-
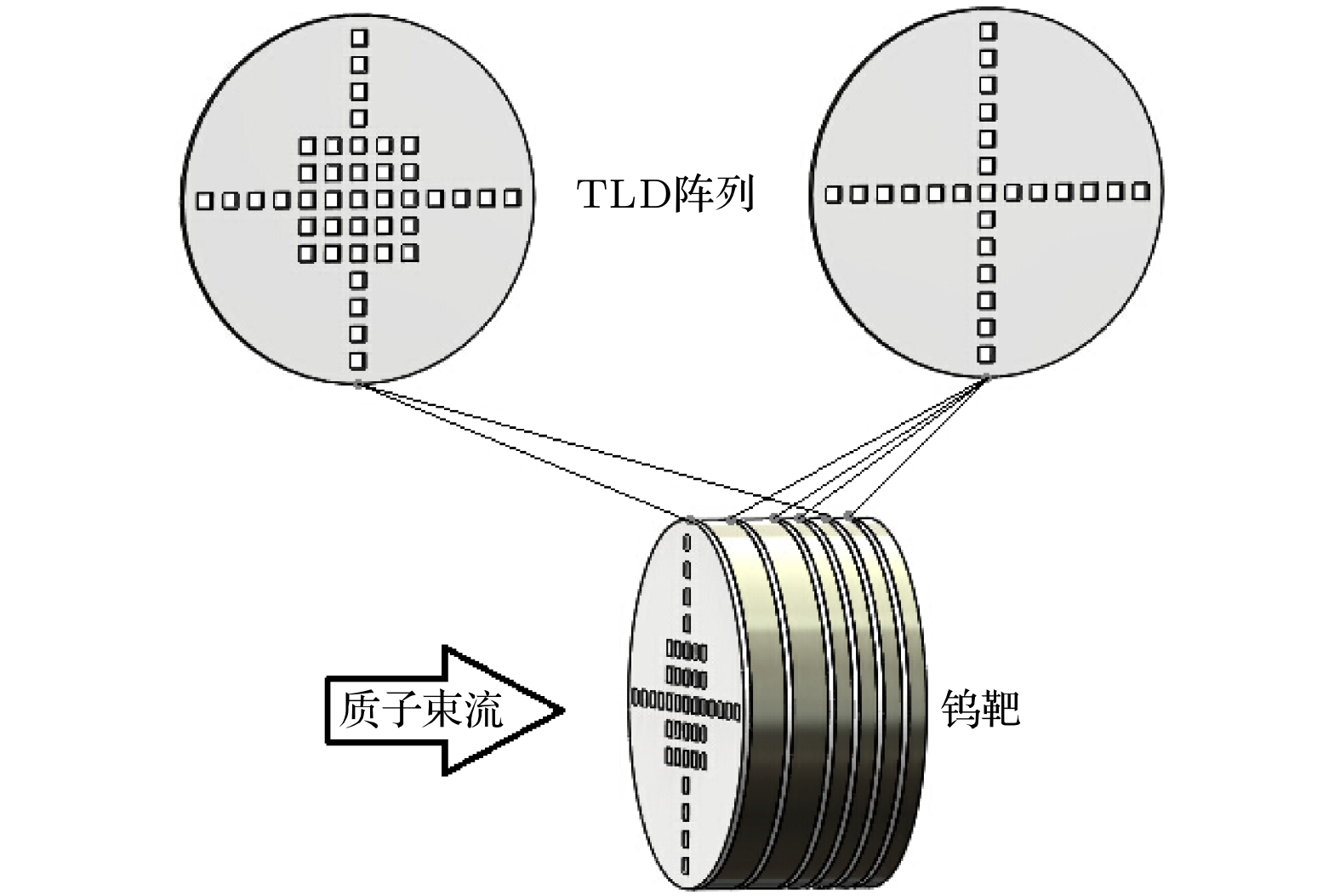
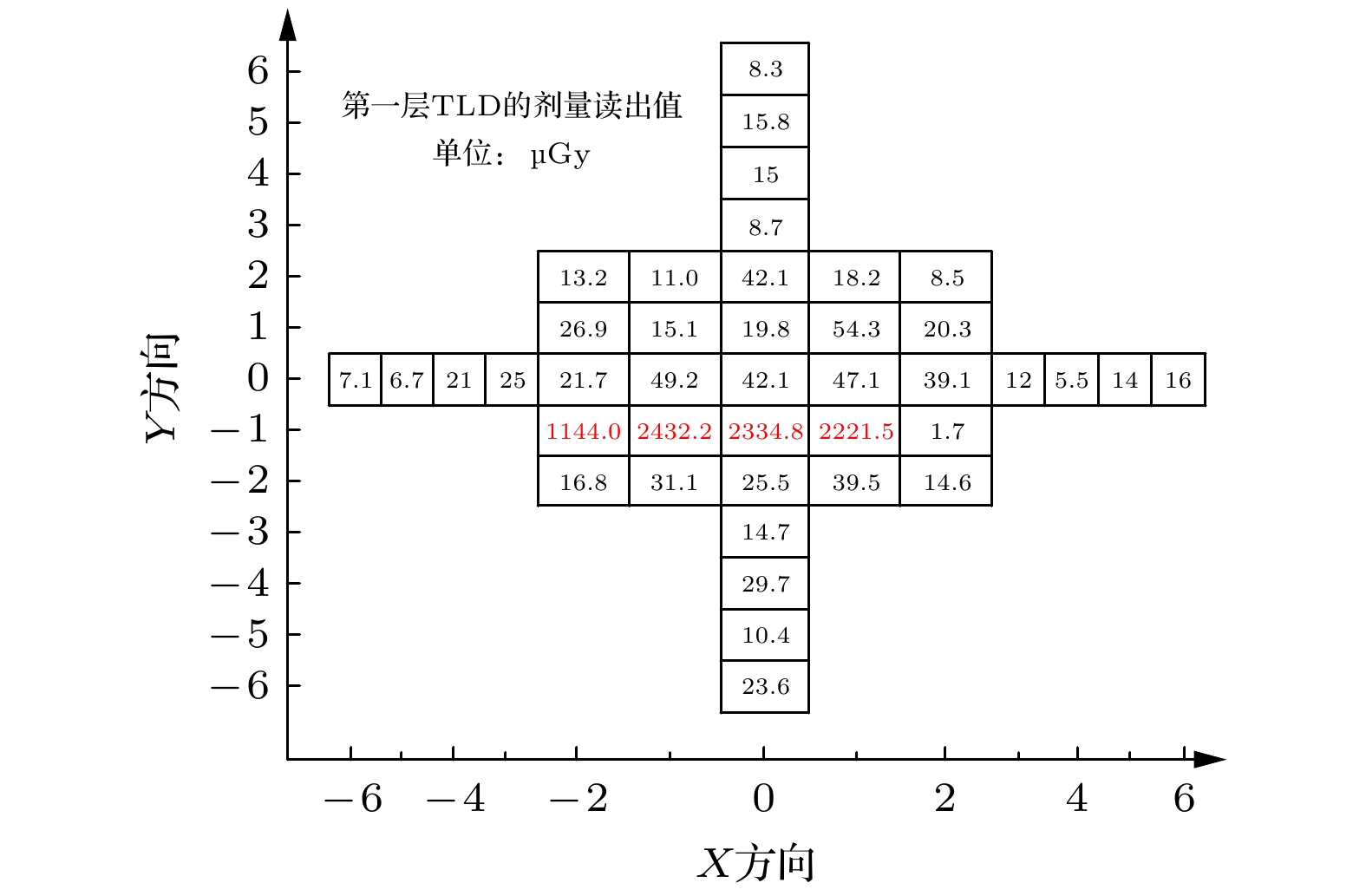
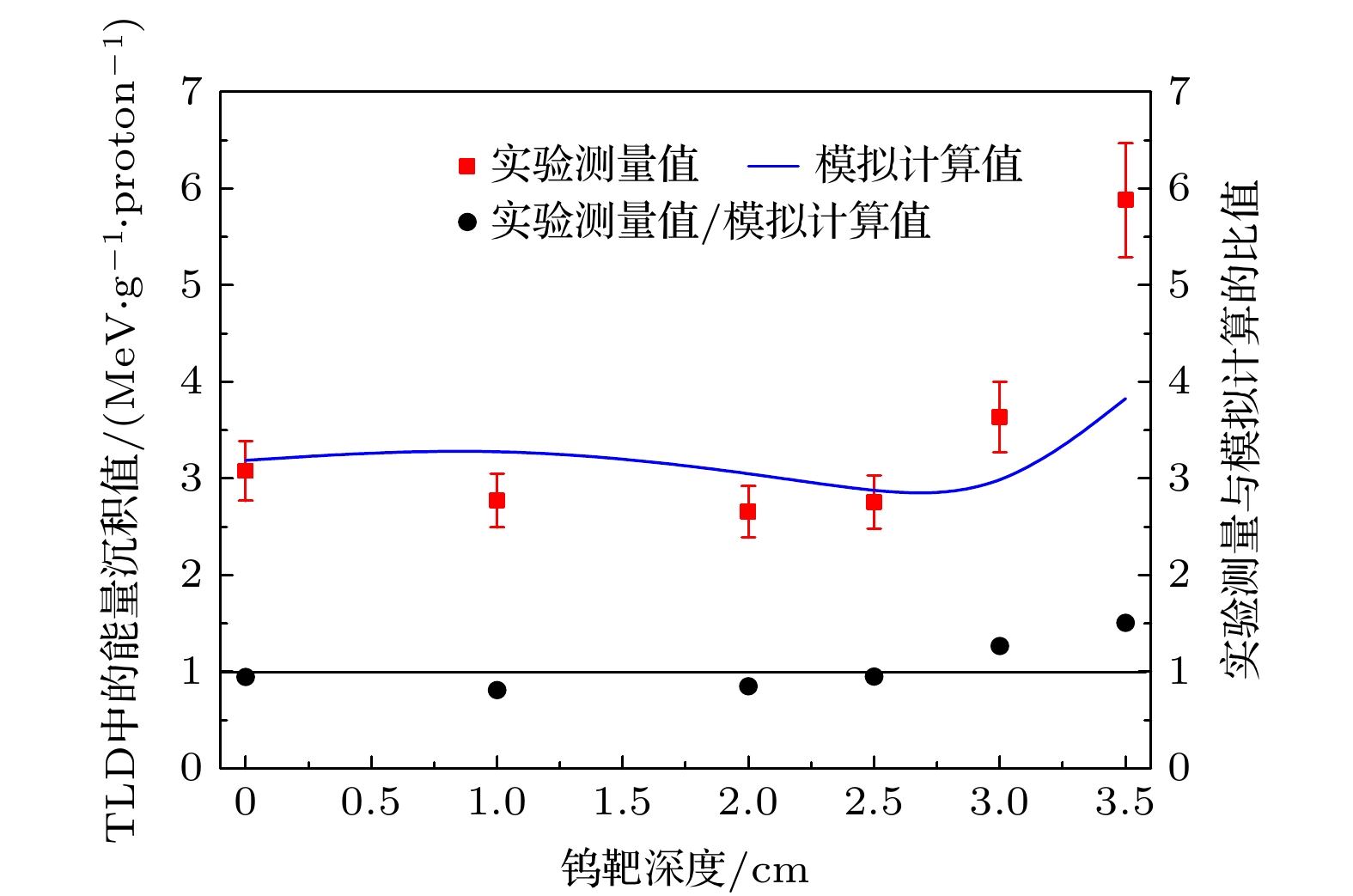
Energy deposition in spallation target induced by energetic protons is the foundation and the premise of the spallation target research. In this paper, several intra-nuclear cascade models including BERTINI, ISABEL, CEM2K and INCL4 contained in MCNPX package, together with FLUKA and PHITS Monte Carlo codes are used to calculate the energy deposition in lead (Pb) and tungsten (W) spallation target impinged by 800, 1000, and 1200 MeV protons. The contributions of different particles to the total energy deposition in the Pb target are obtained and compared with each other as well. The energy deposition distribution caused by 250 MeV protons in the W target is measured with thermoluminescence detectors (TLDs). The results indicate that the calculations from the MCNPX accord with experimental data, verifying that the Monte Carlo code has a high reliability for energy deposition simulation.
-
Keywords:
- energy deposition /
- high energy proton /
- spallation target /
- Monte Carlo simulation
[1] Wang F W, Liang T J, Yin W, Yu Q Z, He L H, Tao J Z, Zhu T, Jia X J, Zhang S Y 2013 Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56 2410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 詹文龙, 徐瑚珊 2012 中国科学院院刊 27 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan W L, Xu H S 2012 Bul. Ch. Acad. Sci. 27 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 于全芝, 殷雯, 梁天骄 2011 60 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Q Z, Yin W, Liang T J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pelowitz D B 2005 MCNPX User’s Manual version 2.5.0 (Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory)
[5] Tatsuhiko S, Koji N, Norihiro M, Shintaro H, Yosuke I, Shusaku N, Tatsuhiko O, Hiroshi I, Hiroshi N, Tokio F, Keisuke O, Tetsuya K, Satoshi C 2013 J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 50 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Alfredo F, Paola R S, Alberto F, Johannes R FLUKA: A Multi-particle Transport Code (Italian National Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) and European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN))
[7] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Kazaritsky V D, Povarov A L, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1990 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 295 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Andreev A M, Dubinsky V D, Kazaritsky V D, Povarov A L, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1992 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 314 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Andreev A M, Dubinsky V D, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1993 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 335 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Azhgirey I L, Degtyarev I I 2007 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 572 935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bauer G S, Spitzer H, Holzen G V, Ni L, Hastings J 1998 14th Meeting of the Int. Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources, Uitica I L USA, June 14–19, 1998 p229
[12] Filges D, Neef R D, Schaal H 1998 Proc. of the Fourth Workshop on Simulating Accelerator Radiation Environments, Konxville TN USA, September 14–16, 1998 p221
[13] Tietze A 2001 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuppertal: University of Wuppertal)
[14] Xia J W, Zhan W L, Wei B W, Yuan Y J, Song M T, Zhang W Z, Yang X D, Yuan P, Gao D Q, Zhao H W, Yang X T, Xiao G Q, Man K T, Dang J R, Cai X H, Wang Y F, Tang J Y, Qiao W M, Rao Y N, He Y, Mao L Z, Zhou Z Z 2002 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 488 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Detlef F, Frank G 2009 Handbook of Spallation Research: Theory, Experiments and Applications (Weinheim: WILEY-VCH)
[16] 奥伯霍弗, 沙尔曼著 (张彤译) 1988 应用热释光剂量学(北京: 中国计量出版社)
Oberhofer M, Scharmann A (translated by Zhang T) 1988 The Applied Thermoluminescence Dosimetry (Beijing: China Metrology Press)(in Chinese)
[17] 赵建兴, 王峰, 唐开勇, 李海俊, 刘大海, 肖无云, 崔辉 2011 核技术 34 103
Zhao J X, Wang F, Tang K Y, Li H J, Liu D H, Xiao W Y, Cui H 2011 J. Nucl. Tech. 34 103
[18] Massillon-JL G, Gamboa-deBuen I, Brandan M E 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 2584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bilski P, Berger T, Hajek M, Reitz G 2011 Radi Meas. 46 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] James F Z, http://www.srim.org [2009]
-
表 1 CEM2K级联模型计算质子入射铅靶产生的不同粒子对总能量沉积的占比贡献
Table 1. The calculated contribution of different particles to the total energy deposition in lead target by CEM2K-Cascade-Mode
粒子 800 MeV 1000 MeV 1200 MeV 沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%全部粒子 497.9 100 572.0 100 648.7 100 质子 413.9 83.13 435.6 76.15 455.0 70.15 光子 47.5 9.54 74.8 13.08 104.0 16.03 π0 0.2 0.04 0.4 0.06 0.5 0.08 带电π介子(± π) 6.6 1.33 13.7 2.39 21.9 3.37 氘 13.7 2.75 21.2 3.71 29.0 4.47 氚 5.0 1.01 8.5 1.48 12.3 1.90 氦–3 2.8 0.57 5.1 0.90 8.0 1.23 α粒子 6.1 1.23 10.1 1.77 14.6 2.26 中子 2.0 0.40 2.7 0.47 3.3 0.51 初级质子
电离作用268.8 52.73 247.9 48.63 233.1 45.72 表 2 BERTINI, ISABEL, CEM2K与INCL4级联模型计算1000 MeV质子入射铅靶产生的不同粒子对总能量沉积值的占比贡献
Table 2. The calculated contribution of different particles to the total energy deposition in lead target by 1000 MeV protons with BERTINI, ISABEL, CEM2K, and INCL4 cascade mode.
粒子 BERTINI ISABEL CEM2 K INCL4 沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%沉积能
量/MeV对总能量沉积值
的占比/%全部粒子 580.3 100 603.0 100 572.0 100.00 594.5 100 质子 474.0 81.67 493.0 81.76 435.6 76.15 500.6 84.20 光子 63.7 10.98 76.2 12.64 74.8 13.08 60.7 10.21 π0 0.3 0.05 0.3 0.05 0.3 0.06 0.3 0.04 带电π介
子(± π)14.9 2.56 13.9 2.31 13.7 2.39 15.5 2.60 氘 6.4 1.10 3.7 0.62 21.2 3.71 4.0 0.67 氚 3.0 0.52 1.9 0.32 8.5 1.48 1.8 0.30 氦–3 0.4 0.06 0.1 0.02 5.1 0.90 0.2 0.03 α粒子 14.8 2.56 11.8 1.96 10.1 1.77 9.1 1.53 中子 2.9 0.49 1.9 0.32 2.7 0.47 2.5 0.42 初级质子电
离作用245.1 48.06 243.6 47.79 247.9 48.63 245.0 48.06 -
[1] Wang F W, Liang T J, Yin W, Yu Q Z, He L H, Tao J Z, Zhu T, Jia X J, Zhang S Y 2013 Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56 2410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 詹文龙, 徐瑚珊 2012 中国科学院院刊 27 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan W L, Xu H S 2012 Bul. Ch. Acad. Sci. 27 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 于全芝, 殷雯, 梁天骄 2011 60 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Q Z, Yin W, Liang T J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Pelowitz D B 2005 MCNPX User’s Manual version 2.5.0 (Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory)
[5] Tatsuhiko S, Koji N, Norihiro M, Shintaro H, Yosuke I, Shusaku N, Tatsuhiko O, Hiroshi I, Hiroshi N, Tokio F, Keisuke O, Tetsuya K, Satoshi C 2013 J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 50 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Alfredo F, Paola R S, Alberto F, Johannes R FLUKA: A Multi-particle Transport Code (Italian National Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) and European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN))
[7] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Kazaritsky V D, Povarov A L, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1990 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 295 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Andreev A M, Dubinsky V D, Kazaritsky V D, Povarov A L, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1992 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 314 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Andreev A M, Dubinsky V D, Chuvilo I V, Sherstnev V A 1993 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 335 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Belyakov-Bodin V I, Azhgirey I L, Degtyarev I I 2007 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 572 935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bauer G S, Spitzer H, Holzen G V, Ni L, Hastings J 1998 14th Meeting of the Int. Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources, Uitica I L USA, June 14–19, 1998 p229
[12] Filges D, Neef R D, Schaal H 1998 Proc. of the Fourth Workshop on Simulating Accelerator Radiation Environments, Konxville TN USA, September 14–16, 1998 p221
[13] Tietze A 2001 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuppertal: University of Wuppertal)
[14] Xia J W, Zhan W L, Wei B W, Yuan Y J, Song M T, Zhang W Z, Yang X D, Yuan P, Gao D Q, Zhao H W, Yang X T, Xiao G Q, Man K T, Dang J R, Cai X H, Wang Y F, Tang J Y, Qiao W M, Rao Y N, He Y, Mao L Z, Zhou Z Z 2002 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 488 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Detlef F, Frank G 2009 Handbook of Spallation Research: Theory, Experiments and Applications (Weinheim: WILEY-VCH)
[16] 奥伯霍弗, 沙尔曼著 (张彤译) 1988 应用热释光剂量学(北京: 中国计量出版社)
Oberhofer M, Scharmann A (translated by Zhang T) 1988 The Applied Thermoluminescence Dosimetry (Beijing: China Metrology Press)(in Chinese)
[17] 赵建兴, 王峰, 唐开勇, 李海俊, 刘大海, 肖无云, 崔辉 2011 核技术 34 103
Zhao J X, Wang F, Tang K Y, Li H J, Liu D H, Xiao W Y, Cui H 2011 J. Nucl. Tech. 34 103
[18] Massillon-JL G, Gamboa-deBuen I, Brandan M E 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 2584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bilski P, Berger T, Hajek M, Reitz G 2011 Radi Meas. 46 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] James F Z, http://www.srim.org [2009]
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10553
- PDF Downloads: 245
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: