-
金属纳米结构中传导电子的集体振荡所产生的表面等离子体不仅可以在时间和空间上重新分布电磁场, 还可以重新分布被激发的载流子. 由表面等离子体引起的各种效应, 包括增强的电磁场、局部加热、激发的电子和激发的空穴, 可以驱动化学反应等. 本文基于阳极氧化铝模板制备出排列规则的金纳米阵列催化基底, 当特定波长的激发光作用于该基底时其表面将会产生大量排列规则的局域表面等离子体增强区域. 借助表面增强拉曼光谱技术具有指纹普的优势, 实时监测以对氨基硫酚作为探针分子在局域表面等离子体的驱动下发生光催化反应生成4,4′-二巯基偶氮苯. 此后, 原位引入硼氢化钠在相同的实验条件下, 可以将生成物4,4′-二巯基偶氮苯在等离子体的驱动下再一次发生逆向化学反应生成对氨基硫酚分子. 该项研究工作将在微纳尺度下实现分子图形的绘制和擦除, 基于该技术进行信息加密、读取和擦写等领域具有潜在的应用价值.The surface plasmons produced by the collective oscillation of conduction electrons in metal nanostructures can redistribute not only the electromagnetic field spatiotemporally, but also the excited carriers. Various effects caused by surface plasmons, including enhanced electromagnetic fields, local heating, excited electrons and excited holes, can drive chemical reactions. In this work, the regularly-arranged Au nanoarray catalytic substrate is prepared based on an anodic aluminum oxide template. When the excitation light of a specific wavelength irradiates on the substrate, a large number of regularly-arranged local surface plasmon enhancement regions will be generated on its surface. By taking advantage of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy, the 4,4′-dimercaptoazobenzene is synthesized by the photocatalytic reaction of p-aminothiophenol as a probe driven by local surface plasmon. After that, the sodium borohydride is introduced in situ. Under the same experimental conditions, the product 4,4′-dimercaptoazobenzene is driven by plasma to produce p-aminothiophenol again. This research work will achieve the drawing and erasing of molecular graphics on a micro scale and a nano scale, as well as information encryption, reading and erasing, which has a strong application value.
-
Keywords:
- gold nanoarrays /
- surface plasmon /
- Raman spectroscopy /
- photocatalysis
[1] Fleischmann M, Hendra P J, McQuillan A J Raman 1974 Chem. Phys. Lett. 26 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Jeanmaire D L, van Duyne R P 1977 J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem 84 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu X J, Tang L H, Niessner R, Ying Y B, Haisch C 2015 Anal. Chem. 87 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhan C, Chen X J, Huang Y F, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q 2019 Acc. Chem. Res. 52 2784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang Z Y, Kneipp J 2018 Anal. Chem. 90 9199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qi X N, Wei Y Q, Jiang C X, Zhang L S, Wang P J, Fang Y 2020 SpectrochimicaActa Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 237 118362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lin W H, Cao Y Q, Wang P J, Sun M T 2017 Langmuir 33 12102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sheng S X, Ji Y F, Yan X H, Wei H, Luo Y, Xu H X 2020 J. Phys. Chem. C 124 11586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jiang C X, Wei Y Q, Zhao P C, Wang P J, Fang Y, Zhang L S 2020 Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135 671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mayer K M, Hafner J H 2011 Chem. Rev. 111 3828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jain P K, Huang X, El-Sayed I H, El-Sayed M A 2008 Acc. Chem. Res. 41 1578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lal S, Clare S E, Halas N J 2008 Acc. Chem. Res. 41 1842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhan C, Chen X J, Yi J, Li J F, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q 2018 Nat. Rev. Chem. 2 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y, He S, Guo W, Hu Y, Huang J, Mulcahy J R, Wei W D 2018 Chem. Rev. 118 2927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aslam U, Rao V G, Chavez S, Linic S 2018 Nat. Catal. 1 656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim S, Kim J M, Park J E, Nam J M 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1704528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun M, Xu H 2012 Small 8 2777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Aslam U, Chavez S, Linic S 2017 Nat. Nanotechnol. 12 1000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zayats A V, Maier S 2017 Adv. Opt. Mater. 5 1700508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang Y F, Wang W, Guo H Y, Zhan C, Duan S, Zhan D P, Wu D Y, Ren B, Tian Z Q 2020 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 8483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zeng Z, Qi X N, Li X J, Zhang L S, Wang P J, Fang Y 2019 Appl. Surf. Sci. 480 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y Q, Zhao L J, Li X J, Zeng Z, Wang P J, Zhang L S, Fang Y 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 428 900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Linic S, Aslam U, Boerigter C, Morabito M 2015 Nat. Mater. 14 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang Z L, Xu P, Yang X Z, Liang W J, Sun M T 2016 J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 27 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Moskovits M 1985 Rev. Mod. Phys. 57 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Itzkan I, Dasari R R, Feld M S 1999 Chem. Rev. 99 2957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lombardi J R, Birke R L 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 5605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
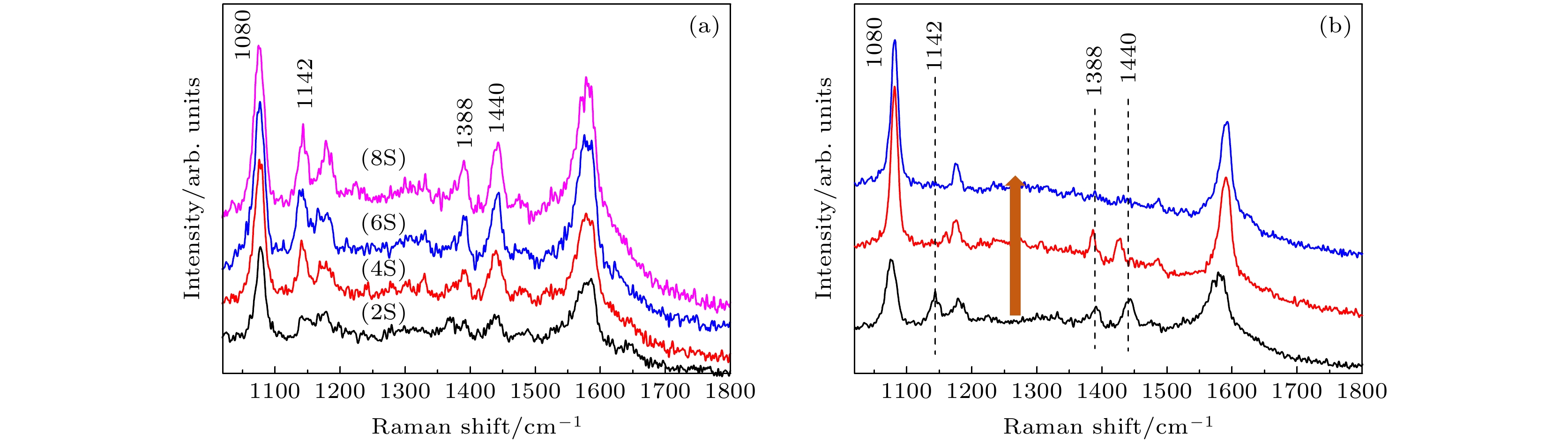
图 1 ATP表面等离子体驱动光催化反应生成DMAB过程 (a) PATP拉曼特征峰; (b) DMAB拉曼特征峰; (c)等离子体驱动光催化反应示意图
Fig. 1. Formation process of DMAB from PATP surface plasma driven photocatalytic reaction: (a) PATP Raman characteristic peak; (b) DMAB Raman characteristic peak; (c) schematic diagram of plasma driven photocatalytic reaction.
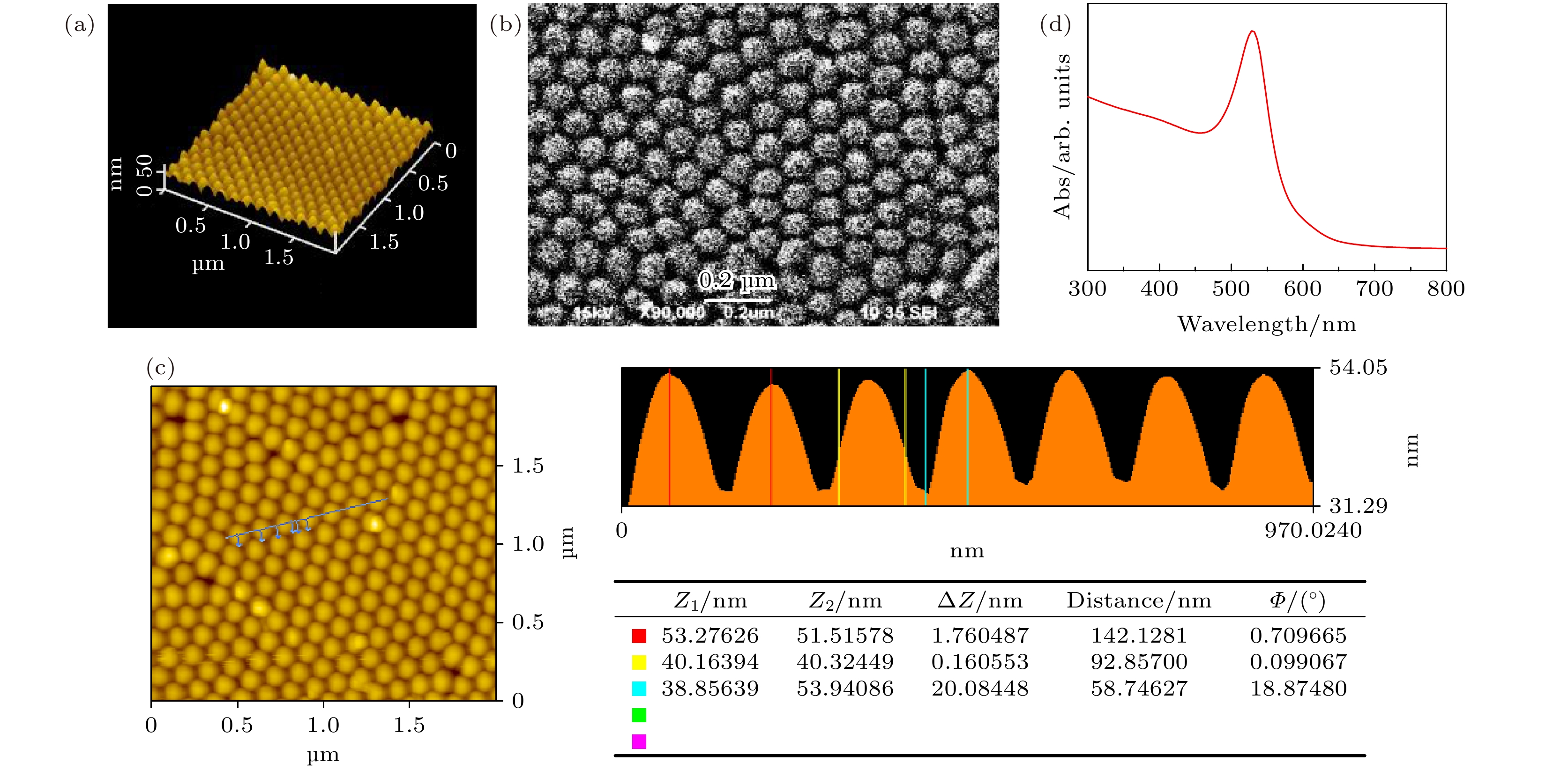
图 2 金纳米阵列基底的形貌表征 (a)金纳米阵列的三维原子力显微镜图片; (b)金纳米阵列的扫面电子显微镜图片; (c)金纳米阵列几何尺寸分析; (d)采用FDTD模拟得出金纳米阵列的消光谱
Fig. 2. Surface topography of gold nanoarray substrate: (a)Three-dimensional AFM image of gold nanoarray; (b) SEM image of gold nanoarray; (c) geometric dimension analysis of gold nanoarray; (d) extinction spectrum of gold nano array by FDTD simulation.
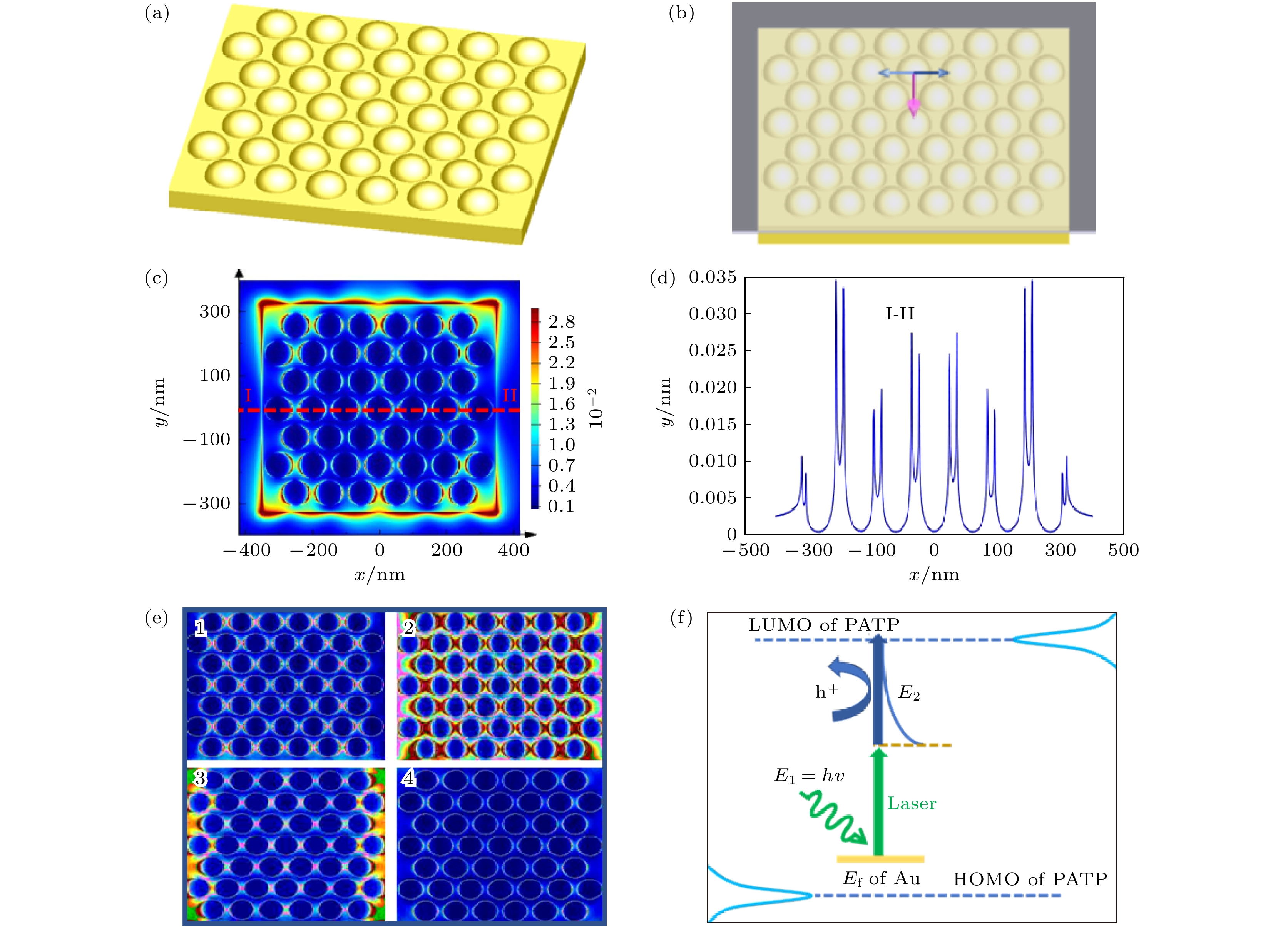
图 4 金纳米阵列基底等离子体驱动光催化机制 (a)金纳米阵列理论模型; (b)金纳米阵列表面等离子体模拟激发光偏振方向; (c)金纳米阵列表面等离子体强度分布特性计算结果; (d)金纳米阵列表面等离子体模拟强度分布分析; (e)金纳米阵列表面等离子体分布随时间变化模拟结果; (f)金纳米阵列基底等离子体驱动光催化机制示意图, 其中E2是来自于633 nm激光激发热电子/空穴的能量
Fig. 4. Mechanism of gold nanoarray substrate plasma driven photocatalysis is as follows: (a)Theoretical model of gold nanoarray; (b) polarization direction of stimulated luminescence simulated by surface plasmon of gold nanoarray; (c) calculation results of intensity distribution characteristics of surface plasmon of gold nanoarray; (d) analysis of intensity distribution simulated by surface plasmon of gold nanoarray; (e) surface plasmon distribution of gold nanoarray; (f) mechanism of Au nanoarray substrate plasma driven photocatalysis, E2 is energy distribution of hot electrons/holes excited by 633 nm laser.
-
[1] Fleischmann M, Hendra P J, McQuillan A J Raman 1974 Chem. Phys. Lett. 26 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Jeanmaire D L, van Duyne R P 1977 J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem 84 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu X J, Tang L H, Niessner R, Ying Y B, Haisch C 2015 Anal. Chem. 87 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhan C, Chen X J, Huang Y F, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q 2019 Acc. Chem. Res. 52 2784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang Z Y, Kneipp J 2018 Anal. Chem. 90 9199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qi X N, Wei Y Q, Jiang C X, Zhang L S, Wang P J, Fang Y 2020 SpectrochimicaActa Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 237 118362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lin W H, Cao Y Q, Wang P J, Sun M T 2017 Langmuir 33 12102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sheng S X, Ji Y F, Yan X H, Wei H, Luo Y, Xu H X 2020 J. Phys. Chem. C 124 11586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jiang C X, Wei Y Q, Zhao P C, Wang P J, Fang Y, Zhang L S 2020 Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135 671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mayer K M, Hafner J H 2011 Chem. Rev. 111 3828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jain P K, Huang X, El-Sayed I H, El-Sayed M A 2008 Acc. Chem. Res. 41 1578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lal S, Clare S E, Halas N J 2008 Acc. Chem. Res. 41 1842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhan C, Chen X J, Yi J, Li J F, Wu D Y, Tian Z Q 2018 Nat. Rev. Chem. 2 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y, He S, Guo W, Hu Y, Huang J, Mulcahy J R, Wei W D 2018 Chem. Rev. 118 2927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aslam U, Rao V G, Chavez S, Linic S 2018 Nat. Catal. 1 656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim S, Kim J M, Park J E, Nam J M 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1704528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun M, Xu H 2012 Small 8 2777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Aslam U, Chavez S, Linic S 2017 Nat. Nanotechnol. 12 1000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zayats A V, Maier S 2017 Adv. Opt. Mater. 5 1700508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang Y F, Wang W, Guo H Y, Zhan C, Duan S, Zhan D P, Wu D Y, Ren B, Tian Z Q 2020 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 8483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zeng Z, Qi X N, Li X J, Zhang L S, Wang P J, Fang Y 2019 Appl. Surf. Sci. 480 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y Q, Zhao L J, Li X J, Zeng Z, Wang P J, Zhang L S, Fang Y 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 428 900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Linic S, Aslam U, Boerigter C, Morabito M 2015 Nat. Mater. 14 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang Z L, Xu P, Yang X Z, Liang W J, Sun M T 2016 J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 27 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Moskovits M 1985 Rev. Mod. Phys. 57 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Itzkan I, Dasari R R, Feld M S 1999 Chem. Rev. 99 2957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lombardi J R, Birke R L 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 5605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7218
- PDF下载量: 111
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: