-
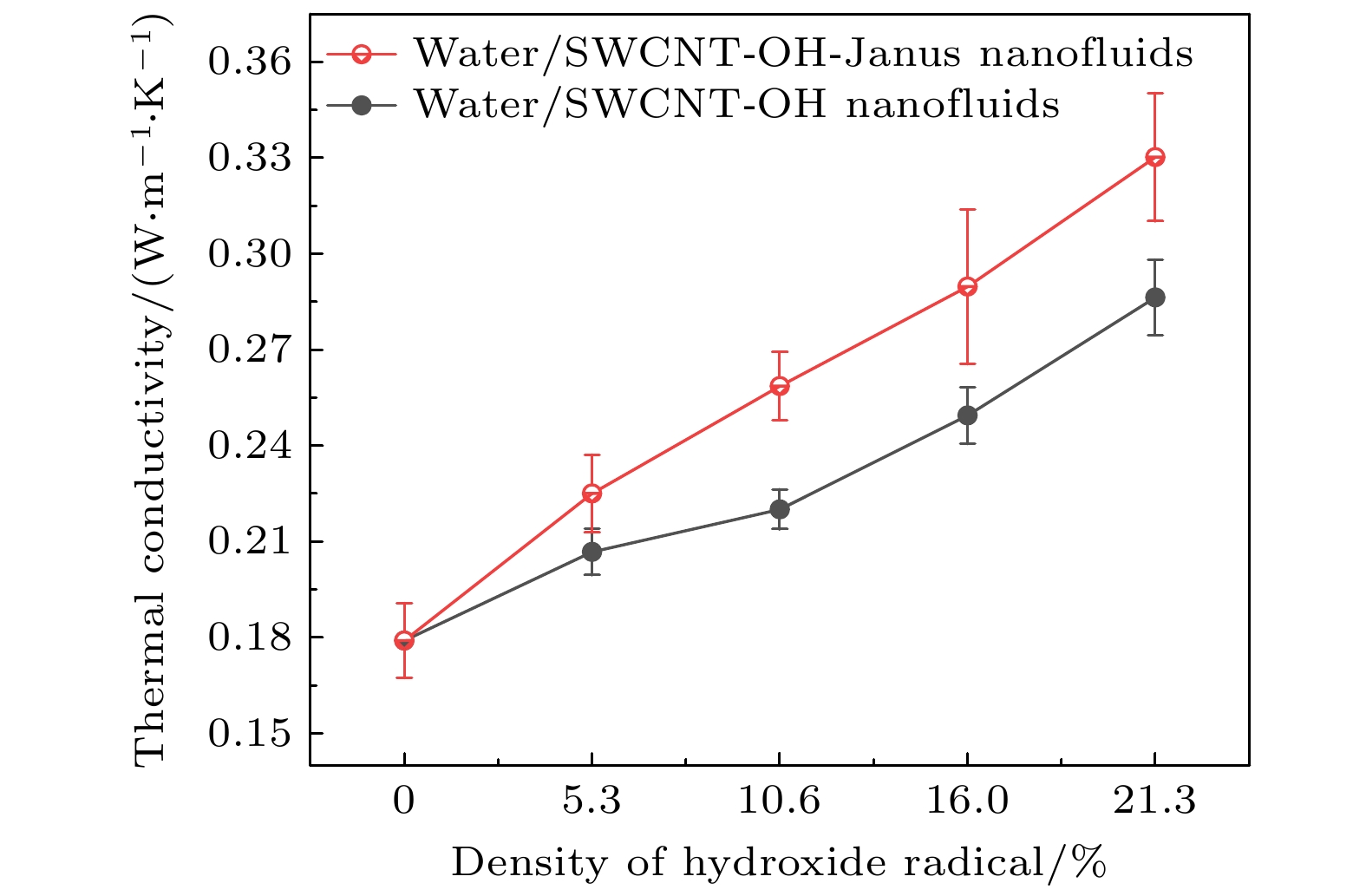
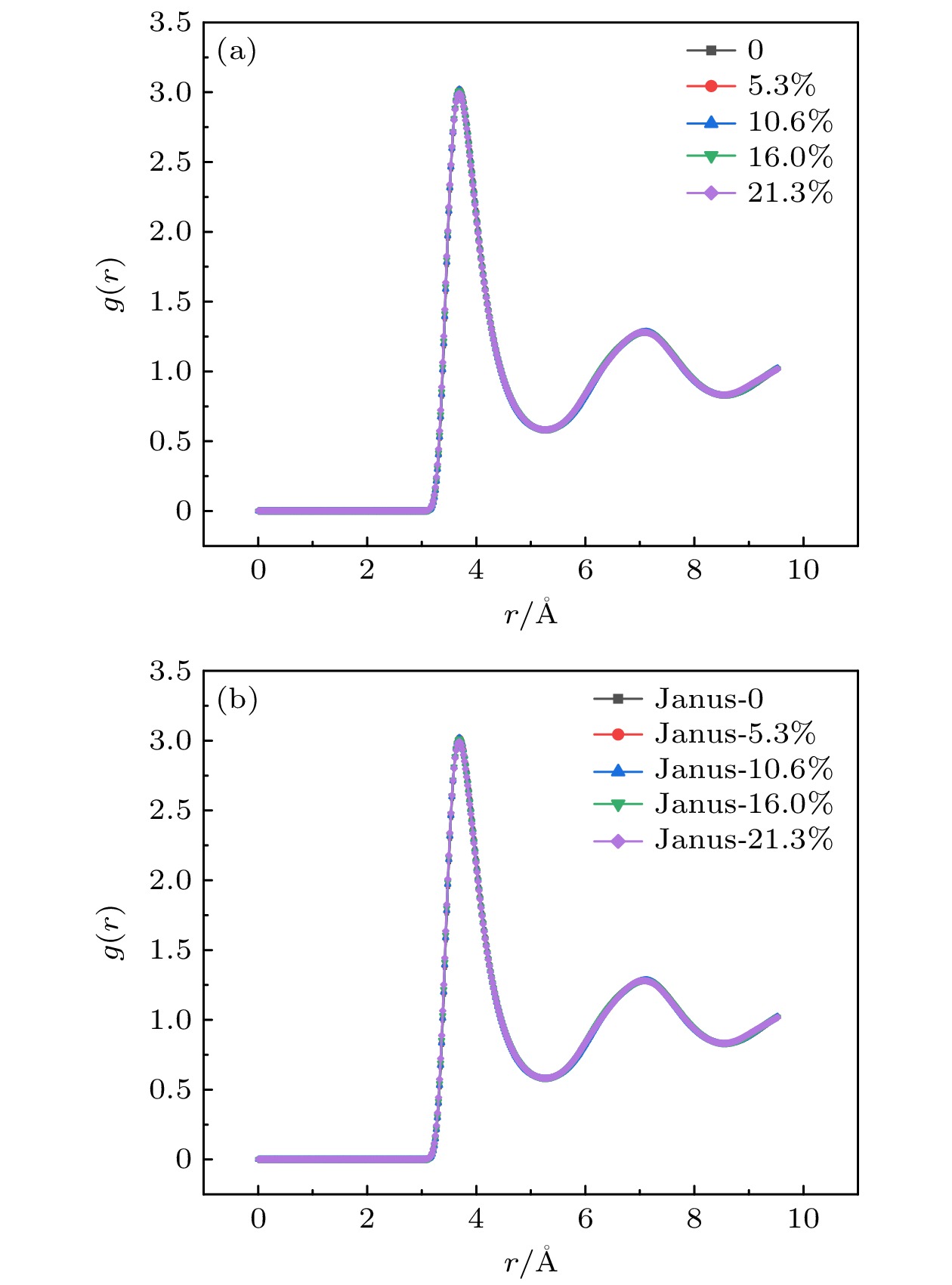
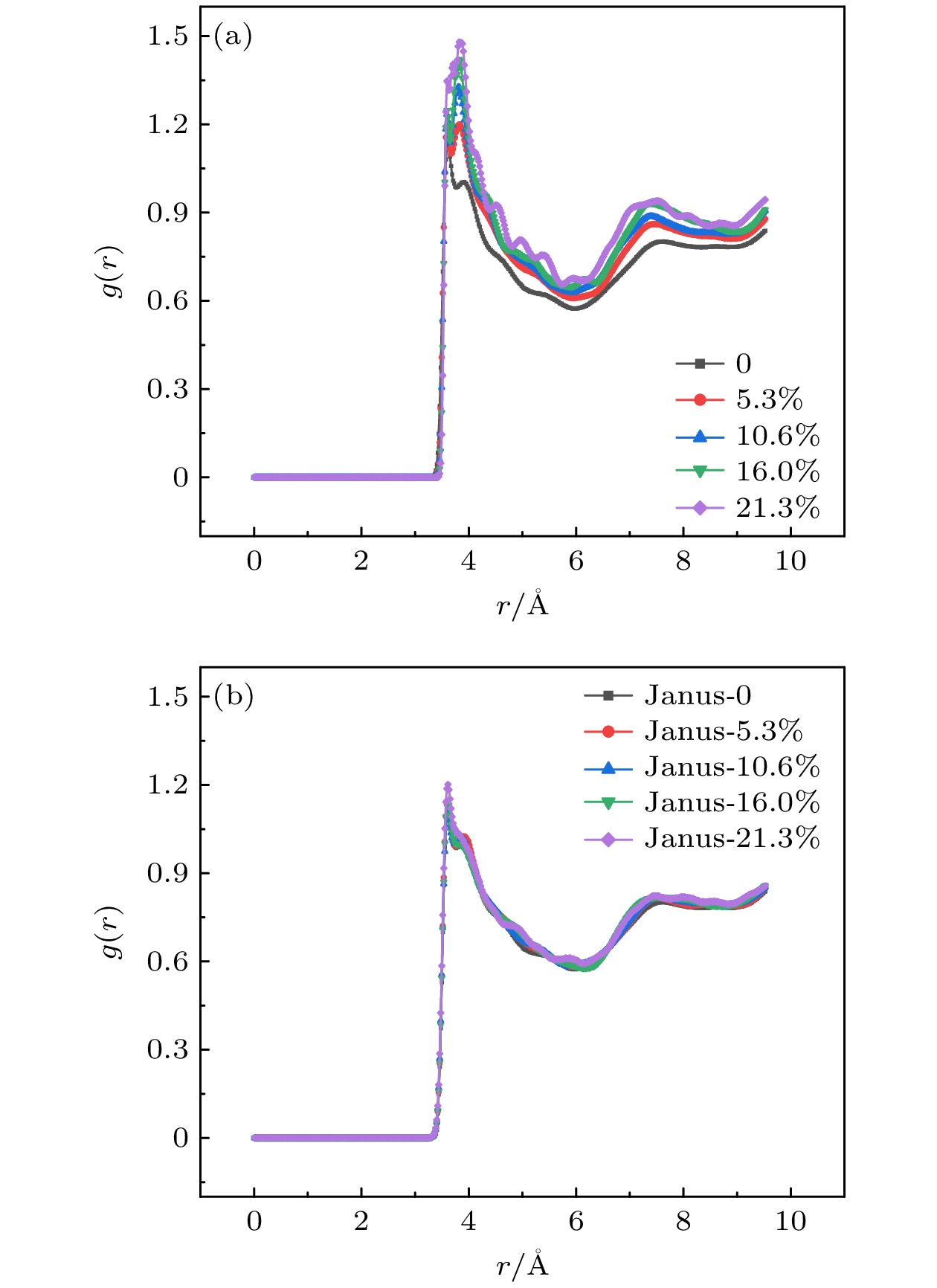
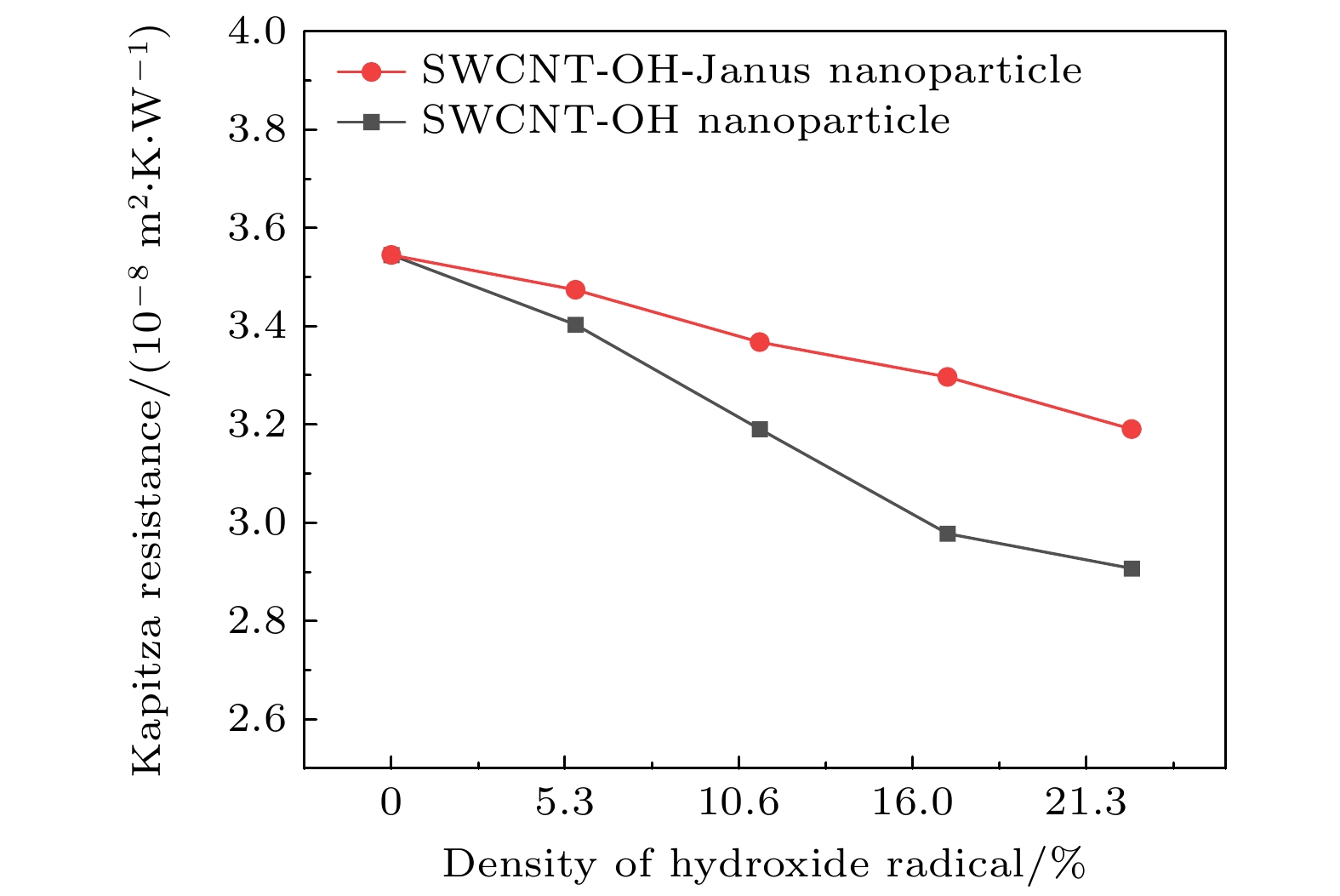
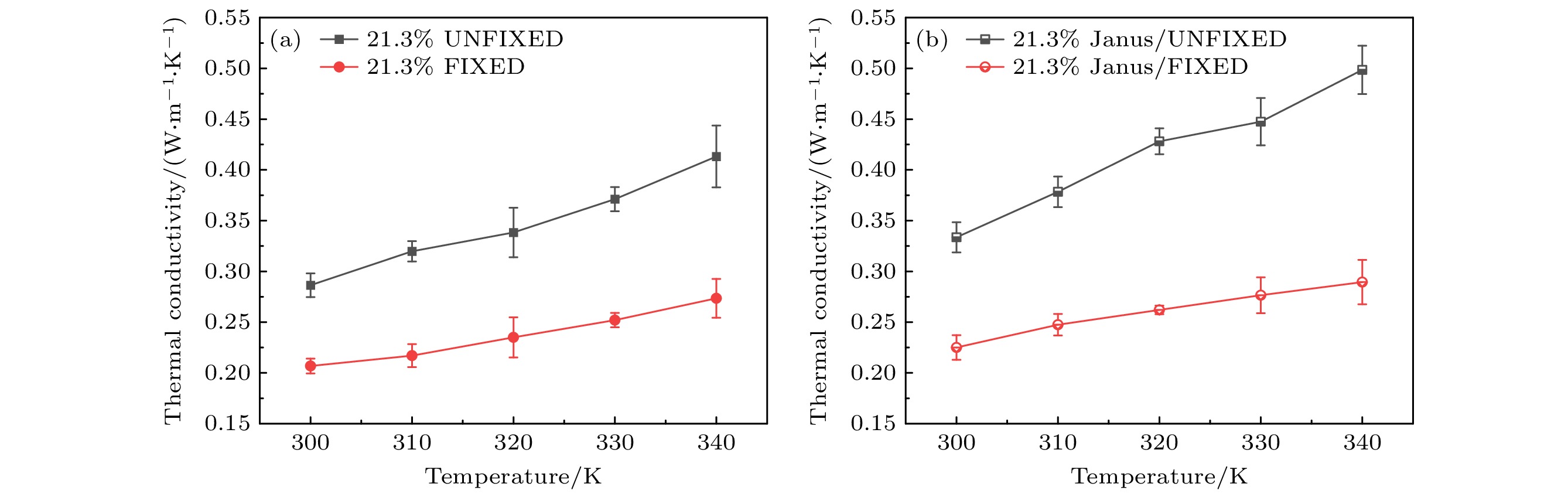
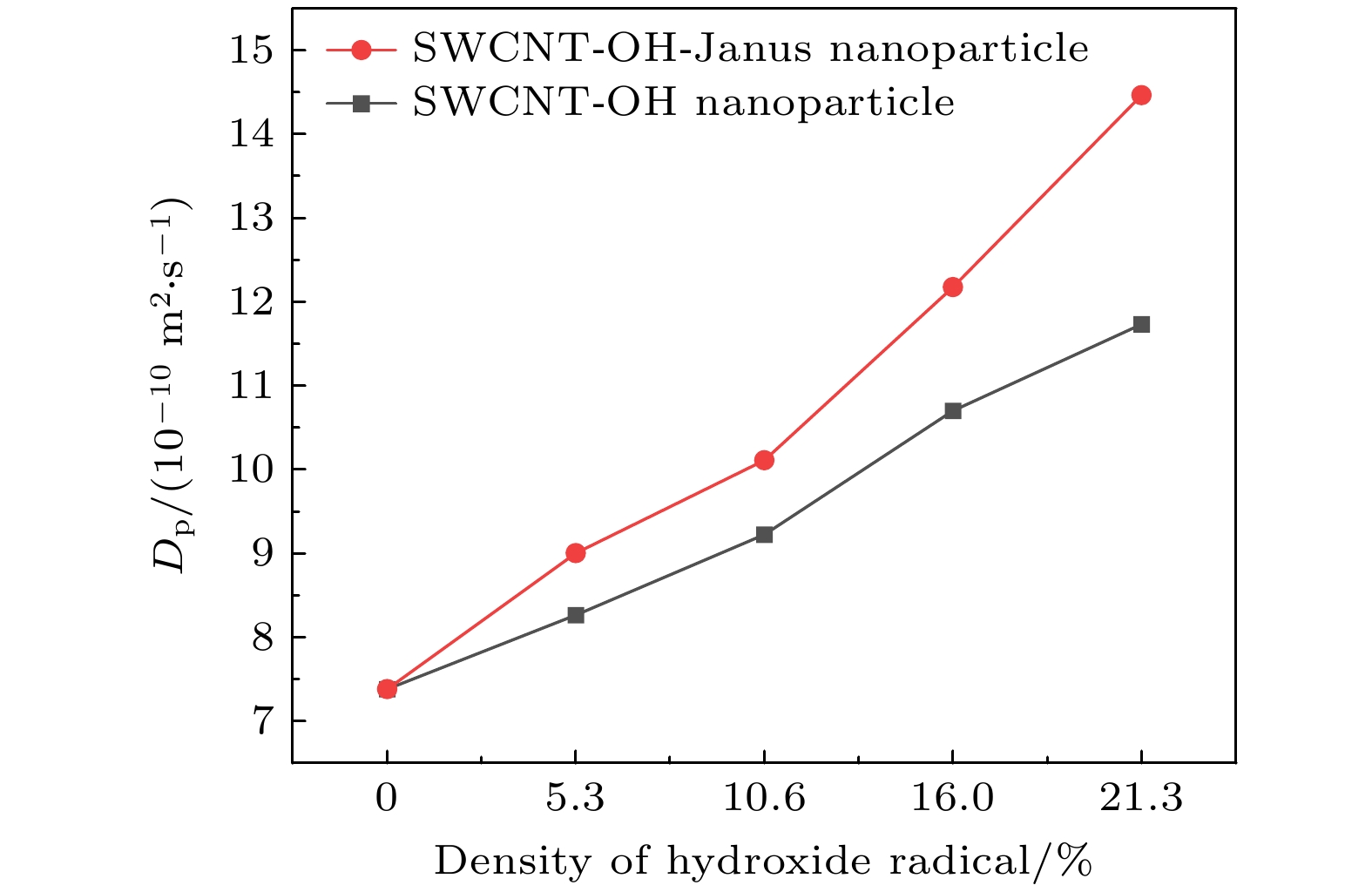
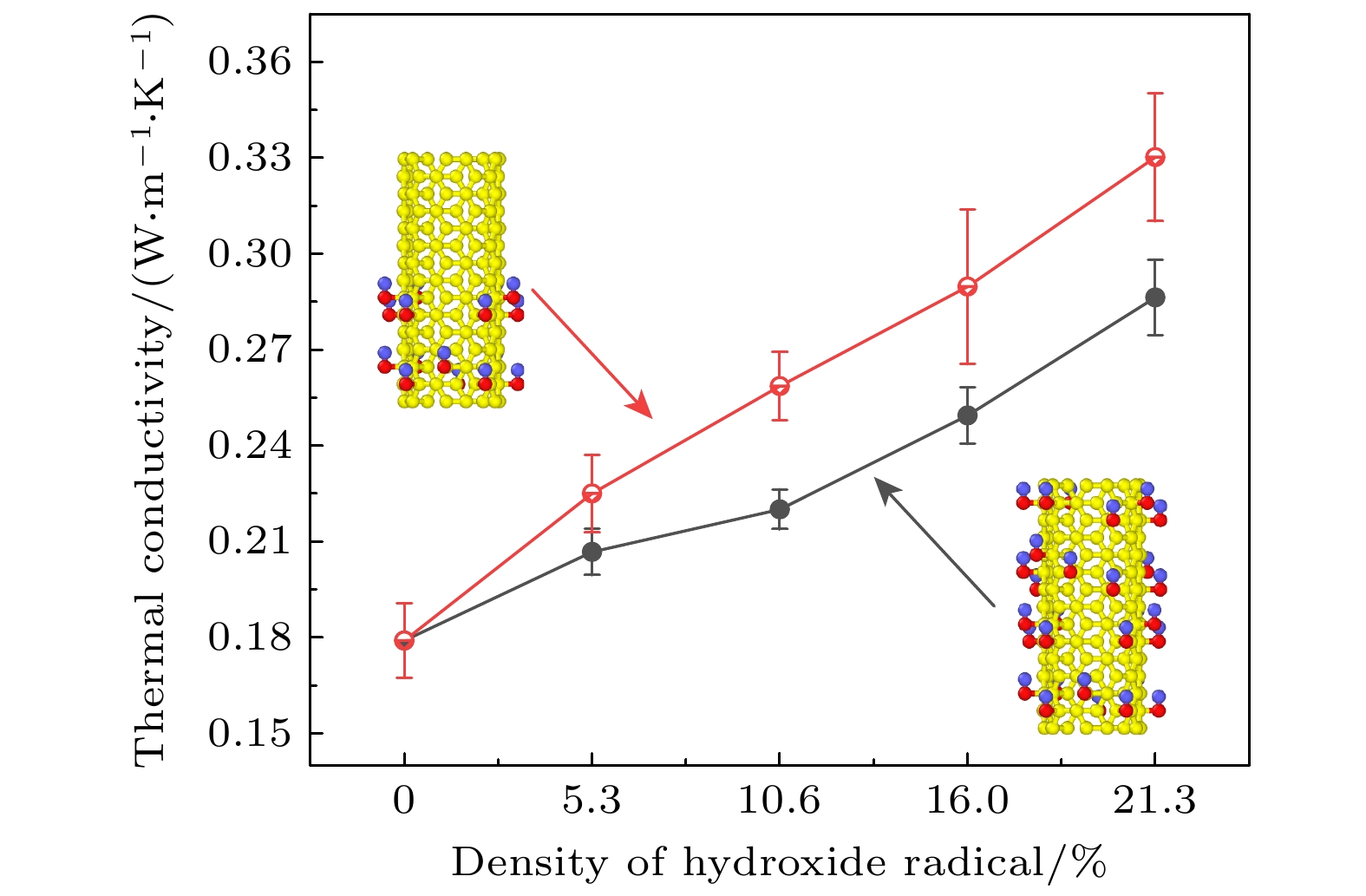
The excellent thermal conductivity of the carbon nanotubes leads to the high thermal conductivity of the nanofluids prepared by carbon nanotubes. The addition of functional groups on the surface of the carbon nanotubes canimprove the stability of the water/CNT nanofluids. The excellent diffusion properties of the Janus particles result in the elevated thermal conductivity of the Janus nanofluids. In thiswork, hydroxylated single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT-OH) particles, as Janus particles, are constructed and a water/SWCNT-OH-Janus nanofluid model is proposed by introducing SWCNT-OH particles into a base fluid (water). By using equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations, the thermal conductivity of nanofluids is calculated. The mechanism of the enhanced thermal conductivity is investigated by analyzing the solid-like liquid layers formed by liquid molecules around particles, Brownian motion of CNT particles, and CNT/water interfacial thermal resistance. It can be concluded that the thermal conductivity of the nanofluids with SWCNT-OH particles can be enhanced compared with that of the nanofluids with normal SWCNT particles. The hydrogen bond between hydroxyl group and water molecules results in the adsorption of water molecules onto the surface of carbon nanotube. This process increases the density of the liquid adsorption layer on the CNT surface, thereby enhancing the effect of the solid-liquid layer. The hydroxyl groups on the CNT surface degrade the solid-liquid interfacial thermal resistance, which promotes the heat transfer within the nanofluids. Moreover, the hydroxyl groups also enhance the interaction between the CNT particles and the water molecules,leading to stronger Brownian motionof particles. The combination of these factors will be responsible for the enhancement thermal conductivity of the water/SWCNT-OH nanofluids.For SWCNT-OH-Janus nanofluids, the thermal conductivity can be further enhanced, owing to the strong Brownian motion of the Janus particles.
-
Keywords:
- nanofluids /
- single-walled carbon nanotubes /
- Janus particles /
- hydroxide /
- molecular dynamics simulation
[1] Liu M S, Lin M C, Tsai C Y, Wang C C 2006 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49 3028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Choi S U S, Zhang Z G, Yu W, Lockwood F E, Grulke E A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Han X F, Lu L W, Yan S Y, Yang X H, Tian R, Zhao X Y 2021 J. Therm. Sci. 30 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ishii K, Ogiyama T, Fumoto K, Nishina Y 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 125 023104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王军, 崔鑫, 夏国栋 2023 北京工业大学学报 49 1116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Cui X, Xia G D 2023 J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 49 1116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xuan Y M, Li Q 2000 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 21 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu B, Liang W H, Luo Z M, Sarvar S, Fereidooni L, Kasaeian A 2024 Mol. Liq. 414 126052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xuan Y M, Duan H L, Li Q 2014 RSC Adv. 4 16206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rapp B, Hussam A 2023 J. Appl. Phys. 133 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dai J H, Zhai Y L, Li Z H, Wang H 2024 J. Mol. Liq. 400 124518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu W W, Wang J, Xia G D, Li Z G 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 083316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu W W, Cui J, Wang J, Xia G D, Li Z G 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 032004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu W, Choi S U S 2004 J. Nanopart. Res. 6 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 谢华清, 奚同庚, 王锦昌 2003 52 1444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie H Q, Xi T G, Wang J C 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xue L, Keblinski P, Phillpot S R, Choi S U S, Eastman J A 2004 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张智奇, 钱胜, 王瑞金, 朱泽飞 2019 68 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z Q, Qian S, Wang R J, Zhu Z F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Karthik V, Sahoo S, Pabi S K, Ghosh S 2013 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 64 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cui W Z, Shen Z J, Yang J G, Wu S H 2015 Appl. Therm. Eng. 76 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李屹同, 沈谅平, 王浩, 汪汉斌 2013 62 124401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li YT, Shen L P, Wang H, Wang H B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 124401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lenin R, Joy P A, Bera C 2021 J. Mol. Liq. 338 116929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘旺旺, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋 2024 73 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W W, Zhang K X, Wang J, Xia G D 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Roni M R H, Shahadat M R B, Morshed A M M 2021 Micro Nano Lett. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jabbari F, Rajabpour A, Saedodin S 2017 Chem. Eng. Sci. 174 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cui W Z, Shen Z J, Yang J G, Wu S H, Bai M L 2014 RSC Adv. 4 55580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kamalvand M, Karami M 2013 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 65 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 侯泉文, 曹炳阳, 过增元 2009 58 7809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Q W, Cao B Y, Guo Z Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 7809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jabbari F, Rajabpour A, Saedodin S 2021 Microfluid. Nanofluid. 25 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xing M B, Yu J L, Wang R X 2015 Appl. Therm. Eng. 87 344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li X K, Chen W J, Zou C J 2020 Powder Technol. 361 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 陈文哲, 王霜, 翟玉玲, 李舟航 2023 化工进展 42 5700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W Z, Wang S, Zhai Y L, Li Z H 2023 Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 42 5700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Pang C W, Jung J, Kang Y T 2014 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 72 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hou J M, Shao C, Huang L Z, Du J Y, Wang R J 2023 Powder Technol. 430 119005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhou L, Zhu J W, Zhao Y F, Ma H H 2022 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 183 122124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Rennhofer H, Zanghellini B 2021 Nanomaterials 11 1469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Premalatha M, Jeevaraj A K S 2017 Part. Sci. Technol. 36 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Rathinavel S, Priyadharshini K, Panda D 2021 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 268 115095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang X, Zhang Y H, Yan Y R, Chen Z H 2022 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 236 111546
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Cui X, Wang J, Xia G D 2022 Nanoscale 14 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Kobayashi Y, Arai N 2019 J. Electrochem. Soc. 166 B3223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Sarkar S, Selvam R P 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 074302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Tersoff J 1988 Phys. Rev. B 37 6991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Rudyak V Y, Krasnolutskii S L 2017 Tech. Phys. 62 1456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Huang J, Sang L X, Yang Q F, Wu Y T 2024 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 277 113150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Koo J, Kleinstreuer C 2004 J. Nanopart. Res. 6 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Zhang C Z, Puligheddu M, ZhangL F, Car R, Galli G 2023 J. Phys. Chem. B 127 7011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Wang R J, Qian S, Zhang Z Q 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 127 1138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 亲疏水性不同的SWCNT-OH颗粒
Table 1. SWCNT-OH particles with different hydrophilicity.
颗粒类型 SWCNT-OH颗粒 羟基数量 0 8 16 24 32 羟基密度/% 0 5.3 10.6 16.0 21.3 示意图 




表 2 亲疏水性不同的SWCNT-OH-Janus颗粒
Table 2. SWCNT-OH-Janus particles with different hydrophilicity.
颗粒类型 SWCNT-OH-Janus颗粒 羟基数量 0 4 8 12 16 羟基密度/% 0 5.3 10.6 16.0 21.3 示意图 




-
[1] Liu M S, Lin M C, Tsai C Y, Wang C C 2006 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49 3028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Choi S U S, Zhang Z G, Yu W, Lockwood F E, Grulke E A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Han X F, Lu L W, Yan S Y, Yang X H, Tian R, Zhao X Y 2021 J. Therm. Sci. 30 1581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ishii K, Ogiyama T, Fumoto K, Nishina Y 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 125 023104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王军, 崔鑫, 夏国栋 2023 北京工业大学学报 49 1116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Cui X, Xia G D 2023 J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 49 1116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xuan Y M, Li Q 2000 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 21 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu B, Liang W H, Luo Z M, Sarvar S, Fereidooni L, Kasaeian A 2024 Mol. Liq. 414 126052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xuan Y M, Duan H L, Li Q 2014 RSC Adv. 4 16206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rapp B, Hussam A 2023 J. Appl. Phys. 133 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Dai J H, Zhai Y L, Li Z H, Wang H 2024 J. Mol. Liq. 400 124518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu W W, Wang J, Xia G D, Li Z G 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 083316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu W W, Cui J, Wang J, Xia G D, Li Z G 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 032004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu W, Choi S U S 2004 J. Nanopart. Res. 6 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 谢华清, 奚同庚, 王锦昌 2003 52 1444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie H Q, Xi T G, Wang J C 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xue L, Keblinski P, Phillpot S R, Choi S U S, Eastman J A 2004 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张智奇, 钱胜, 王瑞金, 朱泽飞 2019 68 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z Q, Qian S, Wang R J, Zhu Z F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Karthik V, Sahoo S, Pabi S K, Ghosh S 2013 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 64 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cui W Z, Shen Z J, Yang J G, Wu S H 2015 Appl. Therm. Eng. 76 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李屹同, 沈谅平, 王浩, 汪汉斌 2013 62 124401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li YT, Shen L P, Wang H, Wang H B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 124401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lenin R, Joy P A, Bera C 2021 J. Mol. Liq. 338 116929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘旺旺, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋 2024 73 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W W, Zhang K X, Wang J, Xia G D 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 075101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Roni M R H, Shahadat M R B, Morshed A M M 2021 Micro Nano Lett. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jabbari F, Rajabpour A, Saedodin S 2017 Chem. Eng. Sci. 174 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cui W Z, Shen Z J, Yang J G, Wu S H, Bai M L 2014 RSC Adv. 4 55580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kamalvand M, Karami M 2013 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 65 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 侯泉文, 曹炳阳, 过增元 2009 58 7809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Q W, Cao B Y, Guo Z Y 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 7809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jabbari F, Rajabpour A, Saedodin S 2021 Microfluid. Nanofluid. 25 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xing M B, Yu J L, Wang R X 2015 Appl. Therm. Eng. 87 344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li X K, Chen W J, Zou C J 2020 Powder Technol. 361 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 陈文哲, 王霜, 翟玉玲, 李舟航 2023 化工进展 42 5700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W Z, Wang S, Zhai Y L, Li Z H 2023 Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 42 5700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Pang C W, Jung J, Kang Y T 2014 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 72 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hou J M, Shao C, Huang L Z, Du J Y, Wang R J 2023 Powder Technol. 430 119005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhou L, Zhu J W, Zhao Y F, Ma H H 2022 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 183 122124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Rennhofer H, Zanghellini B 2021 Nanomaterials 11 1469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Premalatha M, Jeevaraj A K S 2017 Part. Sci. Technol. 36 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Rathinavel S, Priyadharshini K, Panda D 2021 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 268 115095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang X, Zhang Y H, Yan Y R, Chen Z H 2022 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 236 111546
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Cui X, Wang J, Xia G D 2022 Nanoscale 14 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Kobayashi Y, Arai N 2019 J. Electrochem. Soc. 166 B3223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Sarkar S, Selvam R P 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 074302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Tersoff J 1988 Phys. Rev. B 37 6991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Rudyak V Y, Krasnolutskii S L 2017 Tech. Phys. 62 1456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Huang J, Sang L X, Yang Q F, Wu Y T 2024 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 277 113150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Koo J, Kleinstreuer C 2004 J. Nanopart. Res. 6 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Zhang C Z, Puligheddu M, ZhangL F, Car R, Galli G 2023 J. Phys. Chem. B 127 7011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Wang R J, Qian S, Zhang Z Q 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 127 1138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3407
- PDF Downloads: 94
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: