-
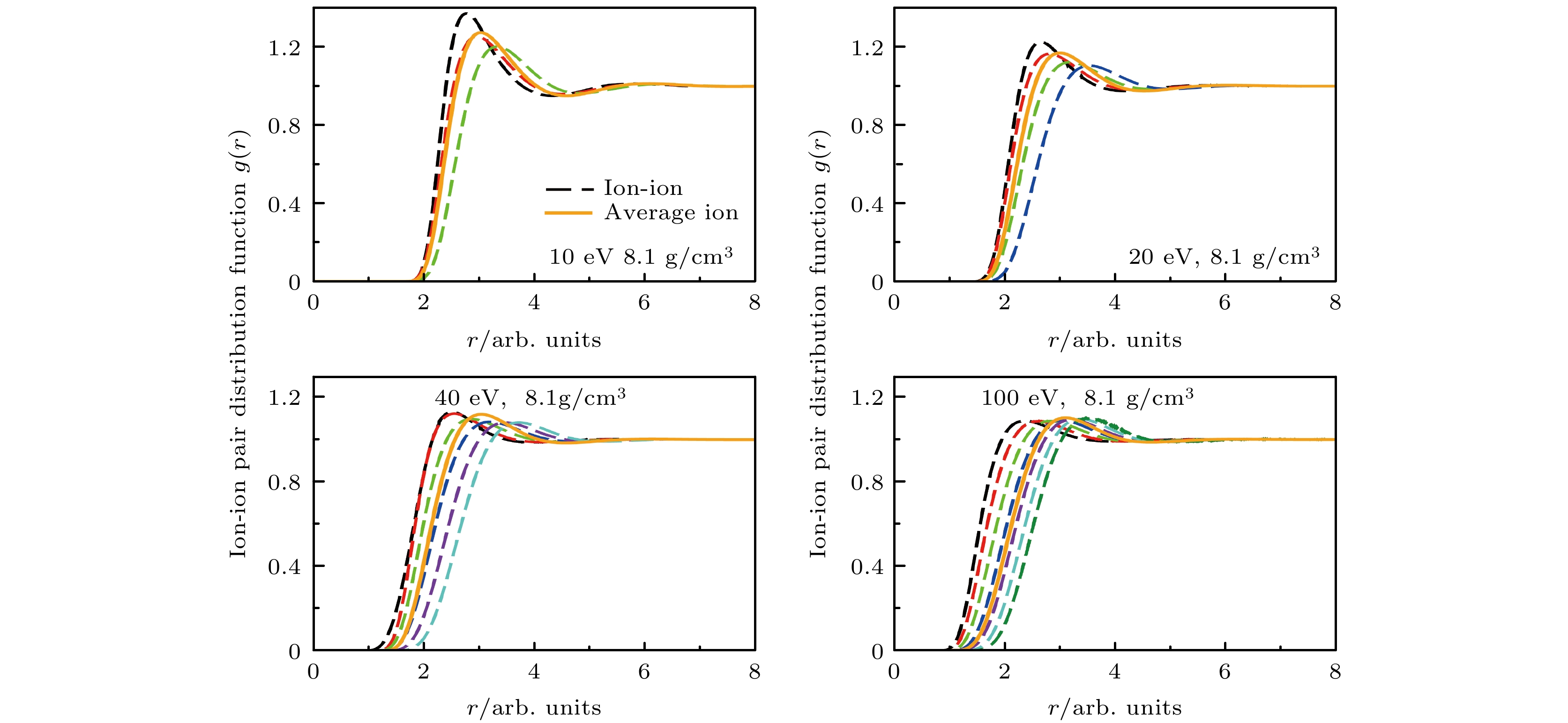
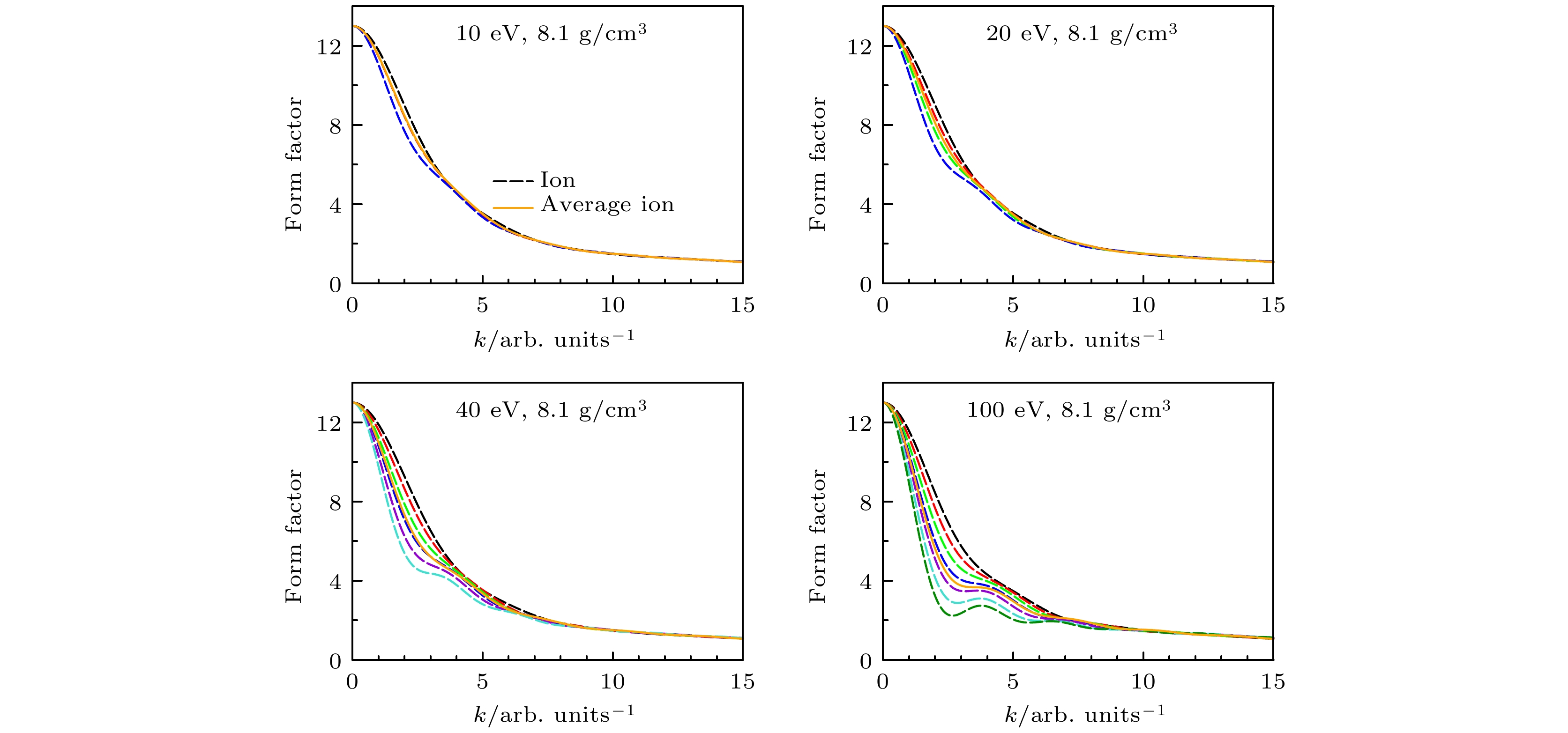
The study of warm dense matter is very important for the evolution of celestial bodies and inertial confinement fusion, which often contains a mixture of multiple elements and different charge-state ions. The ionic structure and distribution of different charge-states directly affect the diagnosis and physical properties of warm dense matter. At the same time, the influence of high-temperature dense plasma on the ionic structure should be considered when we study the physical properties from the first-principle calculation of electron structure. In the present work, the radial distribution functions of multiple charge-state ions (gold, carbon-hydrogen mixture, and aluminum) are developed in the hypernetted-chain approximation, and elastic x-ray scattering of different charge-state ions are calculated in the warm dense matter regime. Firstly, the electron structure of different charge-state ions is self-consistently computed in the ionic sphere, in which the ion-sphere radii are determined by the plasma density and their charges. And then the ionic fraction is obtained by solving the modified Saha equation, with the interactions among different charge-state ions taken into account, and ion-ion pair potentials are obtained by Yukawa model. Finally, the ion features of x-ray elastic scattering for Al are calculated on the basis of electronic distribution around the nuclei and ionic radial distribution function. By comparing the results of different charge-sate ions with the result of mean charge-sate ion, it is shown that different statistical methods can affect the physical properties which are dependent on the electronic and ionic structure.
-
Keywords:
- warm dense matter /
- radial distribution function /
- hypernetted-chain approximation /
- elastic scattering
[1] Clérouin J, Arnault P, Gréa B J, Guisset S, Vandenboomgaerde M, White A J, Collins L A, Kress J D, Ticknor C 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 033207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wünsch K, Hilse P, Schlanges M, Gericke D.O 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 056404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hou Y, Bredow R, Yuan J M, Redmer R 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 033114
[4] Daligault J, Baalrud S D, Starrett C E, SaumonD, Sjostrom T 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 075002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 马桂存, 张其黎, 宋红州, 李琼, 朱希睿, 孟续军 2017 66 036401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma G C, Zhang Q L, Song H Z, Li Q, Zhu X R, Meng X J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Dai J Y, Hou Y, Yuan J M 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 245001
[7] Desjarlais M P 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 064204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kuhne T D, Krack M, Mohamed F R, Parrinello M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 066401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zérah G, Clérouin J, Pollock E L 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fu Y S, Hou Y, Kang D D, Gao C, Jin F T, Yuan J M 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 012701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bredow R, Bornath T, Kraeft W D, Redmer R 2013 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 53 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Salzmann D 1998 Atomic Physics in Hot Plasmas (Oxford : Oxford University Press) pp54−55
[14] Tanaka S 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 145 214104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gu M F 2008 Can. J. Phys 86 675
[16] 王天浩, 王坤, 张阅, 姜林村 2020 69 099101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang T H, Wang K, Zhang Y, Jiang L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 099101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brush S G, Sahlin H L, Teller E 1966 J. Chem. Phys. 45 2102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Deutsch C 1977 Phys. Lett. A 60 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schwarz V, Bornath T, Kraeft W D, Glenzer S H, Höll A, Redmer R 2007 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 47 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kelbg G 1964 Ann. Phys. 13 354
[21] Chihara J 2000 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wünsch K, Vorberger J, Gregorz G, Gericke D O 2011 EPL 94 25001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Iglesias C A 2018 High Energy Density Phys. 26 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rüter H R, Redmer R 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 145007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Souza A N, Perkins D J, Starrett C E, Saumon D, Hansen S B 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 023108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma T, Döppner T, Falcone R W, Fletcher L, Fortmann C, Gericke D O, Landen O L, Lee H J, Pak A, Vorberger J, Wünsch K, Glenzer S H 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 065001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Clérouin J, Robert G, Arnault P 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 011101(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hou Y, Fu Y S, Bredow R, Kang D D, Redmer R, Yuan J M 2017 High Energy Density Phys. 22 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
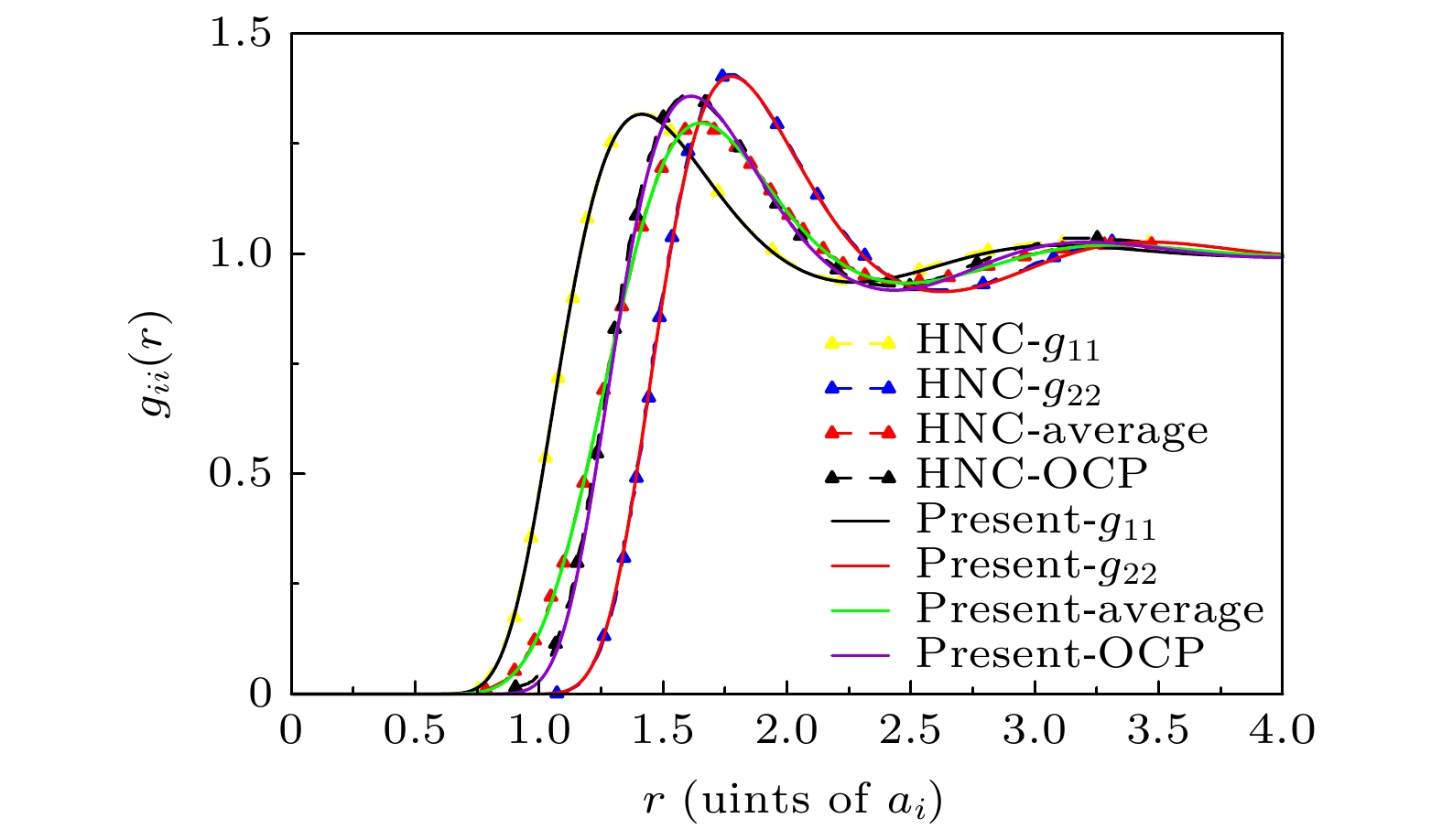
图 1 在温度为104 K、离子数密度为1024 cm–3时, Au1+和Au2+混合离子价态的径向分布函数. Present表示本文工作的计算结果(实线); HNC表示文献[2]中采用HNC近似计算的结果(虚线 + 上三角); OCP表示平均成一种价态离子的径向分布函数; average表示各价离子的径向分布函数的算数平均
Figure 1. The radial distribution function of Au1+, Au2+ in gold plasma with ion number density of 1024 cm–3 and temperature of 104 K. Present represents the result of the present paper (solid line); HNC represents the result of HNC approximation in the Ref. [2] (dotted line + upper triangle); OCP is the radial distribution function of mean charge-state ion; average labels the average results of the radial distribution function of different charge-state ions.
图 2 在离子数密度为nH = nC = 2.5 × 1023 cm–3、温度为T = 2 × 104 K时, 碳-氢混合等离子体中C4+和H+的径向分布函数; Present是本文计算结果(实线), HNC是文献[2]中用HNC近似的计算结果(虚线 + 上三角)
Figure 2. The radial distribution function of C4+ and H+ in the CH mixture plasma at number density, nH = nC = 2.5 × 1023 cm–3, and the temperature, T = 2 × 104 K. And solid lines label the present results; and dashed lines with upper triangles are the results of Ref. [2].
图 5 在密度为8.1 g/cm3、温度10 eV下温稠密铝等离子体中, 离子结构随不同散射角的变化关系. Multi-ion表示本文使用的方法给出的计算结果(虚线); AAHNC表示AAHNC模型的计算结果(实线)[3]; QMD表示量子分子动力学计算结果(点-虚线)[24]; HNC表示文献[25]中采用HNC近似计算离子结构的结果(点线); 带有误差范围的点表示实验结果[26]
Figure 5. Ion feature for Al as function of k at a temperature of 10 eV and a density of 8.1 g/cm3: Multi-ion (dashed line), AAHNC (solid line)[3], QMD (dot-dashed line)[24], HNC (dot line)[25] and experimental data (points with error bars)[26].
表 1 在密度为8.1 g/cm3、不同温度下温稠密铝的离子丰度, A表示平均电离度
Table 1. Charge-state fractions of Al at density, 8.1 g/cm3, A is average charge state.
100 eV价态 A = 7.196丰度 40 eV价态 A = 4.28丰度 20 eV价态 A = 3.27丰度 10 eV价态 A = 3.007丰度 4 0.016 2 0.001 2 0.003 2 0.001 5 0.081 3 0.175 3 0.735 3 0.991 6 0.212 4 0.438 4 0.251 4 0.008 7 0.247 5 0.315 5 0.011 8 0.290 6 0.067 9 0.132 7 0.004 10 0.021 -
[1] Clérouin J, Arnault P, Gréa B J, Guisset S, Vandenboomgaerde M, White A J, Collins L A, Kress J D, Ticknor C 2020 Phys. Rev. E 101 033207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wünsch K, Hilse P, Schlanges M, Gericke D.O 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 056404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hou Y, Bredow R, Yuan J M, Redmer R 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 033114
[4] Daligault J, Baalrud S D, Starrett C E, SaumonD, Sjostrom T 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 075002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 马桂存, 张其黎, 宋红州, 李琼, 朱希睿, 孟续军 2017 66 036401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma G C, Zhang Q L, Song H Z, Li Q, Zhu X R, Meng X J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Dai J Y, Hou Y, Yuan J M 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 245001
[7] Desjarlais M P 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 064204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kuhne T D, Krack M, Mohamed F R, Parrinello M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 066401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 汤文辉, 徐彬彬, 冉宪文, 徐志宏 2017 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang W H, Xu B B, Ran X W, Xu Z H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 030505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zérah G, Clérouin J, Pollock E L 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fu Y S, Hou Y, Kang D D, Gao C, Jin F T, Yuan J M 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 012701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bredow R, Bornath T, Kraeft W D, Redmer R 2013 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 53 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Salzmann D 1998 Atomic Physics in Hot Plasmas (Oxford : Oxford University Press) pp54−55
[14] Tanaka S 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 145 214104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gu M F 2008 Can. J. Phys 86 675
[16] 王天浩, 王坤, 张阅, 姜林村 2020 69 099101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang T H, Wang K, Zhang Y, Jiang L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 099101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brush S G, Sahlin H L, Teller E 1966 J. Chem. Phys. 45 2102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Deutsch C 1977 Phys. Lett. A 60 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schwarz V, Bornath T, Kraeft W D, Glenzer S H, Höll A, Redmer R 2007 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 47 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kelbg G 1964 Ann. Phys. 13 354
[21] Chihara J 2000 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wünsch K, Vorberger J, Gregorz G, Gericke D O 2011 EPL 94 25001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Iglesias C A 2018 High Energy Density Phys. 26 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rüter H R, Redmer R 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 145007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Souza A N, Perkins D J, Starrett C E, Saumon D, Hansen S B 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 023108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma T, Döppner T, Falcone R W, Fletcher L, Fortmann C, Gericke D O, Landen O L, Lee H J, Pak A, Vorberger J, Wünsch K, Glenzer S H 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 065001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Clérouin J, Robert G, Arnault P 2015 Phys. Rev. E 91 011101(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hou Y, Fu Y S, Bredow R, Kang D D, Redmer R, Yuan J M 2017 High Energy Density Phys. 22 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6051
- PDF Downloads: 71
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: