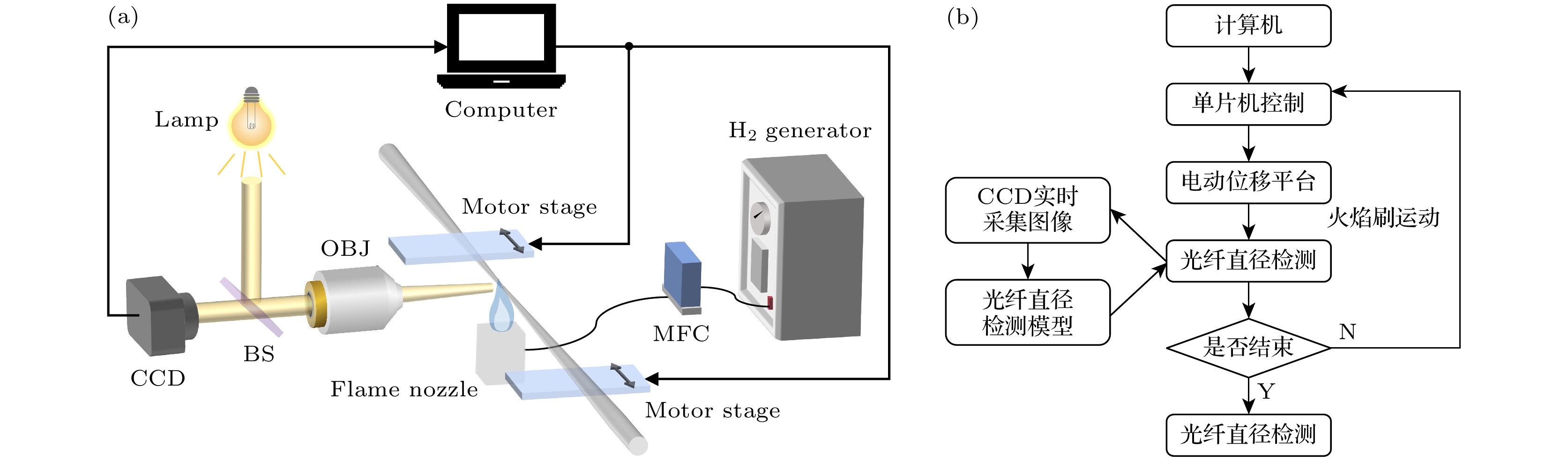
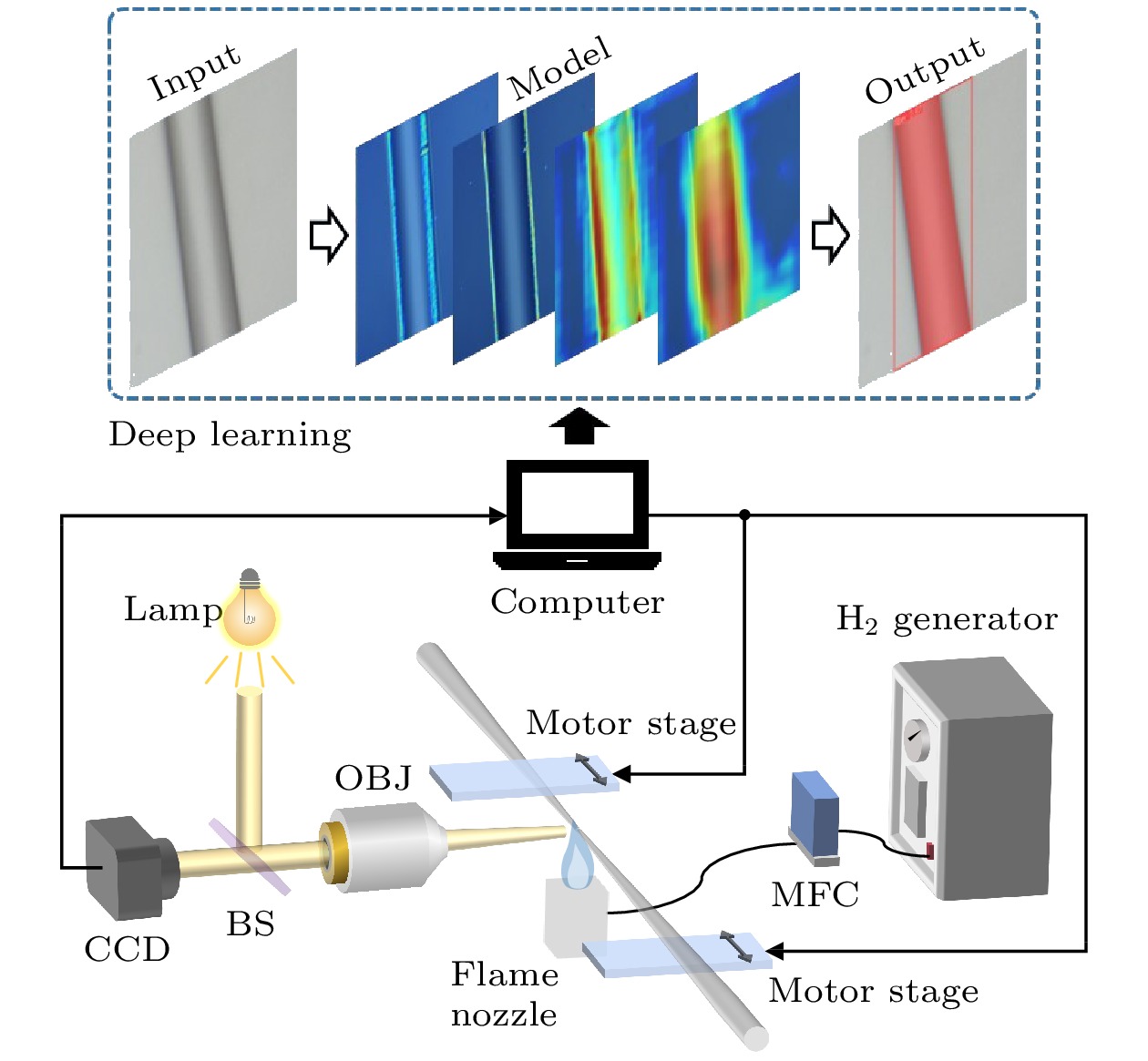
-
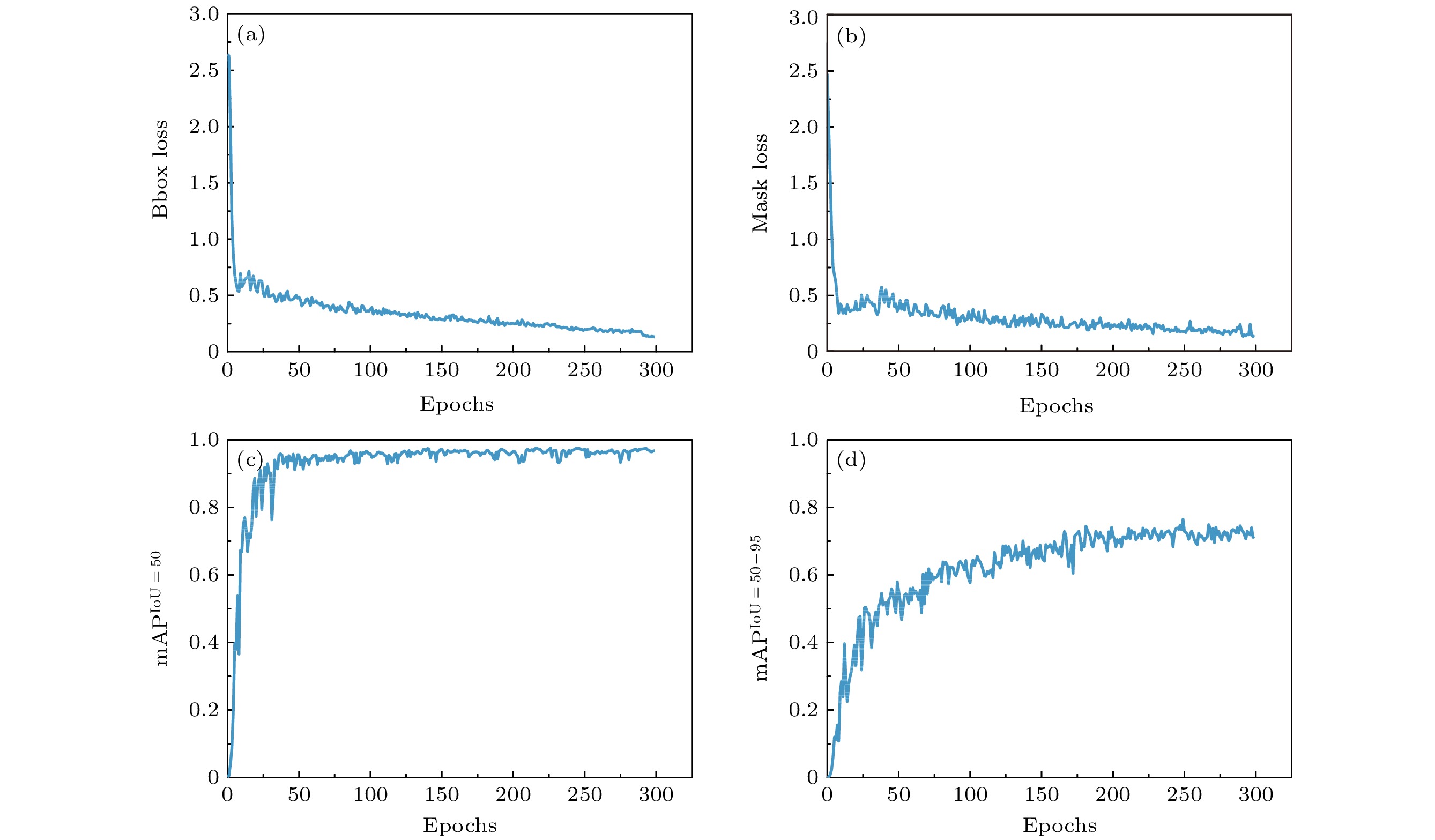
The wide range, high precision, and dynamic real-time measurement of micro-/nanofiber diameter are crucial for achieving low loss transmission and controlling dispersion in the preparation process of micro-nanofiber. In view of the problems of small diameter regulation range, complex operation and long-time consumption of the existing preparation methods, the automatic detection system of micro-nanofiber is realized based on deep learning neural network algorithm in this work. The image segmentation method in computer vision is used to make high-quality multi-scale micro-/nanofiber datasets, and the improved YOLOv8-FD (You Only Look Once version 8-Fiber Detection) algorithm based on small target detection is used to automatically detect the diameter of micro-nanofiber. Through image segmentation and identification of the target of single pixel size in the microscopic image, the diameter detection of micro-nanofiber is finally realized. In this process, the real-time diameter of micro-nanofiber is obtained through image information, and then the micro-nanofiber small target is accurately segmented to achieve the precise detection of mAPIoU=50 = 0.975 and mAPIoU=50—95 = 0.765 on the micro-nanofiber multi-scale target dataset with extremely high accuracy. The algorithm-based construction of a high-precision micro-nanofiber automatic preparation system enables real-time accurate segmentation of fiber edges, calculation of fiber diameter, and feedback to the control system for achieving automated preparation of fibers with arbitrary diameters. Additionally, it facilitates the detection of micro-nanofiber in a range from 462 nm to 125 μm. The average response time for reasoning is 9.6 ms, and the detection error is kept below 2.95%. In addition, compared with other micro-/nanofiber diameter detection methods based on optical imaging and mode cutoff, this method shows advantages of high precision, high speed and arbitrary diameter preparation for diameter detection based on deep learning neural networks. The system is very suitable for high-precision real-time measurement and automatic and accurate preparation of micro-/nanofibers, thereby providing a novel method of developing micro-nanofiber devices with low-loss transmission and adjustable dispersion. -
Keywords:
- micro-nanofiber /
- diameter measurement /
- deep learning /
- image segmentation
[1] 童利民 2022 光学学报 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong L M 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang L, Pan J, Zhang Z, Wu H, Yao N, Cai D W, Xu Y X, Zhang J, Sun G F, Wang L Q, Geng W D, Jin W G, Fang W, Di D W, Tong L M 2020 Opto-Electron Adv. 3 190022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yan Z Y, Wang J J, Wang C Y, Yu R W, Shi L, Xiao L M 2022 Opt. Express 30 18044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cen Q Q, Pian S J, Liu X H, Tang Y W, He X Y, Ma Y G 2023 eLight 3 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li Y H, Wang L Z, Li L J, Tong L M 2019 Appl. Phys. B 125 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lu J S, Li Q, Qiu C W, Hong Y, Ghosh P, Qiu M 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 8271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tkachenko G, Toftul I, Esporlas C, Maimaiti A, Kien F L, Truong V G, Chormaic S N 2020 Optica 7 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Linghu S Y, Gu Z Q, Lu J S, Fang W, Yang Z Y, Yu H K, Li Z Y, Zhu R L, Peng J, Zhan Q W, Zhuang S L, Gu M, Gu F X 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hao Z, Jiang B Q, Ma Y X, Yi R X, Gan X T, Zhao J L 2023 Opto-Electron Adv. 6 230012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang J B, Kang Y, Guo X, Li Y H, Liu K Y, Xie Y, Wu H, Cai D W, Gong J, Shi Z X, Jin Y Y, Wang P, Fang W, Zhang L, Tong L M 2023 Light Sci. Appl. 12 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J H, Xiong Y F, Xu F, Lu Y Q 2021 Light Sci. Appl. 10 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou J, Li Y, Ma Y, Yang Q, Liu Q 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Linghu S Y, Ma Y N, Gu Z Q, Zhu R L, Liu Y F, Liu H J, Gu F X 2022 Opt. Express 30 22755
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao F, Yu J X, Gu Z Q, Yang Z Y, Hasan T, Linghu S Y, Pang J, Fang W, Zhuang S L, Gu M, Gu F X 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 7398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 康仪, 刘可盈, 谢宇, 龚珏, 姚妮, 方伟, 郭欣, 张磊, 王攀, 童利民 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 084212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Y, Liu K Y, Xie Y, Gong Y, Yao N, Fang W, Guo X, Zhang L, Wang P, Tong L M 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. As. 50 084212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ni Y, Linghu S L, Xu Y X, Zhu R L, Zhou N, Gu F X, Zhang L, Fang W, Ding W, Tong L M 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 1069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Warken F, Giessen H 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Little D J, Kane D M 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu Y, Zhang X L, Song Z Q, Wang J F, Meng Z 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 8222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu Y X, Fang W, Tong L M 2017 Opt. Express 25 10434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kang Y, Gong J, Xu Y X, Yao N, Fang W, Guo X, Tong L M 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Azzoune A, Delaye P, Pauliat G 2019 Opt. Express 27 24403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李华, 麻艳娜, 谷付星 2022 光学仪器 44 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Ma Y N, Gu F X 2022 Opt. Instruments 44 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y 2017 ECCV 3 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 应大卫, 张思慧, 邓书金, 武海斌 2023 72 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ying D W, Zhang S H, Deng S J, Wu H B 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 南虎, 麻晓晶, 赵海博, 汤少杰, 刘卫华, 王大威, 贾春林 2021 70 076803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nan H, Ma X J, Zhao H B, Tang S J, Liu W H, Wang D W, Jia C L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 076803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollar P, Girshick R 2017 ICCV 17 2980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gu Z, Zhu R L, Shen T C, Dou L, Liu H J, Liu Y F, Liu X, Liu J, Zhuang S L, Gu F X 2023 Nat. Commun. 14 7663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 4 YOLOv8-FD热图可视化及结果 (a)第1层卷积层; (b)第4层卷积层; (c)第7层卷积层; (d)第10层卷积层; (e) 1280$ \times $1024 pixel微纳光纤图; (f) 640$ \times $512 pixel微纳光纤图; (g)图像分割时间9.8 ms; (h)图像分割时间9.5 ms
Figure 4. YOLOv8-FD heatmap visualization and segmentation results: (a) Layer 1 convolution layer; (b) layer 4 convolution layer; (c) layer 7 convolution layer; (d) layer 10 convolution layer; (e) 1280$ \times $1024 pixel micro-nanofiber image; (f) 640$ \times $512 pixel micro-nanofiber image; (g) image segmentation time 9.8 ms; (h) image segmentation time 9.5 ms.
图 5 原始YOLOv8与YOLOv8-FD图像分割结果对比 (a)—(d) YOLOv8不同尺度目标图像分割结果; (e)—(h) YOLOv8-FD不同尺度目标图像分割结果
Figure 5. Comparison of segmentation results between original YOLOv8 and YOLOv8-FD images: (a)–(d) Original YOLOv8 different scale target image segmentation results; (e)–(h) YOLOv8-FD different scale target image segmentation results.
图 6 (a)—(c)不同直径微纳光纤的原子力显微镜(AFM)扫描图; (d)—(f) 相应的光学显微图, 红色方框标记出AFM的扫描位置和ROI
Figure 6. (a)–(c) Atomic force microscope (AFM) scanning of micro-nanofiber of different diameters; (d)–(f) optical imaging of micro-nanofiber with different diameters and AFM scanning position, and the red box marks the scan location for AFM and ROI.
表 1 标定系数测量结果
Table 1. Measurement results of micro-nanofiber diameter.
标定次数 1 2 3 4 像素个数/pixel 845.01 843.52 844.25 843.24 标定系数/(nm·pixel–1) 65.89 66.01 65.95 66.03 表 2 微纳光纤直径测量结果
Table 2. Measurement results of micro-nanofiber diameter.
-
[1] 童利民 2022 光学学报 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tong L M 2022 Acta Opt. Sin. 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang L, Pan J, Zhang Z, Wu H, Yao N, Cai D W, Xu Y X, Zhang J, Sun G F, Wang L Q, Geng W D, Jin W G, Fang W, Di D W, Tong L M 2020 Opto-Electron Adv. 3 190022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yan Z Y, Wang J J, Wang C Y, Yu R W, Shi L, Xiao L M 2022 Opt. Express 30 18044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cen Q Q, Pian S J, Liu X H, Tang Y W, He X Y, Ma Y G 2023 eLight 3 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li Y H, Wang L Z, Li L J, Tong L M 2019 Appl. Phys. B 125 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lu J S, Li Q, Qiu C W, Hong Y, Ghosh P, Qiu M 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 8271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tkachenko G, Toftul I, Esporlas C, Maimaiti A, Kien F L, Truong V G, Chormaic S N 2020 Optica 7 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Linghu S Y, Gu Z Q, Lu J S, Fang W, Yang Z Y, Yu H K, Li Z Y, Zhu R L, Peng J, Zhan Q W, Zhuang S L, Gu M, Gu F X 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hao Z, Jiang B Q, Ma Y X, Yi R X, Gan X T, Zhao J L 2023 Opto-Electron Adv. 6 230012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang J B, Kang Y, Guo X, Li Y H, Liu K Y, Xie Y, Wu H, Cai D W, Gong J, Shi Z X, Jin Y Y, Wang P, Fang W, Zhang L, Tong L M 2023 Light Sci. Appl. 12 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen J H, Xiong Y F, Xu F, Lu Y Q 2021 Light Sci. Appl. 10 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou J, Li Y, Ma Y, Yang Q, Liu Q 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Linghu S Y, Ma Y N, Gu Z Q, Zhu R L, Liu Y F, Liu H J, Gu F X 2022 Opt. Express 30 22755
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liao F, Yu J X, Gu Z Q, Yang Z Y, Hasan T, Linghu S Y, Pang J, Fang W, Zhuang S L, Gu M, Gu F X 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 7398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 康仪, 刘可盈, 谢宇, 龚珏, 姚妮, 方伟, 郭欣, 张磊, 王攀, 童利民 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 084212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Y, Liu K Y, Xie Y, Gong Y, Yao N, Fang W, Guo X, Zhang L, Wang P, Tong L M 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. As. 50 084212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ni Y, Linghu S L, Xu Y X, Zhu R L, Zhou N, Gu F X, Zhang L, Fang W, Ding W, Tong L M 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 1069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Warken F, Giessen H 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Little D J, Kane D M 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu Y, Zhang X L, Song Z Q, Wang J F, Meng Z 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 8222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu Y X, Fang W, Tong L M 2017 Opt. Express 25 10434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kang Y, Gong J, Xu Y X, Yao N, Fang W, Guo X, Tong L M 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Azzoune A, Delaye P, Pauliat G 2019 Opt. Express 27 24403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李华, 麻艳娜, 谷付星 2022 光学仪器 44 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Ma Y N, Gu F X 2022 Opt. Instruments 44 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y 2017 ECCV 3 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 应大卫, 张思慧, 邓书金, 武海斌 2023 72 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ying D W, Zhang S H, Deng S J, Wu H B 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 144201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 南虎, 麻晓晶, 赵海博, 汤少杰, 刘卫华, 王大威, 贾春林 2021 70 076803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nan H, Ma X J, Zhao H B, Tang S J, Liu W H, Wang D W, Jia C L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 076803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollar P, Girshick R 2017 ICCV 17 2980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gu Z, Zhu R L, Shen T C, Dou L, Liu H J, Liu Y F, Liu X, Liu J, Zhuang S L, Gu F X 2023 Nat. Commun. 14 7663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6309
- PDF Downloads: 205
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: