-
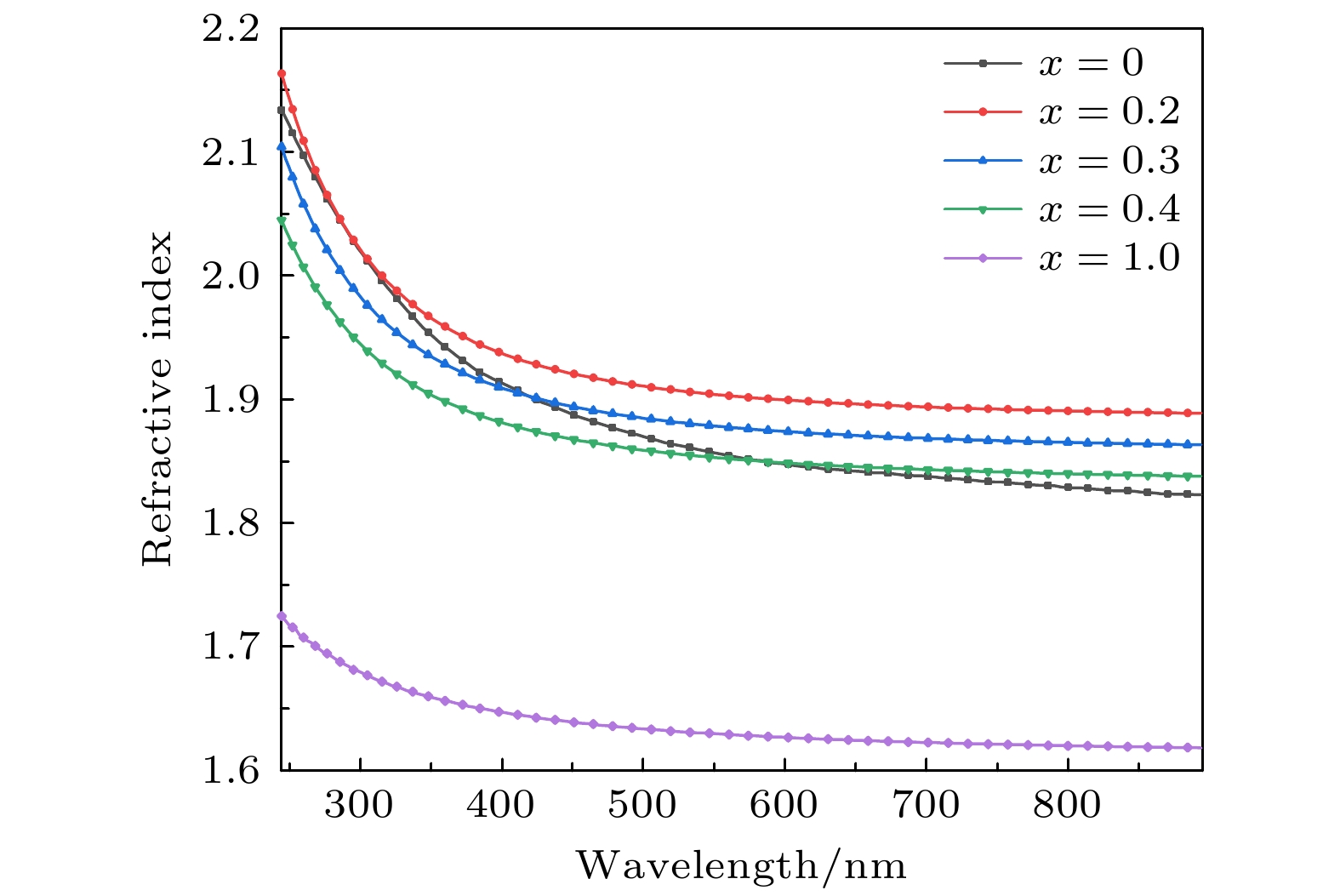
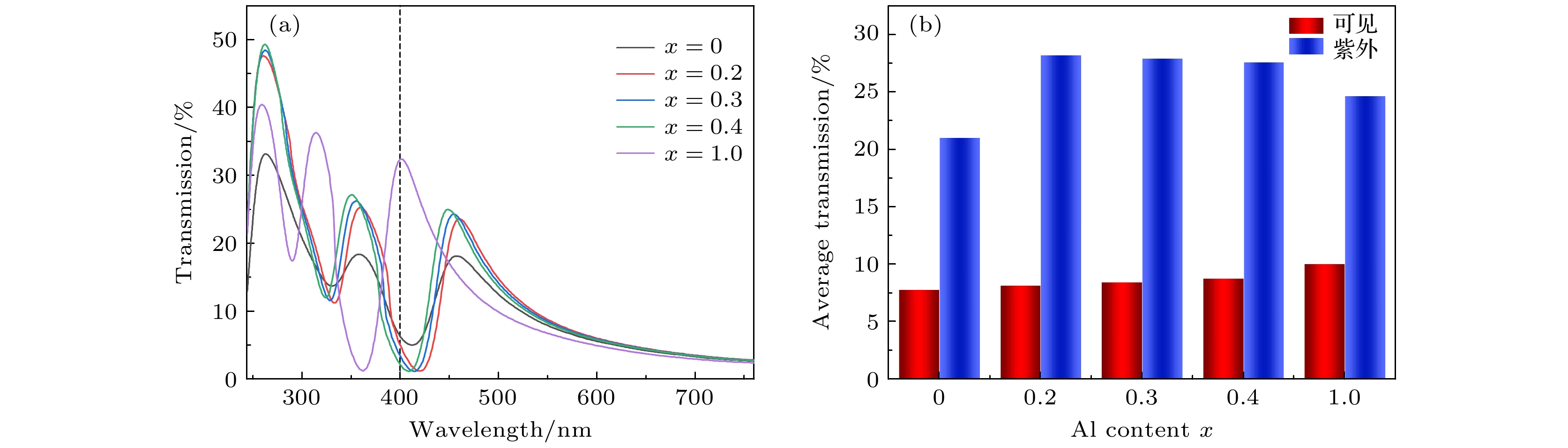
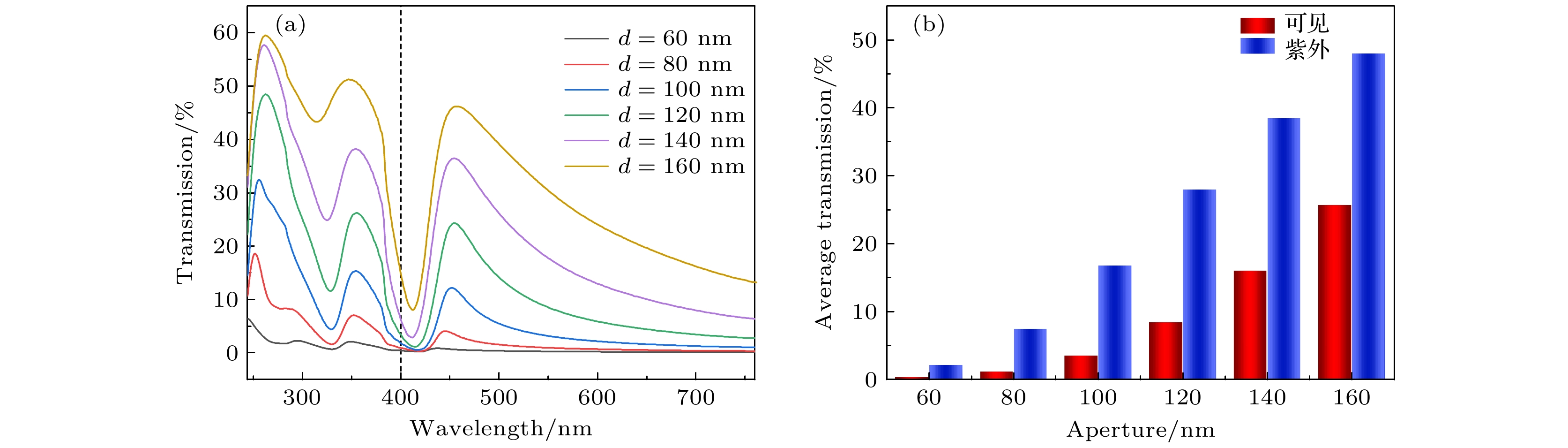
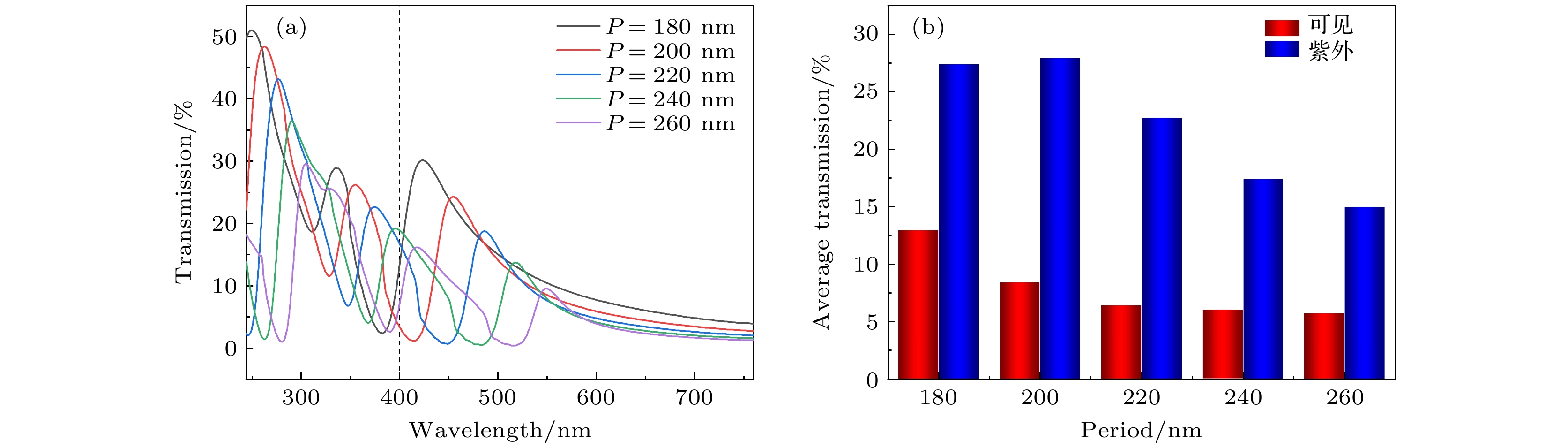
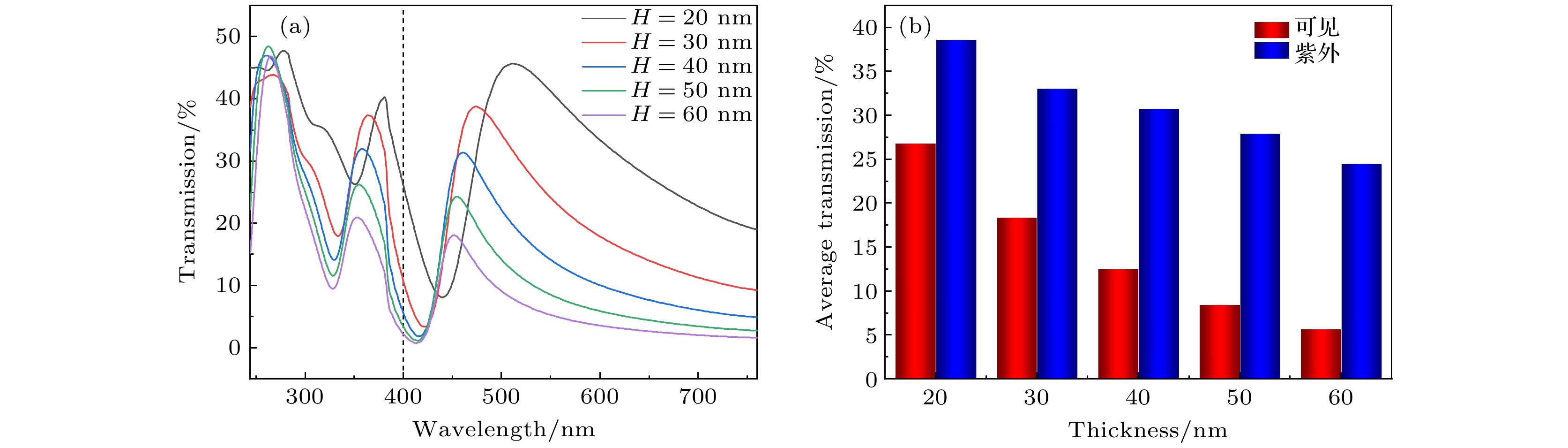
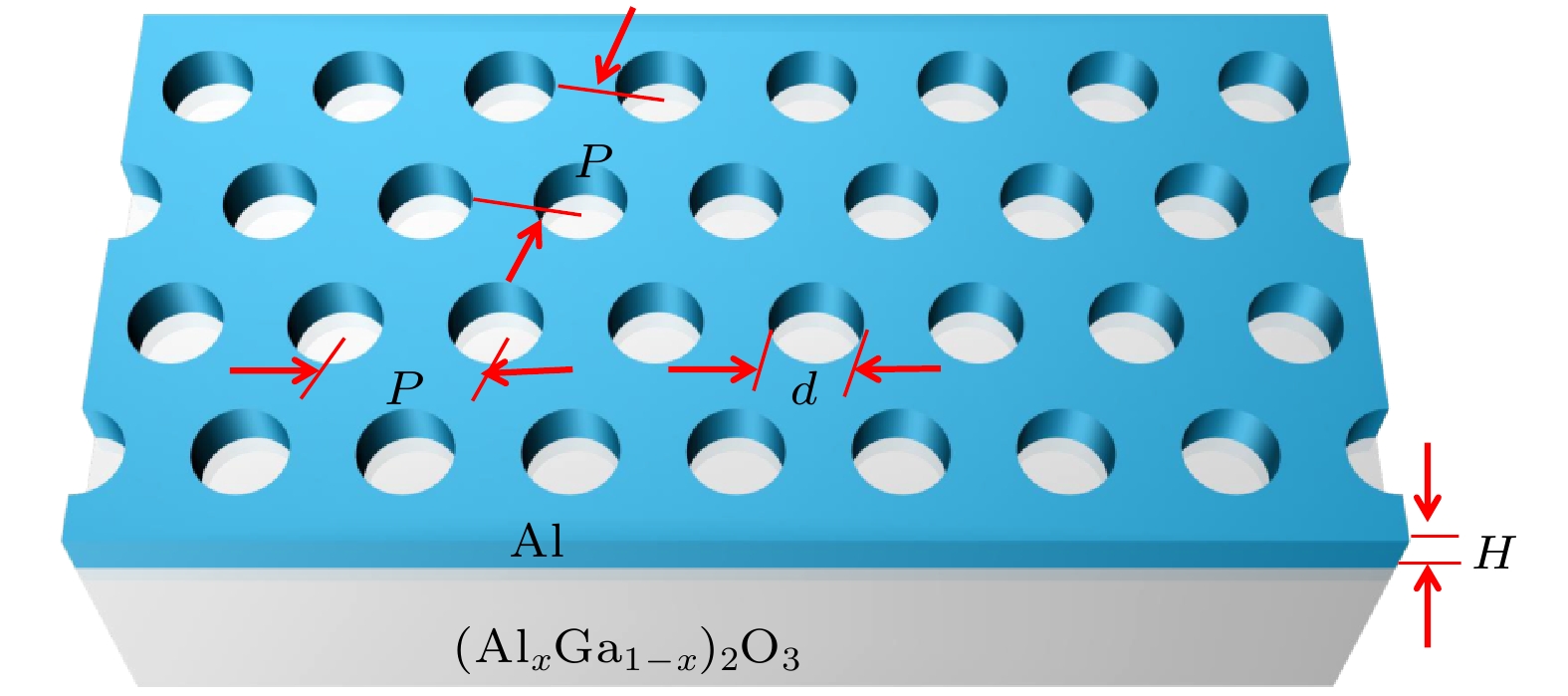
The finite difference time domain method is used to compute the transmissions of periodic triangular-lattice Al nanopore arrays on (AlxGa1–x)2O3 thin film substrates. The influences of Al component x in(AlxGa1–x)2O3 substrate, and the thickness, aperture and period of Al nanopore array on their optical transmission behaviors are studied systematically. The numerical results indicate that when x = 0, there are two strong transmission peaks at 263 nm and 358 nm, respectively. As x increases, the transmission peak at 263 nm exhibits a slight blue-shift, with intensity first increasing and then decreasing. Meanwhile, the transmission peak at 358 nm demonstrates a noticeable blue-shift and its intensity strengthens continuously. The change of Al component x has a significant effect on the peak position of the transmission peak in the longer ultraviolet band and the peak transmission in the shorter ultraviolet band. If the periodic structure of the nanopore array keeps unchangeable, the two prominent transmission peaks appear near 244 nm and 347 nm, respectively, as the air column apertures enlarge. Remarkably, these dual peaks initially undergo a red-shift, followed by a blue-shift, while the transmission steadily increases and the reflectivity decreases. The change in aperture size can significantly affect the peak transmission, and by controlling the aperture size appropriately, the transmission intensity can be significantly enhanced. With the expansion of the period, the two strong transmission peaks are located at 249 nm and 336 nm, respectively, and the two transmission peaks show obvious red-shift. The former transmission peak is redshifted to 304 nm, and the latter one is redshifted to 417 nm. Moreover, the transmissions at these peaks continue to decrease. The change in period can significantly affect the central wavelength of the transmission peak, and the periodicity of the array plays a dominant role in modulating the peak position in a large wavelength range. As Al thickness increases, a blue-shift of the transmission peak occurs at 380 nm , and the transmission decreases continuously. The change in thickness significantly affects the transmission intensity of the transmission peak in the longer ultraviolet band and the visible light region, but it is not so pronounced as the effect of aperture size on transmission intensity. Through reasonable design and optimization of structural parameters of Al nanopore array/(AlxGa1–x)2O3, the peak position of transmission peak can be effectively regulated and the extraordinary transmission in ultraviolet band can be achieved. -
Keywords:
- (AlxGa1–x)2O3 /
- nanopore array /
- local surface plasmon resonance /
- extraordinary transmission
[1] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, Thio T, Wolff P A 1998 Nature 391 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang L S, Wang G X, Yang K, Zhang W N, Liu W J 2023 Opt. Commun. 535 129336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hou Y M 2011 Plasmonics 6 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tam H T T, Kajikawa K 2021 Opt. Express 29 35191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yue W S, Wang Z H, Yang Y, Li J Q, Wu Y, Chen L Q, Ooi B, Wang X B, Zhang X X 2014 Nanoscale 6 7917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 关建飞, 俞潇, 丁冠天, 陈陶, 陆云清 2024 73 117301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan J F, Yu X, Ding G T, Chen T, Lu y Q 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 117301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陆云清, 成心怡, 许敏, 许吉, 王瑾 2016 65 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Y Q, Cheng X Y, Xu M, Xu J, Wang J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Du B B, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Jia P P, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H, Ruan Y L, Yang D X 2019 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52 275201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ozbay E 2006 Science 311 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barnes W L, Dereux A, Ebbesen T W 2003 Nature 424 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ekinci Y, Solak H H, David C 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hu J L, Shen M Z, Li Z G, Li X H, Liu G Q, Wang X D, Kan C X, Li Y 2017 Nanotechnology 28 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang X G, Liu G Q, Liu, Z Q, Hu Y, Cai Z J, Liu X S, Fu G L, Liu M L 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 107108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Watanabe Y, Inami W, Kawata Y 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 023112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ekinci Y, Solak H H, Loeffler J F 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 083107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H J, Wu Z Y, Wu S Y, Tian P F, Fang Z L 2023 J. Alloys Compd. 960 170671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bhuiyan A F M A U, Feng Z X, Meng L Y, Fiedler A, Huang H L, Neal A T, Steinbrunner E, Mou S, Hwang J, Rajan S, Zhao H P 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 145301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang R, Wang Z Y, Wu K, Xu H, Wang Q, Guo Y C 2024 J. Semicond. 45 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xi H R, Yang T F, Xie M Y, Liang X J, Fang Z L, Ye Y, Chen Y, Wei Y M, Wang Z, Guan H Y, Lu H H 2024 Laser Photon. Rev. 18 2301129
[20] Dashkov A S, Khakhulin S A, Shapran D A, Glinskii G F, KostrominN A, Vasilev A L, Yakunin S N, Komkov O S, Pirogov E V, Sobolev M S, Goray L I, Bouravleuv A D 2024 J. Semicond. 45 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhukovsky S V, Andryieuski A, Takayama O, Shkondin E, Malureanu R, Jensen F, Lavrinenko A V 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 177402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tolmachev V A, Mavlyanov R K, Kalinin D A, Zharova Y A, Zaitseva N V, Pavlov S I 2017 Opt. Spectrosc. 123 928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 潘磊, 宋宝安, 肖传富, 张培晴, 林常规, 戴世勋 2020 69 114201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L, Song B A, Xiao C F, Zhang P Q, Lin C G, Dai S X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 114201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Schmidt-Grund R, Kranert C, von Wenckstern H, Zviagin V, Lorenz M, Grundmann M 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 165307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] MALITSON I H 1962 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 52 1377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Genet C, Ebbesen T W 2007 Nature 445 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Van der Molen K L, Klein Koerkamp K J, Enoch S, Segerink F B, van Hulst N F, Kuipers L 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 045421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Han J G, Azad A K, Gong M F, Lu X C, Zhang W L 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 071122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Z W, Steele J M, Srituravanich W, Pikus Y, Sun C, Zhang X 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Bethe H A 1944 Phys. Rev. 66 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
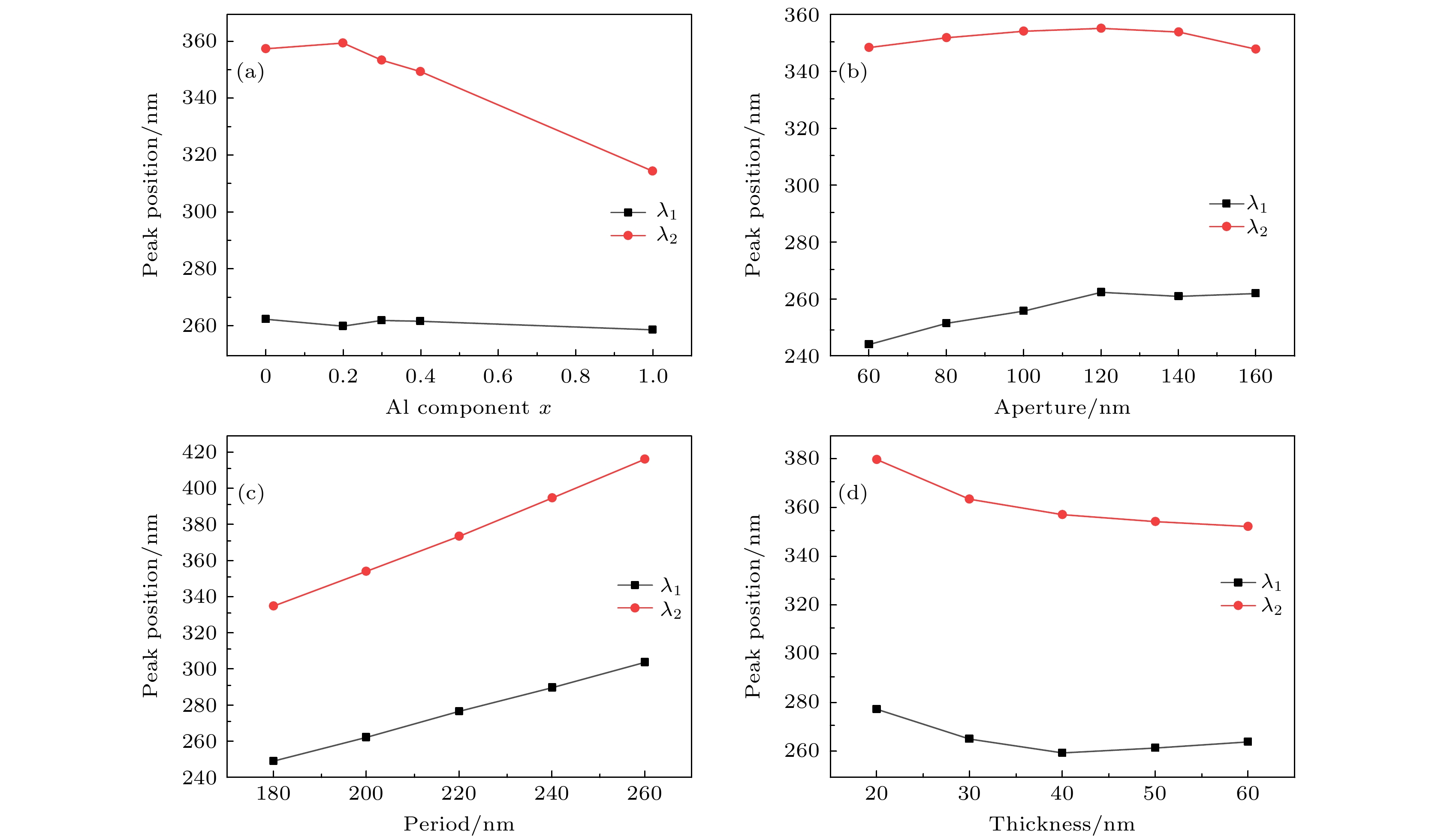
图 7 紫外波段透射峰中心波长λ1和λ2随结构参数x, d, P, H的变化 (a) 中心波长随Al组分x的演变规律; (b) 中心波长随孔径d的演变规律; (c) 中心波长随周期P的演变规律; (d) 中心波长随厚度H的演变规律
Figure 7. Changes of the peak position of the transmission peaks in the ultraviolet band with structural parameters x, d, P and H: (a) Evolution of peak position with Al component x; (b) evolution of peak position with aperture d; (c) evolution of peak position with period P; (d) evolution of peak position with thickness H.
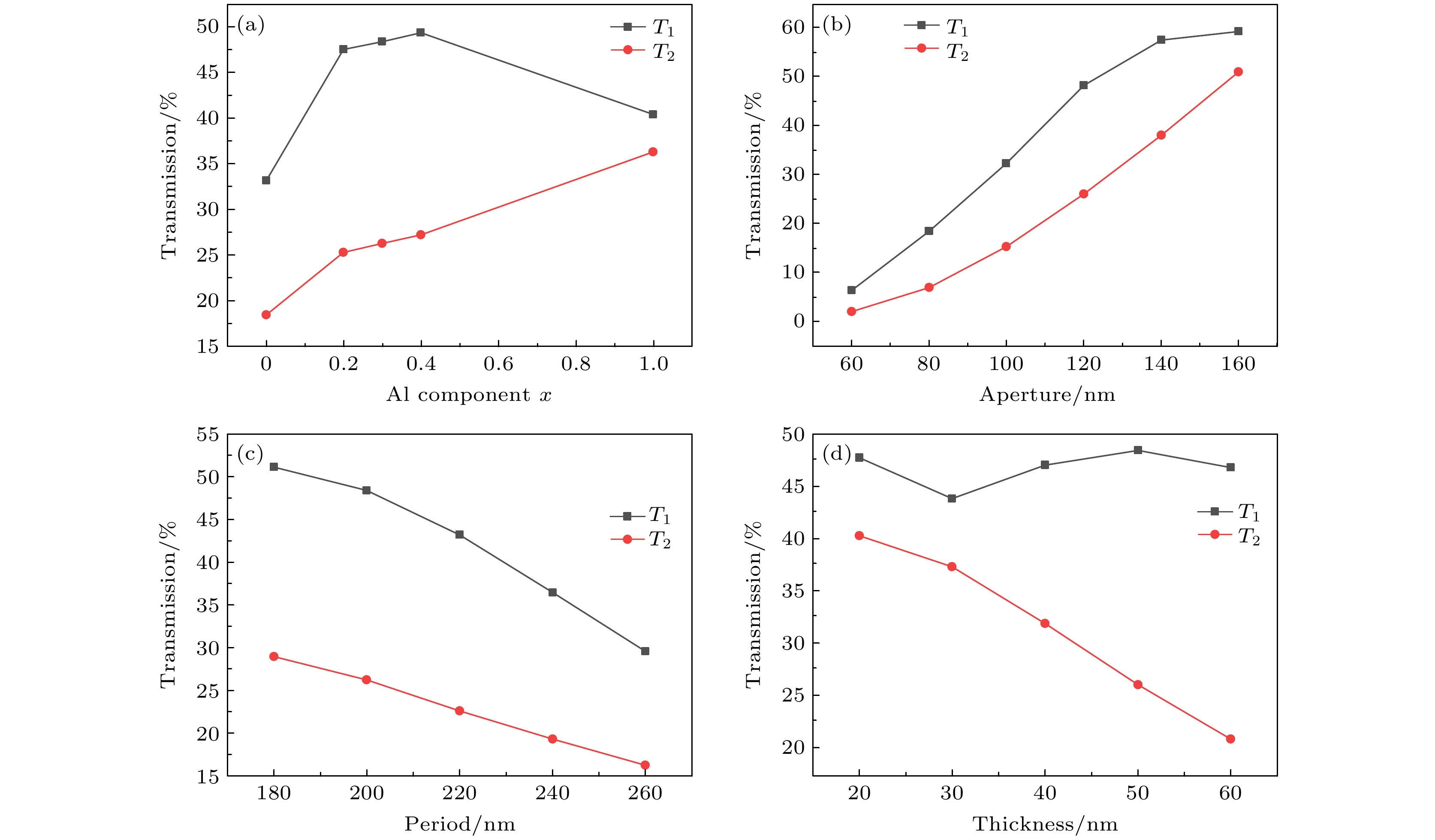
图 8 紫外波段透射峰峰值处透过率T1和T2随结构参数x, d, P, H的变化 (a) 峰值处透过率随Al组分x的演变规律; (b) 峰值处透过率随孔径d的演变规律; (c) 峰值处透过率随周期P的演变规律; (d) 峰值处透过率随厚度H的演变规律
Figure 8. Changes of peak transmission in the ultraviolet band with structural parameters x, d, P and H: (a) Evolution of peak transmission with Al component x; (b) evolution of peak transmission with aperture d; (c) evolution of peak transmission with period P; (d) evolution of peak transmission with thickness H.
-
[1] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, Thio T, Wolff P A 1998 Nature 391 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang L S, Wang G X, Yang K, Zhang W N, Liu W J 2023 Opt. Commun. 535 129336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hou Y M 2011 Plasmonics 6 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tam H T T, Kajikawa K 2021 Opt. Express 29 35191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yue W S, Wang Z H, Yang Y, Li J Q, Wu Y, Chen L Q, Ooi B, Wang X B, Zhang X X 2014 Nanoscale 6 7917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 关建飞, 俞潇, 丁冠天, 陈陶, 陆云清 2024 73 117301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan J F, Yu X, Ding G T, Chen T, Lu y Q 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 117301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陆云清, 成心怡, 许敏, 许吉, 王瑾 2016 65 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Y Q, Cheng X Y, Xu M, Xu J, Wang J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Du B B, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Jia P P, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H, Ruan Y L, Yang D X 2019 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52 275201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ozbay E 2006 Science 311 189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barnes W L, Dereux A, Ebbesen T W 2003 Nature 424 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ekinci Y, Solak H H, David C 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hu J L, Shen M Z, Li Z G, Li X H, Liu G Q, Wang X D, Kan C X, Li Y 2017 Nanotechnology 28 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang X G, Liu G Q, Liu, Z Q, Hu Y, Cai Z J, Liu X S, Fu G L, Liu M L 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 107108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Watanabe Y, Inami W, Kawata Y 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 023112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ekinci Y, Solak H H, Loeffler J F 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 083107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H J, Wu Z Y, Wu S Y, Tian P F, Fang Z L 2023 J. Alloys Compd. 960 170671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bhuiyan A F M A U, Feng Z X, Meng L Y, Fiedler A, Huang H L, Neal A T, Steinbrunner E, Mou S, Hwang J, Rajan S, Zhao H P 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 145301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang R, Wang Z Y, Wu K, Xu H, Wang Q, Guo Y C 2024 J. Semicond. 45 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xi H R, Yang T F, Xie M Y, Liang X J, Fang Z L, Ye Y, Chen Y, Wei Y M, Wang Z, Guan H Y, Lu H H 2024 Laser Photon. Rev. 18 2301129
[20] Dashkov A S, Khakhulin S A, Shapran D A, Glinskii G F, KostrominN A, Vasilev A L, Yakunin S N, Komkov O S, Pirogov E V, Sobolev M S, Goray L I, Bouravleuv A D 2024 J. Semicond. 45 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhukovsky S V, Andryieuski A, Takayama O, Shkondin E, Malureanu R, Jensen F, Lavrinenko A V 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 177402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tolmachev V A, Mavlyanov R K, Kalinin D A, Zharova Y A, Zaitseva N V, Pavlov S I 2017 Opt. Spectrosc. 123 928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 潘磊, 宋宝安, 肖传富, 张培晴, 林常规, 戴世勋 2020 69 114201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L, Song B A, Xiao C F, Zhang P Q, Lin C G, Dai S X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 114201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Schmidt-Grund R, Kranert C, von Wenckstern H, Zviagin V, Lorenz M, Grundmann M 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 165307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] MALITSON I H 1962 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 52 1377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Genet C, Ebbesen T W 2007 Nature 445 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Van der Molen K L, Klein Koerkamp K J, Enoch S, Segerink F B, van Hulst N F, Kuipers L 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 045421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Han J G, Azad A K, Gong M F, Lu X C, Zhang W L 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 071122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Z W, Steele J M, Srituravanich W, Pikus Y, Sun C, Zhang X 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Bethe H A 1944 Phys. Rev. 66 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
 20-20240928数据.zip
20-20240928数据.zip

Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3412
- PDF Downloads: 121
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: