-
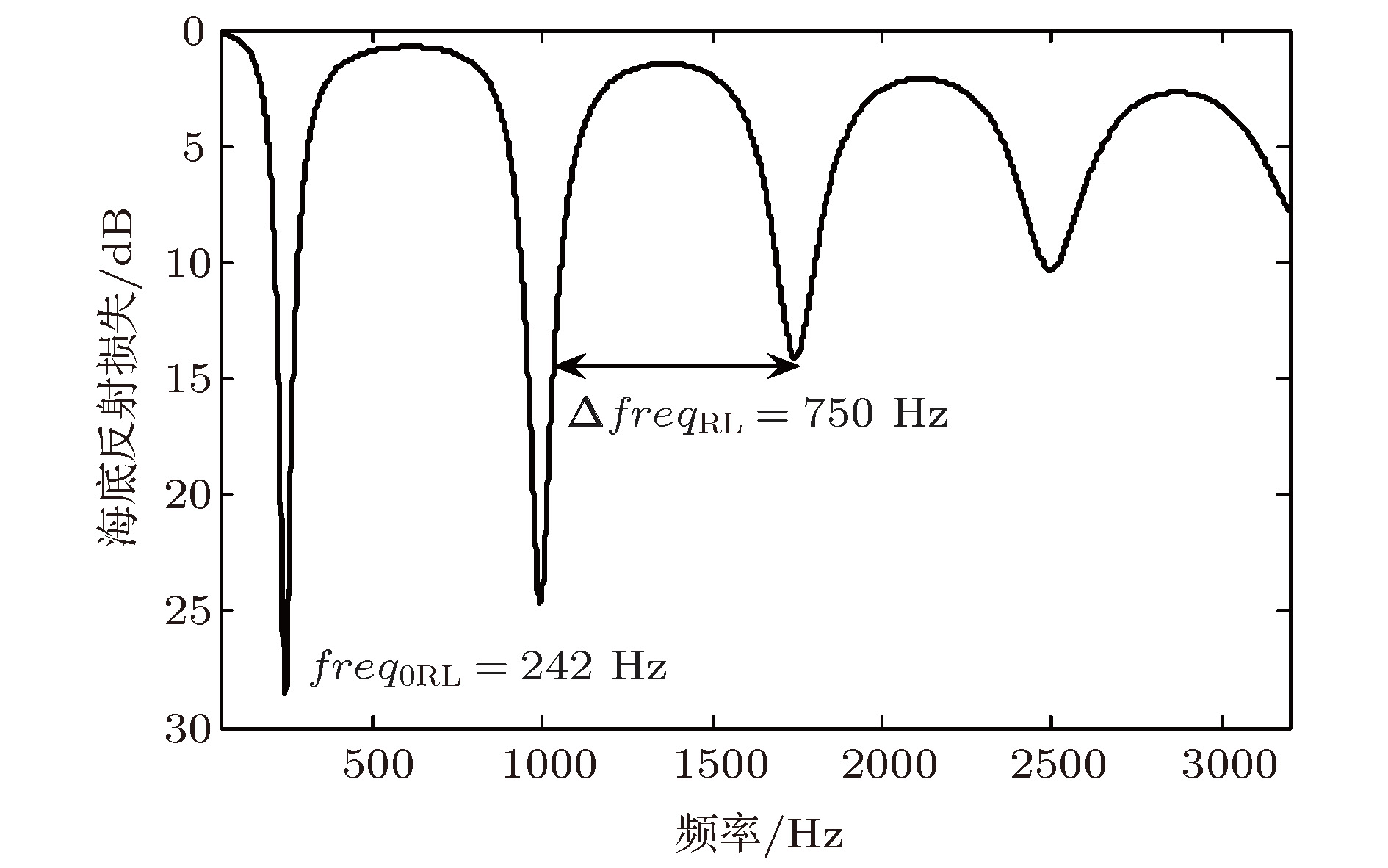
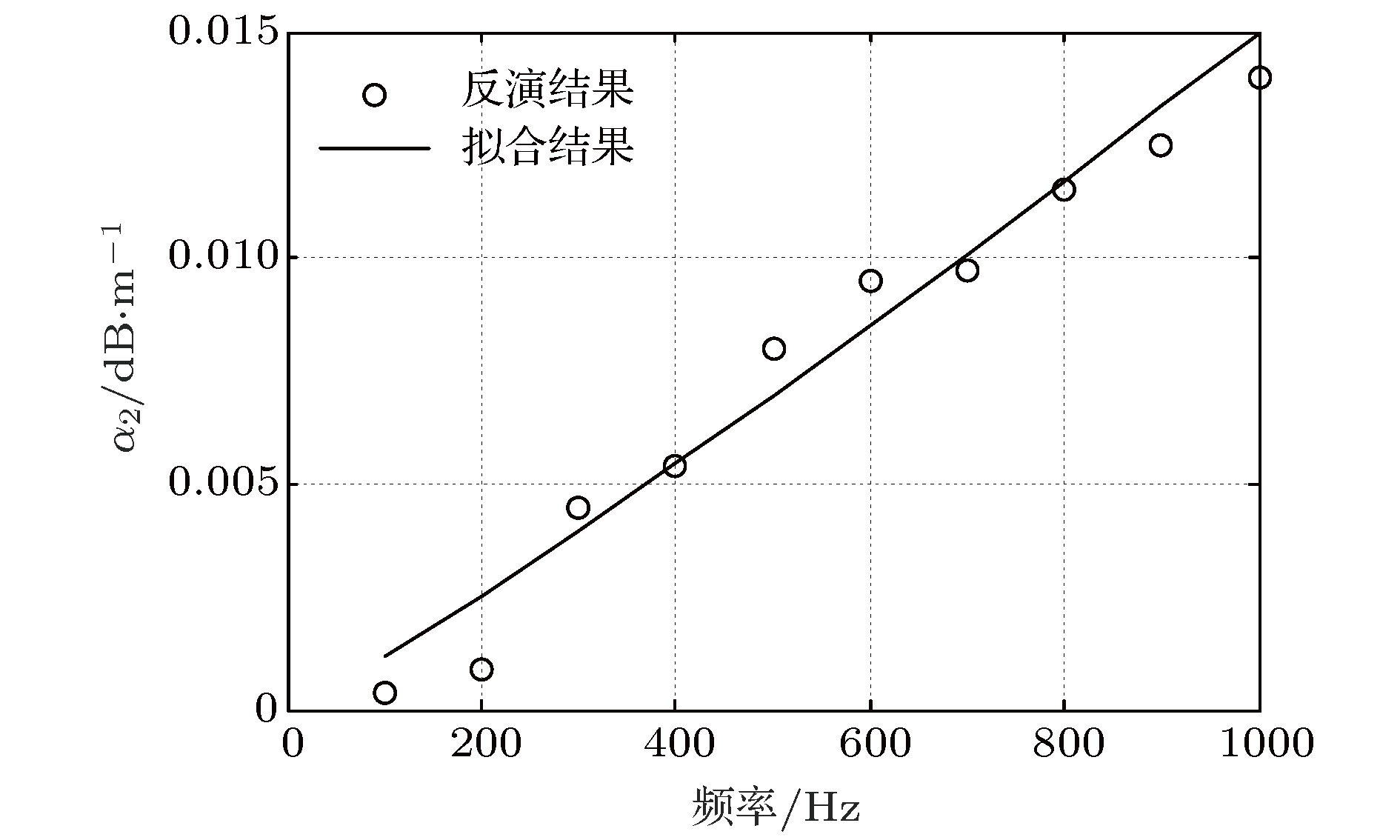
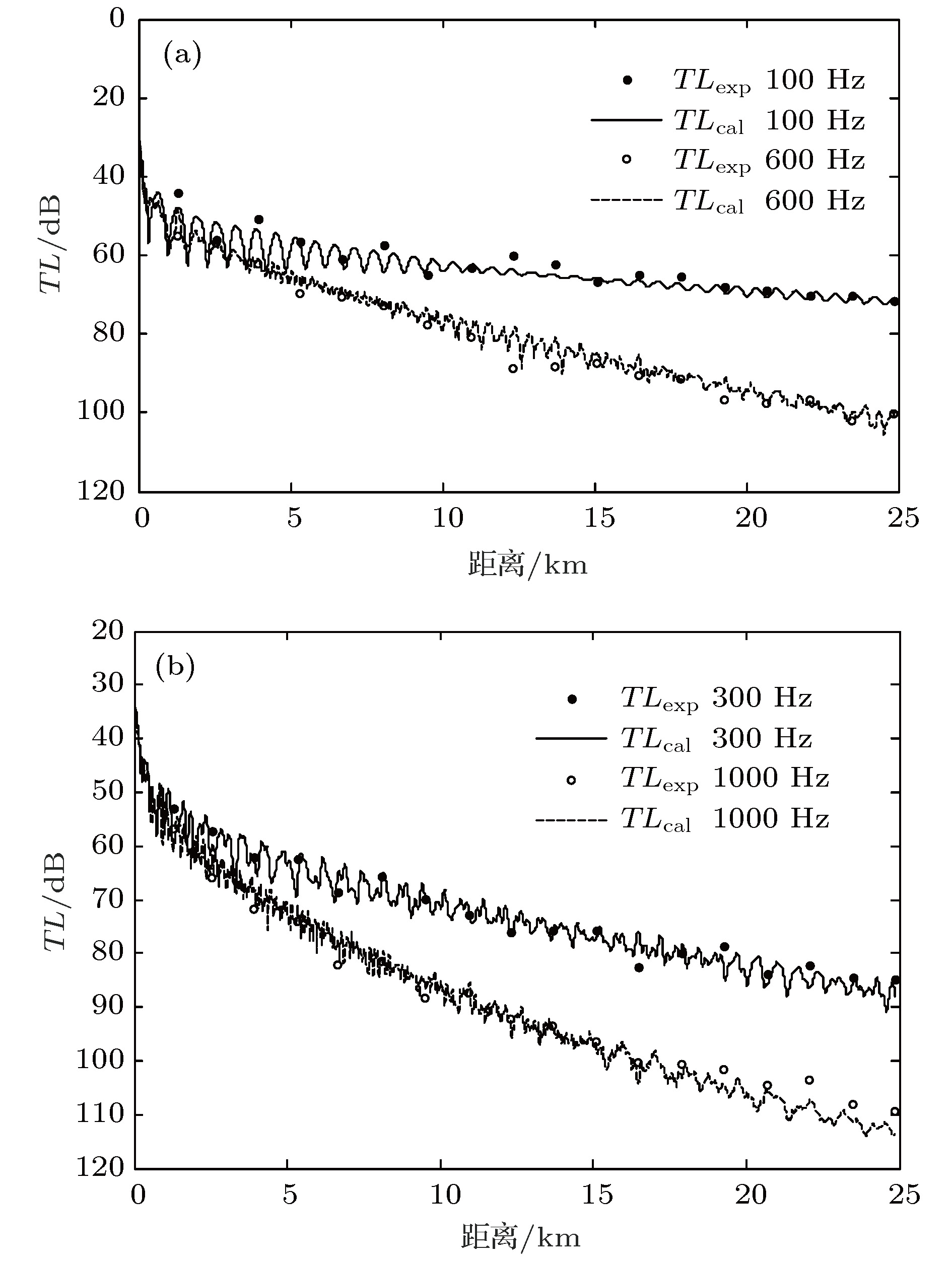
软泥底环境下沉积层参数的声学反演是国际水声领域的一个研究热点. 浅海中, 当高声速基底和海水之间存在一层低声速(小于海水声速)的沉积层时, 小掠射角情况下不同频率声传播损失会出现周期性增大现象. 基于此现象, 提出一种适用于低声速沉积层的海底参数声学反演方法. 首先, 推导给出小掠射角情况下传播损失周期增大的频率间隔与沉积层声速、厚度及近海底海水声速之间的解析表达式; 其次, 利用一次黄海实验中软泥底环境下的宽带声传播信号, 提取了小掠射角下传播损失增大的频率周期; 再次, 把该解析表达式作为约束条件, 结合Hamilton密度与声速的经验公式, 采用匹配场处理反演给出沉积层的声速、密度、厚度及基底的声速、密度; 然后, 利用声传播损失数据反演得到泥底环境下不同频率的声衰减系数, 通过拟合发现泥底声衰减系数随频率近似呈线性关系; 最后, 给出了双层海底模型和半无限大海底模型等效性的讨论. 反演结果为低声速沉积层海底声传播规律研究与应用提供了海底声学参数.Acoustic inversion of sediment parameters in muddy bottom environment has received much attention in the field of underwater acoustics. In shallow water, when there is a low-speed layer of unconsolidated sediment, such as mud in which the sound speed is lower than that of the sea water, on the top of a high-speed bottom, the transmission losses at different frequencies will increase periodically under the condition of small grazing angles. Based on this phenomenon, an acoustic inversion method of seabed parameters for low speed sediments is proposed. Firstly, the analytical expressions between the frequency interval of the transmission loss (TL) periodical increasing and geoacoustic parameters, including the sound speed and the thickness of sediment layer and the sound speed of seawater near the bottom, are derived under the condition of small grazing angles. Secondly, using the broadband sound propagation signals received under the thermocline in the 2002 summer acoustic experiment conducted in the Yellow Sea, the TL at small grazing angles increases periodically with the frequency, and it is determined that the sediment of this sea area is a low-speed sediment. Then, taking the analytical expression as the constraint condition and combining with Hamilton's empirical formula, the sound speed, density, thickness of sediment layer and the sound speed and density of the seabed are inverted by matched field processing. Finally, the bottom attenuation coefficients at different frequencies are inverted by using the long-range TL, and the linear relationship between the attenuation coefficients and the frequencies is obtained. The equivalence between the two different bottom models is discussed in the end. The inversion results can provide seabed parameters for the study and application of the sound propagation law in shallow water with a low-speed sediment.
-
Keywords:
- low-speed sedimentary seabed /
- geoacoustic inversion /
- matched field processing /
- transmission loss
[1] Gerstoft P, Gingras D F 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99 2839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] D’Spain G L, Murray J J, Hodgkiss W S, Booth N O 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 3291
[3] Zhou J X 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 78 1003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z, Rogers P H, Simmen J A, Dahl P H, Jin G L, Peng Z H 2004 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 29 988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 高伟, 王宁, 王好忠 2008 声学学报 33 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Wang N, Wang H Z 2008 Acta Acustica 33 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Carbone N M, Deane G B, Buckingham M J 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2004 Chin. Phys. Lett. 21 1100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李风华, 张仁和 2000 声学学报 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F H, Zhang R H 2000 Acta Acustica 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu S L, Li Z L, Qin J X 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li Z L, Zhang R H, Yan J, Li F H, Liu J J 2004 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 29 973
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Z L 2003 Chin. J. Acoust. 22 176
[12] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2007 Chin. Phys. Lett. 24 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z L, Li F H 2010 Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 28 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 2847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Press F, Ewing M. 1948 Geophysics 13 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rubano L A 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 1608
[17] Kuperman W A, Jensen F B 1980 Bottom-interacting Ocean Acoustics (New York: Plenum Press) pp135−152
[18] Bonnel J, Lin Y T, Eleftherakis D, Goff J A, Stan D, Ross C, James H M, Gopu R P 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wan L, Badiey M, Knobles D P, Wilson P S 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Porter M B, Bucker H P 1987 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 82 1349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Porter M, Reiss E L 1984 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 76 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hamilton E L, Bachman R T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 1891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stoffa P L, Sen M K 1991 Geophysics 56 1794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hamilton E L 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68 1313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gerstoft P, Mecklenbrauker C F 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104 808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 低声速沉积海底环境参数
Table 1. Seabed environmental parameters for low-speed sediment simulation.
c1/m·s–1 ρ1/g·cm–3 α1/dB·λ–1 c2/m·s–1 ρ2/g·cm–3 α2/dB·λ–1 d/m c3/m·s–1 ρ3/g·cm–3 α3/dB·λ–1 1488 1.0 0.0 1460 1.4 0.10 5 1620 1.8 0.10 表 2 计算得到的不同距离下的有效海底掠射角
Table 2. Effective bottom grazing angles at different ranges.
收发距离/km 1 5 10 20 有效海底掠射角 10.41° 6.16° 2.15° 0.52° 标准差 7.84° 6.44° 3.75° 0.70° 表 3 待反演参数搜素范围及反演结果
Table 3. Search ranges of the unknown parameters and the inverted results.
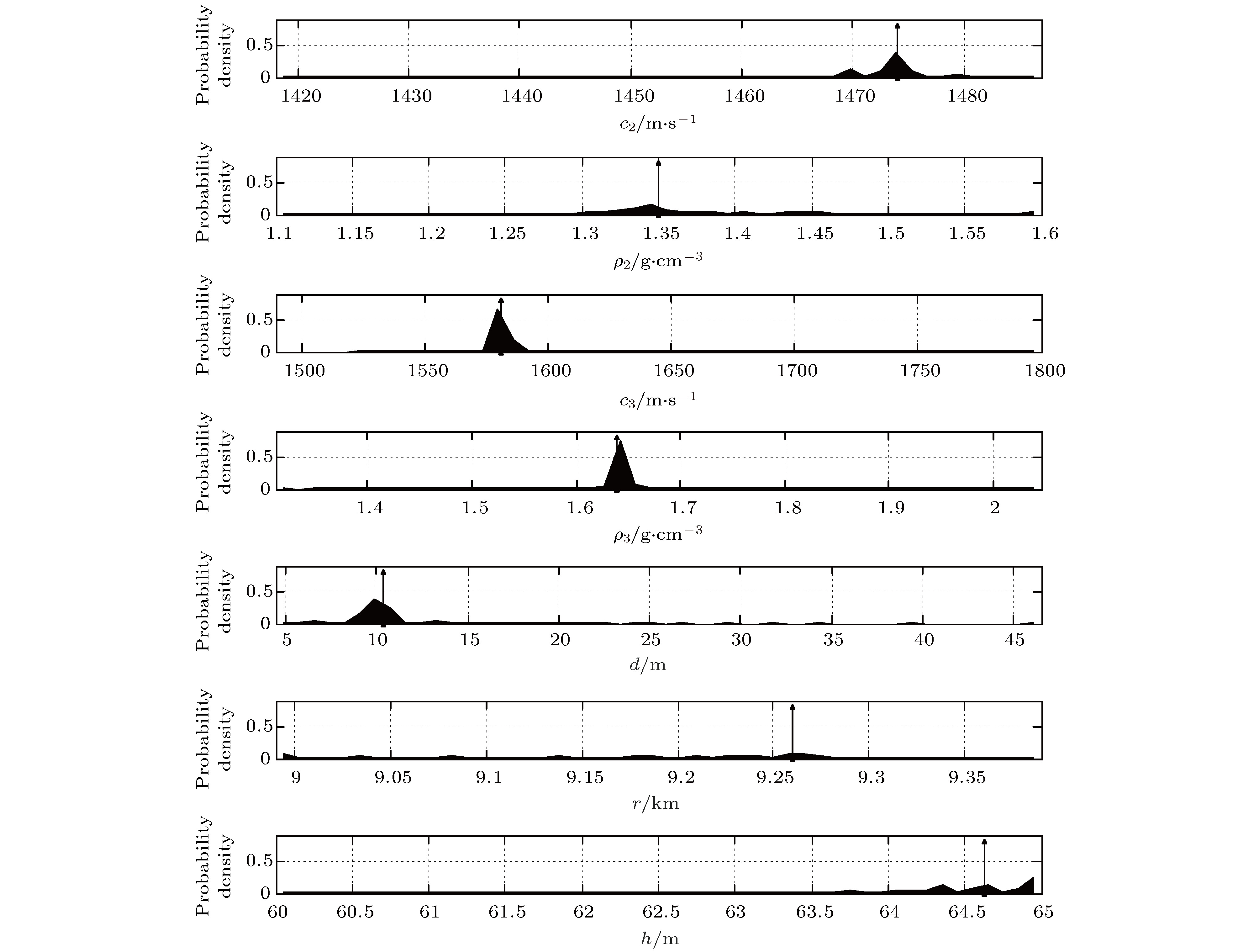
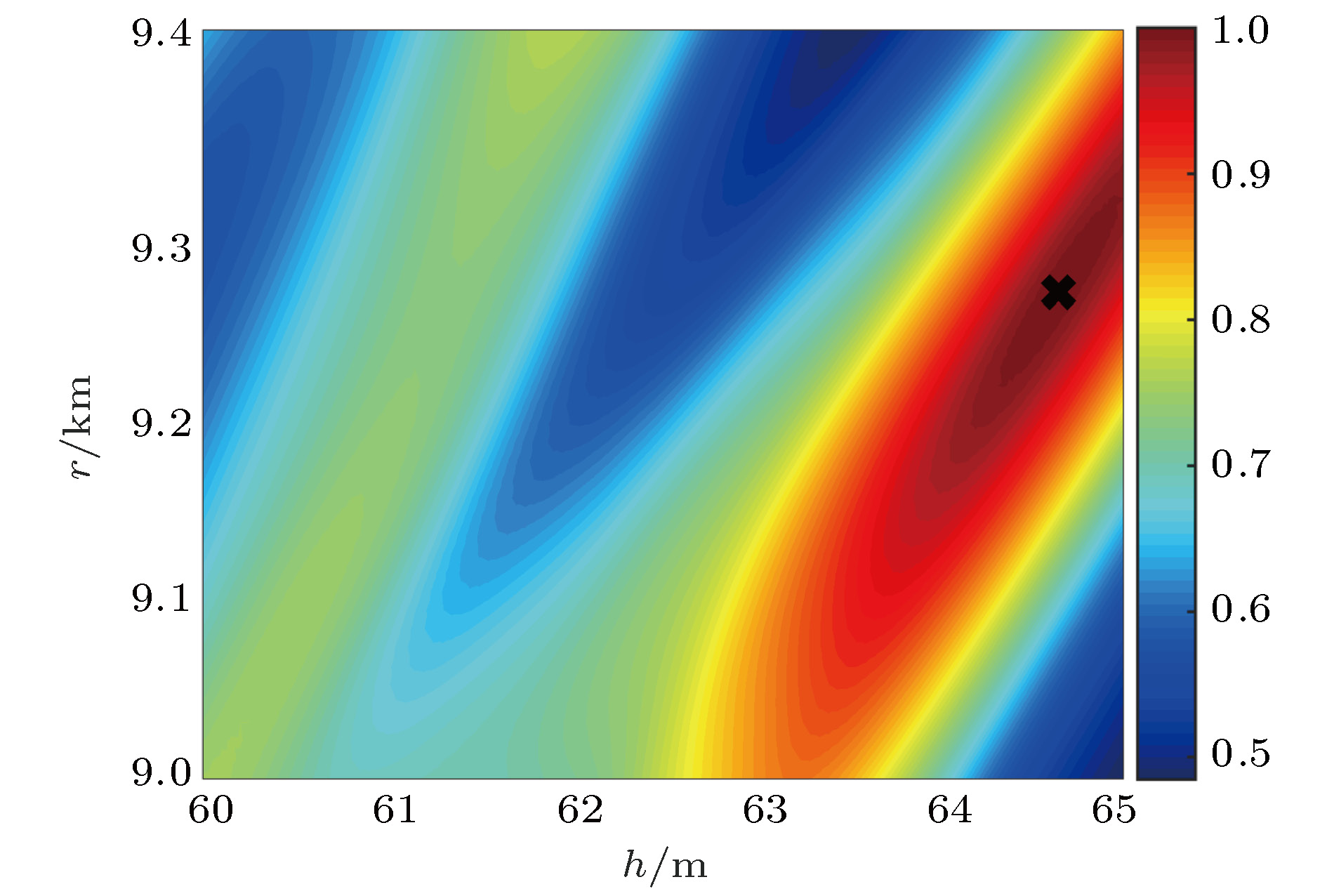
c2/m·s–1 ρ2/g·cm–3 c3/m·s–1 ρ3/g·cm–3 d/m r/km h/m 搜索范围 1418—1487 1.1—1.6 1489—1800 — — 9.0—9.4 60—65 最优值 1474.01 1.35 1580.47 1.64 10.32 9.26 64.63 平均值 1474.12 1.39 1581.02 1.64 10.48 9.22 64.65 标准差 2.22 0.07 1.52 0.00 0.98 0.10 0.34 -
[1] Gerstoft P, Gingras D F 1996 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99 2839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] D’Spain G L, Murray J J, Hodgkiss W S, Booth N O 1995 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 97 3291
[3] Zhou J X 1985 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 78 1003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z, Rogers P H, Simmen J A, Dahl P H, Jin G L, Peng Z H 2004 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 29 988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 高伟, 王宁, 王好忠 2008 声学学报 33 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao W, Wang N, Wang H Z 2008 Acta Acustica 33 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Carbone N M, Deane G B, Buckingham M J 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2004 Chin. Phys. Lett. 21 1100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李风华, 张仁和 2000 声学学报 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F H, Zhang R H 2000 Acta Acustica 25 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu S L, Li Z L, Qin J X 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 124301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li Z L, Zhang R H, Yan J, Li F H, Liu J J 2004 IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 29 973
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Z L 2003 Chin. J. Acoust. 22 176
[12] Li Z L, Zhang R H 2007 Chin. Phys. Lett. 24 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z L, Li F H 2010 Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 28 990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou J X, Zhang X Z 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 2847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Press F, Ewing M. 1948 Geophysics 13 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rubano L A 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 67 1608
[17] Kuperman W A, Jensen F B 1980 Bottom-interacting Ocean Acoustics (New York: Plenum Press) pp135−152
[18] Bonnel J, Lin Y T, Eleftherakis D, Goff J A, Stan D, Ross C, James H M, Gopu R P 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wan L, Badiey M, Knobles D P, Wilson P S 2018 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 143 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Porter M B, Bucker H P 1987 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 82 1349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Porter M, Reiss E L 1984 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 76 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hamilton E L, Bachman R T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 1891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stoffa P L, Sen M K 1991 Geophysics 56 1794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hamilton E L 1980 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68 1313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gerstoft P, Mecklenbrauker C F 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104 808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11361
- PDF下载量: 152
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: