-
偏振成像技术在去除后向散射光方面是有效的. 针对该技术依赖免靶区域以计算后向散射光信息限制其适用范围和实时成像能力的问题, 本文提出了无免靶区域的偏振成像方法. 该方法结合主动偏振成像和透射率去散射模型, 将相机接收到的图像分解为具有偏振信息和无偏振信息的部分, 具有偏振信息的部分采用主动成像模型计算, 而无偏振信息的部分基于Stokes矢量计算. 同时, 结合透射率校正原理实现去散射. 实验和真实世界水下成像结果表明, 本文方法能够有效去除大部分后向散射光, 且具有速率优势, 能够助力实时复杂条件下的水下成像技术, 在海底资源探测与研究等领域具有广阔的应用前景.
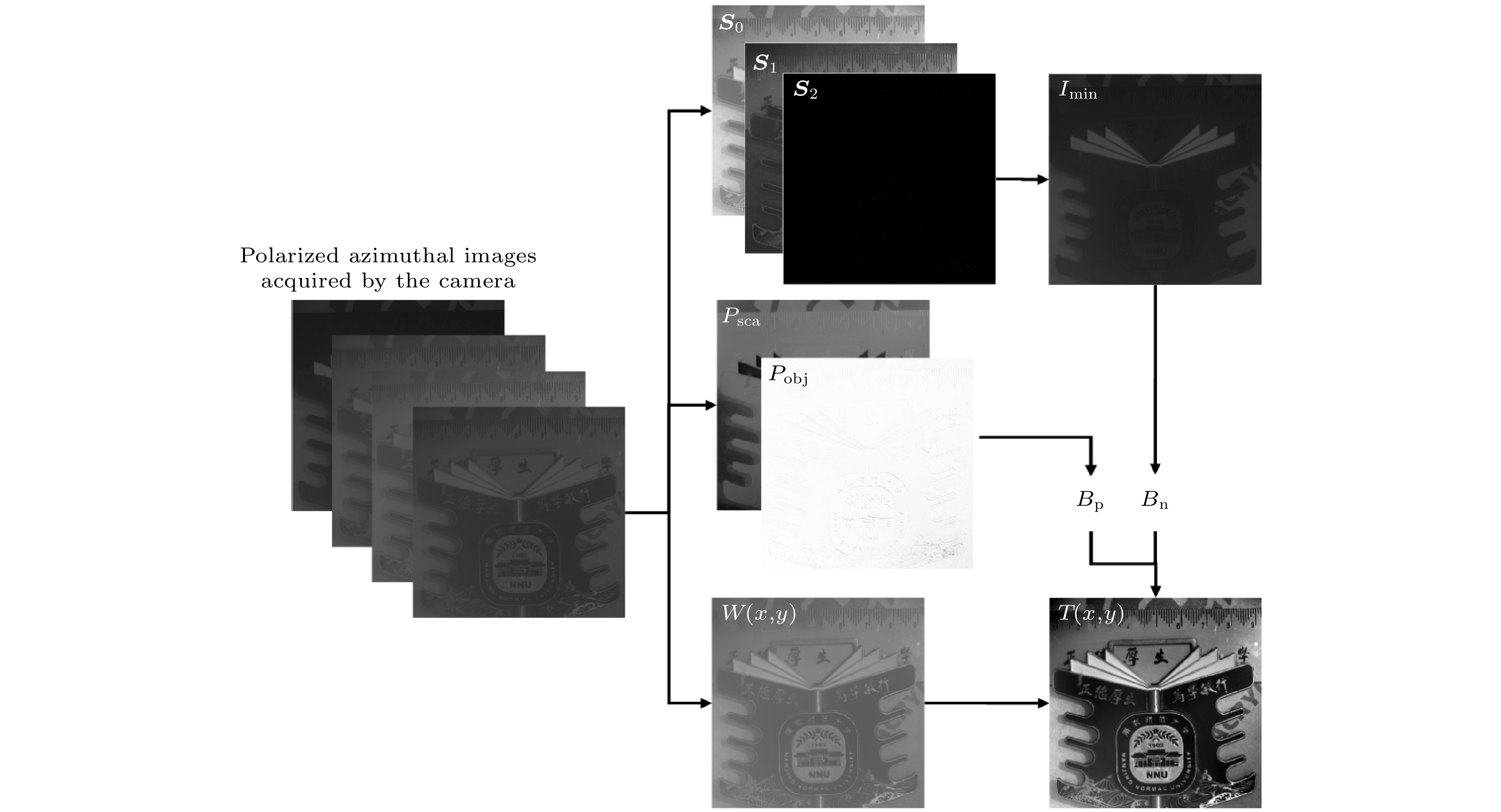
Underwater optical imaging technology possesses broad application prospects in fields such as marine resource exploration, underwater ecological environment monitoring, and seabed topography detection. The technology employs the polarization characteristics of light, particularly those of the background and target, to achieve a clear image. However, the traditional methods rely on target-free regions to compute the backscattered light information, which is infrequently present in the actual scene captured by the camera. Then the full-space resolution of target information light and backscattered light information are required. At this time, the traditional methods may be difficult to adapt in practical application. In this work, an underwater polarization de-scattering method independent of target-free regions is proposed by combining active polarization imaging and transmittance de-scattering model. Initially, the total light intensity within the camera’s field of view is decomposed into its polarized and unpolarized components. By removing the backscattered light with polarized and unpolarized information from the total light intensity, a clear underwater target can be obtained. Based on the active polarization imaging model, the backscattered light with polarization information is calculated, in which the polarization angle of the backscattered light is considered to be zero in the full-space. Thus, the polarization degree of the target information light occupying the camera’s entire field of view can be derived. According to the polarization correlation, the polarization degree of the backscattered light can be characterized, and the intensity of the backscattered light with polarization information in the camera’s entire field of view can also be obtained. Then the unpolarized component is calculated using the minimum intensity image with Stokes vector transformation. Finally, the underwater scene is obtained by combining the transmittance de-scattering principle and introducing adjustment parameters. Experimental and real-world underwater imaging results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively remove the majority of the backscattered light and improve the image contrast and entropy, regardless of whether there are target-free regions. Additionally, this method possesses a certain rate advantage, which can facilitate the real-time complex underwater imaging technology. -
Keywords:
- target-free regions /
- underwater polarization imaging /
- de-scattering /
- transmittance correction
[1] Bailey G, Flemming N 2008 Quat. Sci. Rev. 27 2153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ji T T, Wang G Y 2015 J. Ocean Univ. China 14 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S 2016 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 41 541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li X B, Han Y L, Wang H Y, Liu T G, Chen S C, Hu H F 2022 Front. Phys. 10 815296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] McLean E A, Burris H R, Strand M P 1995 Appl. Opt. 34 4343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jaffe J S 2005 Opt. Express 13 738
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gong W L, Han S S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le M N, Wang G, Zheng H B, Liu J B, Zhou Y, Xu Z 2017 Opt. Express 25 22859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2005 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 管今哥, 朱京平, 田恒, 侯洵 2015 64 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan J G, Zhu J P, Tian H, Hou X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 韩平丽, 刘飞, 张广, 陶禹, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han P L, Liu F, Zhang G, Tao Y, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schechner Y Y, Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang B J, Liu T G, Hu H F, Han J H, Yu M X 2016 Opt. Express 24 9826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hu H F, Zhao L, Huang B J, Li X B, Wang H, Liu T G 2017 IEEE Photonics J. 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 卫毅, 刘飞, 杨奎, 韩平丽, 王新华, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y, Liu F, Yang K, Han P L, Wang X H, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Treibitz T, Schechner Y Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wei Y, Han P L, Liu F, Liu J P, Shao X J 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wei Y, Han P L, Liu F, Shao X P 2021 Opt. Express 29 22275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu H F, Zhao L, Li X B, Wang H, Liu T G 2018 IEEE Photonics J. 10 6900309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 封斐, 吴国俊, 吴亚风, 苗宇宏, 刘博 2020 光学学报 40 2111002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng F, Wu G J, Wu Y F, Miao Y H, Liu B 2020 Acta Opt. Sin. 40 2111002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu F, Cao L, Shao X P, Han P L, Bin X L 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng J, Zhu J, Li H, Zhang X, Guo F, Hou X 2023 Opt. Lasers Eng. 169 107721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Fang M, Cai Y X, Zhang J R 2024 Opt. Express 32 19801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang J J, Wan M J, Cao X Q, Zhang X J, Gu G H, Chen Q 2022 Opt. Express 30 46926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shen L H, Reda M, Zhang X, Zhao Y Q, Kong S G 2024 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62 4202615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pour A M, Seyedarabi H, Jahromi S H A, Javadzadeh A 2020 IEEE Access 8 136668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Coifman R R, Wickerhauser M V 1992 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 38 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yang L M, Liang J, Zhang W F, Ju H J, Ren L Y, Shao X P 2019 Opt. Commun. 438 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
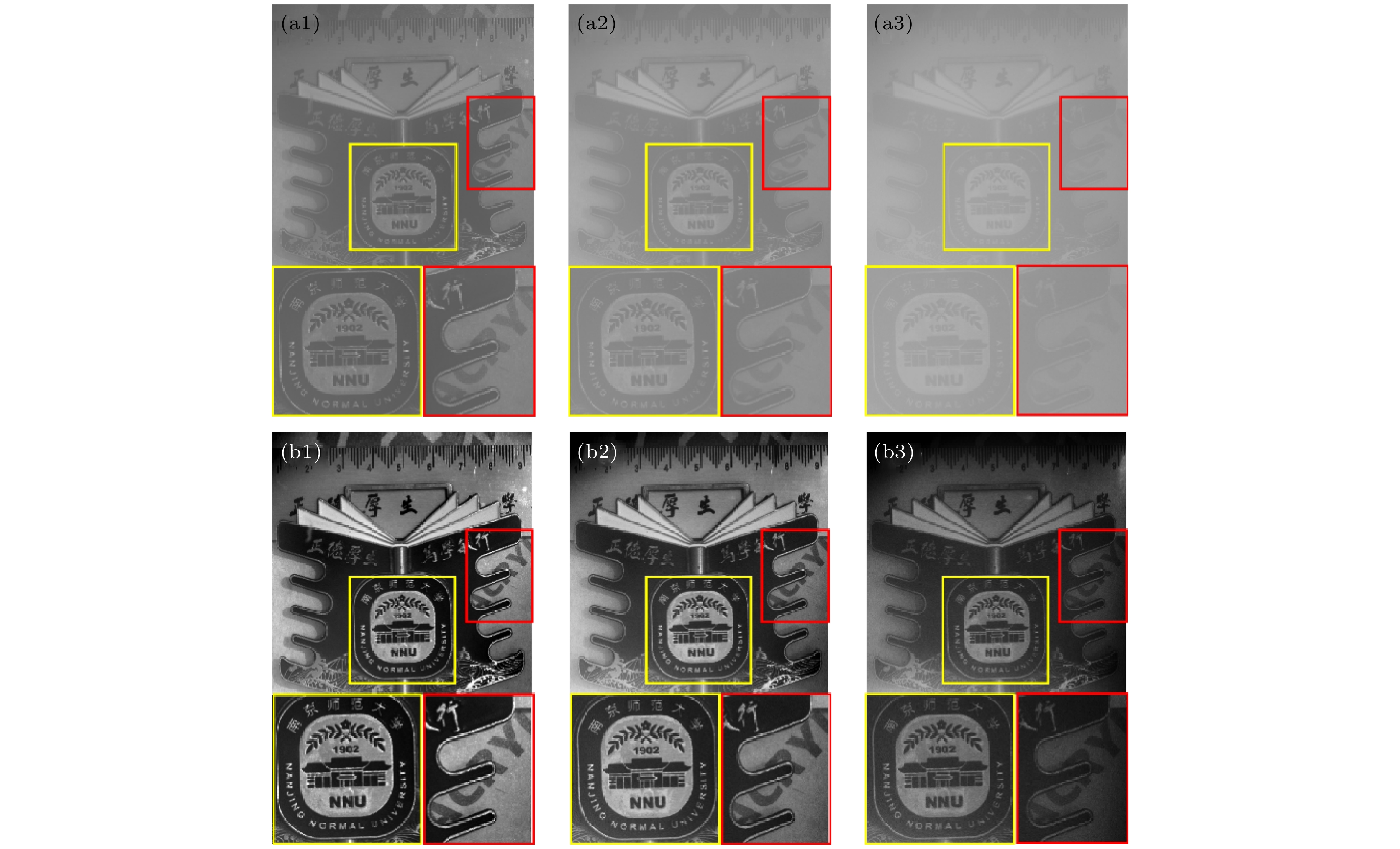
图 3 水下偏振成像实验结果 (a1)—(a3) 强度成像结果, 环境浑浊度为25 NTU, 35 NTU和58 NTU; (b1)—(b3) 本文方法成像结果, 黄色和红色矩形框内展示图像细节
Fig. 3. Results of underwater polarization imaging experiments: (a1)–(a3) The intensity imaging results with ambient turbidity of 25 NTU, 35 NTU and 58 NTU; (b1)–(b3) the imaging results of the proposed method in this paper, the yellow and red rectangles show the imaging details.
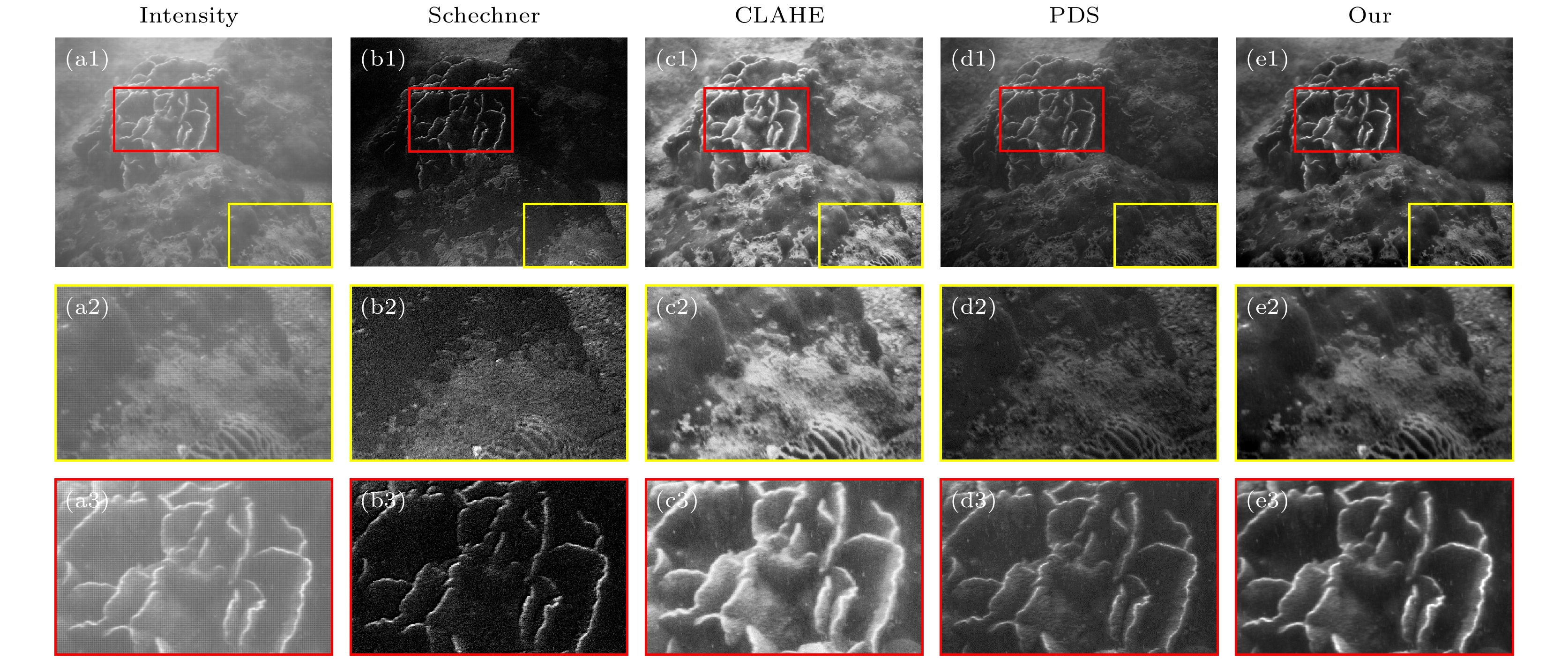
图 4 无免靶区域不同方法成像结果比较 (a1)—(a3) 强度成像; (b1)—(b3) Schechner的方法; (c1)—(c3) CLAHE方法; (d1)—(d3) PDS方法; (e1)—(e3) 本文方法
Fig. 4. Comparison of imaging results using different methods independent of target-free regions: (a1)–(a3) The intensity imaging; (b1)–(b3) Schechner’s method; (c1)–(c3) CLAHE method; (d1)–(d3) PDS method; (e1)–(e3) the proposed method in this paper.
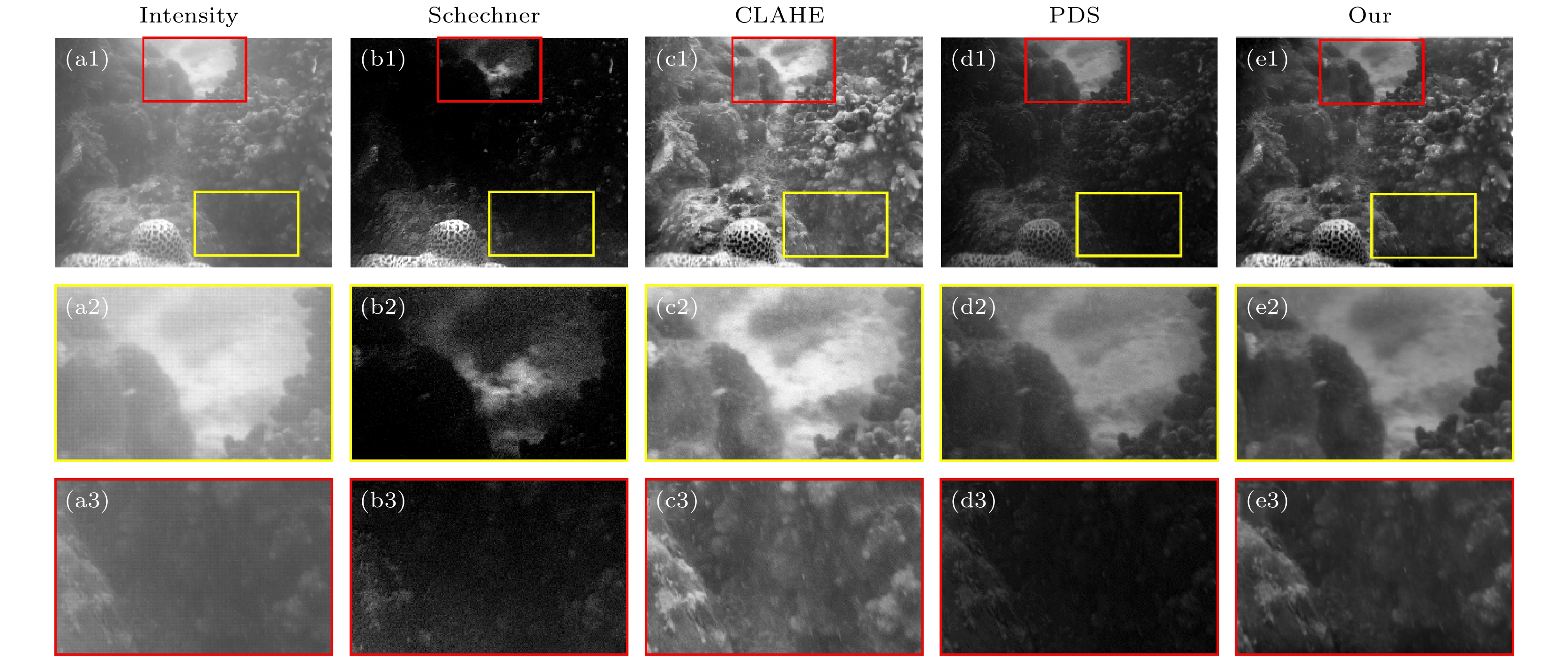
图 5 存在免靶区域不同方法成像结果比较 (a1)—(a3) 强度成像; (b1)—(b3) Schechner的方法; (c1)—(c3) CLAHE方法; (d1)—(d3) PDS方法; (e1)—(e3) 本文方法
Fig. 5. Comparison of imaging results using different methods in the presence of target-free regions: (a1)–(a3) The intensity imaging; (b1)–(b3) Schechner’s method; (c1)–(c3) CLAHE method; (d1)–(d3) PDS method; (e1)–(e3) the proposed method in this paper
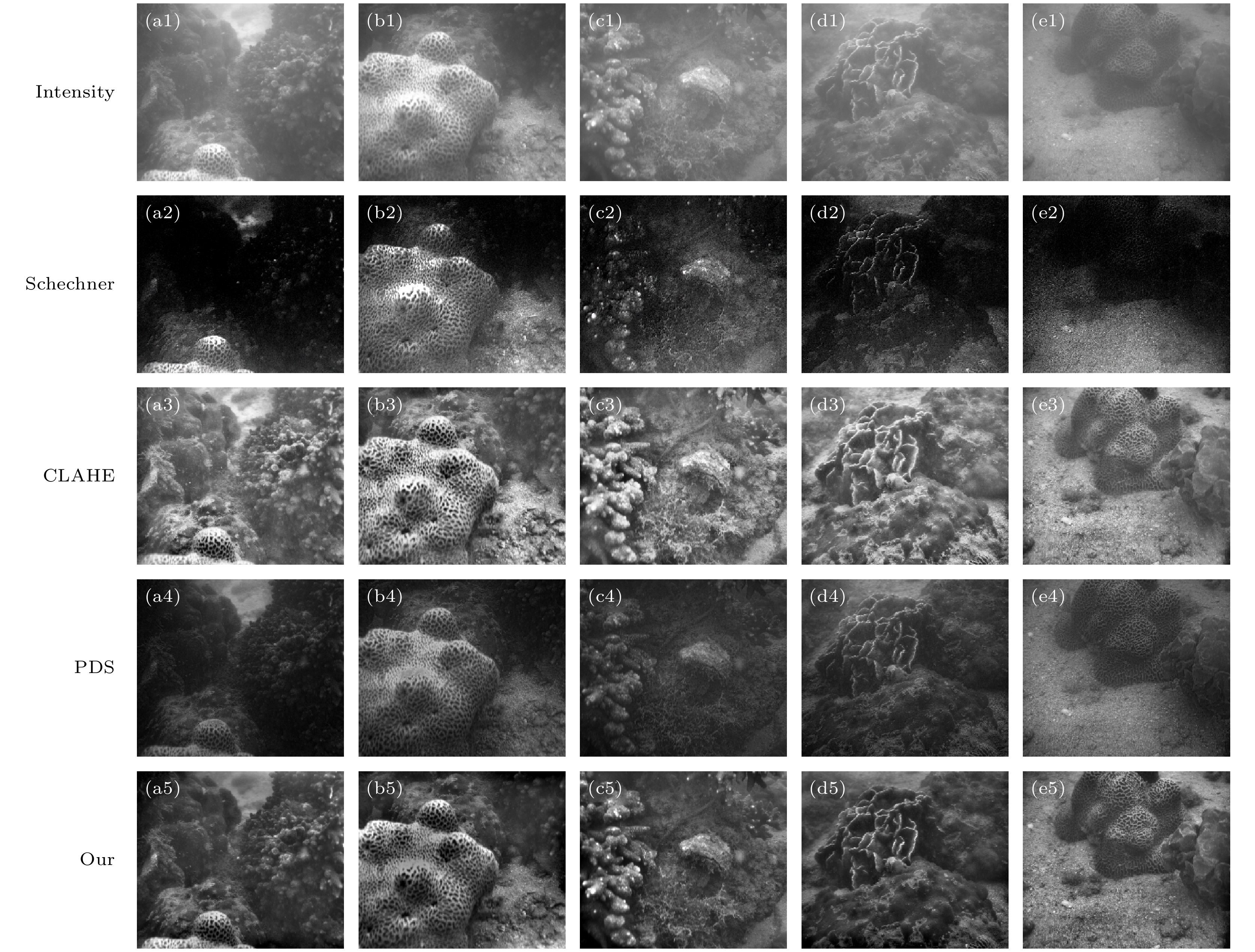
图 6 各种场景不同方法成像结果比较 (a1)—(e1) 强度成像; (a2)—(e2) Schechner的方法; (a3)—(e3) CLAHE方法; (a4)—(e4) PDS方法; (a5)—(e5) 本文方法
Fig. 6. Comparison of imaging results using different methods in various scenes: (a1)–(e1) The intensity imaging; (a2)–(e2) Schechner’s method; (a3)–(e3) CLAHE method; (a4)–(e4) PDS method; (a5)–(e5) the proposed method in this paper.
表 1 图6成像结果定量分析与比较, 最佳值采用加粗标注, 次之采用*标注
Table 1. Quantitative analysis and comparison of imaging results from Fig.6, the best values are highlighted in bold, and the second-best values are marked in *.
Figures Evaluation Intensity Schechner CLAHE PDS Our (a1)—(a5) Entropy 7.0835 5.2074 7.1600 6.3775 6.9319* Contrast 0.2933 –∞ 0.3620 0.7076 0.4968* (b1)—(b5) Entropy 7.1815 7.2357 7.2334 7.0689 7.3007 Contrast 0.3495 –∞ 0.4143 0.6053 0.5608* (c1)—(c5) Entropy 6.6501 6.8566 7.3142 6.0976 6.9915* Contrast 0.1996 0.7476 0.3625 0.3573 0.4523* (d1)—(d5) Entropy 6.6219 6.0931 7.1348 6.5029 6.7891* Contrast 0.1947 –∞ 0.3249 0.4311 0.4566 (e1)—(e5) Entropy 6.8163 6.2458 7.1551 6.9662 7.1863 Contrast 0.2249 –∞ 0.2909 0.3916 0.3725* -
[1] Bailey G, Flemming N 2008 Quat. Sci. Rev. 27 2153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ji T T, Wang G Y 2015 J. Ocean Univ. China 14 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S 2016 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 41 541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li X B, Han Y L, Wang H Y, Liu T G, Chen S C, Hu H F 2022 Front. Phys. 10 815296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] McLean E A, Burris H R, Strand M P 1995 Appl. Opt. 34 4343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jaffe J S 2005 Opt. Express 13 738
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gong W L, Han S S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le M N, Wang G, Zheng H B, Liu J B, Zhou Y, Xu Z 2017 Opt. Express 25 22859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2005 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 管今哥, 朱京平, 田恒, 侯洵 2015 64 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan J G, Zhu J P, Tian H, Hou X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 韩平丽, 刘飞, 张广, 陶禹, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han P L, Liu F, Zhang G, Tao Y, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schechner Y Y, Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang B J, Liu T G, Hu H F, Han J H, Yu M X 2016 Opt. Express 24 9826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hu H F, Zhao L, Huang B J, Li X B, Wang H, Liu T G 2017 IEEE Photonics J. 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 卫毅, 刘飞, 杨奎, 韩平丽, 王新华, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y, Liu F, Yang K, Han P L, Wang X H, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Treibitz T, Schechner Y Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wei Y, Han P L, Liu F, Liu J P, Shao X J 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wei Y, Han P L, Liu F, Shao X P 2021 Opt. Express 29 22275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu H F, Zhao L, Li X B, Wang H, Liu T G 2018 IEEE Photonics J. 10 6900309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 封斐, 吴国俊, 吴亚风, 苗宇宏, 刘博 2020 光学学报 40 2111002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng F, Wu G J, Wu Y F, Miao Y H, Liu B 2020 Acta Opt. Sin. 40 2111002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu F, Cao L, Shao X P, Han P L, Bin X L 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng J, Zhu J, Li H, Zhang X, Guo F, Hou X 2023 Opt. Lasers Eng. 169 107721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Fang M, Cai Y X, Zhang J R 2024 Opt. Express 32 19801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang J J, Wan M J, Cao X Q, Zhang X J, Gu G H, Chen Q 2022 Opt. Express 30 46926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shen L H, Reda M, Zhang X, Zhao Y Q, Kong S G 2024 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62 4202615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pour A M, Seyedarabi H, Jahromi S H A, Javadzadeh A 2020 IEEE Access 8 136668
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Coifman R R, Wickerhauser M V 1992 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 38 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yang L M, Liang J, Zhang W F, Ju H J, Ren L Y, Shao X P 2019 Opt. Commun. 438 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3258
- PDF下载量: 105
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: