-
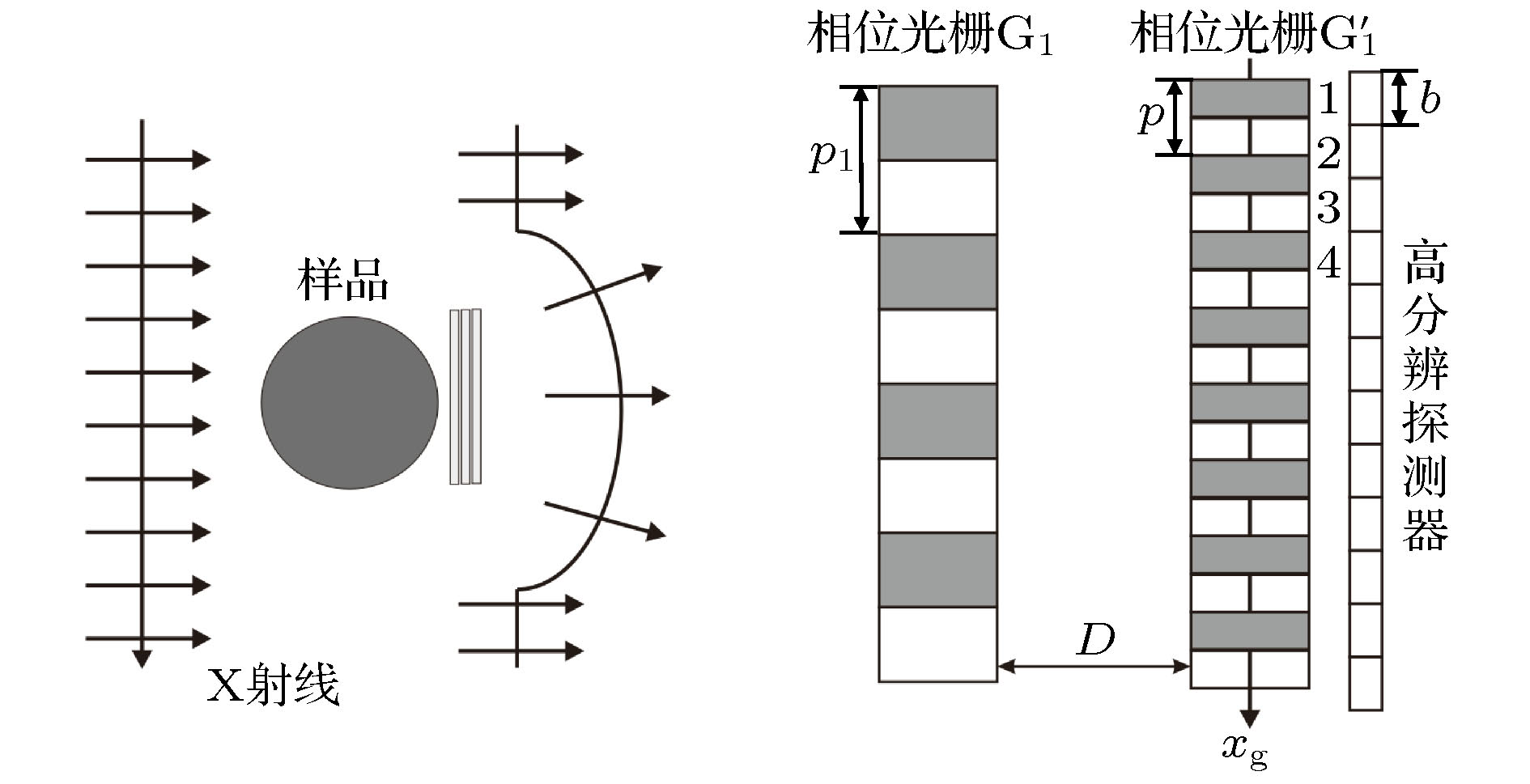
X射线光栅微分相位衬度成像技术可以观察到常规吸收衬度成像难以分辨的弱吸收物质的精细结构信息, 因而在医学、材料学等研究领域具有巨大的应用前景. 但传统的X射线光栅微分相位衬度成像技术由于采用分析光栅作为空间滤波器, 需要采用相位步进法扫描分析光栅来获得样品的多张投影图像才能够分离出样品的吸收、折射和散射信息, 因此存在样品曝光时间长、辐射剂量高以及X射线光通量利用率低等问题, 限制了其在各个学科领域的应用研究. 为克服上述问题, 本文提出一种基于免分析光栅相位衬度成像系统的一次曝光样品信息提取算法. 该算法只需要利用一块相位光栅, 进而采用高分辨探测器进行样品投影数据的一次采集即可提取样品的吸收、折射和散射信息. 理论和模拟研究结果表明: 与传统相位步进法相比, 该算法具有样品信息提取精度高, 且不受光栅的自成像周期需为探测器像素尺寸的整数倍条件的限制. 此外, 该算法还能够有效地减少对生物样品的辐射损伤, 因此在生物医学成像等研究领域中具有广泛的应用前景.X-ray differential phase contrast imaging technology can reveal the weakly absorbing fine structure which cannot be observed by the conventional X-ray absorption contrast imaging. Hence, it has potential applications in many fields such as medical science, and material science. But in the traditional X-ray grating differential phase contrast imaging system, the analyser grating is used as a spatial filter, and needs to be phase stepped, then multiple exposures are required for information extraction. Thus this leads to high-dose radiation exposure and low efficiency of X-ray utilization. All these disadvantages limit its application in various disciplines. In order to cope with the above issues, a new algorithm based on single-shot grating differential phase contrast imaging system without analyzer grating is proposed. In such a system the absorption, refraction and scattering information can be obtained from one projective image of the sample acquired by a high-resolution detector. The reliability of this new algorithm is confirmed by numerical simulation. Compared with the phase stepping algorithm, the proposed algorithm can provide very accurate and reliable information extraction results without requiring the grating period to match with detector pixel size. It facilitates the reduction of the radiation damage to sample. We emphasize that this method is highly compatible with the future X-ray phase contrast imaging clinical applications.
-
Keywords:
- X-ray phase-contrast imaging /
- phase grating /
- one exposure /
- information separation
[1] Momose A, Kawamoto S, Koyama I, Hamaishi Y, Takai K, Suzuki Y 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 L866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, David C 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu P P, Zhang K, Wang Z L, Liu Y J, Liu X S, Wu Z Y, McDonald S A, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2010 P. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 107 13576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Endrizzi M, Astolfo A, Vittoria F A, Millard T P, Olivo A 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 25466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fu J, Shi X H, Guo W, Peng P 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 1113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei C X, Wu Z, Wali F, Wei W B, Bao Y, Luo R H, Wang L, Liu G, Tian Y C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ge Y S, Li K, Garrett J, Chen G H 2014 Opt. Express 22 14246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Balles A, Fella C, Dittmann J, Wiest W, Zabler S, Hanke R 2016 XRM 2014: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on X-Ray Microscopy Melbourne, Austalia, January 28, 2016 p020043
[9] Marathe S, Zdora M C, Zanette I, Cipiccia S, Rau C 2017 Developments in X-ray Tomography XI San Diego, US, October 11, 2017 p103910S
[10] Wen H H, Bennett E E, Kopace R, Stein A F, Pai V 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bennett E E, Kopace R, Stein A F, Wen H 2010 Med. Phys. 37 6047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Berry M V, Klein S 1996 J. Mod. Opt. 43 2139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wernick M N, Wirjadi O, Chapman D, Zhong Z, Galatsanos N P, Yang Y, Brankov J G, Oltulu O, Anastasio M A, Muehleman C 2003 Phys. Med. Biol. 48 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li P, Zhang K, Bao Y, Ren Y, Ju Z, Wang Y, He Q, Zhu Z, Huang W, Yuan Q 2016 Opt. Express 24 5829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Weitkamp T, Diaz A, David C, Pfeiffer F, Stampanoni M, Cloetens P, Ziegler E 2005 Opt. Express 13 6296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Diemoz P C, Coan P, Zanette I, Bravin A, Lang S, Glaser C, Weitkamp T 2011 Opt. Express 19 1691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chou C Y, Anastasio M A, Brankov J G, Wernick M N, Brey E M, Connor Jr D M, Zhong Z 2007 Phys. Med. Biol. 52 1923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Pfeiffer F, Bech M, Bunk O, Kraft P, Eikenberry E F, Brönnimann C, Grünzweig C, David C 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Z T, Kang K J, Huang Z F, Chen Z Q 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 094105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Momose A, Yashiro W, Takeda Y, Suzuki Y, Hattori T 2006 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 5254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Oltulu O, Zhong Z, Hasnah M, Wernick M N, Chapman D 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 2152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 钱晓凡 2015 信息光学数字实验室 (Matlab版) (北京: 科学出版社) 第036039页
Qian X F 2015 Information Optics Digital Laboratory (Matlab Ed.) p036039(Beijing: Science Press) (in Chinese)
[23] 王振天 2010 博士论文 (北京: 清华大学)
Wang Z T 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Tsinghua University) (in Chinese)
[24] Huang Z F, Kang K J, Zhang L, Chen Z Q, Ding F, Wang Z T, Fang Q G 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 013815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 模拟所用的样品示意图. 样品由直径为0.461 mm PMMA圆柱状和PMMA后不同厚度(0—3层)的纸组成, 其中PMMA圆柱状对X光具有吸收和折射效应, 而纸张对X光只有散射效应
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the simulation sample. The simulation sample has a 0.46 mm diameter PMMA cylinder that combined refraction and absorption effects. The PMMA cylinder overlie paper layers (0−3 layers) that exhibit the scattering effects.
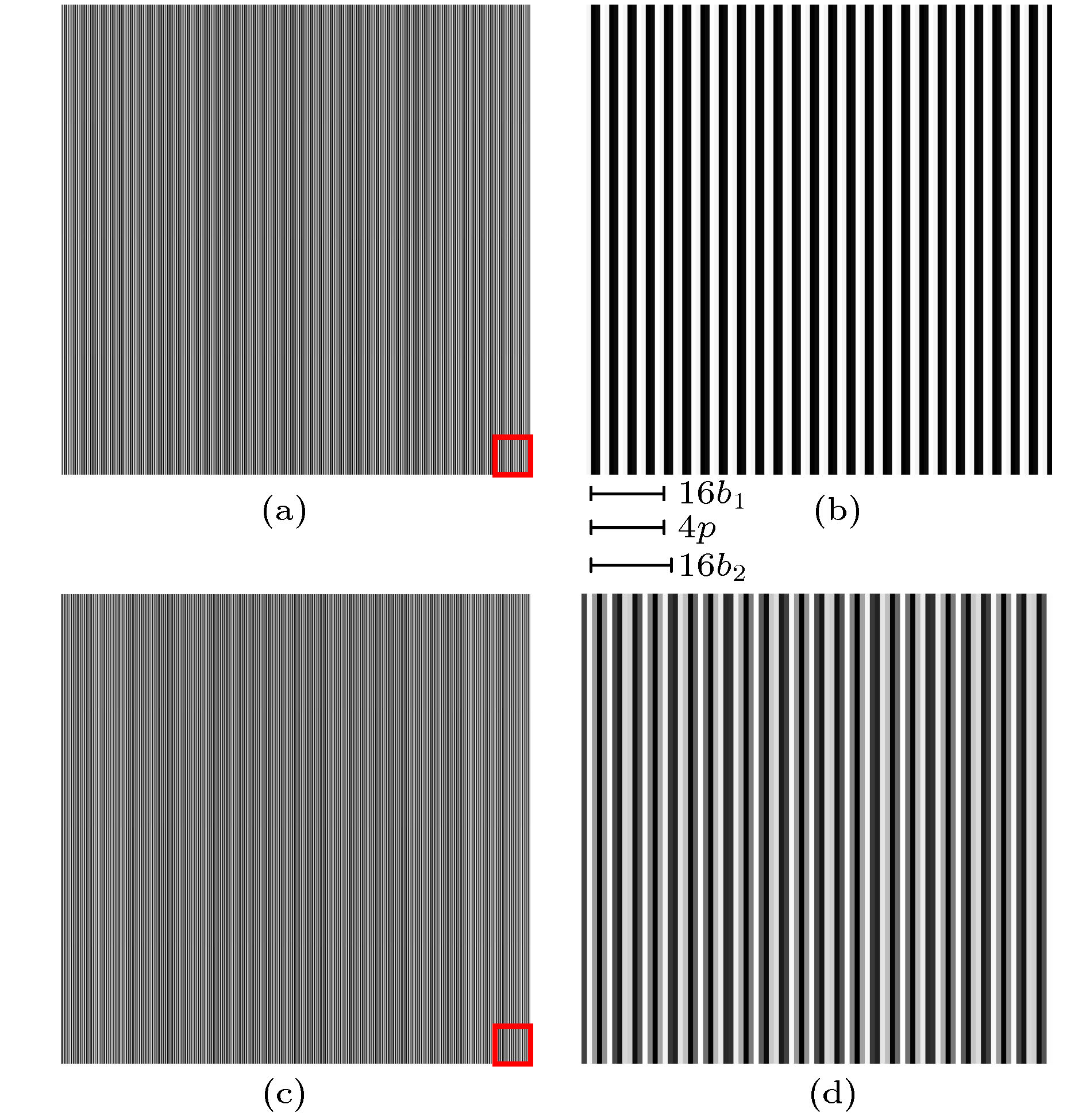
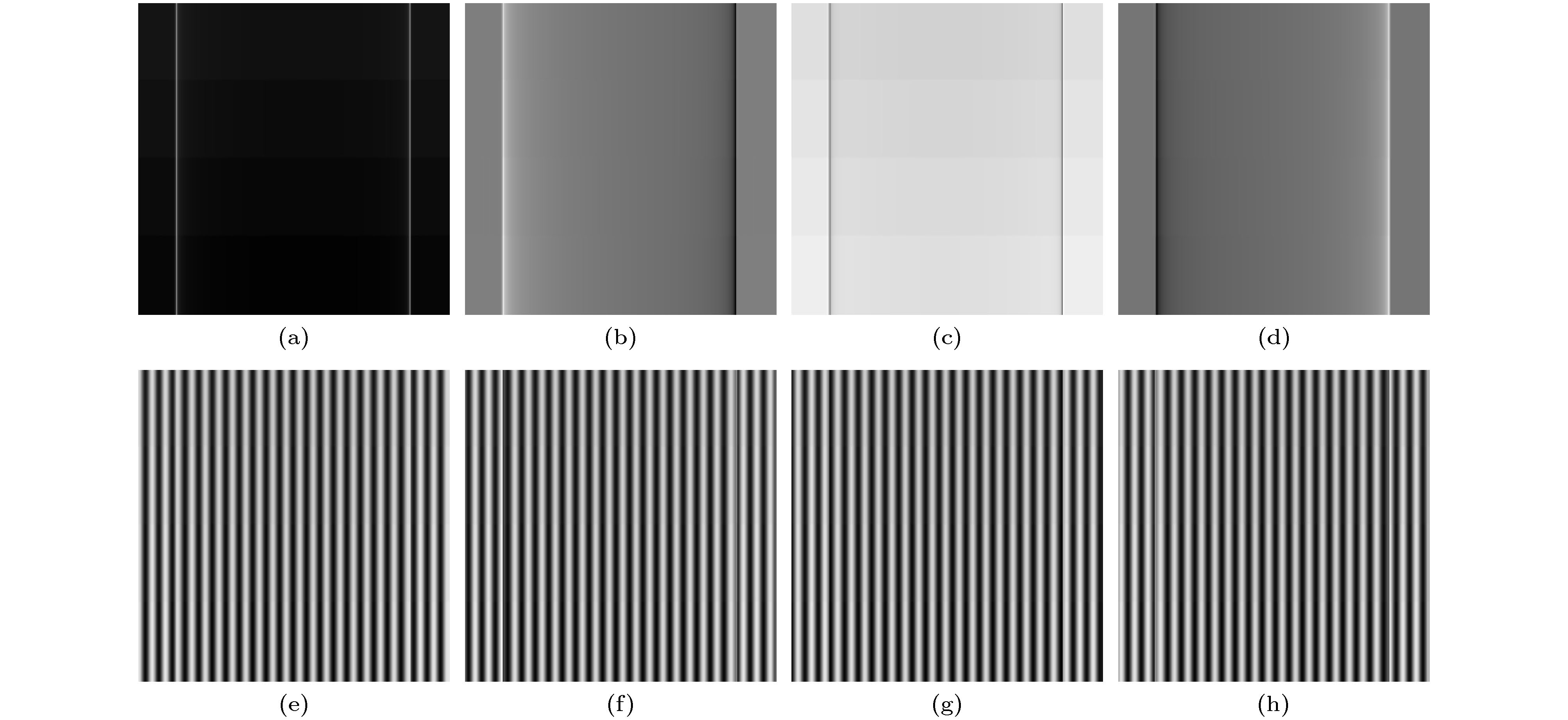
图 4 探测器上的样品投影图 (a) 探测器像素尺寸为0.60 μm (α = 0)时模拟样品的投影图像; (b) 图(a)的局部(红框内)放大图; (c) 探测器像素尺寸为0.66 μm (α ≠ 0)时模拟样品的投影图像; (d) 图(c)的局部放大图
Fig. 4. The projective images of the simulation sample: (a) The projective image of the simulation sample with pixel size of 0.60 μm (α = 0); (b) local enlarged drawing of Fig. (a); (c) the projective image of the simulation sample with pixel size of 0.66 μm (α ≠ 0); (d) local enlarged drawing of Fig. (c).
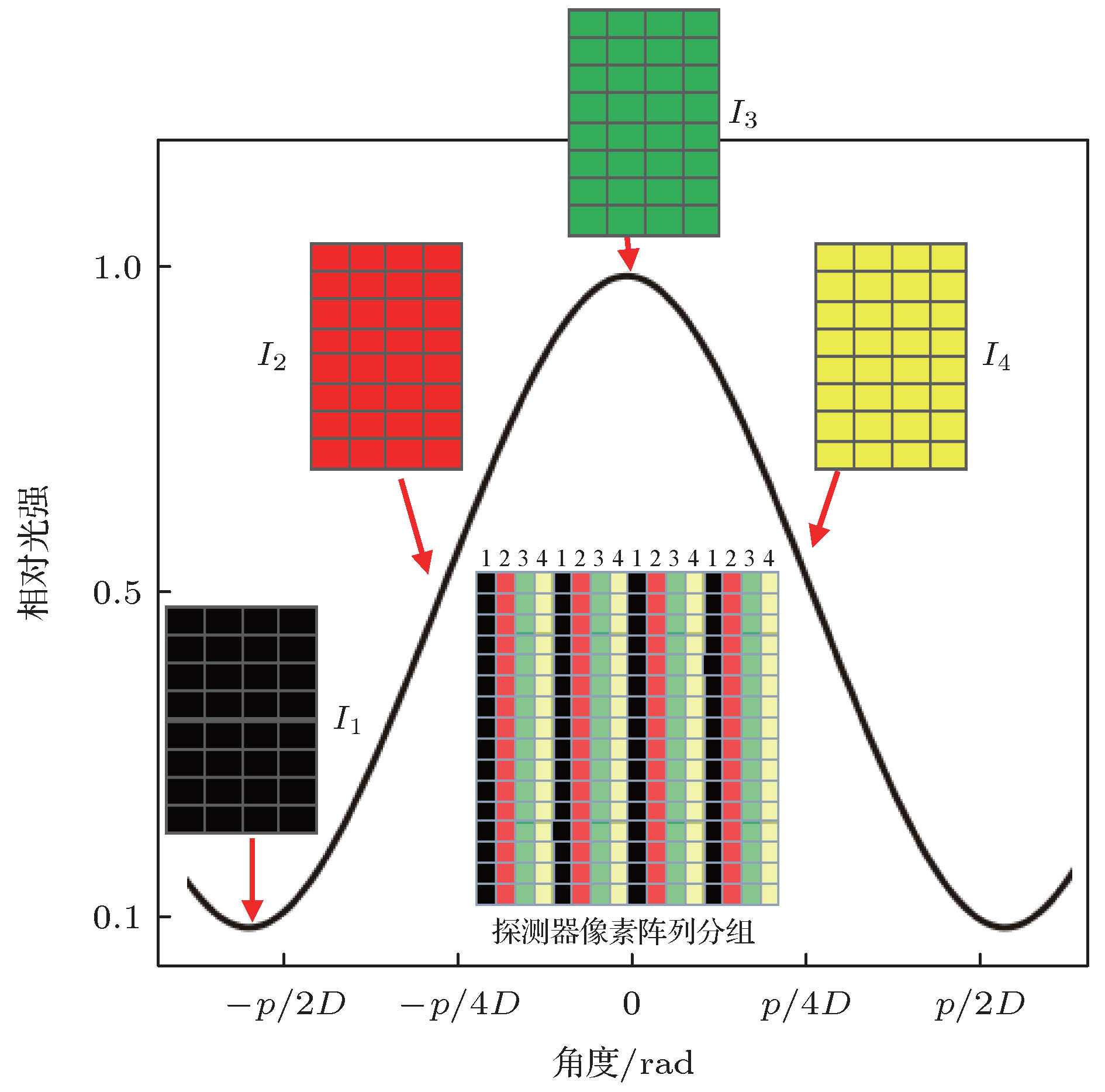
图 5 由原始的样品投影图组成的4张新图像 (a)—(d) 探测器像素尺寸为0.60 μm (α = 0)时所得到的4张新投影图; (e)—(h) 探测器像素尺寸为0.66 μm (
$\alpha \ne {\rm{0}}$ )时所得到的4张新投影图Fig. 5. Four new images extracted from one original projective image: (a)−d) Contain four new images with the pixel size of 0.60 μm (α = 0); (e)−(h) contain four new images with the pixel size of 0.66 μm (α ≠ 0).
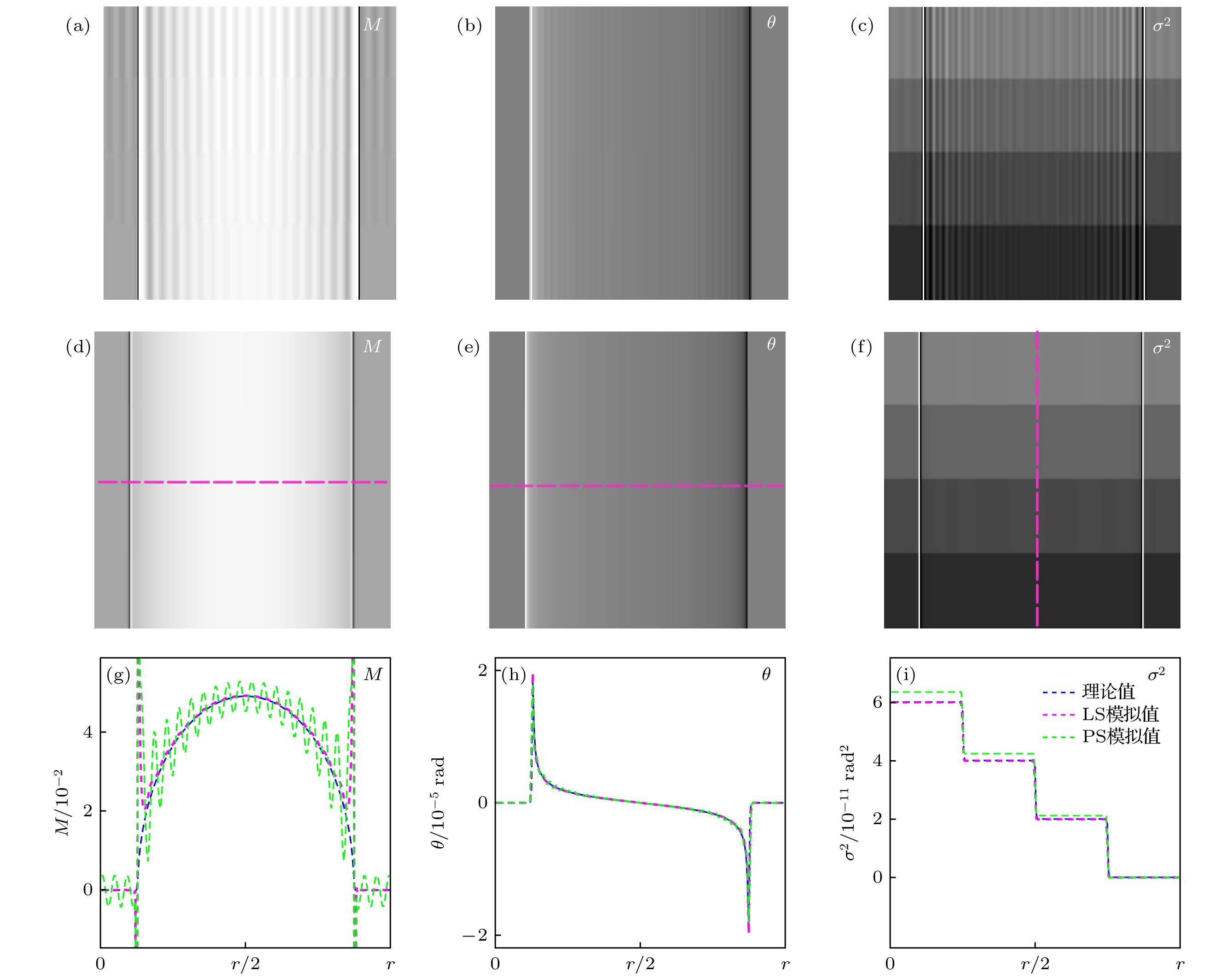
图 6 探测器像素尺寸为0.60 μm时模拟样品的信息提取结果 (a)—(c) PS算法时提取的吸收、折射和散射信息; (d)—(f) LS算法时提取的吸收、折射和散射信息; (g)—(i) 在虚线位置处(PS算法(绿色)和LS算法(紫色))的提取的吸收、折射和散射信息与理论值(蓝色)的对比图
Fig. 6. Sample information extracted with pixel size of 0.60 μm: (a)−(c) Depict the absorption, refraction and scattering information of the simulated sample obtained by PS algorithm; (d)−(f) depict the absorption, refraction and scattering information obtained by LS algorithm; (g)−(i) are profiles of the absorption, refraction and scattering images extracted by LS (purple) and PS (green) at the dotted lines in (a)−(f), as well as the theoretical values (blue).
图 7 探测器像素尺寸为0.66 μm时模拟用样品的信息提取结果 (a)—(c) PS算法时提取的吸收、折射和散射信息; (d)—(f) LS算法时提取的吸收、折射和散射信息; (g)—(i) 在虚线位置处(PS算法(绿色)和LS算法(紫色))的提取的吸收、折射和散射信息与理论值(蓝色)的对比图
Fig. 7. Sample information extracted with pixel size of 0.66 μm: (a)−(c) Depict the absorption, refraction and scattering information of the simulated sample obtained by PS algorithm; (d)−(f) depict the absorption, refraction and scattering information obtained by LS algorithm; (g)−(i) are profiles of the absorption, refraction and scattering images extracted by LS (purple) and PS (green) at the dotted lines in Fig. (a)−(f), as well as the theoretical values (blue).
图 8 不同像素尺寸的探测器提取样品的吸收、折射和散射信息 (a)—(c) 利用PS算法提取的样品吸收、折射和散射信息的强度曲线; (d)—(f) 利用LS算法提取的样品吸收、折射和散射信息的强度曲线
Fig. 8. The absorption, refraction, and scattering information of the simulated sample with different pixel sizes: (a)−(c) Depict the profiles of extracted absorption, refraction and scattering images with different pixel sizes by PS algorithm; (d)−(f) depict the profiles of extracted absorption, refraction and scattering images with different pixel sizes by LS algorithm.
表 1 PS和LS算法的理论值和提取值的平均绝对误差
Table 1. Mean absolute error of theoretical and extracted information by PS and LS algorithm.
探测器的
像素尺寸M/${10^{ - 4}}$ $\theta $/${10^{ - 9}}\;{\rm{ rad}}$ ${\sigma ^2}/{10^{ - 13}}\;{\rm{ ra}}{{\rm{d}}^{\rm{2}}}$ PS LS PS LS PS LS 0.60 μm 2.10 2.10 4.53 4.53 1.36 1.36 0.66 μm 43.00 6.08 115.92 13.80 35.80 5.90 -
[1] Momose A, Kawamoto S, Koyama I, Hamaishi Y, Takai K, Suzuki Y 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 L866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, David C 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu P P, Zhang K, Wang Z L, Liu Y J, Liu X S, Wu Z Y, McDonald S A, Marone F, Stampanoni M 2010 P. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 107 13576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Endrizzi M, Astolfo A, Vittoria F A, Millard T P, Olivo A 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 25466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fu J, Shi X H, Guo W, Peng P 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 1113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wei C X, Wu Z, Wali F, Wei W B, Bao Y, Luo R H, Wang L, Liu G, Tian Y C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 108701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ge Y S, Li K, Garrett J, Chen G H 2014 Opt. Express 22 14246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Balles A, Fella C, Dittmann J, Wiest W, Zabler S, Hanke R 2016 XRM 2014: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on X-Ray Microscopy Melbourne, Austalia, January 28, 2016 p020043
[9] Marathe S, Zdora M C, Zanette I, Cipiccia S, Rau C 2017 Developments in X-ray Tomography XI San Diego, US, October 11, 2017 p103910S
[10] Wen H H, Bennett E E, Kopace R, Stein A F, Pai V 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bennett E E, Kopace R, Stein A F, Wen H 2010 Med. Phys. 37 6047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Berry M V, Klein S 1996 J. Mod. Opt. 43 2139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wernick M N, Wirjadi O, Chapman D, Zhong Z, Galatsanos N P, Yang Y, Brankov J G, Oltulu O, Anastasio M A, Muehleman C 2003 Phys. Med. Biol. 48 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li P, Zhang K, Bao Y, Ren Y, Ju Z, Wang Y, He Q, Zhu Z, Huang W, Yuan Q 2016 Opt. Express 24 5829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Weitkamp T, Diaz A, David C, Pfeiffer F, Stampanoni M, Cloetens P, Ziegler E 2005 Opt. Express 13 6296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Diemoz P C, Coan P, Zanette I, Bravin A, Lang S, Glaser C, Weitkamp T 2011 Opt. Express 19 1691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chou C Y, Anastasio M A, Brankov J G, Wernick M N, Brey E M, Connor Jr D M, Zhong Z 2007 Phys. Med. Biol. 52 1923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Pfeiffer F, Bech M, Bunk O, Kraft P, Eikenberry E F, Brönnimann C, Grünzweig C, David C 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Z T, Kang K J, Huang Z F, Chen Z Q 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 094105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Momose A, Yashiro W, Takeda Y, Suzuki Y, Hattori T 2006 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 5254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Oltulu O, Zhong Z, Hasnah M, Wernick M N, Chapman D 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 2152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 钱晓凡 2015 信息光学数字实验室 (Matlab版) (北京: 科学出版社) 第036039页
Qian X F 2015 Information Optics Digital Laboratory (Matlab Ed.) p036039(Beijing: Science Press) (in Chinese)
[23] 王振天 2010 博士论文 (北京: 清华大学)
Wang Z T 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Tsinghua University) (in Chinese)
[24] Huang Z F, Kang K J, Zhang L, Chen Z Q, Ding F, Wang Z T, Fang Q G 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 013815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8199
- PDF下载量: 184
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: