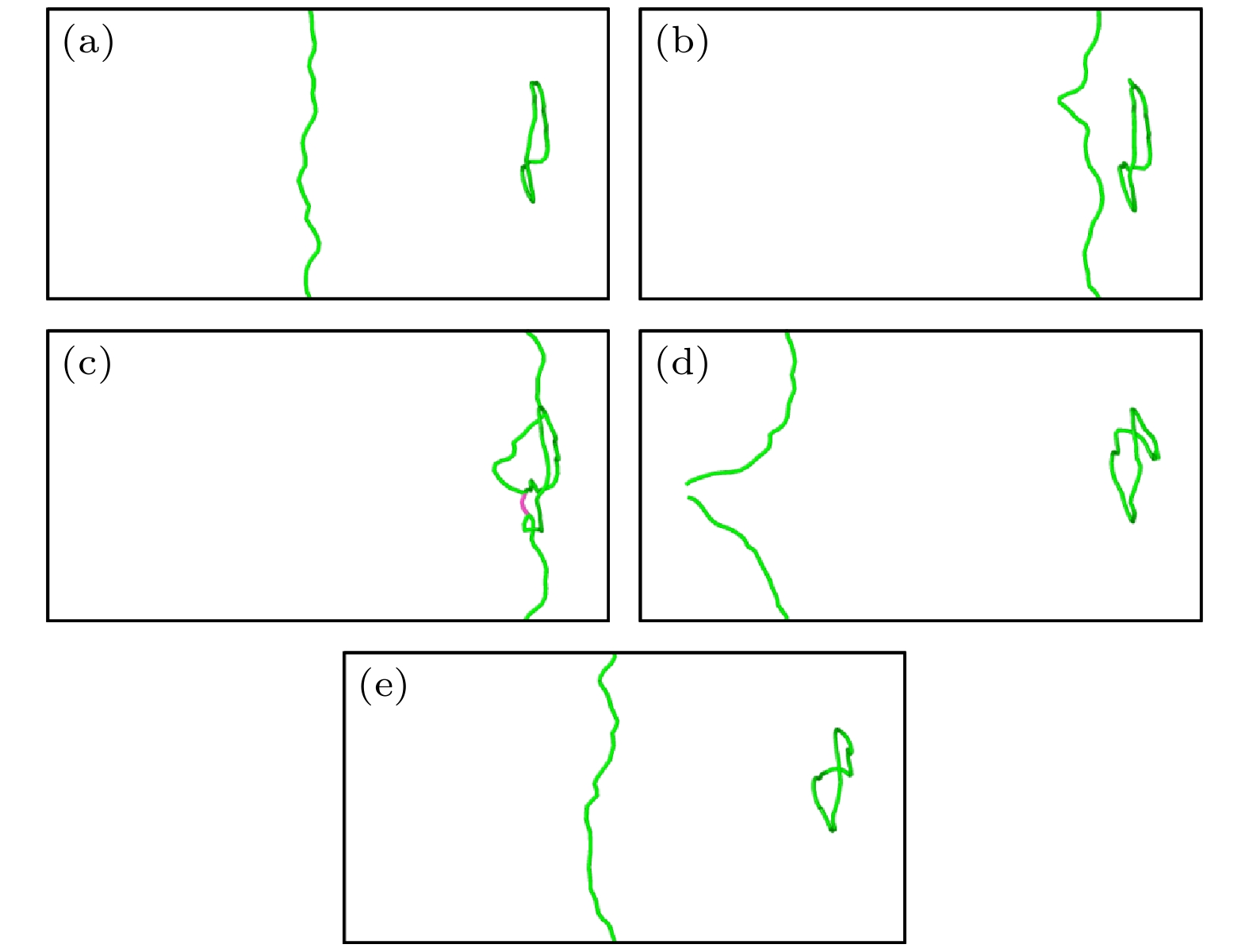
图 12 550 MPa下TiVTa合金中位错与间隙数为400的$ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $环的相互作用 (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 32 ps; (c) t = 36 ps; (d) t = 52 ps; (e) t = 60 ps
Fig. 12. Interaction between dislocation and $ \left\langle {111} \right\rangle $ loop with 400 self interstitial atoms in TiVTa alloy at 550 MPa: (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 32 ps; (c) t = 36 ps; (d) t = 52 ps; (e) t = 60 ps.
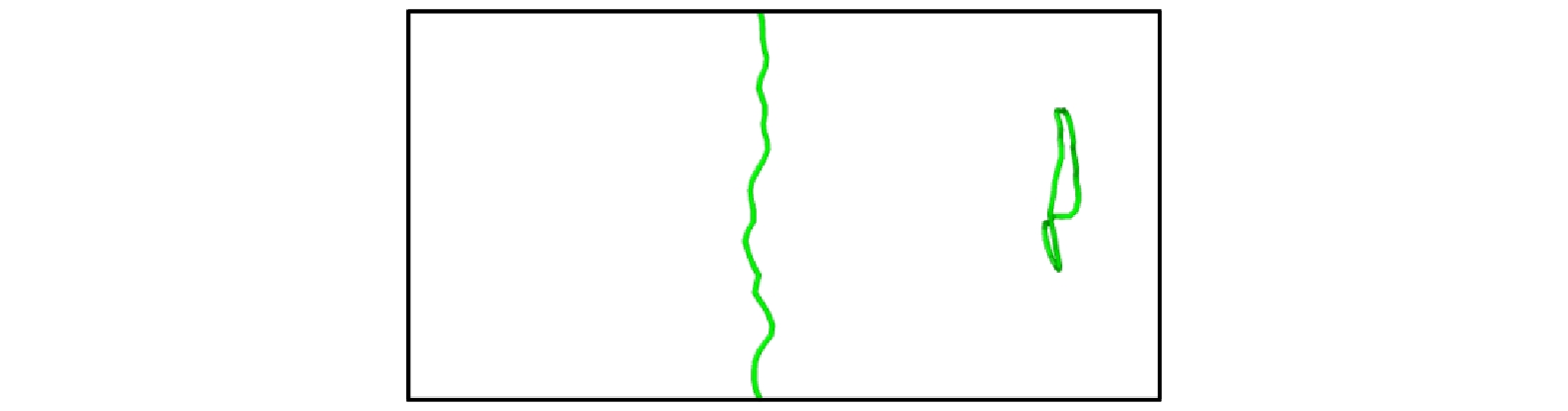
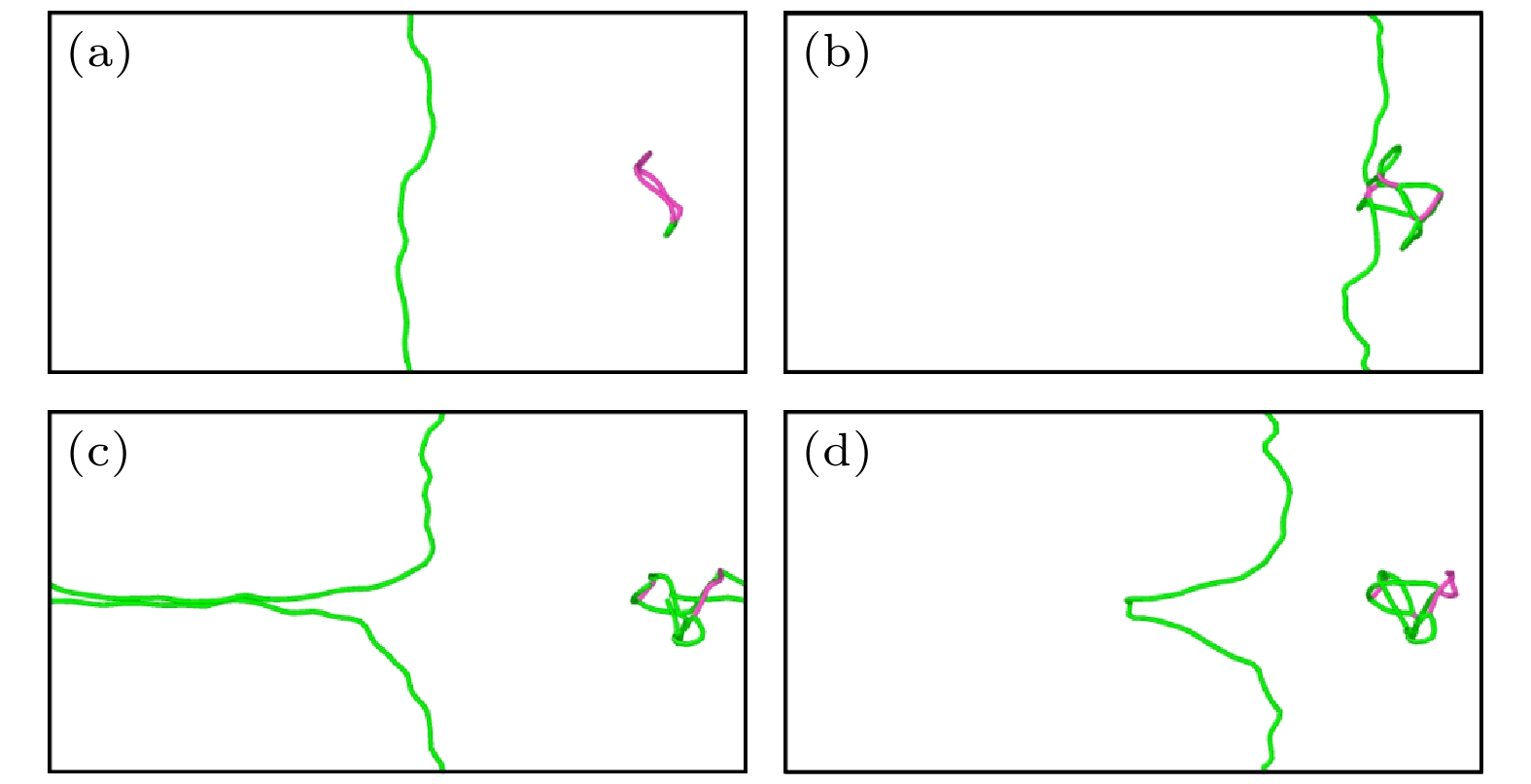
图 13 550 MPa下TiVTa合金中位错与间隙数为416的$ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $环的相互作用 (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 28 ps; (c) t = 60 ps; (d) t = 68 ps
Fig. 13. Interaction between dislocation and $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loop with 416 self interstitial atoms in TiVTa alloy at 550 MPa: (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 28 ps; (c) t = 60 ps; (d) t = 68 ps.
图 14 700 K下纯V中位错与间隙数为144的$ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $环的相互作用 (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 24 ps; (c) t = 28 ps; (d) t = 40 ps; (e) t = 48 ps
Fig. 14. Interaction between dislocation and $ \left\langle {100} \right\rangle $ loop with 144 self interstitial atoms at 700 K in pure V: (a) t = 0 ps; (b) t = 24 ps; (c) t = 28 ps; (d) t = 40 ps; (e) t = 48 ps.
-
[1] Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsau C H, Chang S Y 2004 Adv. Eng. Mater. 6 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Senkov O N, Wilks G B, Scott J M, Miracle D B 2011 Intermetallics 19 698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Couzinié J P, Dirras G 2019 Mater. Charact. 147 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Fu A, Guo W M, Liu B, Cao Y K, Xu L Y, Fang Q H, Yang H, Liu Y 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 815 152466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yang C, Aoyagi K, Bian H K, Chiba A 2019 Mater. Lett. 254 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sadeghilaridjani M, Ayyagari A, Muskeri S, Hasannaeimi V, Salloom R, Chen W Y, Mukherjee S 2020 J. Nucl. Mater. 529 151955
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kareer A, Waite J C, Li B, Couet A, Armstrong D E J, Wilkinson A J 2019 J. Nucl. Mater. 526 151744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] El-Atwani O, Alvarado A, Unal K, Fensin S, Hinks J A, Greaves G, Baldwin J K S, Maloy S A, Martinez E 2021 Mater. Today Energy 19 100599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lu Y P, Huang H F, Gao X Z, Ren C L, Gao J, Zhang H Z, Zheng S J, Jin Q Q, Zhao Y H, Lu C Y, Wang T M, Li T J 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mei L, Zhang Q, Dou Y, Fu E G, Li L, Chen S, Dong Y, Guo X, He X, Yang W, Xue Y, Jin K 2023 Scr. Mater. 223 115070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] George E P, Raabe D, Ritchie R O 2019 Nat. Rev. Mater. 4 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen B, Li S Z, Zong H X, Ding X D, Sun J, Ma E 2020 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117 16199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lee C, Maresca F, Feng R, Chou Y, Ungar T, Widom M, An K, Poplawsky J D, Chou Y C, Liaw P K, Curtin W A 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yin X, Dou Y K, He X F, Jin K, Wang C L, Dong Y G, Wang C Y, Xue Y F, Yang W 2023 Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett. ) 36 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bacon D J, Osetsky Y N, Rong Z 2006 Philos. Mag. 86 3921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Marian J, Wirth B D, Schäublin R, Odette G R, Perlado J M 2003 J. Nucl. Mater. 323 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rong Z, Osetsky Y N, Bacon D J 2005 Philos. Mag. 85 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nomoto A, Soneda N, Takahashi A, Ishino S 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 林盼栋, 聂君锋, 刘美丹 2022 清华大学学报 (自然科学版) 62 2029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin P D, Nie J F, Liu M D 2022 J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol. ) 62 2029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王瑾, 贺新福, 曹晗, 王东杰, 豆艳坤, 杨文 2021 原子能科学技术 55 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, He X F, Cao H, Wang D J, Dou Y K, Yang W 2021 At. Energy Sci. Technol. 55 1210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王瑾, 贺新福, 曹晗, 贾丽霞, 豆艳坤, 杨文 2021 70 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, He X F, Cao H, Jia L X, Dou Y K, Yang W 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 068701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu M S, Wang Z Q, Wang F, Setyawan W, Long X H, Liu Y, Dong L M, Gao N, Gao F, Wang X L 2023 Acta Mater. 245 118651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li J, Chen H T, Fang Q H, Jiang C, Liu Y, Liaw P K 2020 Int. J. Plast. 133 102819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dou Y K, Cao H, He X F, Gao J, Cao J L, Yang W 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 857 157556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Thompson A P, Aktulga H M, Berger R, Bolintineanu D S, Brown W M, Crozier P S, in't Veld P J, Kohlmeyer A, Moore S G, Nguyen T D, Shan R, Stevens M J, Tranchida J, Trott C, Plimpton S J 2022 Comput. Phys. Commun. 271 108171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Daw M S, Foiles S M, Baskes M I 1993 Mater. Sci. Rep. 9 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Stukowski A 2009 Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18 015012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Qiu R Y, Chen Y C, Liao X C, He X F, Yang W, Hu W Y, Deng H Q 2021 J. Nucl. Mater. 557 153231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chen B, Li S Z, Ding J, Ding X D, Sun J, Ma E 2023 Scr. Mater. 222 115048
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma E 2020 Scr. Mater. 181 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang F L, Balbus G H, Xu S Z, Su Y Q, Shin J, Rottmann P F, Knipling K E, Stinville J C, Mills L H, Senkov O N, Beyerlein I J, Pollock T M, Gianola D S 2020 Science 370 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kubilay R E, Ghafarollahi A, Maresca F, Curtin W A 2021 npj Comput. Mater. 7 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bu Y Q, Wu Y, Lei Z F, Yuan X Y, Wu H H, Feng X B, Liu J B, Ding J, Lu Y, Wang H T, Lu Z P, Yang W 2021 Mater. Today 46 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1714
- PDF下载量: 32
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: