-
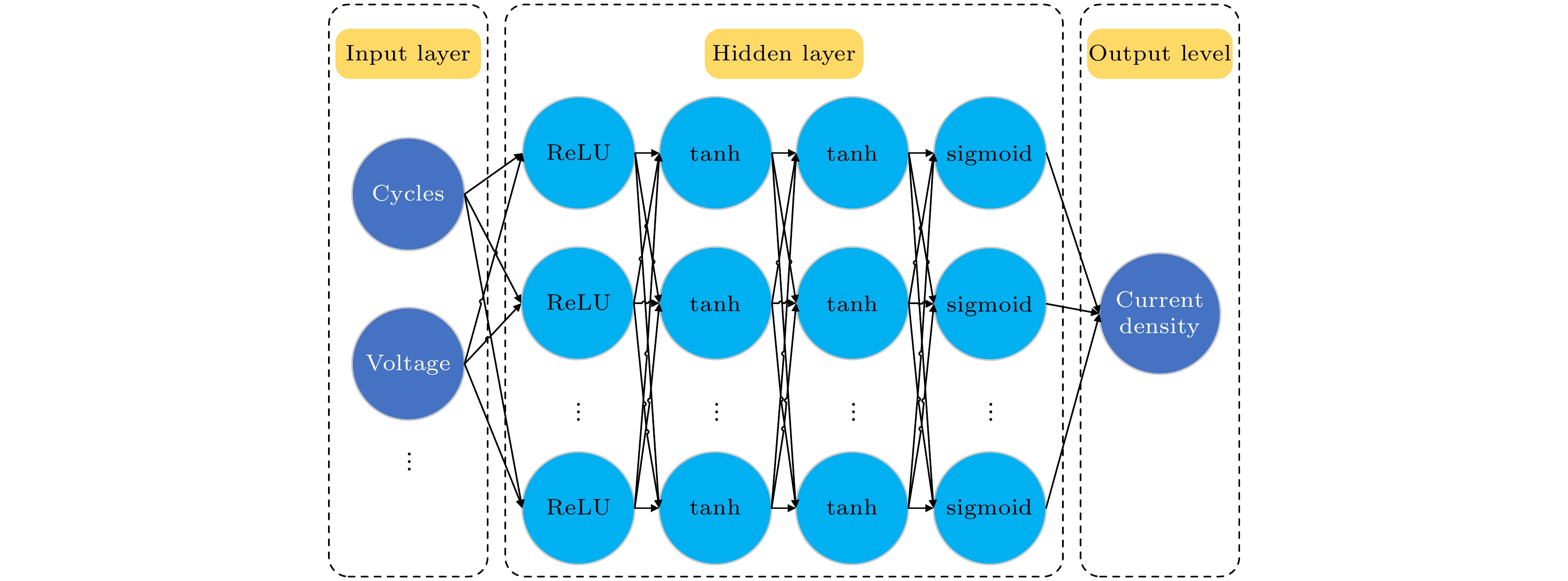
In recent years, with the development of gas discharge technology at atmospheric pressure, the application of low temperature plasma has received widespread attention in pollution prevention, disinfection, sterilization, energy conversion and other fields. Atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge is widely used to produce low temperature plasma in various applications, which is usually numerically investigated by using fluid models. The unique advantages of machine learning in various branches of physics have been discovered with the advancement of big data processing technology. Recent studies have shown that artificial neural networks with multiple hidden layers have a pivotal role in the simulation of complex datasets. In this work, a fully connected multilayer BP (back propagation) network together with a universal hidden layer structure is developed to explore the characteristics of one or more current pulses per half voltage cycle of atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge. The calculated data are used as training sets, and the discharge characteristics such as current density, electron density, ion density, and electric field of atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge can be quickly predicted by using artificial neural network program. The computational results show that for a given training set, the constructed machine learning program can describe the properties of atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge with almost the same accuracy as the fluid model. Also, the computational efficiency of the machine learning is much higher than that of the fluid model. In addition, the use of machine learning programs can also greatly extend the calculation range of parameters. Limiting discharge parameter range is considered as a major challenge for numerical calculation. By substituting a relatively limited set of training data obtained from the fluid model into the machine learning, the discharge characteristics can be accurately predicted within a given range of discharge parameters, leading an almost infinite set of data to be generated, which is of great significance for studying the influence of discharge parameters on discharge evolution. The examples in this paper show that the combination of machine learning and fluid models can greatly improve the computational efficiency, which can enhance the understanding of discharge plasmas.
-
Keywords:
- dielectric barrier discharge /
- machine learning /
- fluid model /
- kinetic model /
- discharge parameters
[1] Von Woedtke T, Metelmann H R, Weltmann K D 2014 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 54 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Agarwal P, Girshick S L 2014 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 34 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen Q, Li J, Li Y 2015 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48 424005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Von Keudell A, Schulz-Von Der Gathen V 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 113001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bruggeman P J, Iza F, Brandenburg R 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 123002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang Y T, Chi Y Y, He J 2014 Plasma Process. Polym. 11 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang X C, Bai J X, Zhang T H, Sun Y, Zhang Y T 2022 Vacuum 203 111200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张泰恒, 王绪成, 张远涛 2021 70 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T H, Wang X C, Zhang Y T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Iqbal M M, Turner M M 2015 Plasma Process. Polym. 12 1104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 98 113308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Alves L, Bogaerts A, Guerra V, Turner M 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 023002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang G, Kuang Y, Zhang Y T 2019 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 015404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brodtkorb A R, Hagen T R, Sætra M L 2013 J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 73 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pandey M, Fernandez M, Gentile F, Isayev O, Tropsha A, Stern A C, Cherkasov A 2022 Nat. Mach. Intell. 4 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Eklund A, Dufort P, Forsberg D, LaConte S M 2013 Med. Image Anal. 17 1073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Carleo G, Cirac I, Cranmer K, Daudet L, Schuld M, Tishby N, Vogt-Maranto L, Zdeborová L 2019 Rev. Mod. Phys. 91 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Piccione A, Berkery J, Sabbagh S, Andreopoulos Y 2020 Nucl. Fusion 60 046033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fu Y, Eldon D, Erickson K, Kleijwegt K, Lupin-Jimenez L, Boyer M D, Eidietis N, Barbour N, Izacard O, Kolemen E 2020 Phys. Plasma 27 022501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mesbah A, Graves D B 2019 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52 30LT02
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jordan M I, Mitchell T M 2015 Science 349 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang H, Lei Z, Zhang X, Zhou B, Peng J 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 198 111799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bonzanini A D, Shao K, Stancampiano A, Graves D B, Mesbah A 2021 IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 6 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hong Y, Hou B, Jiang H, Zhang J 2020 Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 10 e1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Abiodun O I, Jantan A, Omolara A E, Dada K V, Mohamed N A, Arshad H 2018 Heliyon 4 e00938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dongare A, Kharde R, Kachare A D 2012 IJEIT 2 189
[26] Kukreja H, Bharath N, Siddesh C, Kuldeep S 2016 Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 1 27
[27] Han J, Jentzen A, Weinan E 2018 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115 8505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhong L, Gu Q, Wu B 2020 Comput. Phys. Commun. 257 107496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 张远涛, 王德真, 王艳辉 2005 54 4808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Wang Y H 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 4808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 王艳辉, 王德真 2003 52 1694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y H, Wang D Z 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Massines F, Rabehi A, Decomps P, Gadri R B, Ségur P, Mayoux C 1998 J. Appl. Phys. 83 2950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 100 063304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] He J, Zhang Y T 2012 Plasma Process. Polym. 9 919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 071501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yuan X, Raja L L 2003 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 31 495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Song S, Guo Y, Choe W, Zhang J, Zhang J, Shi J 2012 Phys. Plasma 19 123508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang Y T, Wang Y H 2018 Phys. Plasma 25 023509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Simeni M S, Zheng Y, Barnat E V, Bruggeman P J 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 055004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 王艳辉 2006 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Wang Y H 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[40] Vanraes P, Nikiforov A, Bogaerts A, Leys C 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Massines F, Segur P, Gherardi N, Khamphan C, Ricard A 2003 Surf. Coat. Tech. 174 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 徐学基, 诸定昌 1996 气体放电物理 (上海: 复旦大学出版社) 第277页
Xu X J, Zhu D C 1996 Discharge Physics of Gas (Shanghai: Fudan University Press) p277 (in Chinese)
[43] 刘勇, 何湘宁, 马飞 2005 高电压技术 31 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, He X N, Ma F 2005 High Volt. Eng. 31 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Sadeghi B 2000 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 103 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Gawehn E, Hiss J A, Brown J B, Schneider G 2018 Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 13 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] He J, Hu J T, Liu D W, Zhang Y T 2013 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 22 035008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Golubovskii Y B, Maiorov V, Behnke J, Behnke J 2002 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
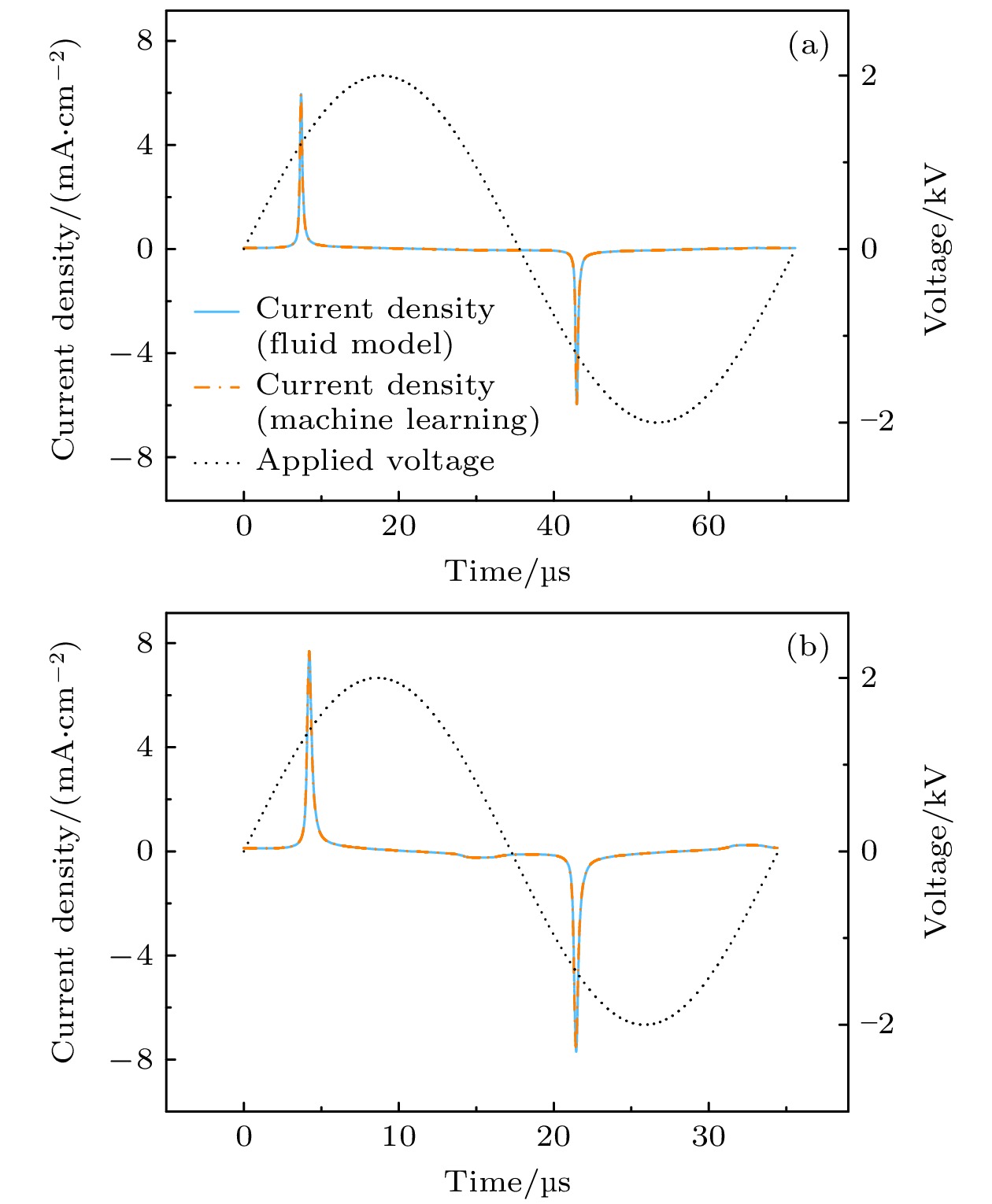
图 3 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在频率为10 kHz下的电流密度, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) V0 = 2150 V下的电流密度; (b) V0 = 2450 V下的电流密度
Figure 3. Prediction of current density of He plasma at ambient pressure (f = 10 kHz) via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Current density at ambient pressure (V0 = 2150 V); (b) current density at ambient pressure (V0 = 2450 V)
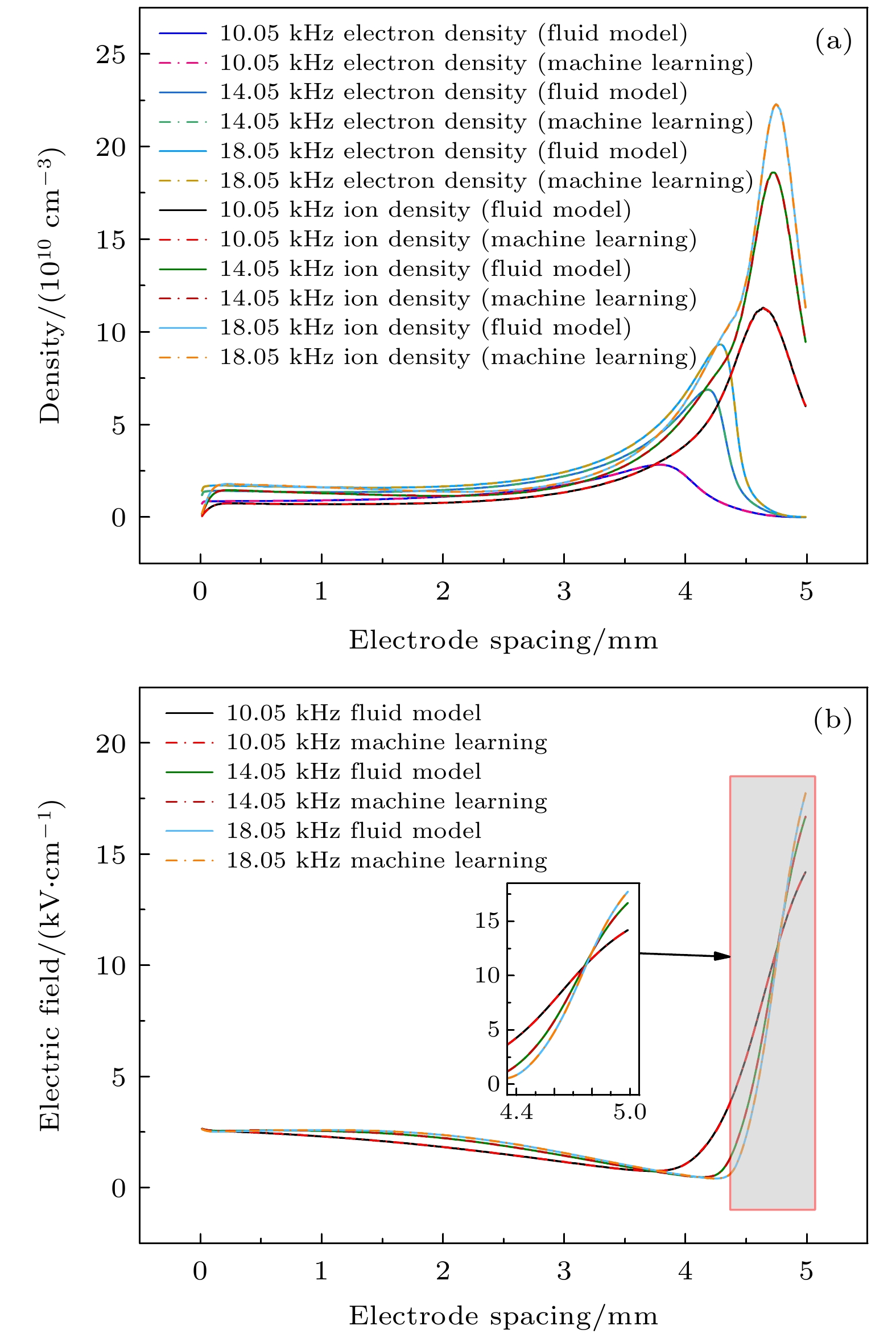
图 4 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在f = 10 kHz下的电子密度、离子密度和电场分布, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) 电子密度与离子密度; (b) 电场强度
Figure 4. Prediction of electron density, ion density and electric field of He plasma at ambient pressure (f = 10 kHz) via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Electron density and ion density; (b) electric field
图 7 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在V0 = 2000 V下的电流密度, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) f = 14.05 kHz下的电流密度; (b) f = 29.05 kHz下的电流密度
Figure 7. Prediction of current density of He plasma at ambient pressure (V0 = 2000 V) via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Current density at ambient pressure (f = 14.05 kHz); (b) current density at ambient pressure (f = 29.05 kHz)
图 8 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在V0 = 2000 V下的电子密度、离子密度和电场分布, 并与流体模型模拟的结果进行比较 (a)电子密度与离子密度; (b) 电场强度
Figure 8. Prediction of electron density, ion density and electric field of He plasma at ambient pressure (V0 = 2000 V) via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Electron density and ion density; (b) electric field
图 11 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在多输入属性变化下的电流密度, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) f = 14.05 kHz下的电流密度; (b) f = 29.05 kHz下的电流密度
Figure 11. Prediction of current density of He plasma under the change of multi input attributes machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Current density at ambient pressure (f = 14.05 kHz); (b) current density at ambient pressure (f = 29.05 kHz)
图 12 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在多输入属性变化下的电子密度和离子密度, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) f = 14.05 kHz的电子密度; (b) f = 29.05 kHz的离子密度
Figure 12. Prediction of electron density and ion density of He plasma under the change of multi input attributes via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Electron density at ambient pressure (f = 14.05 kHz); (b) ion density at ambient pressure (f = 29.05 kHz)
图 13 通过机器学习预测He等离子体在多输入参数变化下的电场强度分布, 并与流体模拟的结果进行比较 (a) f = 14.05 kHz的场强分布; (b) f = 29.05 kHz的场强分布
Figure 13. Prediction of electric field of He plasma under the change of multi input attributes via machine learning with comparison of the results by fluid simulation: (a) Electric field at ambient pressure (f = 14.05 kHz); (b) electric field at ambient pressure (f = 29.05 kHz)
-
[1] Von Woedtke T, Metelmann H R, Weltmann K D 2014 Contrib. Plasma Phys. 54 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Agarwal P, Girshick S L 2014 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 34 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen Q, Li J, Li Y 2015 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48 424005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Von Keudell A, Schulz-Von Der Gathen V 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 113001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bruggeman P J, Iza F, Brandenburg R 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 123002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang Y T, Chi Y Y, He J 2014 Plasma Process. Polym. 11 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang X C, Bai J X, Zhang T H, Sun Y, Zhang Y T 2022 Vacuum 203 111200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张泰恒, 王绪成, 张远涛 2021 70 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T H, Wang X C, Zhang Y T 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 215201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Iqbal M M, Turner M M 2015 Plasma Process. Polym. 12 1104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 98 113308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Alves L, Bogaerts A, Guerra V, Turner M 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 023002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang G, Kuang Y, Zhang Y T 2019 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 015404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brodtkorb A R, Hagen T R, Sætra M L 2013 J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 73 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pandey M, Fernandez M, Gentile F, Isayev O, Tropsha A, Stern A C, Cherkasov A 2022 Nat. Mach. Intell. 4 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Eklund A, Dufort P, Forsberg D, LaConte S M 2013 Med. Image Anal. 17 1073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Carleo G, Cirac I, Cranmer K, Daudet L, Schuld M, Tishby N, Vogt-Maranto L, Zdeborová L 2019 Rev. Mod. Phys. 91 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Piccione A, Berkery J, Sabbagh S, Andreopoulos Y 2020 Nucl. Fusion 60 046033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fu Y, Eldon D, Erickson K, Kleijwegt K, Lupin-Jimenez L, Boyer M D, Eidietis N, Barbour N, Izacard O, Kolemen E 2020 Phys. Plasma 27 022501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mesbah A, Graves D B 2019 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52 30LT02
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jordan M I, Mitchell T M 2015 Science 349 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang H, Lei Z, Zhang X, Zhou B, Peng J 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 198 111799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bonzanini A D, Shao K, Stancampiano A, Graves D B, Mesbah A 2021 IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 6 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hong Y, Hou B, Jiang H, Zhang J 2020 Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 10 e1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Abiodun O I, Jantan A, Omolara A E, Dada K V, Mohamed N A, Arshad H 2018 Heliyon 4 e00938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dongare A, Kharde R, Kachare A D 2012 IJEIT 2 189
[26] Kukreja H, Bharath N, Siddesh C, Kuldeep S 2016 Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 1 27
[27] Han J, Jentzen A, Weinan E 2018 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115 8505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhong L, Gu Q, Wu B 2020 Comput. Phys. Commun. 257 107496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 张远涛, 王德真, 王艳辉 2005 54 4808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Wang Y H 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 4808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 王艳辉, 王德真 2003 52 1694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y H, Wang D Z 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Massines F, Rabehi A, Decomps P, Gadri R B, Ségur P, Mayoux C 1998 J. Appl. Phys. 83 2950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhang Y T, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 100 063304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] He J, Zhang Y T 2012 Plasma Process. Polym. 9 919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang D Z, Kong M G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 071501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yuan X, Raja L L 2003 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 31 495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Song S, Guo Y, Choe W, Zhang J, Zhang J, Shi J 2012 Phys. Plasma 19 123508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang Y T, Wang Y H 2018 Phys. Plasma 25 023509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Simeni M S, Zheng Y, Barnat E V, Bruggeman P J 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 055004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 王艳辉 2006 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Wang Y H 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[40] Vanraes P, Nikiforov A, Bogaerts A, Leys C 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Massines F, Segur P, Gherardi N, Khamphan C, Ricard A 2003 Surf. Coat. Tech. 174 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 徐学基, 诸定昌 1996 气体放电物理 (上海: 复旦大学出版社) 第277页
Xu X J, Zhu D C 1996 Discharge Physics of Gas (Shanghai: Fudan University Press) p277 (in Chinese)
[43] 刘勇, 何湘宁, 马飞 2005 高电压技术 31 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, He X N, Ma F 2005 High Volt. Eng. 31 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Sadeghi B 2000 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 103 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Gawehn E, Hiss J A, Brown J B, Schneider G 2018 Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 13 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] He J, Hu J T, Liu D W, Zhang Y T 2013 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 22 035008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Golubovskii Y B, Maiorov V, Behnke J, Behnke J 2002 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5835
- PDF Downloads: 101
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: