-
基于暗通道先验去雾的图像增质方法在目标探测中表现良好, 但其以光强信息为载体, 光学维度单一的不足导致其目标表征效能下降. 本文借助偏振对物理属性的敏感特性, 提出在传统暗通道先验去雾方法中引入偏振信息来增强不同物体之间的辨识程度. 研究了暗通道先验去雾方法中退散射与偏振探测的理论, 并搭建机械式偏振滤波成像设备在雾天环境对所提方法的目标表征功能进行了实验验证. 研究表明, 基于偏振的暗通道先验去雾方法能够同时获取物体的光强与偏振信息, 与传统暗通道先验去雾方法相比, 利用目标与背景的偏振差异能够明显地提高二者对比度. 此研究结果可应用于现有的偏振成像仪器系统, 实现退散射与偏振信息的实时提取, 进一步提高雾天目标探测与表征的效率.The image enhancement method based on dark channel priori defogging performs well in target detection, but it takes the light intensity information as the carrier and the single optical dimension leads the target characterization efficiency to decline. Based on the sensitivity of polarization to physical properties, in this paper a proposal is made that polarization information is introduced into the traditional dark channel priori defogging method to enhance the recognition degree between different objects. The theory of backscattering and polarization detection in dark channel priori defogging method is studied, and the mechanical polarization filtering imaging equipment is built to verify the target characterization function of the proposed method in foggy environment. The research shows that the dark channel priori defogging method based on polarization can obtain the light intensity and polarization information of the object at the same time. Compared with the traditional dark channel priori defogging method, using the polarization difference between the target and the background can significantly improve their contrast. This research result can be applied to the existing polarization imaging instrument system to realize real-time backscattering and polarization information extraction, and further improve the efficiency of target detection and characterization in fog.
-
Keywords:
- polarization /
- haze removal using dark channel prior /
- target representation /
- elimination of scattering
[1] Yi W J, Liu H B, Wang P, Fu M C, Tan J C, Li X J 2017 Opt. Express 25 7392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Huang S S 2021 The 2020 International Symposium on Geographic Information, Energy and Environmental Sustainable Development Tianjin, China, December 26–27, 2020 p012083
[3] 宋强, 孙晓兵, 刘晓, 提汝芳, 黄红莲, 王昊 2021 70 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Q, Sun X B, Liu X, Ti R F, Huang H L, Wang H 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu F L, Li G, Yang S Q, Yan W J, He G G, Lin L 2020 Appl. Spectrosc. 74 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 刘欣宇, 杨苏辉, 廖英琦, 林学彤 2021 70 184205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X Y, Yang S H, Liao Y Q, Lin X T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 184205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Duan D Y, Zhu R, Xia Y J 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O 2011 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33 2341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O 2013 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu H R, Guo J M, Liu Q, Ye L L 2012 Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology Wuhan, China, March 23−25, 2012 p663
[10] Zhang W, Dong L, Pan X, Zhou J, Qin J, Xu W 2019 IEEE Access 7 72492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qu Y F, Zou Z F 2017 Opt. Express 25 25004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liang J, Ren L Y, Qu E S, Hu B L, Wang Y L 2014 Photon. Res. 2 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fang S, Xia X S, Huo X, Chen C W 2014 Opt. Express 22 19523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liang J, Ren L Y, Ju H J, Qu E S, Wang Y L 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 173107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2005 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jacques S L, Roussel S, Samatham R V 2016 J. Biomed. Opt. 21 071115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘飞, 孙少杰, 韩平丽, 赵琳, 邵晓鹏 2021 70 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Sun S J, Han P L, Zhao L, Shao X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schechner Y Y, Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Turner R N, Norris K S 1966 J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 9 535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang B J, Liu T G, Hu H F 2016 Opt. Express 24 9826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 韩平丽, 刘飞, 张广, 陶禹, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han P L, Liu F, Zhang G, Tao Y, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王成, 范之国, 金海红, 汪先球, 华豆 2021 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Fan Z G, Jin H H, Wang X Q, Hua D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen L X, Huang X G, Zhu J H, Li G C, Lan S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 2761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] McCartney E J 1977 Phys. Today 30 76
-
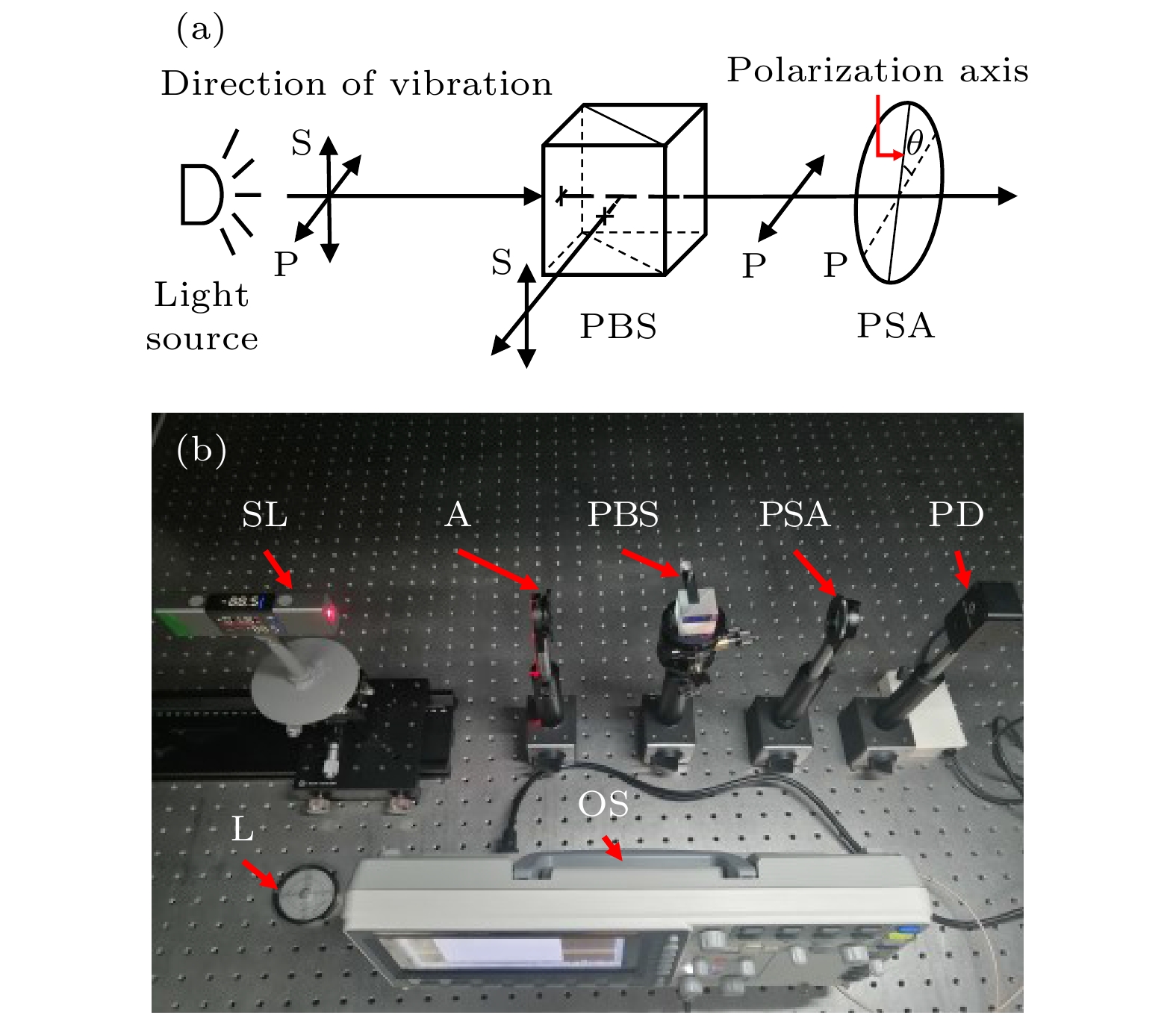
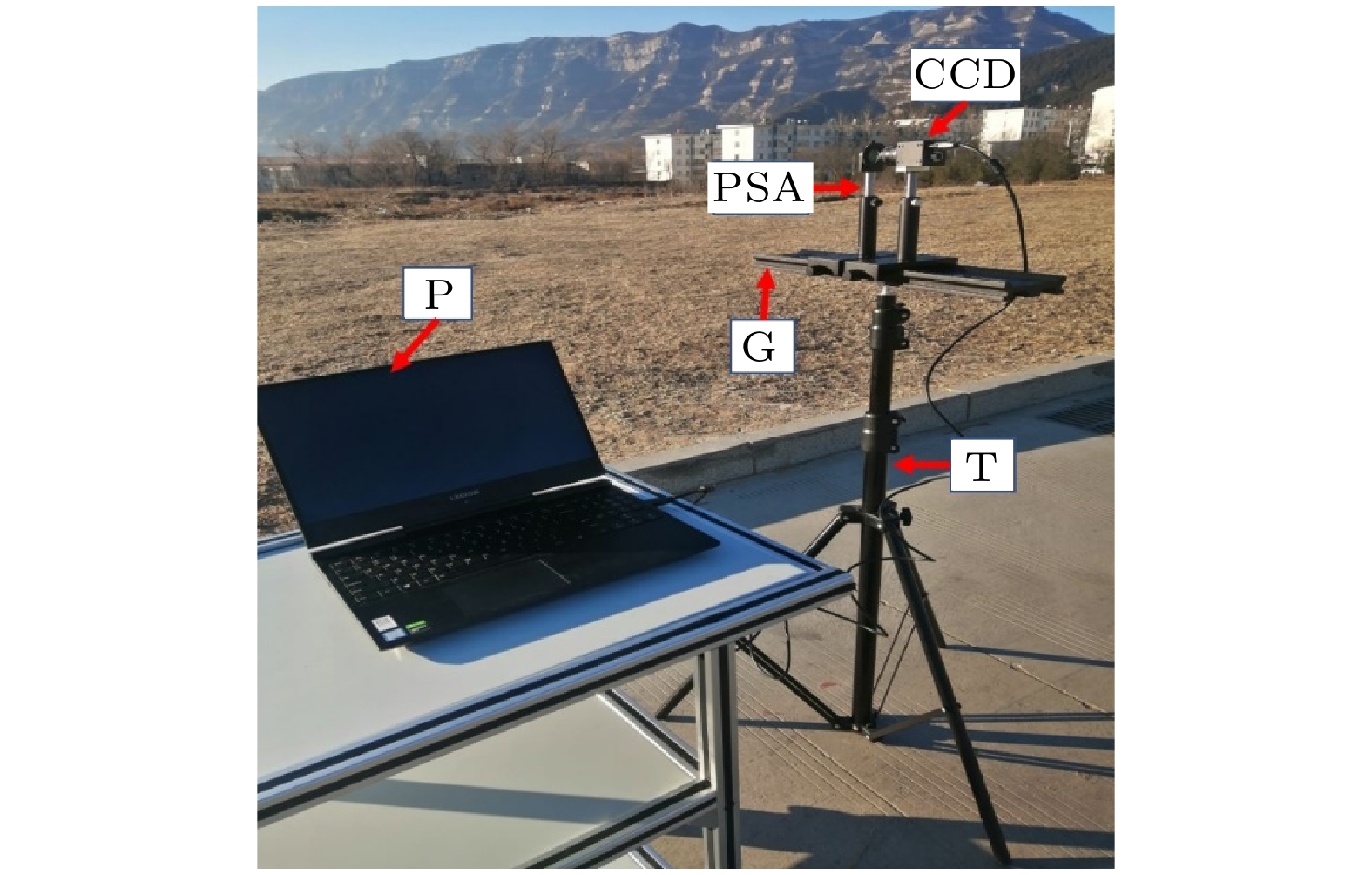
图 2 偏振轴标定系统 (a)原理图; (b)系统光路图 SL, 半导体激光器; A, 衰减片; PBS, 偏振型分光棱镜; PSA, 检偏器; PD, 光电探测器; L, 水平仪; OS, 示波器
Fig. 2. Polarization axis calibration system: (a) Schematic diagram; (b) system physical diagram: SL, semiconductor lasers; A, attenuator; PBS, polarization beam splitter cube; PSA, polarization state analyzer; PD, photodetector; L, leveler; OS, oscilloscope.
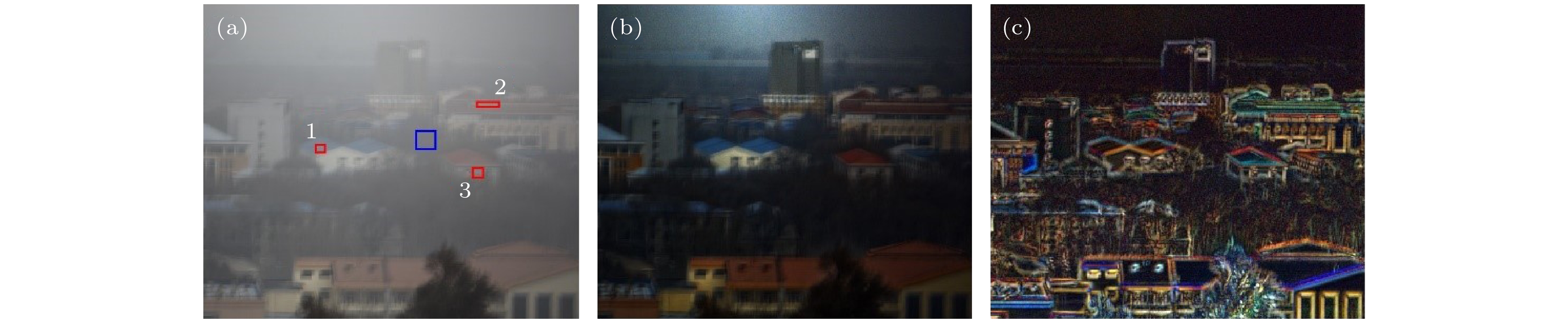
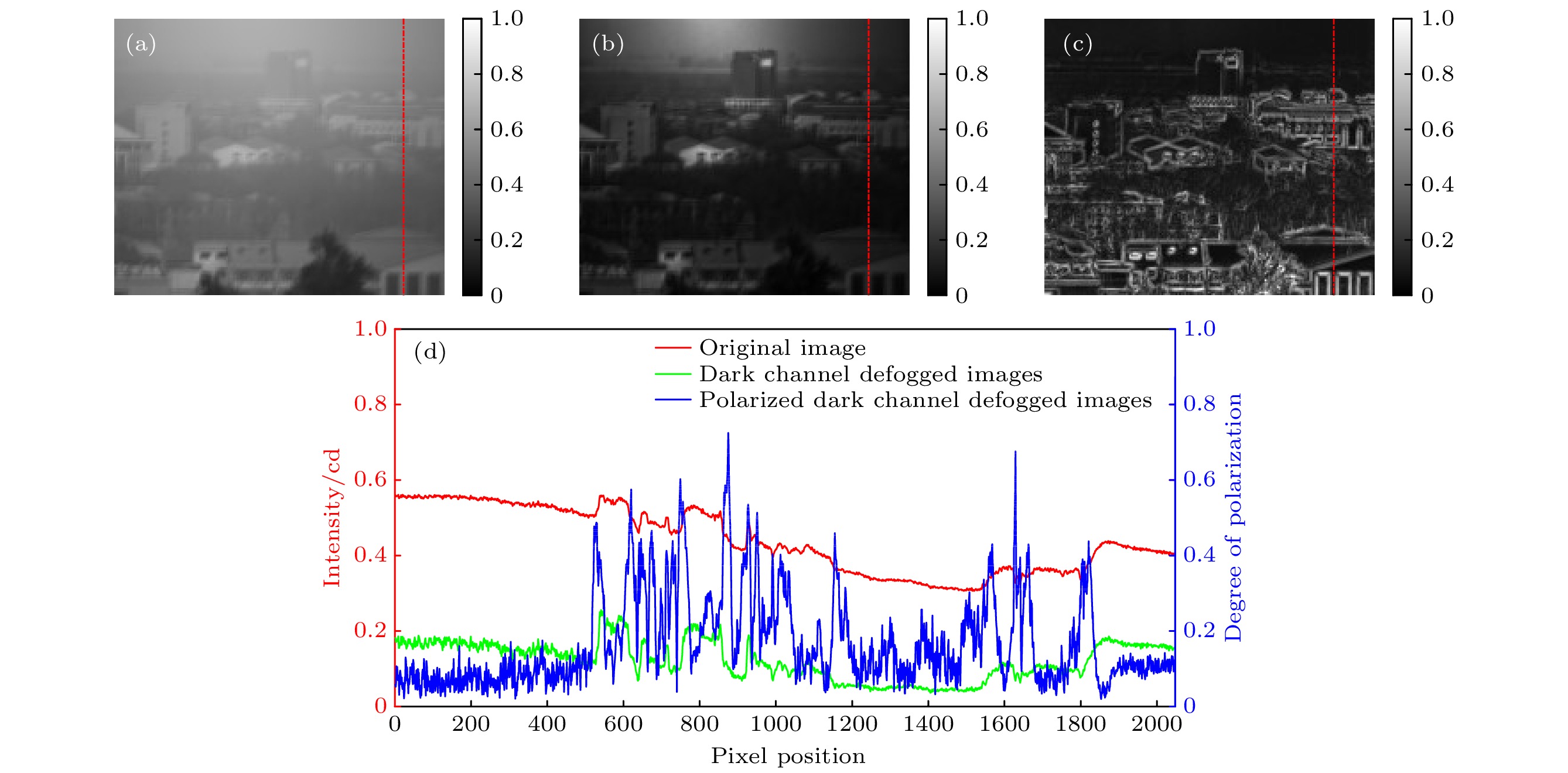
图 9 光强图像与偏振度图像的比较 (a) 原始场景灰度图像; (b)去雾后场景灰度图像; (c)偏振度灰度图像; (d) 不同方案的表征能力
Fig. 9. Comparison of light intensity image and polarization image: (a) Original scene grayscale image; (b) scene grayscale image after defogging; (c) polarization grayscale image; (d) characterization capabilities of different programs.
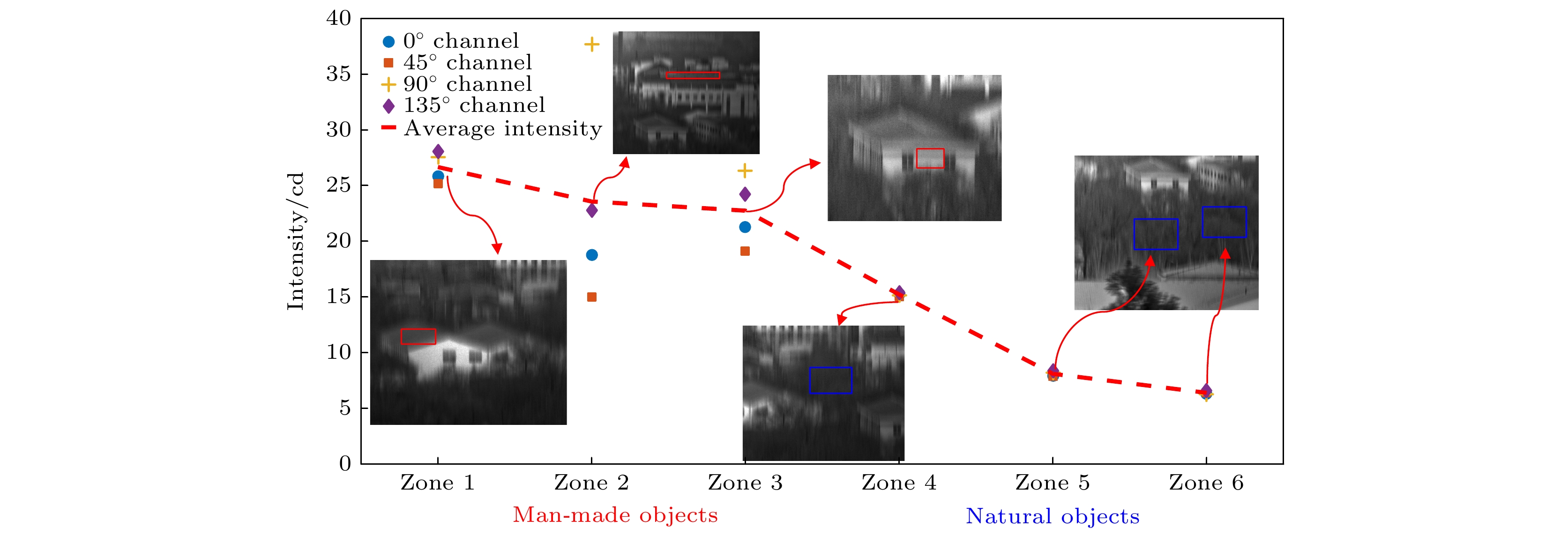
表 1 不同区域的偏振信息记录
Table 1. Polarization information in different regions.
偏振参量 人造目标 非人造目标 1 2 3 4 5 6 s0 53.391 56.469 47.615 30.452 16.187 12.582 s1 0.032 0.334 0.107 0.005 0.017 0.003 s2 0.054 0.138 0.107 0.011 0.030 0.012 PL 0.063 0.361 0.152 0.012 0.035 0.012 表 2 不同人造目标与指定自然目标的对比度
Table 2. Contrast between different man-made objects and designated natural objects.
区域 原始图像 先验去雾 偏振先验去雾 1 0.142 0.343 0.406 2 0.012 0.299 0.424 3 0.010 0.217 0.544 -
[1] Yi W J, Liu H B, Wang P, Fu M C, Tan J C, Li X J 2017 Opt. Express 25 7392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Huang S S 2021 The 2020 International Symposium on Geographic Information, Energy and Environmental Sustainable Development Tianjin, China, December 26–27, 2020 p012083
[3] 宋强, 孙晓兵, 刘晓, 提汝芳, 黄红莲, 王昊 2021 70 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Q, Sun X B, Liu X, Ti R F, Huang H L, Wang H 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu F L, Li G, Yang S Q, Yan W J, He G G, Lin L 2020 Appl. Spectrosc. 74 883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 刘欣宇, 杨苏辉, 廖英琦, 林学彤 2021 70 184205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X Y, Yang S H, Liao Y Q, Lin X T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 184205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Duan D Y, Zhu R, Xia Y J 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O 2011 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33 2341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O 2013 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu H R, Guo J M, Liu Q, Ye L L 2012 Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology Wuhan, China, March 23−25, 2012 p663
[10] Zhang W, Dong L, Pan X, Zhou J, Qin J, Xu W 2019 IEEE Access 7 72492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qu Y F, Zou Z F 2017 Opt. Express 25 25004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liang J, Ren L Y, Qu E S, Hu B L, Wang Y L 2014 Photon. Res. 2 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fang S, Xia X S, Huo X, Chen C W 2014 Opt. Express 22 19523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liang J, Ren L Y, Ju H J, Qu E S, Wang Y L 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 173107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2005 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jacques S L, Roussel S, Samatham R V 2016 J. Biomed. Opt. 21 071115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘飞, 孙少杰, 韩平丽, 赵琳, 邵晓鹏 2021 70 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Sun S J, Han P L, Zhao L, Shao X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schechner Y Y, Narasimhan S G, Nayar S K 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Turner R N, Norris K S 1966 J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 9 535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang B J, Liu T G, Hu H F 2016 Opt. Express 24 9826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 韩平丽, 刘飞, 张广, 陶禹, 邵晓鹏 2018 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han P L, Liu F, Zhang G, Tao Y, Shao X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 054202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王成, 范之国, 金海红, 汪先球, 华豆 2021 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Fan Z G, Jin H H, Wang X Q, Hua D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 104201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen L X, Huang X G, Zhu J H, Li G C, Lan S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 2761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] McCartney E J 1977 Phys. Today 30 76
计量
- 文章访问数: 8573
- PDF下载量: 261
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: