-
The spatial chirp based single-shot pump-probe technique represents a pivotal technology for studying electron non-equilibrium dynamics in warm dense matter created with intense laser pulses. Notably, its time resolution can reach tens of femtoseconds. In this work, we introduce the single-shot measurement technique of ac conductivity of warm dense matter, as well as a detailed account of the experimental setup. In addition, the main factors limiting the time resolution of the system are discussed in depth. We show the system can achieve a resolution of 13.8 femtoseconds. Nevertheless, during practical application, several aspects, namely the calibration of the zero-delay, the depth of field of the imaging system, and the low-pass filtering effect inherent in the imaging system, will exert a substantial influence on the time-resolution. This research has important reference for enhancing the time accuracy of single-shot measurement of ac conductivity of warm dense matter. Moreover, it serves as a potent tool for the in-depth study of the ultrafast dynamic processes of materials under strong-field conditions.
[1] 陈其峰, 顾云军, 郑君, 李江涛, 李治国, 权伟龙, 付志坚, 李成军 2017 科学通报 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Zheng J, Li J T, Li Z G, Quan W L, Fu Z J, Li C J 2017 Chin. Sci. Bull. 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kang D, Dai J 2018 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30 073002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ichimaru S 1982 Rev. Mod. Phys. 54 1017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Koenig M, Benuzzi-Mounaix A, Ravasio A, Vinci T, Ozaki N, Lepape S, Batani D, Huser G, Hall T, Hicks D, MacKinnon A, Patel P, Park H S, Boehly T, Borghesi M, Kar S, Romagnani L 2005 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 B441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Falk K 2018 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 6 e59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 康冬冬, 曾启昱, 张珅, 王小伟, 戴佳钰 2020 强激光与粒子束 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang D D, Zeng Q Y, Zhang S, Wang X W, Dai J Y 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lee R W, Moon S J, Chung H K, Rozmus W, Baldis H A, Gregori G, Cauble R C, Landen O L, Wark J S, Ng A, Rose S J, Lewis C L, Riley D, Gauthier J C, Audebert P 2003 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20 770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu D, Yu W, Sheng Z M, Fritzsche S, He X T 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 051202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fletcher L B, Lee H J, Döppner T, Galtier E, Nagler B, Heimann P, Fortmann C, LePape S, Ma T, Millot M, Pak A, Turnbull D, Chapman D A, Gericke D O, Vorberger J, White T, Gregori G, Wei M, Barbrel B, Falcone R W, Kao C C, Nuhn H, Welch J, Zastrau U, Neumayer P, Hastings J B, Glenzer S H 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Graziani F, Moldabekov Z, Olson B, Bonitz M 2022 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 62 e202100170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dornheim T, Böhme M, Kraus D, Döppner T, Preston T R, Moldabekov Z A, Vorberger J 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 7911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mercadier L, Benediktovitch A, Krušič Š, Kas J J, Schlappa J, Agåker M, Carley R, Fazio G, Gerasimova N, Kim Y Y, Le Guyader L, Mercurio G, Parchenko S, Rehr J J, Rubensson J E, Serkez S, Stransky M, Teichmann M, Yin Z, Žitnik M, Scherz A, Ziaja B, Rohringer N 2024 Nat. Phys. 20 1564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Forsman A, Ng A, Chiu G, More R M 1998 Phys. Rev. E 58 R1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ping Y, Correa A A, Ogitsu T, Draeger E, Schwegler E, Ao T, Widmann K, Price D F, Lee E, Tam H, Springer P T, Hanson D, Koslow I, Prendergast D, Collins G, Ng A 2010 High Energy Density Phys. 6 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ofori-Okai B K, Descamps A, McBride E E, Mo M Z, Weinmann A, Seipp L E, Ali S J, Chen Z, Fletcher L B, Glenzer S H 2024 Phys. Plasmas 31 042711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ng A, Sterne P, Hansen S, Recoules V, Chen Z, Tsui Y Y, Wilson B 2016 Phys. Rev. E 94 03321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 孙旭, 吴海忠, 王小伟, 吕治辉, 张栋文, 刘东晓, 范伟, 粟敬钦, 周维民, 谷渝秋, 赵增秀, 袁建民 2023 中国激光 50 1714013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X, Wu H Z, Wang X W, Lü Z H, Zhang D W, Liu D X, Fan W, Su J Q, Zhou W M, Gu Y Q, Zhao Z X, Yuan J M 2023 Chin. J. Lasers 50 1714013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ofori-Okai B K, Descamps A, Lu J, Seipp L E, Weinmann A, Glenzer S H, Chen Z 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10D109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ao T, Ping Y, Widmann K, Price D F, Lee E, Tam H, Springer P T, Ng A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Widmann K, Ao T, Foord M E, Price D F, Ellis A D, Springer P T, Ng A 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ping Y, Hanson D, Koslow I, Ogitsu T, Prendergast D, Schwegler E, Collins G, Ng A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 255003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen Z, Holst B, Kirkwood S E, Sametoglu V, Reid M, Tsui Y Y, Recoules V, Ng A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 135001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen Z, Sametoglu V, Tsui Y Y, Ao T, Ng A 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 165001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dhar L, Fourkas J T, Nelson K A 1994 Opt. Lett. 19 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lindenberg A M, Larsson J, Sokolowski-Tinten K, Gaffney K J, Blome C, Synnergren O, Sheppard J, Caleman C, MacPhee A G, Weinstein D, Lowney D P, Allison T K, Matthews T, Falcone R W, Cavalieri A L, Fritz D M, Lee S H, Bucksbaum P H, Reis D A, Rudati J, Fuoss P H, Kao C C, Siddons D P, Pahl R, Als-Nielsen J, Duesterer S, Ischebeck R, Schlarb H, Schulte-Schrepping H, Tschentscher Th, Schneider J, Von Der Linde D, Hignette O, Sette F, Chapman H N, Lee R W, Hansen T N, Techert S, Wark J S, Bergh M, Huldt G, Van Der Spoel D, Timneanu N, Hajdu J, Akre R A, Bong E, Krejcik P, Arthur J, Brennan S, Luening K, Hastings J B 2005 Science 308 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen Z, Hering P, Brown S B, Curry C, Tsui Y Y, Glenzer S H 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu Y Y, Zhao K, He P, Huang H D, Teng H, Wei Z Y 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 074204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Wang S, Rockwood A, Luther B M, Hollinger R, Curtis A, Calvi C, Menoni C S, Rocca J J 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xiao F, Fan X H, Wang L, Zhang D W, Wu J H, Wang X W, Zhao Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chang H T, Zürch M, Kraus P M, Borja L J, Neumark D M, Leone S R 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 5365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang X W, Wang L, Xiao F, Zhang D W, Lue Z H, Yuan J M, Zhao Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 023201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Born M, Wolf E 1999 Principles of Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[33] Shillaber C P 1945 Photomicrography: In Theory and Practice (New York: Wiley
-
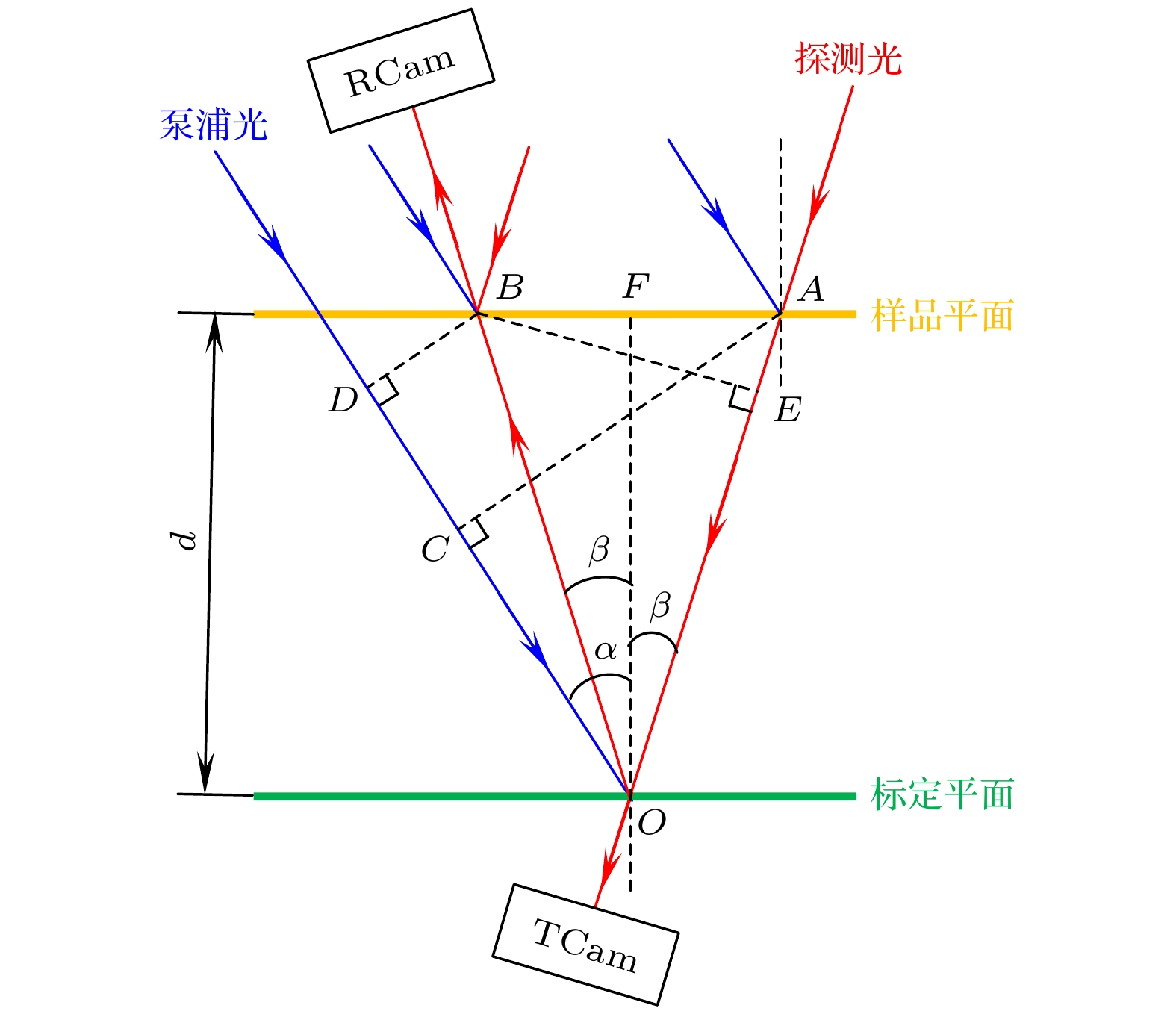
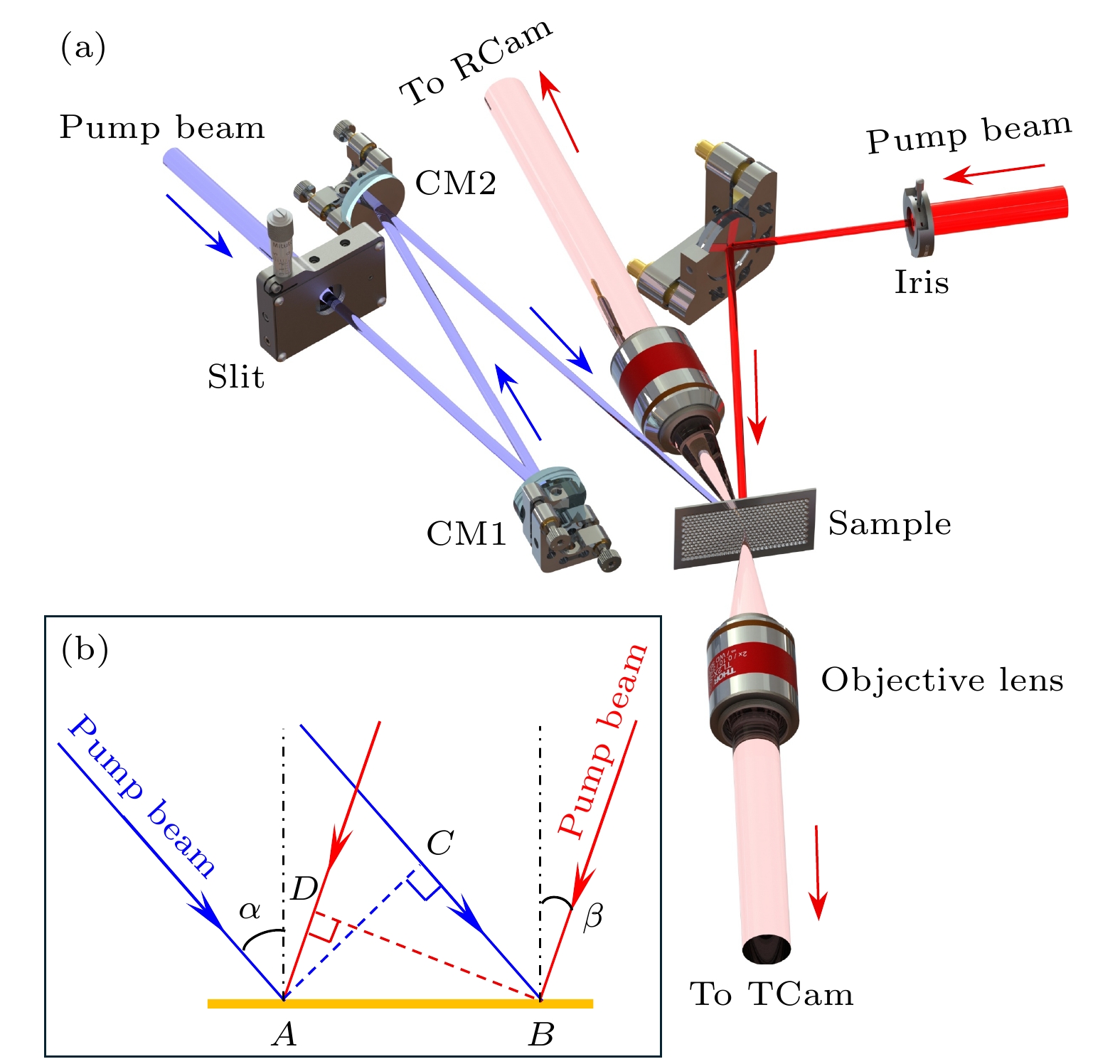
图 1 WDM交流电导率时间演化的单发测量原理 (a) 实验系统示意图, 其中CM1和CM2为两个柱面镜, RCam和Tcam分别为反射光成像相机和透射光成像相机; (b) 空间啁啾把不同延时映射在不同空间位置上的原理
Figure 1. Single-shot measurement principle for time-dependent AC conductivity evolution in WDM: (a) Schematic of the experimental system, where CM1 and CM2 are two cylindrical mirrors, and RCam and Tcam are the reflection light imaging camera and transmission light imaging camera, respectively; (b) principle of spatial chirp which maps different time delays to different spatial positions.
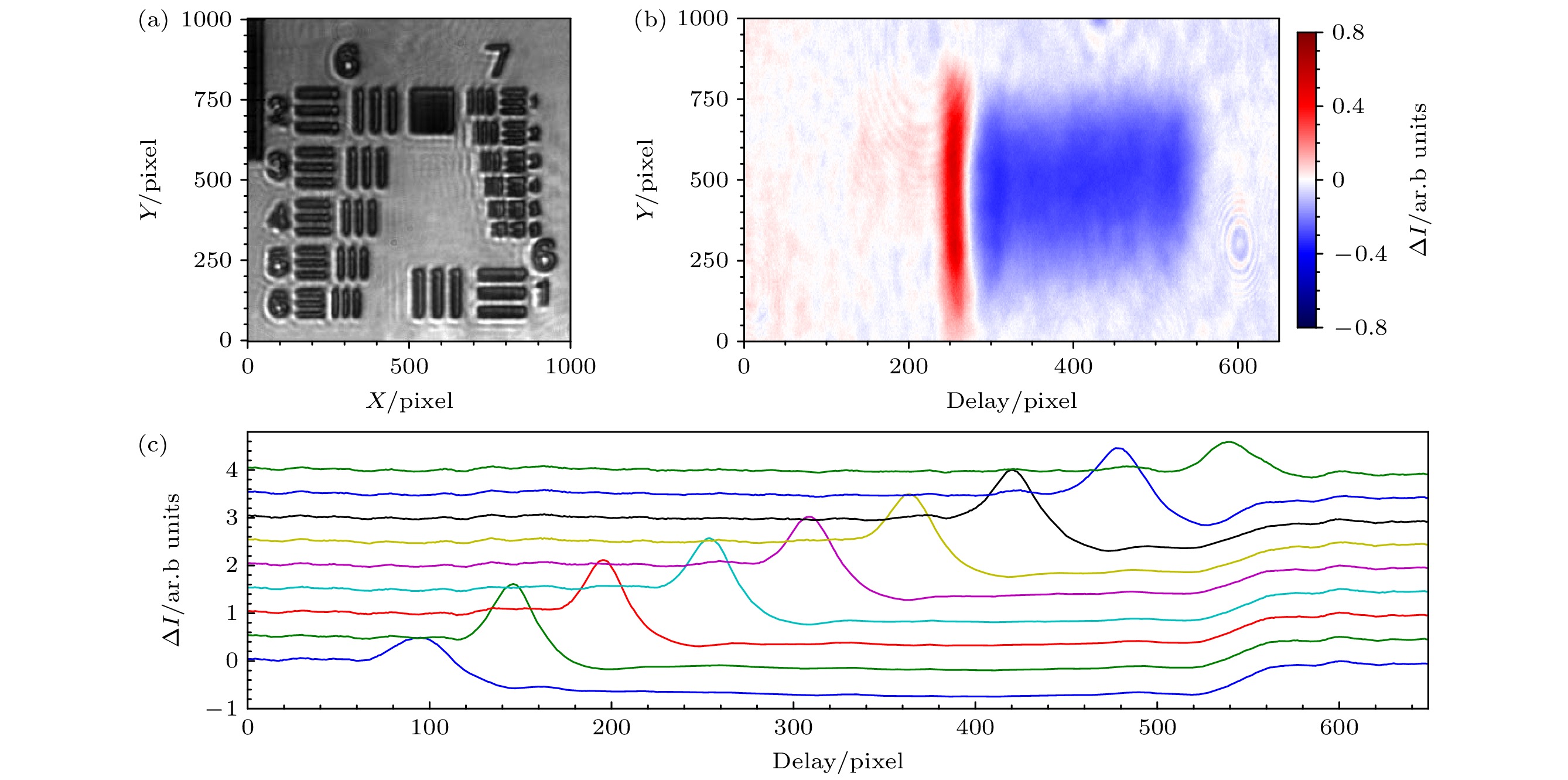
图 2 成像分辨率与延时标定 (a) USAF 1951分辨率板的像, 成像系统在水平方向能分辨至第7组第1个元素 (128 lp/mm); (b) 在偏振选通法(PG)中测得的透射光光强变化($ \Delta I $)随空间的分布; (c) 利用PG标定延时, 图中9条曲线代表9个间隔为33.3 fs的不同延时点测得的$ \Delta I $的空间分布
Figure 2. Imaging resolution and time delay calibration: (a) Image of the USAF 1951 resolution target, where the imaging system resolves down to the Group 7 Element 1 (128 lp/mm) in the horizontal direction; (b) spatial distribution of transmitted light intensity variation (∆I ) measured via the polarization gating (PG) method; (c) time delay calibration using PG, where the 9 curves represents 9 different measurements of ∆I vs. space with delay increment of 33.3 fs.
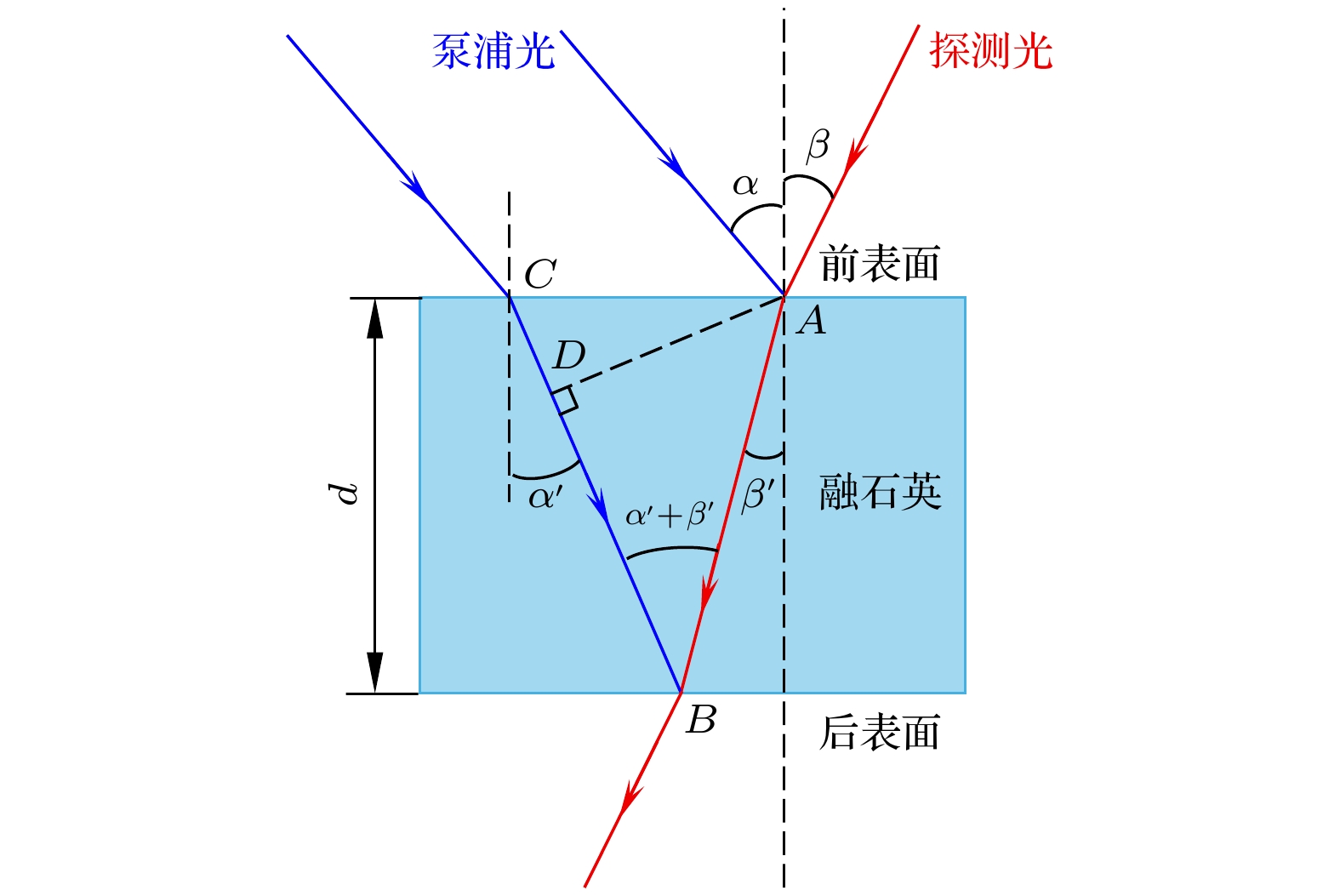
图 4 样品平面与标定平面不重合时带来的延时误差, 其中O点是利用偏振门方案标定的延时零点, A点是透射相机“认为”的样品上的延时零点, B点是反射相机“认为”的样品上的延时零点
Figure 4. Delay error introduced when sample plane and calibration plane do not coincide. Point O is the delay zero point calibrated using the polarization gate method, Point A is the delay zero point on the sample perceived by the transmission camera, Point B is the delay zero point on the sample perceived by the reflection camera.
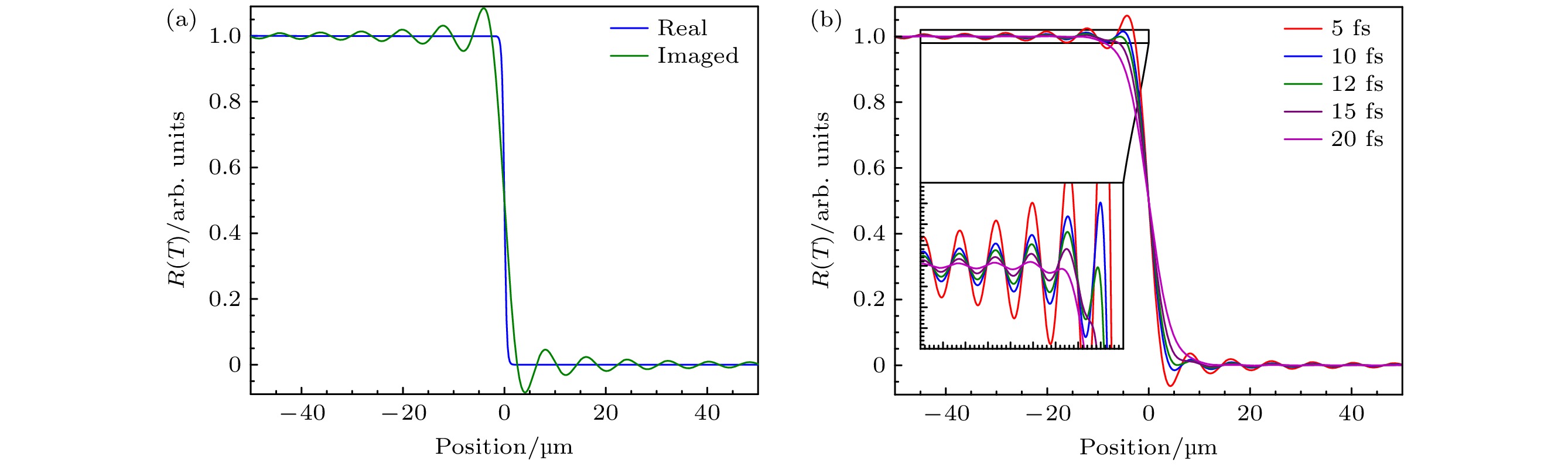
图 5 突变结构的成像模拟 (a)一个瞬时突变结构(real)经过成像系统后的像(imaged)带有衍射振荡结构; (b) 5—20 fs缓变结构的像
Figure 5. Imaging simulation of abrupt structures: (a) An instantaneous abrupt structure (real) after passing through the imaging system, the image (imaged) exhibits a diffractive oscillatory structure; (b) images of 5, 10, 12, 15 and 20 fs gradually varying structures.
表 1 单发测量温稠密交流电导率演化的误差分析
Table 1. Error analysis of conductivity evolution in single-shot measurements of warm dense matter.
系统物理量 误差来源 依赖关系 典型值 系统时间分辨率$ \Delta \tau $ 泵浦光脉宽$ {\tau }_{1} $ $ \Delta \tau =\sqrt{{\tau }_{1}^{2}+{\tau }_{2}^{2}+{\left(\chi {{\Delta }}x\right)}^{2}} $ $ {\tau }_{1}=9.7\;{\mathrm{fs}}; {\tau }_{2}=5\;{\mathrm{fs}} $
$ \chi =2.1\;{\mathrm{fs/μm}}, $
$ \Delta x=4\;\text{μm},\; \Delta \tau =13.8\;{\mathrm{fs}} $探测光脉宽$ {\tau }_{2} $ 成像系统分辨率$ \Delta x $ 延时零点标定误差$ \Delta {\tau }_{0} $ 融石英片厚度$ L $ $ \Delta {\tau }_{0}[{\mathrm{fs}}]\approx 0.42 L\;[\text{μm}] $ $ L=30\text{ μm},\; \Delta {\tau }_{0}=12.7\;{\mathrm{fs}} $ 透射延时零点定位误差$ \Delta {\tau }_{\rm 0T} $ 成像定位精度$ d $ $ {\Delta \tau }_{\rm 0T}\left[{\mathrm{fs}}\right]\approx -0.72 d\left[\text{μm}\right] $, $ d=35\text{ μm}, \; \Delta {\tau }_{\rm 0T}=25.2\;{\mathrm{fs}} $ 反射延时零点定位误差$ \Delta {\tau }_{\rm 0R} $ $ {\Delta \tau }_{\rm 0R} \left[{\mathrm{fs}}\right]\approx 0.038 d\left[\text{μm}\right] $ $ d=35\text{ μm} ,\; \Delta {\tau }_{\rm 0T}=1.33\;{\mathrm{fs}} $ 动力学突变的时间分辨率$ \Delta {\tau }_{{\mathrm{f}}} $ 成像系统数值孔径$ NA $ $ \Delta {\tau }_{{\mathrm{f}}}\propto {1}/{{{NA}}} $ $ {{NA}}=0.1 ,\; \Delta {\tau }_{{\mathrm{f}}} > 20\;{\mathrm{fs}} $ -
[1] 陈其峰, 顾云军, 郑君, 李江涛, 李治国, 权伟龙, 付志坚, 李成军 2017 科学通报 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Q F, Gu Y J, Zheng J, Li J T, Li Z G, Quan W L, Fu Z J, Li C J 2017 Chin. Sci. Bull. 62 812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kang D, Dai J 2018 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30 073002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ichimaru S 1982 Rev. Mod. Phys. 54 1017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Koenig M, Benuzzi-Mounaix A, Ravasio A, Vinci T, Ozaki N, Lepape S, Batani D, Huser G, Hall T, Hicks D, MacKinnon A, Patel P, Park H S, Boehly T, Borghesi M, Kar S, Romagnani L 2005 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 B441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Falk K 2018 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 6 e59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 康冬冬, 曾启昱, 张珅, 王小伟, 戴佳钰 2020 强激光与粒子束 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang D D, Zeng Q Y, Zhang S, Wang X W, Dai J Y 2020 High Power Laser Part. Beams 32 092006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lee R W, Moon S J, Chung H K, Rozmus W, Baldis H A, Gregori G, Cauble R C, Landen O L, Wark J S, Ng A, Rose S J, Lewis C L, Riley D, Gauthier J C, Audebert P 2003 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20 770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu D, Yu W, Sheng Z M, Fritzsche S, He X T 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 051202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fletcher L B, Lee H J, Döppner T, Galtier E, Nagler B, Heimann P, Fortmann C, LePape S, Ma T, Millot M, Pak A, Turnbull D, Chapman D A, Gericke D O, Vorberger J, White T, Gregori G, Wei M, Barbrel B, Falcone R W, Kao C C, Nuhn H, Welch J, Zastrau U, Neumayer P, Hastings J B, Glenzer S H 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Graziani F, Moldabekov Z, Olson B, Bonitz M 2022 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 62 e202100170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dornheim T, Böhme M, Kraus D, Döppner T, Preston T R, Moldabekov Z A, Vorberger J 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 7911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mercadier L, Benediktovitch A, Krušič Š, Kas J J, Schlappa J, Agåker M, Carley R, Fazio G, Gerasimova N, Kim Y Y, Le Guyader L, Mercurio G, Parchenko S, Rehr J J, Rubensson J E, Serkez S, Stransky M, Teichmann M, Yin Z, Žitnik M, Scherz A, Ziaja B, Rohringer N 2024 Nat. Phys. 20 1564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Forsman A, Ng A, Chiu G, More R M 1998 Phys. Rev. E 58 R1248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ping Y, Correa A A, Ogitsu T, Draeger E, Schwegler E, Ao T, Widmann K, Price D F, Lee E, Tam H, Springer P T, Hanson D, Koslow I, Prendergast D, Collins G, Ng A 2010 High Energy Density Phys. 6 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ofori-Okai B K, Descamps A, McBride E E, Mo M Z, Weinmann A, Seipp L E, Ali S J, Chen Z, Fletcher L B, Glenzer S H 2024 Phys. Plasmas 31 042711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ng A, Sterne P, Hansen S, Recoules V, Chen Z, Tsui Y Y, Wilson B 2016 Phys. Rev. E 94 03321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 孙旭, 吴海忠, 王小伟, 吕治辉, 张栋文, 刘东晓, 范伟, 粟敬钦, 周维民, 谷渝秋, 赵增秀, 袁建民 2023 中国激光 50 1714013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X, Wu H Z, Wang X W, Lü Z H, Zhang D W, Liu D X, Fan W, Su J Q, Zhou W M, Gu Y Q, Zhao Z X, Yuan J M 2023 Chin. J. Lasers 50 1714013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ofori-Okai B K, Descamps A, Lu J, Seipp L E, Weinmann A, Glenzer S H, Chen Z 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10D109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ao T, Ping Y, Widmann K, Price D F, Lee E, Tam H, Springer P T, Ng A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Widmann K, Ao T, Foord M E, Price D F, Ellis A D, Springer P T, Ng A 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ping Y, Hanson D, Koslow I, Ogitsu T, Prendergast D, Schwegler E, Collins G, Ng A 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 255003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen Z, Holst B, Kirkwood S E, Sametoglu V, Reid M, Tsui Y Y, Recoules V, Ng A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 135001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen Z, Sametoglu V, Tsui Y Y, Ao T, Ng A 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 165001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dhar L, Fourkas J T, Nelson K A 1994 Opt. Lett. 19 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lindenberg A M, Larsson J, Sokolowski-Tinten K, Gaffney K J, Blome C, Synnergren O, Sheppard J, Caleman C, MacPhee A G, Weinstein D, Lowney D P, Allison T K, Matthews T, Falcone R W, Cavalieri A L, Fritz D M, Lee S H, Bucksbaum P H, Reis D A, Rudati J, Fuoss P H, Kao C C, Siddons D P, Pahl R, Als-Nielsen J, Duesterer S, Ischebeck R, Schlarb H, Schulte-Schrepping H, Tschentscher Th, Schneider J, Von Der Linde D, Hignette O, Sette F, Chapman H N, Lee R W, Hansen T N, Techert S, Wark J S, Bergh M, Huldt G, Van Der Spoel D, Timneanu N, Hajdu J, Akre R A, Bong E, Krejcik P, Arthur J, Brennan S, Luening K, Hastings J B 2005 Science 308 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen Z, Hering P, Brown S B, Curry C, Tsui Y Y, Glenzer S H 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 11E548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu Y Y, Zhao K, He P, Huang H D, Teng H, Wei Z Y 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 074204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Wang S, Rockwood A, Luther B M, Hollinger R, Curtis A, Calvi C, Menoni C S, Rocca J J 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xiao F, Fan X H, Wang L, Zhang D W, Wu J H, Wang X W, Zhao Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chang H T, Zürch M, Kraus P M, Borja L J, Neumark D M, Leone S R 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 5365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang X W, Wang L, Xiao F, Zhang D W, Lue Z H, Yuan J M, Zhao Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 023201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Born M, Wolf E 1999 Principles of Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[33] Shillaber C P 1945 Photomicrography: In Theory and Practice (New York: Wiley
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2903
- PDF Downloads: 150
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: