-
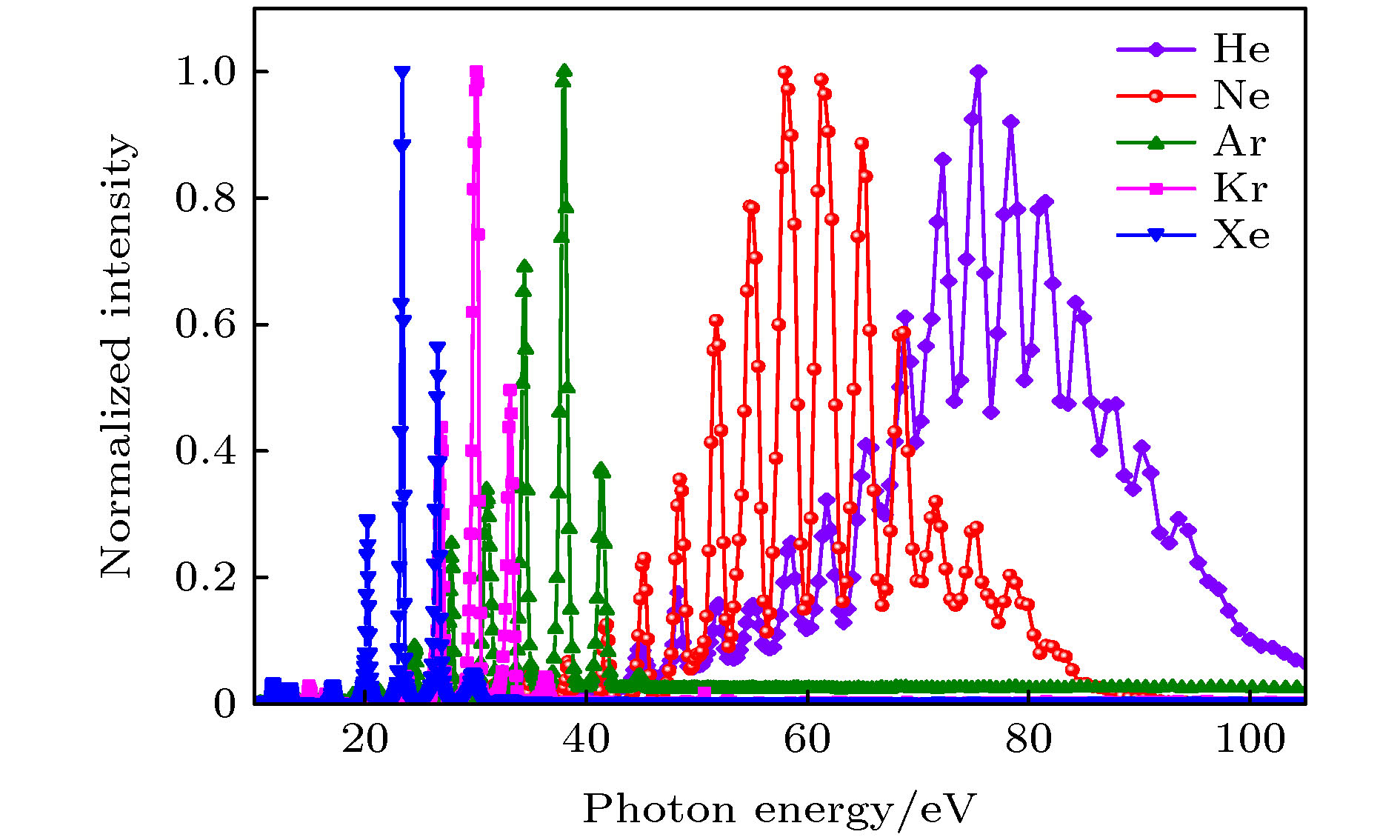
飞秒极紫外光脉冲是研究原子分子超快动力学过程的重要工具, 是同步辐射及自由电子激光这样的大科学装置的重要补充, 而且具有非常诱人的发展前景. 本工作基于大功率飞秒近红外激光在气体介质中的高次谐波过程, 搭建了一套桌面飞秒极紫外光源. 使用充气的中空波导管产生高次谐波, 增大了驱动光与介质的作用长度, 显著提高了光子产额. 使用了光栅的圆锥衍射模式来实现高次谐波光子能量的选择, 在保证高衍射效率的同时, 减小了光栅衍射对于光脉冲的时间展宽效应. 通过实际测量, 光源的输出光子能量可覆盖20—90 eV的范围. 在光子能量为40 eV附近, 输出光子流强达1 × 1010 photons/s, 光子能量分辨约为0.4 eV. 该光源结合新研制的反应显微成像谱仪, 为研究极紫外光与原子分子的相互作用提供了独特的手段. 目前已成功开展多次原子及分子电离实验, 系统性能稳定.Femtosecond extreme ultraviolet (XUV) light pulses play an important role in investigating the ultrafast dynamics of atoms and molecules, and are complementary to the conventional large facilities like synchrotron radiation and free electron laser. We build a table-top femtosecond extreme ultraviolet light source based on the high-order harmonic generation (HHG) process of gaseous medium in a strong laser field. We implement HHG by focusing an intense IR laser into a 5 cm long gas-filled hollow waveguide, instead of the conventional tightly focusing geometry with gas jet. Inside the waveguide, the laser peak intensity is nearly constant and the gas pressure is well-controlled, making it possible to maintain the phase matching condition over an extended distance. And a fully coherent high harmonic beam builds up along the waveguide, leading to a dramatically higher HHG efficiency. Monochromatic XUV light pulses are obtained by spectral selection of the HHG through employing the conical diffraction method of grating. With this geometry used, the pulse broadening caused by wave front tilting during the diffraction can be strongly suppressed, especially for the case of grazing incidence. And the femtosecond temporal character of the light pulse can be preserved while keeping a high reflectivity. The temporal broadening of the XUV light pulse in our setup is estimated to be within 100 femtosecond. By using different noble gases, photons with energy values ranging from 20 eV to 90 eV are produced. For the 27th-order harmonic centered at 41.9 eV, the flux is measured to be 1 × 1010 photons per second, with an energy spread of 0.4 eV. In order to investigate the ultrafast dynamic behaviors of gaseous atoms and molecules with an HHG-based XUV source, we develop a reaction microscope with ultrahigh vacuum of about 10–11 mbar. The combination of HHG-based XUV with the newly developed reaction microscope provides a unique tool for studying the XUV photon and atom/molecule interaction. A series of experiments has been successfully carried out on the platform and the system shows good performance.
-
Keywords:
- extreme ultraviolet (XUV) photon source /
- high order harmonic generation (HHG) /
- conical diffraction /
- reaction microscope
[1] Zewail H A 1988 Science 242 1645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang L, Xie X H, Roither S, Zhou Y M, Lu P X, Kartashov D, Schoffler M, Shafir D, Corkum P B, Baltuska A, Staudte A, Kitzler M 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 193002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schoenlein R W, Chattopadhyay S, Chong H H W, Glover T E, Heimann P A, Shank C V, Zholents A A, Zolotorev M S 2000 Science 287 2237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mcpherson A, Gibson G, Jara H, Johann U, Luk T S, Mcintyre I A, Boyer K, Rhodes C K 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brandi F, Neshev D, Ubachs W 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 163901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rundquist A, Durfee C, Chang Z H, Herne C, Backus S, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 1998 Science 280 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Frassetto F, Cacho C, Froud C A, Turcu I C E, Villoresi P, Bryan W A, Springate E, Poletto L 2011 Opt. Express 19 19169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Grazioli C, Callegari C, Ciavardini A, Coreno M, Frassetto F, Gauthier D, Golob D, Ivanov R, Kivimaki A, Mahieu B, Bucar B, Merhar M, Miotti P, Poletto L, Polo E, Ressel B, Spezzani C, De Ninno G 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 023104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Plogmaker S, Terschlusen J A, Krebs N, Svanqvist M, Forsberg J, Cappel U B, Rubensson J E, Siegbahn H, Soderstrom J 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 123107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ojeda J, Arrell C A, Grilj J, Frassetto F, Mewes L, Zhang H, Van Mourik F, Poletto L, Chergui M 2016 Struct. Dyn. 3 023602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Von Conta A, Huppert M, Worner H J 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 073102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhan M J, Ye P, Teng H, He X K, Zhang W, Zhong S Y, Wang L F, Yun C X, Wei Z Y 2013 Chinese Phys. Lett. 30 093201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Teng H, He X K, Zhao K, Wei Z Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Niu Y, Liang H J, Liu Y, Liu F Y, Ma R, Ding D J 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 074222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 牛永 2017 博士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Niu Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Jilin: Jilin University) (in Chinese)
[16] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt L P H, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hai B, Zhang S F, Zhang M, Najjari B, Dong D P, Lei J T, Zhao D M, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 052706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang M, Najjari B, Hai B, Zhao D M, Lei J T, Dong D P, Zhang S F, Ma X W 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 063302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Lhuillier A, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Arpin P, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Henke B L, Gullikson E M, Davis J C 1993 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 54 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
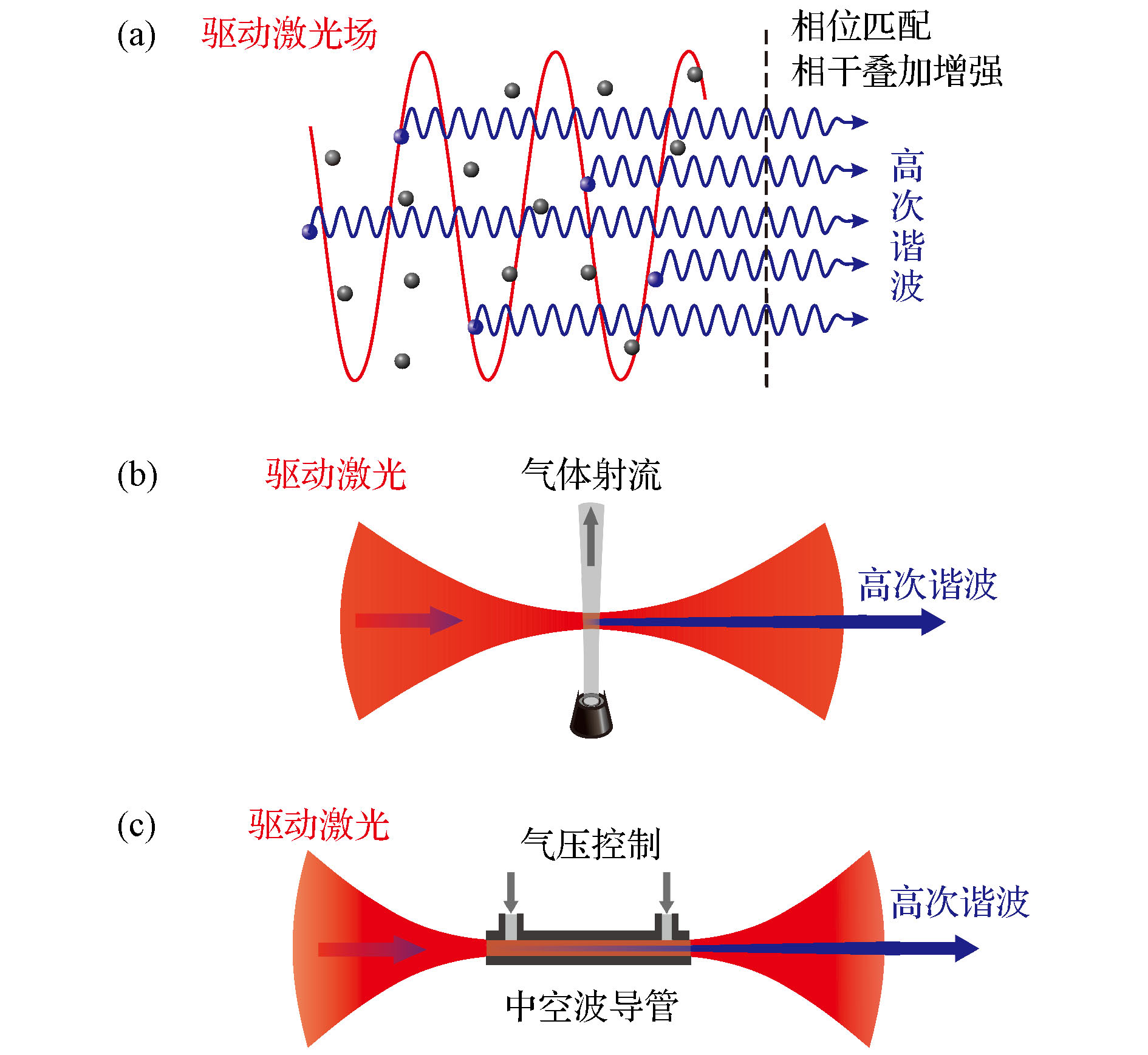
图 2 高次谐波过程中的相位匹配 (a) 在相位匹配条件下, 不同原子释放的谐波相干叠加增强; (b) 使用气体射流产生高次谐波的紧聚焦模式; (c) 使用充气的中空波导管产生高次谐波
Fig. 2. Phase matching of the HHG: (a) Radiations from different atoms add up constructively when phase matched; (b) tightly focusing geometry of HHG with a gas jet; (c) HHG in a gas-filled hollow waveguide.
图 7 光子能量38.5 eV时, 氩原子电离实验的部分结果 (a) 光电子动量在探测器平面内的分布, 图中红色箭头表示光子偏振方向; (b) 3p电离通道(对应于(a)中的最外环)的角分布, 其中的角度为光电子出射方向与光子偏振方向夹角, 红色实线为使用偶极分布公式拟合的理论结果
Fig. 7. Experimental results of Ar ionization with 38.5 eV photons: (a) Photoelectron momentum distribution in the detector plan, and the polarization of the photon is indicated with the red arrow; (b) photoelectron angular distribution of the 3p channel (the outer most ring in (a)), as a function of the angle between the photoelectron emission and the photon polarization. Red line is the theoretical distribution fitted with dipole equation.
-
[1] Zewail H A 1988 Science 242 1645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang L, Xie X H, Roither S, Zhou Y M, Lu P X, Kartashov D, Schoffler M, Shafir D, Corkum P B, Baltuska A, Staudte A, Kitzler M 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 193002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Schoenlein R W, Chattopadhyay S, Chong H H W, Glover T E, Heimann P A, Shank C V, Zholents A A, Zolotorev M S 2000 Science 287 2237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mcpherson A, Gibson G, Jara H, Johann U, Luk T S, Mcintyre I A, Boyer K, Rhodes C K 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brandi F, Neshev D, Ubachs W 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 163901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rundquist A, Durfee C, Chang Z H, Herne C, Backus S, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 1998 Science 280 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Frassetto F, Cacho C, Froud C A, Turcu I C E, Villoresi P, Bryan W A, Springate E, Poletto L 2011 Opt. Express 19 19169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Grazioli C, Callegari C, Ciavardini A, Coreno M, Frassetto F, Gauthier D, Golob D, Ivanov R, Kivimaki A, Mahieu B, Bucar B, Merhar M, Miotti P, Poletto L, Polo E, Ressel B, Spezzani C, De Ninno G 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 023104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Plogmaker S, Terschlusen J A, Krebs N, Svanqvist M, Forsberg J, Cappel U B, Rubensson J E, Siegbahn H, Soderstrom J 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 123107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ojeda J, Arrell C A, Grilj J, Frassetto F, Mewes L, Zhang H, Van Mourik F, Poletto L, Chergui M 2016 Struct. Dyn. 3 023602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Von Conta A, Huppert M, Worner H J 2016 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 073102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhan M J, Ye P, Teng H, He X K, Zhang W, Zhong S Y, Wang L F, Yun C X, Wei Z Y 2013 Chinese Phys. Lett. 30 093201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Teng H, He X K, Zhao K, Wei Z Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Niu Y, Liang H J, Liu Y, Liu F Y, Ma R, Ding D J 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 074222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 牛永 2017 博士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Niu Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Jilin: Jilin University) (in Chinese)
[16] Ullrich J, Moshammer R, Dorn A, Dörner R, Schmidt L P H, Schmidt-Böcking H 2003 Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hai B, Zhang S F, Zhang M, Najjari B, Dong D P, Lei J T, Zhao D M, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 052706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang M, Najjari B, Hai B, Zhao D M, Lei J T, Dong D P, Zhang S F, Ma X W 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 063302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Lhuillier A, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Arpin P, Murnane M M, Kapteyn H C 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Henke B L, Gullikson E M, Davis J C 1993 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 54 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8681
- PDF下载量: 181
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: