-
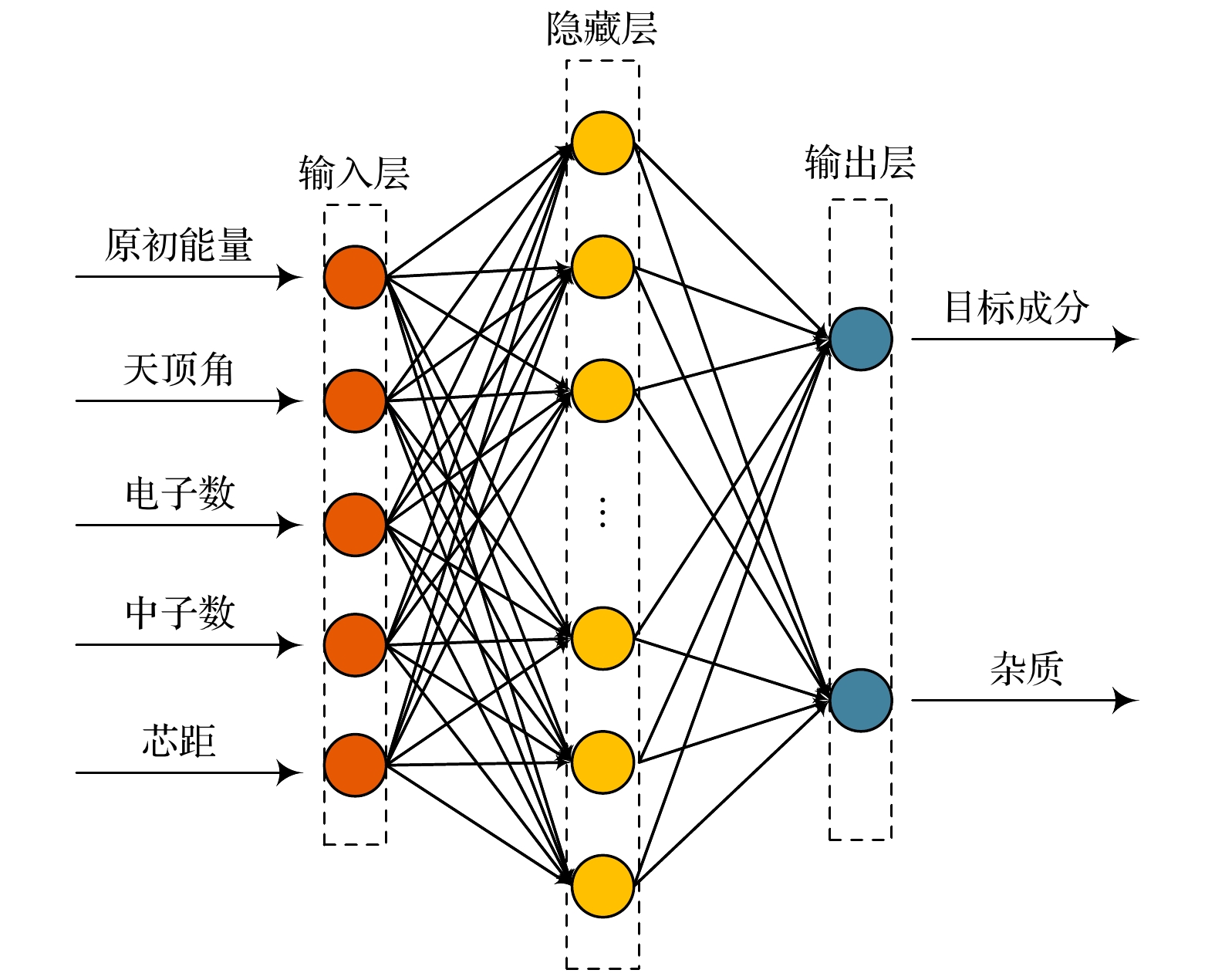
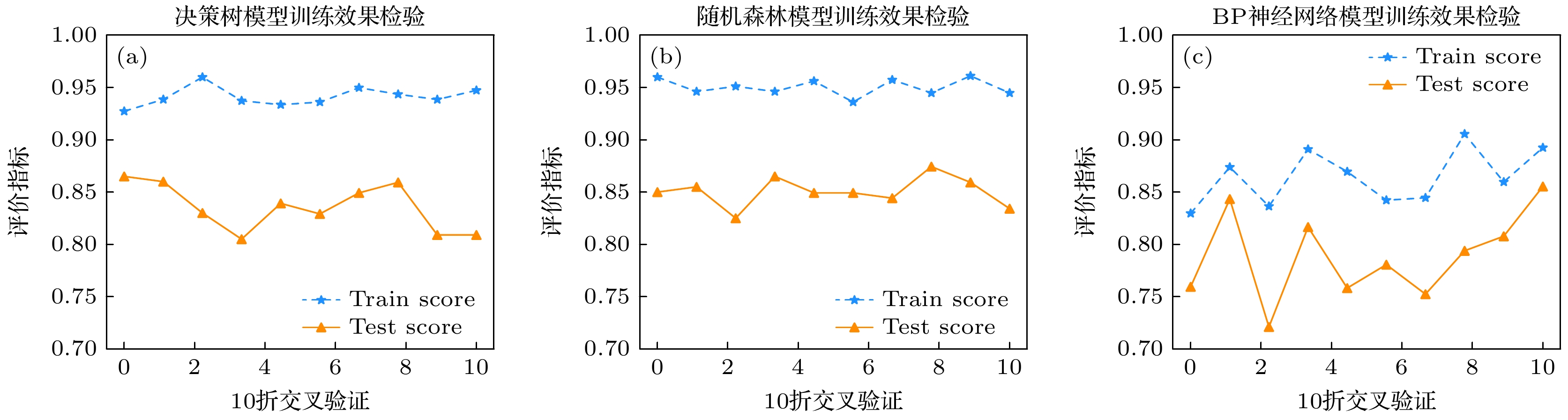
Machine learning algorithms can learn the rules and patterns of big data through computers, excavate potential information hidden behind the data, and be widely used to solve classification, regression, clustering, and other problems. Firstly, this paper uses CORSIKA software to simulate the process of cosmic ray cascade shower in the atmosphere, generating information such as the initial energy, zenith angle, azimuth angle of cosmic ray particles. Then, this paper uses the Geant4 toolkit to conduct thermal neutron detector response simulation, generating 4000 particles in each of proton, helium, CNO, MgAlSi and iron. Based on the experimental simulation data of thermal neutron detector, this paper constructs machine learning models for identifying cosmic ray particles by using decision tree (DT), random forest (RF) and BP neural network (BP NN) respectively. For each particle, all the machine learning algorithms are used for model training based on the simulation data. The cross grid search method is used to adjust the hyper parameters of each machine learning algorithm. The AUC value and Q quality factor value of each algorithm are used as evaluation indexes for particle composition identification. The AUC value is a general indicator for evaluating algorithm performance in machine learning and the Q quality factor value is an evaluation index commonly used in the field of high energy physics. The Experimental results show that different machine learning models have great influence on particle prediction accuracy, and the random forest cosmic ray particle identification model has sufficient accuracy and generalization capability. In the test, the decision tree algorithm adjusted by cross grid search method is sensitive to the medium components (CNO and MgAlSi). The AUC values of the algorithm are all above 0.95 and the Q quality factor values are all above 6. The random forest algorithm adjusted by the cross grid search method has the best effect on the identification of cosmic ray particles. The AUC values of the algorithm are all more than 0.92 and the Q quality factor values are all more than 4. The BP neural network algorithm is only sensitive to proton and iron. This study provides a new method and selection for identifying and screening the cosmic ray particles and it also provides a new idea for the following measurement of cosmic ray energy spectrum by thermal neutron detector.
-
Keywords:
- cosmic rays /
- particle identification /
- machine learning /
- random forest
[1] 胡红波, 王祥玉, 刘四明 2018 科学通报 63 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu H B, Wang X Y, Liu S M 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 胡红波, 郭义庆 2016 科学通报 61 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu H B, Guo Y Q 2016 Chin. Sci. Bull. 61 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 曹臻 2022 科学通报 67 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 曹臻, 陈明君, 陈松战, 胡红波, 刘成, 刘烨, 马玲玲, 马欣华, 盛祥东, 吴含荣, 肖刚, 姚志国, 尹丽巧, 查敏, 张寿山 2019 天文学报 60 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z, Chen M J, Chen S Z, Hu H B, Liu C, Liu Y, Ma L L, Ma X H, Shen X D, Wu H R, Xiao G, Yao Z G, Yin L Q, Zha M, Zhang S S 2019 Acta Astron. Sin. 60 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李川, 王文博, 陈鹏飞 2022 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 52 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Wang W B, Chen P F 2022 Sci. China Phys. Mech. 52 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张丰, 刘虎, 祝凤荣 2022 71 249601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F, Liu H, Zhu F R 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 249601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈秀林 2020 硕士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Chen X L 2020 M. S. Thesis (Beijing University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[8] 严雨婷, 毕文杰 2023 中国管理科学 网络首发 [2023-02-03]
Yan Y T, Bi W J 2023 Chin. J. Manag. Sci. Online First (in Chinese)
[9] Herrera L J, Todero Peixoto C J, Baños O, Carceller J M, Carrillo F, Guillén A 2020 Entropy 22 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pang L G, Zhou K, Su N, Petersen H, Stöcker H, Wang X N 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 高泽鹏, 王永佳, 李庆峰, 刘玲 2022 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 52 252010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Z P, Wang Y J, Li Q F, Liu L 2022 Sci. China Phys. Mech. 52 252010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 骆仕杰, 韩抒真 2023 小型微型计算机系统 网络首发 [2023-03-05]
Luo S J, Han S Z 2023 J. Chin. Comp. Syst. Online First (in Chinese)
[13] 王玉东, 王忠海, 周荣, 陈秀莲, 覃雪, 刘军 2019 核电子学与探测技术 39 567
Wang Y D, Wang Z H, Zhou R, Chen X L, Qin X, Liu J 2019 Nucl. Electron. Detect. Technol. 39 567
[14] 黎威, 龙连春, 刘静毅, 杨洋 2022 71 060202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Long L C, Liu J Y, Yang Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 060202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 崔静静, 胡泽文, 任萍 2022 情报科学 40 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui J J, Hu Z W, Ren P 2022 Inf. Sci. 40 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李勇男 2018 情报科学 36 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y N 2018 Inf. Sci. 36 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lin S, Luo W 2019 Multivar. Behav. Res. 54 578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song S, Park C G 2019 Sustainability 11 6976
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 肖燚, 郭亚会, 李明蔚, 付永硕, 孙峰 2022 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版) 58 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y, Guo Y H, Li M W, Guo Y S, Sun F 2022 J. Beijing Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 58 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 卢小宾, 张杨燚, 杨冠灿, 行佳鑫 2022 情报学报 41 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu X B, Zhang Y Y, Yang G C, Xing J X 2022 Inf. Sci. 41 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pei Y L, Li D D, Xue W X 2020 Concurr. Comp-Pract E 32 e5515
[22] 院琳, 杨雪松, 王秉中 2019 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan L, Yang X S, Wang B Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 赵振宇, 刘宇帆, 刘善存, 马海波 2023 北京航空航天大学学报 (社会科学版) 网络首发 [2023-03-05]
Zhao Z Y, Liu Y F, Liu S C, Ma H B 2023 J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut (Soc. Sci. Ed.) Online First
-
表 1 决策树鉴别不同成分最佳超参数
Table 1. Optimal hyperparameters of decision tree identifying different components.
超参数 目标成分 质子 氦核 碳氮氧 镁铝硅 铁核 criterion Entropy Entropy Entropy Entropy Entropy max_depth 21 29 40 28 19 min_samples_split 2 4 7 2 4 min_weight_fraction_leaf 0 0 0 0 0 min_samples_leaf 1 1 1 1 1 表 2 随机森林鉴别不同成分最佳超参数
Table 2. Optimal hyperparameters of random forest identifying different components.
超参数 目标成分 质子 氦核 碳氮氧 镁铝硅 铁核 criterion Gini Gini Entropy Entropy Entropy n_estimators 48 88 30 15 21 max_depth 20 26 30 27 23 min_samples_split 2 2 2 1 2 min_samples_leaf 1 1 1 1 1 表 3 BP神经网络(鉴别氦核)隐藏层节点核验结果
Table 3. BP neural network (identifying helium) hidden layer nodes verification results.
训练结果 隐藏节点个数 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 迭代次数 20000 20000 20000 25000 27000 20000 20000 20000 20000 算法AUC值 0.5503 0.5045 0.5293 0.5593 0.6329 0.6276 0.6177 0.6142 0.6418 Q品质因子 0.82 0.29 0.58 0.86 1.26 1.25 1.22 1.26 1.34 表 4 BP神经网络鉴别不同成分最佳超参数组合
Table 4. Optimal hyperparameters of BP neural network identifying different components.
超参数 目标成分 质子 氦核 碳氮氧 镁铝硅 铁核 隐藏层节点数 13 11 13 13 11 初始学习率 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 迭代次数 20000 25000 20000 20000 20000 表 5 三种宇宙线粒子鉴别模型鉴别不同成分效率及纯度
Table 5. Efficiency and purity of three cosmic rays identification models identifying different components.
目标成分 效率/% 纯度/% BP神经网络 决策树 随机森林 BP神经网络 决策树 随机森林 质子 64.9 74.8 75.7 74.4 77.6 91.1 氦核 36.0 83.3 79.3 52.8 80.1 95.7 碳氮氧 10.3 93.4 81.5 64.5 94.8 99.4 镁铝硅 16.9 91.8 78.7 69.9 92.1 95.8 铁核 82.8 88.1 91.1 87.5 88.7 93.5 表 6 三种宇宙线粒子鉴别模型鉴别不同成分AUC值及Q品质因子
Table 6. AUC and Q quality factor values of three cosmic rays identification models identifying different components.
目标成分 AUC Q 品质因子 BP神经网络 决策树 随机森林 BP神经网络 决策树 随机森林 质子 0.7962 0.8555 0.9247 2.71 3.15 5.42 氦核 0.6418 0.8805 0.9537 1.34 3.75 8.38 碳氮氧 0.5444 0.9612 0.9739 0.87 7.55 20.1 镁铝硅 0.5754 0.9504 0.9531 1.25 6.54 8.39 铁核 0.8751 0.8952 0.9380 2.96 2.97 4.40 -
[1] 胡红波, 王祥玉, 刘四明 2018 科学通报 63 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu H B, Wang X Y, Liu S M 2018 Chin. Sci. Bull. 63 2440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 胡红波, 郭义庆 2016 科学通报 61 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu H B, Guo Y Q 2016 Chin. Sci. Bull. 61 1188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 曹臻 2022 科学通报 67 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 1558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 曹臻, 陈明君, 陈松战, 胡红波, 刘成, 刘烨, 马玲玲, 马欣华, 盛祥东, 吴含荣, 肖刚, 姚志国, 尹丽巧, 查敏, 张寿山 2019 天文学报 60 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z, Chen M J, Chen S Z, Hu H B, Liu C, Liu Y, Ma L L, Ma X H, Shen X D, Wu H R, Xiao G, Yao Z G, Yin L Q, Zha M, Zhang S S 2019 Acta Astron. Sin. 60 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李川, 王文博, 陈鹏飞 2022 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 52 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Wang W B, Chen P F 2022 Sci. China Phys. Mech. 52 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张丰, 刘虎, 祝凤荣 2022 71 249601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F, Liu H, Zhu F R 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 249601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈秀林 2020 硕士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Chen X L 2020 M. S. Thesis (Beijing University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[8] 严雨婷, 毕文杰 2023 中国管理科学 网络首发 [2023-02-03]
Yan Y T, Bi W J 2023 Chin. J. Manag. Sci. Online First (in Chinese)
[9] Herrera L J, Todero Peixoto C J, Baños O, Carceller J M, Carrillo F, Guillén A 2020 Entropy 22 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pang L G, Zhou K, Su N, Petersen H, Stöcker H, Wang X N 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 高泽鹏, 王永佳, 李庆峰, 刘玲 2022 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 52 252010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Z P, Wang Y J, Li Q F, Liu L 2022 Sci. China Phys. Mech. 52 252010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 骆仕杰, 韩抒真 2023 小型微型计算机系统 网络首发 [2023-03-05]
Luo S J, Han S Z 2023 J. Chin. Comp. Syst. Online First (in Chinese)
[13] 王玉东, 王忠海, 周荣, 陈秀莲, 覃雪, 刘军 2019 核电子学与探测技术 39 567
Wang Y D, Wang Z H, Zhou R, Chen X L, Qin X, Liu J 2019 Nucl. Electron. Detect. Technol. 39 567
[14] 黎威, 龙连春, 刘静毅, 杨洋 2022 71 060202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Long L C, Liu J Y, Yang Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 060202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 崔静静, 胡泽文, 任萍 2022 情报科学 40 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui J J, Hu Z W, Ren P 2022 Inf. Sci. 40 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李勇男 2018 情报科学 36 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y N 2018 Inf. Sci. 36 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lin S, Luo W 2019 Multivar. Behav. Res. 54 578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song S, Park C G 2019 Sustainability 11 6976
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 肖燚, 郭亚会, 李明蔚, 付永硕, 孙峰 2022 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版) 58 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y, Guo Y H, Li M W, Guo Y S, Sun F 2022 J. Beijing Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 58 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 卢小宾, 张杨燚, 杨冠灿, 行佳鑫 2022 情报学报 41 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu X B, Zhang Y Y, Yang G C, Xing J X 2022 Inf. Sci. 41 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pei Y L, Li D D, Xue W X 2020 Concurr. Comp-Pract E 32 e5515
[22] 院琳, 杨雪松, 王秉中 2019 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan L, Yang X S, Wang B Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 赵振宇, 刘宇帆, 刘善存, 马海波 2023 北京航空航天大学学报 (社会科学版) 网络首发 [2023-03-05]
Zhao Z Y, Liu Y F, Liu S C, Ma H B 2023 J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut (Soc. Sci. Ed.) Online First
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6254
- PDF Downloads: 130
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: