-
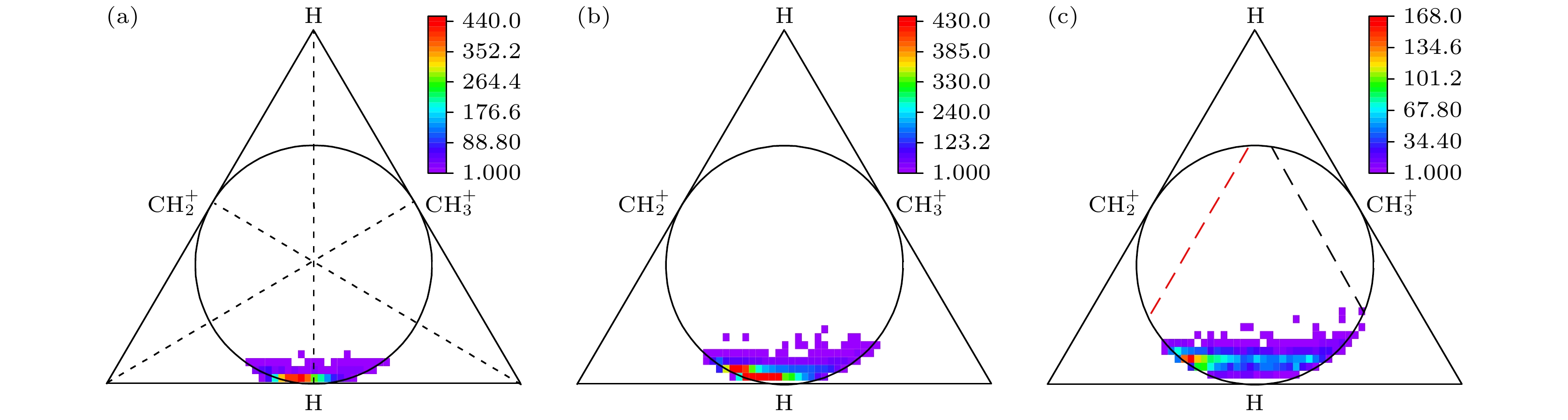
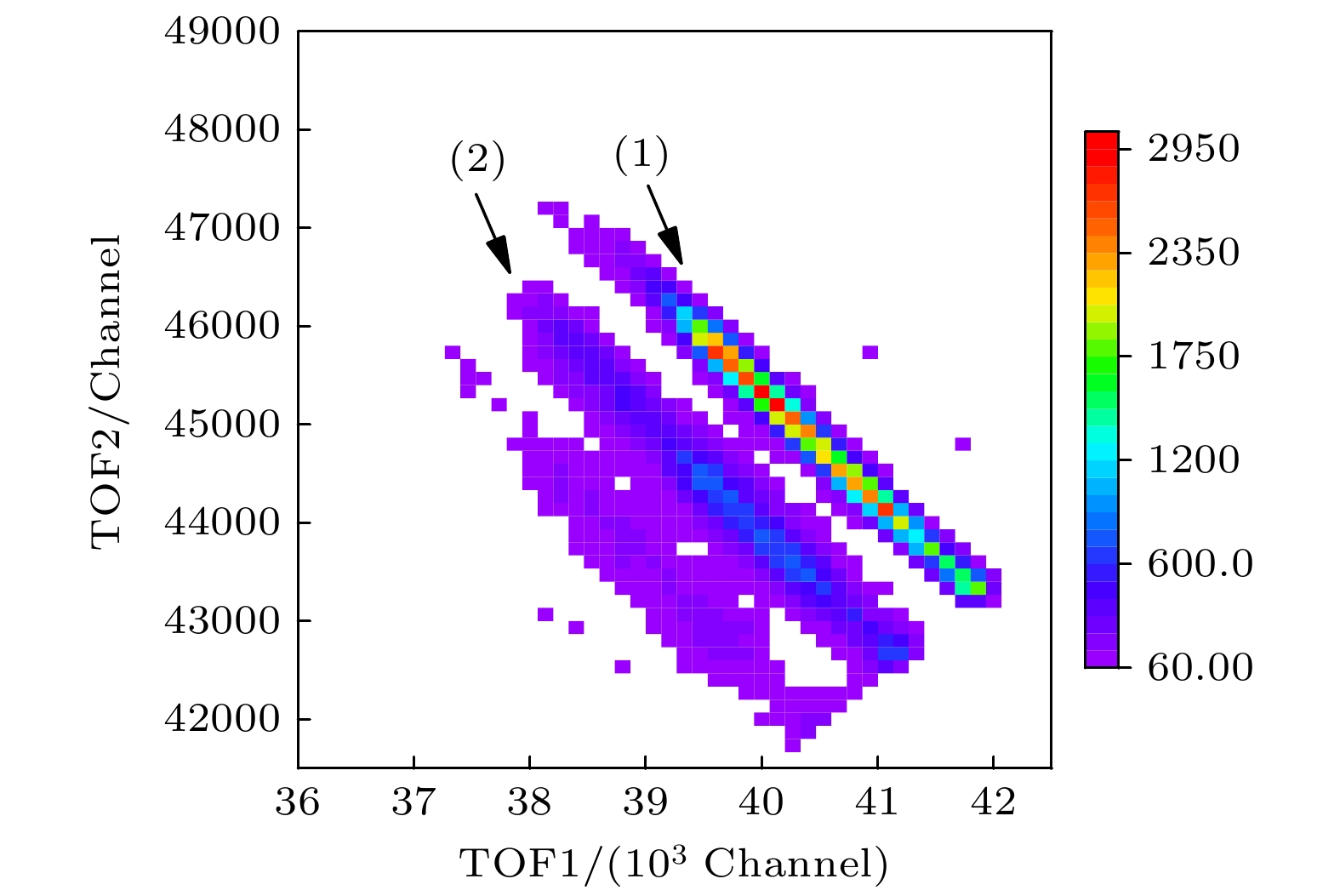
Molecular ions are widely distributed in the ionosphere of planetary atmospheres, and their fragmentations can generate different ions and neutral fragments. Studying the kinetic energy distribution and generation mechanism of the final products is helpful in understanding fundamental phenomena in astrophysics and plasma physics. In particular, ethane is an important molecule found in Titan and comet, and its fragmentation may be involved in the generation of complex hydrocarbons, as well as the atmospheric escape processes on Titan. In this paper, the experiment on ethane fragmentation by electron impact is carried out, focusing on the three-body fragmentation channel from $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_6^{2 + } $ to $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + /{\text{CH}}_2^ + /{\text{H}} $. The three-dimensional momenta of $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ and $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ ions are measured, and then the momentum of the H atom is reconstructed using momentum conservation law. Based on these analyses, the kinetic energy release (KER) spectrum and the fragmentation mechanisms are investigated. The time-of-flight (TOF) coincidence map of the ions shows two channels: channel (1) that represents the two-body dissociation generating $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $/$ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $, and channel (2) that refers to the three-body dissociation generating $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + /{\text{CH}}_2^ + /{\text{H}} $. It is found that the neutral H from channel (2) has a wide kinetic energy distribution, ranging from 0 eV to more than 10 eV. This feature indicates that the dissociation of the C-H bond is from multiple electronic states. Since the escape threshold of H in Titan’s ionosphere is 0.02 eV, the vast majority of the H atoms produced in channel (2) can escape into outer space. In addition, the kinetic energy sum of $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ and $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ in channel (2) is found to be similar to the KER of channel (1), indicating that the C-H dissociation presents limited influence on the energy sum of the CH2+ and $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $. The corresponding fragmentation mechanism of channel (2) is also analyzed in this work. the overall KER spectrum is divided into three parts: 0–6 eV, 6–9 eV, and 9–11 eV, and the respective Dalitz plots and Newton diagrams are reconstructed under different KER conditions. In all Dalitz plots, there are a bright spot representing the concerted dissociation and a horizontal belt representing the sequential dissociation. The concerted dissociation is considered as the main mechanism, while the sequential dissociation plays a secondary role. The bright spot in the Dalitz plot shifts from the center to the left as the KER increases. This feature arises from the fact that the $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ lies between the H and the $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ in the concerted dissociation, and it feels the recoil both from H and from $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $. Considering that the Coulomb potential from $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ is constant, the increase of the C-H dissociation energy will reduce the $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ kinetic energy. The belt in the Dalitz indicates that the sequential dissociation is a two-step process, with the first step being the dissociation of $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_6^{2 + } $ to generate H and metastable $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_5^{2 + } $, and the second step being the fragmentation of $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_5^{2 + } $ into $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ and $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $. The Newton diagrams under different KER conditions are also reconstructed to give further evidence of the sequential dissociation from the metastable $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_5^{2 + } $, rather than from the metastable $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ or $ {\text{CH}}_4^ + $. In fact, for the former case, the center positions of the two half circles in the Newton diagram are correct. Oppositely, for the latter two cases, the center positions notably deviate from the expected values. This means the sequential dissociation from $ {{\text{C}}_2}{\text{H}}_5^{2 + } $ is dominant, which agrees excellently with the conclusion from the Dalitz plots. -
Keywords:
- ethane /
- dissociative ionization /
- three-body fragmentation /
- reaction microscope
[1] Mathur D 2004 Phys. Rep. 391 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Adoui L, Muranaka T, Tarisien M, Legendre S, Laurent G, Cassimi A, Chesnel J Y, Fléchard X, Frémont F, Gervais B, Giglio E, Hennecart D 2006 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 245 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aitelhadjali Z, Kessal S, Quinto M A, Oubaziz D, Champion C 2016 Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 403 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shen Z J, Wang E L, Gong M M, Shan X, Chen X J 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 145 234303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen L, Wang E L, Shan X, Shen Z J, Zhao X, Chen X J 2021 Phys. Rev. A 104 032814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jiang T, Wang B, Zhang Y, Wei L, Chen S, Yu W, Zou Y, Chen L, Wei B 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 022705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Duley A, Kelkar A H 2023 Atoms 11 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang X, Zhang Y, Lu D, Lu G C, Wei B, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei B, Zhang Y, Wang X, Lu D, Lu G C, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y 2014 J. Chem. Phys. 140 124303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y, Jiang T, Wei L, Luo D, Wang X, Yu W, Hutton R, Zou Y, Wei B 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 022703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wei L, Chen S, Zhang Y, Wang B, Yu W, Ren B, Han J, Zou Y, Chen L, Wei B 2020 Eur. Phys. J. D 74 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Das N, De S, Bhatt P, Safvan C P, Majumdar A 2023 J. Chem. Phys. 158 084307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuan H, Xu S, Wang E, Xu J, Gao Y, Zhu X, Guo D, Ma B, Zhao D, Zhang S, Yan S, Zhang R, Gao Y, Xu Z, Ma X 2022 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 13 7594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Y, Li Y, Gao Y, Chen Y, Zhou Z, Shen X, Jin G 2024 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 557 165547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abplanalp M J, Kaiser R I 2016 Astrophys. J. 827 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim Y S, Bennett C J, Chen L H, O'Brien K, Kaiser R I 2010 Astrophys. J. 711 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Russo N D, Vervack Jr R J, Weaver H A, Lisse C M 2009 Icarus 200 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kanya R, Kudou T, Schirmel N, Miura S, Weitzel K M, Hoshina K, Yamanouchi K 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 136 204309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schirmel N, Reusch N, Horsch P, Weitzel K M 2013 Faraday Discuss. 163 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boran Y, Gutsev G L, Kolomenskii A A, Zhu F, Schuessler A, Strohaber J 2018 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 51 035003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Y, Ren B, Yang C L, Wei L, Wang B, Han J, Yu W, Qi Y, Zou Y, Chen L, Wang E, Wei B 2020 Commum. Chem. 3 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wei L, Lam C S, Zhang Y, Ren B, Han J, Wang B, Zou Y, Chen L, Lau K C, Wei B 2021 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12 5789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yoshida S, Majima T, Tsuchida H, Saito M 2020 X-Ray Spectrom. 49 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Moshammer R, Unverzagt M, Schmitt W, Ullrich J, Schmidt-Böcking H 1996 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 108 425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dörner R, Mergel V, Jagutzki O, Spielberger L, Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Schmidt-Böcking H 2000 Phys. Rep. 330 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt L P H, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ullrich J, Schmidt-Böcking H 1987 Phys. Lett. A 125 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 郭大龙, 马新文, 冯文天, 张少锋, 朱小龙 2011 60 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D L, Ma X W, Feng W T, Zhang S F, Zhu X L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yan S, Zhu X L, Zhang S F, Zhao D M, Zhang P, Wei B, Ma X 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 032809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yan S, Zhang P, Stumpf V, Gokhberg K, Zhang X C, Xu S, Li B, Shen L L, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Zhang S F, Zhao D M, Ma X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Falcinelli S, Rosi M, Candori P, Vecchiocattivi F, Farrar J M, Pirani F, Balucani N, Alagia M, Richter R, Stranges, S 2014 Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 8579 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
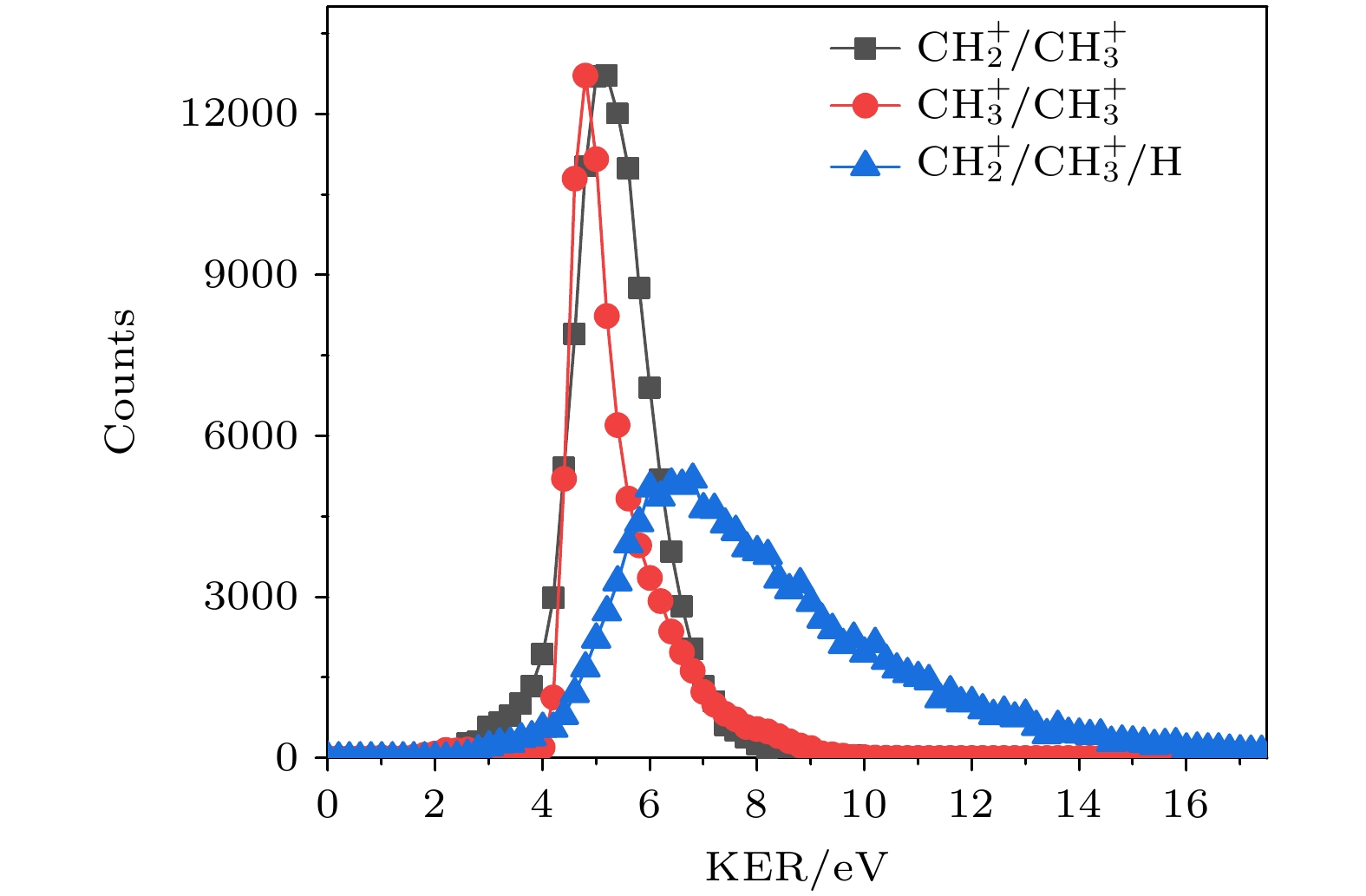
图 2 红线为通道(1)的KER谱, 蓝线为通道(2)的总KER谱, 黑线为通道(2)中$ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $, $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $离子的动能和
Figure 2. Red line is the KER spectrum of channel (1), the blue line is the total KER spectrum of channel (2), and the black line is the sum of the kinetic energies of $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ and $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ ions in channel (2).
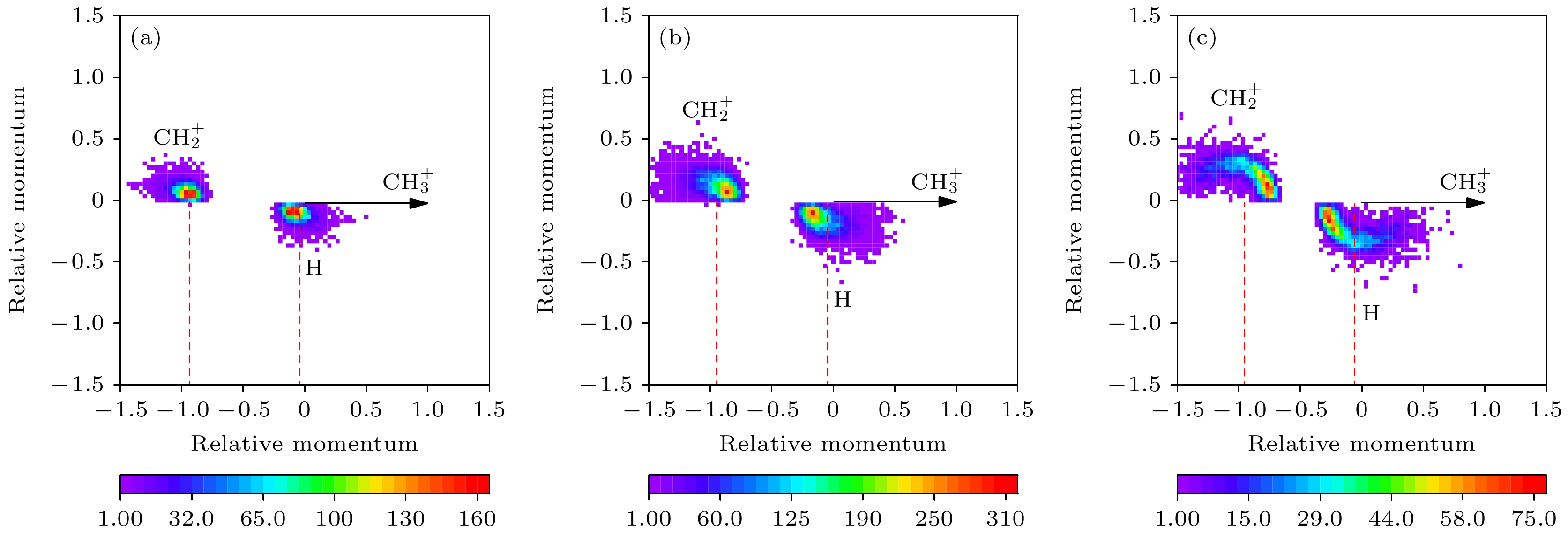
图 4 通道(2)的牛顿图, 其中(a), (b), (c)分别对应的KER范围为0—6 eV, 6—9 eV和9—11 eV; 图中将$ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $的动量大小定义为1, 方向沿X轴; 对$ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $和H离子的动量进行归一化后, 分别展示在上半平面和下半平面
Figure 4. Newton diagrams of channel (2). The panel (a), (b), and (c) correspond to the KER range of 0–6 eV, 6–9 eV, and 9–11 eV, respectively. The momentum magnitude of $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ is defined as 1, and its direction is along X-axis. The momentum vectors of $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ and H are normalized to that of $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $, and displayed in the upper and lower half planes, respectively.
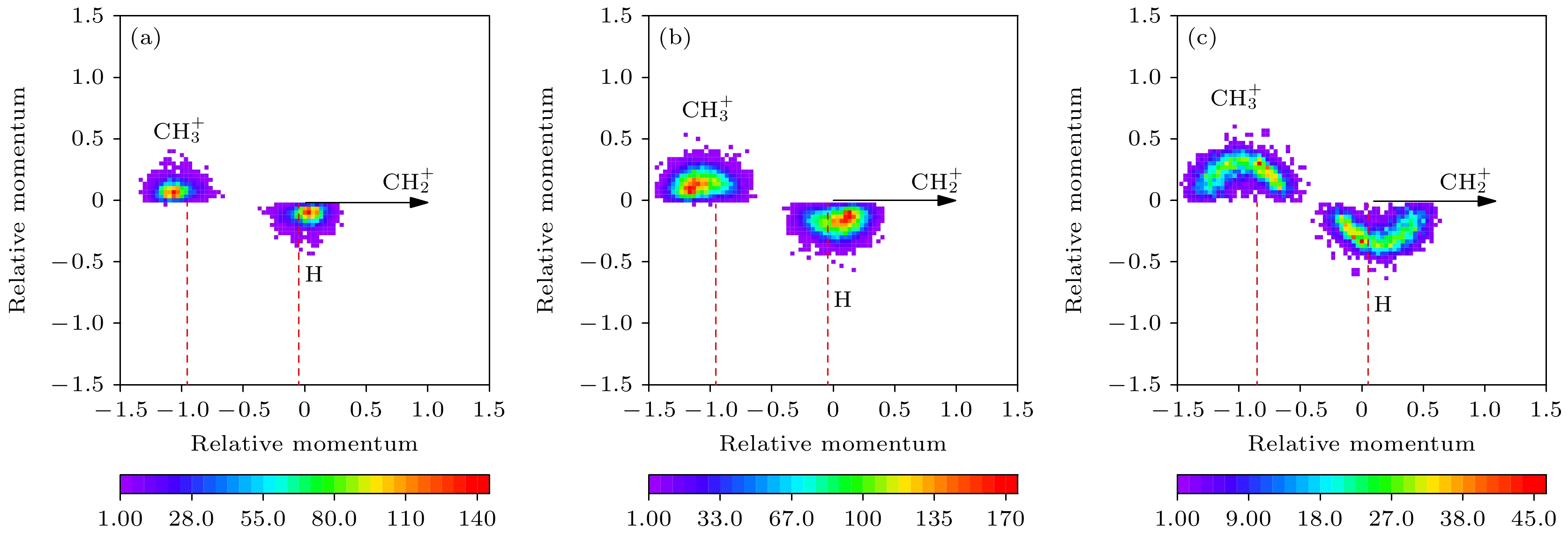
图 5 通道(2)的牛顿图, 其中(a), (b), (c)分别对应的KER范围为0—6 eV, 6—9 eV和9—11 eV; 图中将$ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $的动量大小定义为1, 方向沿X轴; 对$ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $和H的动量进行归一化后, 分别展示于上半平面和下半平面
Figure 5. Newton diagrams of channel (2). The panel (a), (b), and (c) correspond to the KER range of 0–6 eV, 6–9 eV, and 9–11 eV, respectively. The momentum magnitude of $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ is defined as 1, and its direction is along X-axis. The momentum vectors of $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ and H are normalized to that of $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $, and displayed in the upper and lower half planes, respectively.
图 6 通道(2)的牛顿图, 其中(a), (b), (c)分别对应的KER范围为0—6 eV, 6—9 eV和9—11 eV; 图中将H的动量大小定义为1, 方向沿X轴; 对$ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $和$ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $的动量进行归一化后, 分别展示于上半平面和下半平面
Figure 6. Newton diagrams of channel (2). The panel (a), (b), and (c) correspond to the KER range of 0–6 eV, 6–9 eV, and 9–11 eV, respectively. The momentum magnitude of H is defined as 1, and its direction is along X-axis. The momentum vectors of $ {\text{CH}}_2^ + $ and $ {\text{CH}}_3^ + $ are normalized to that of H, and displayed in the upper and lower half planes, respectively.
-
[1] Mathur D 2004 Phys. Rep. 391 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Adoui L, Muranaka T, Tarisien M, Legendre S, Laurent G, Cassimi A, Chesnel J Y, Fléchard X, Frémont F, Gervais B, Giglio E, Hennecart D 2006 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 245 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aitelhadjali Z, Kessal S, Quinto M A, Oubaziz D, Champion C 2016 Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 403 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shen Z J, Wang E L, Gong M M, Shan X, Chen X J 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 145 234303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen L, Wang E L, Shan X, Shen Z J, Zhao X, Chen X J 2021 Phys. Rev. A 104 032814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jiang T, Wang B, Zhang Y, Wei L, Chen S, Yu W, Zou Y, Chen L, Wei B 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 022705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Duley A, Kelkar A H 2023 Atoms 11 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang X, Zhang Y, Lu D, Lu G C, Wei B, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei B, Zhang Y, Wang X, Lu D, Lu G C, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y 2014 J. Chem. Phys. 140 124303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Y, Jiang T, Wei L, Luo D, Wang X, Yu W, Hutton R, Zou Y, Wei B 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 022703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wei L, Chen S, Zhang Y, Wang B, Yu W, Ren B, Han J, Zou Y, Chen L, Wei B 2020 Eur. Phys. J. D 74 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Das N, De S, Bhatt P, Safvan C P, Majumdar A 2023 J. Chem. Phys. 158 084307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuan H, Xu S, Wang E, Xu J, Gao Y, Zhu X, Guo D, Ma B, Zhao D, Zhang S, Yan S, Zhang R, Gao Y, Xu Z, Ma X 2022 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 13 7594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Y, Li Y, Gao Y, Chen Y, Zhou Z, Shen X, Jin G 2024 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 557 165547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abplanalp M J, Kaiser R I 2016 Astrophys. J. 827 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim Y S, Bennett C J, Chen L H, O'Brien K, Kaiser R I 2010 Astrophys. J. 711 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Russo N D, Vervack Jr R J, Weaver H A, Lisse C M 2009 Icarus 200 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kanya R, Kudou T, Schirmel N, Miura S, Weitzel K M, Hoshina K, Yamanouchi K 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 136 204309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schirmel N, Reusch N, Horsch P, Weitzel K M 2013 Faraday Discuss. 163 461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Boran Y, Gutsev G L, Kolomenskii A A, Zhu F, Schuessler A, Strohaber J 2018 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 51 035003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Y, Ren B, Yang C L, Wei L, Wang B, Han J, Yu W, Qi Y, Zou Y, Chen L, Wang E, Wei B 2020 Commum. Chem. 3 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wei L, Lam C S, Zhang Y, Ren B, Han J, Wang B, Zou Y, Chen L, Lau K C, Wei B 2021 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12 5789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yoshida S, Majima T, Tsuchida H, Saito M 2020 X-Ray Spectrom. 49 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Moshammer R, Unverzagt M, Schmitt W, Ullrich J, Schmidt-Böcking H 1996 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 108 425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dörner R, Mergel V, Jagutzki O, Spielberger L, Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Schmidt-Böcking H 2000 Phys. Rep. 330 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt L P H, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ullrich J, Schmidt-Böcking H 1987 Phys. Lett. A 125 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 郭大龙, 马新文, 冯文天, 张少锋, 朱小龙 2011 60 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D L, Ma X W, Feng W T, Zhang S F, Zhu X L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yan S, Zhu X L, Zhang S F, Zhao D M, Zhang P, Wei B, Ma X 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 032809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yan S, Zhang P, Stumpf V, Gokhberg K, Zhang X C, Xu S, Li B, Shen L L, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Zhang S F, Zhao D M, Ma X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Falcinelli S, Rosi M, Candori P, Vecchiocattivi F, Farrar J M, Pirani F, Balucani N, Alagia M, Richter R, Stranges, S 2014 Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 8579 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2734
- PDF Downloads: 79
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: