-
Quantum communication has the advantages of wide coverage and security, and is currently a hot research topic in the field of communication. In the process of free space quantum communication, quantum signals need transmitting at a certain height above the surface. Various environmental factors in free space, such as snowfall, sandstorms, rainfall, haze and floating dust, will inevitably affect quantum communication performance. However, so far, the influence of snowfall on the performance of quantum channels in free space near the surface has not been investigated. Thus, according to the intensity of snowfall, the snowfall is divided into four levels: light snow (
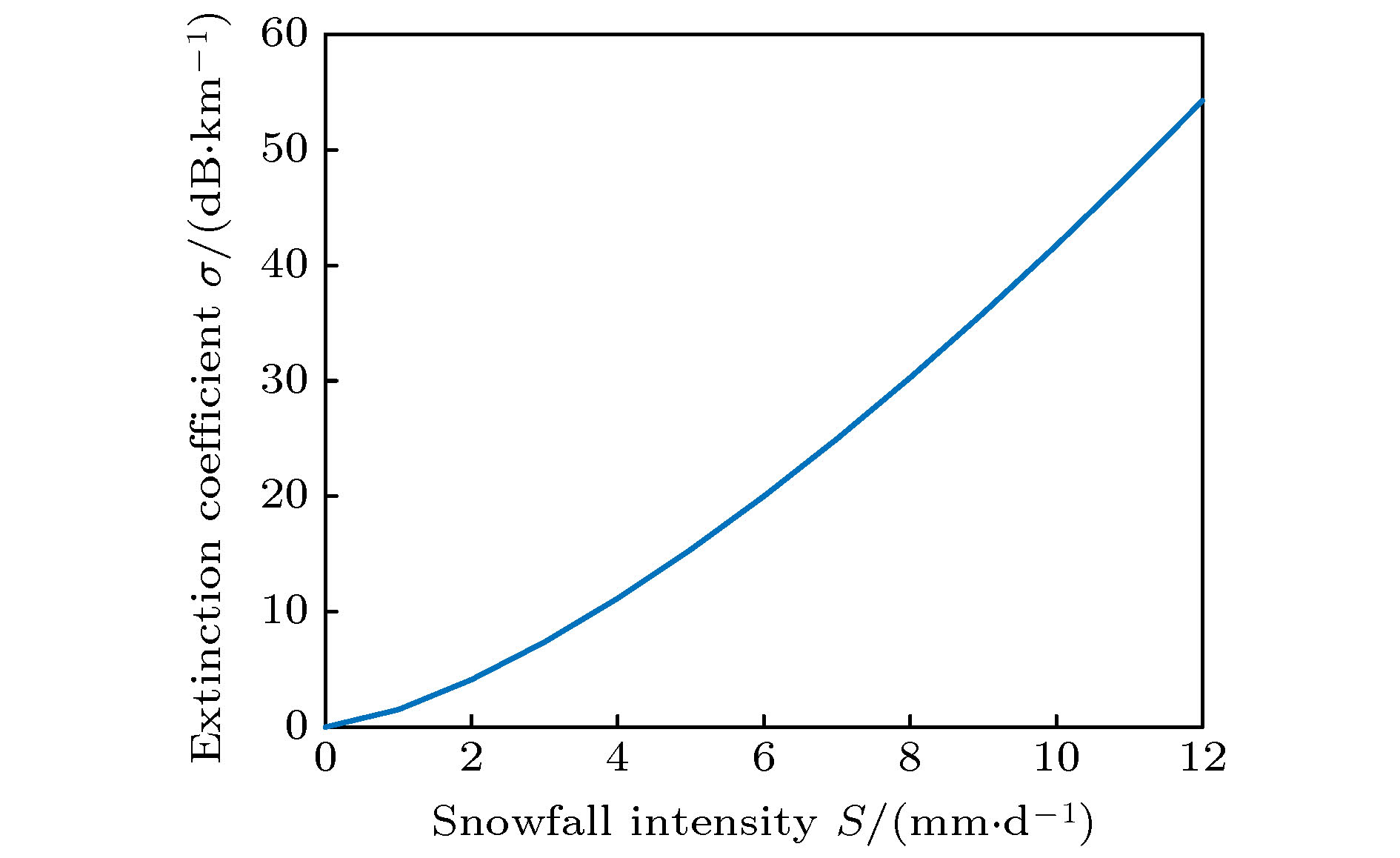
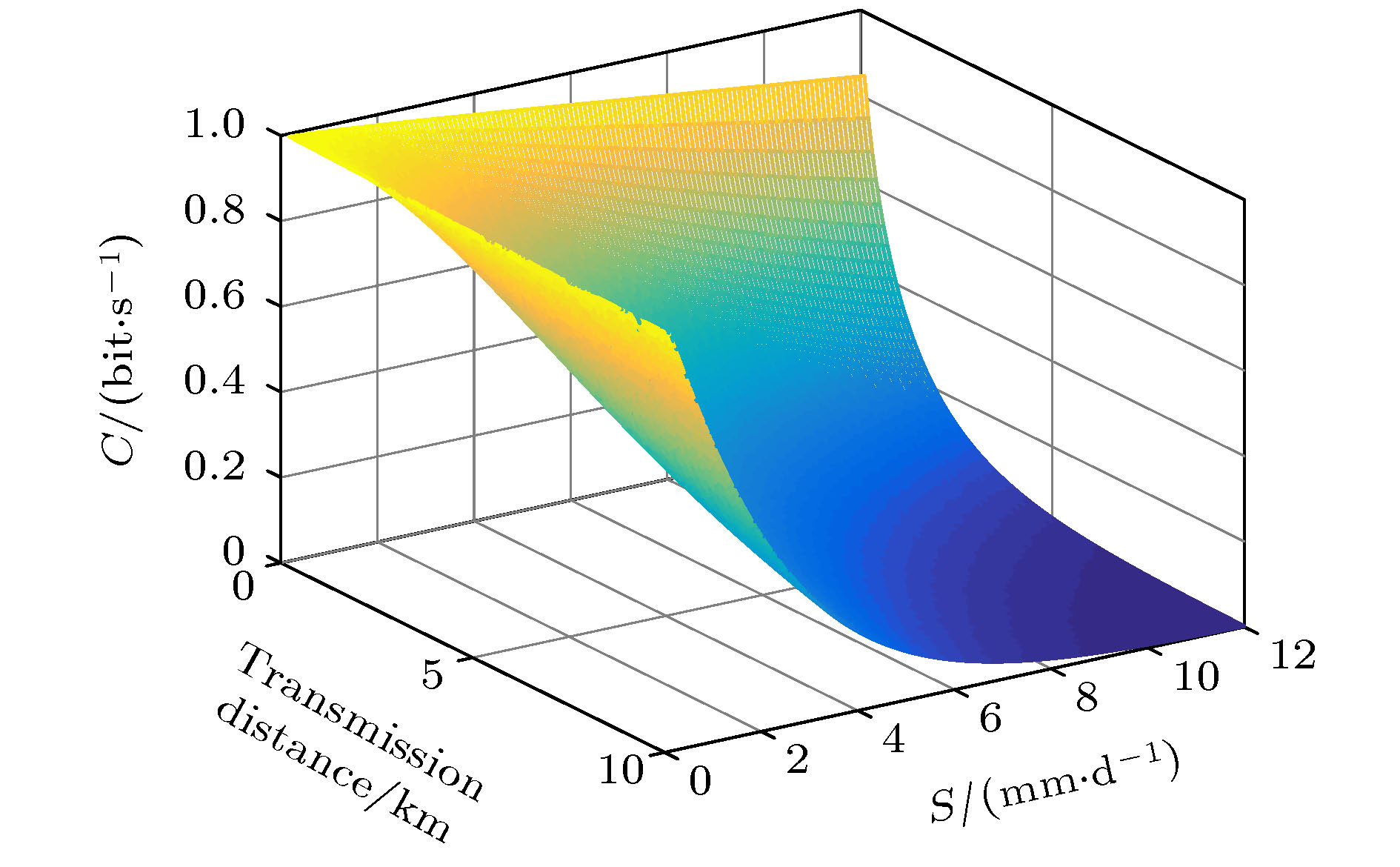
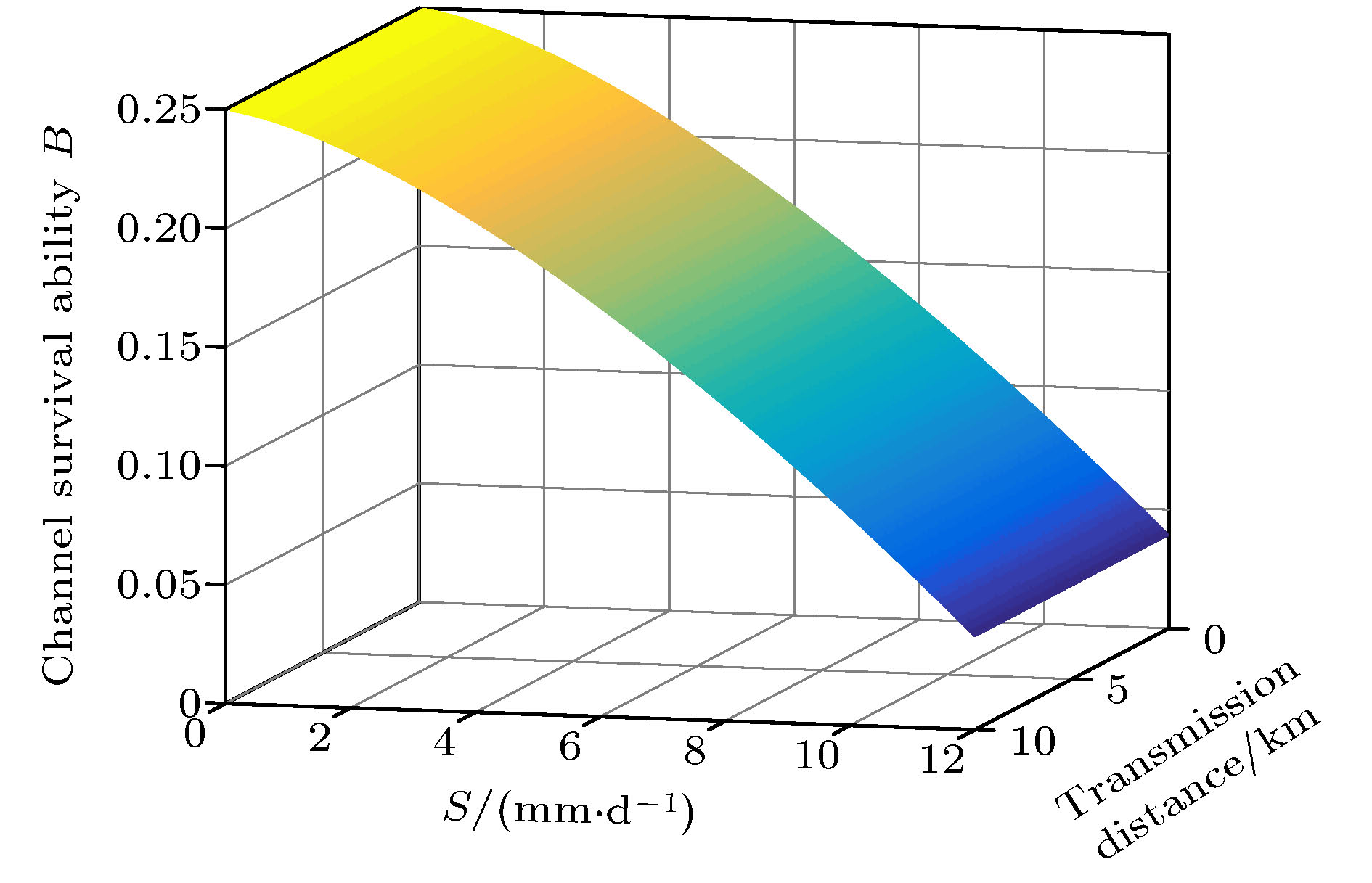
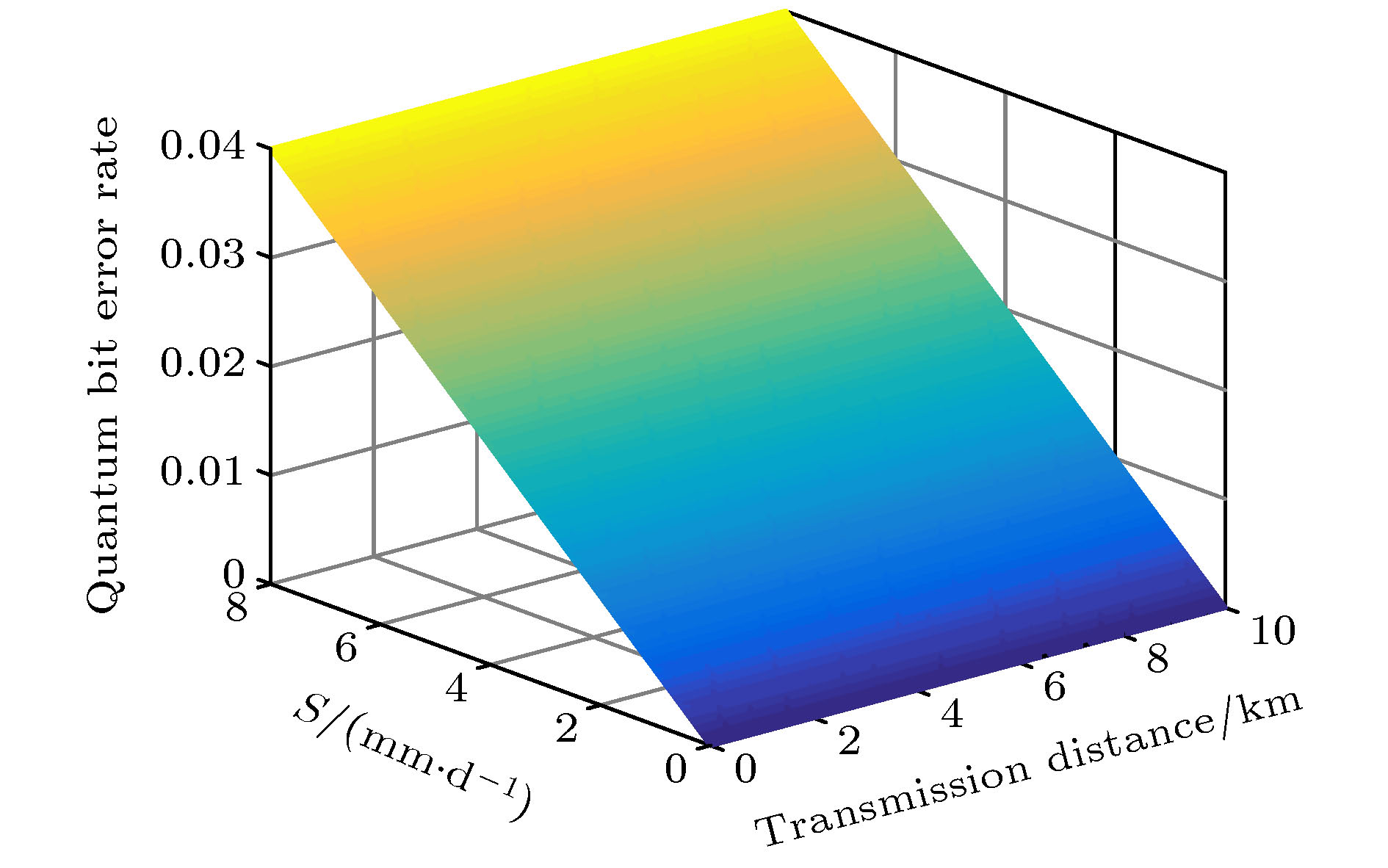
${S_{\rm{1}}}$ ), medium snow (${S_{\rm{2}}}$ ), heavy snow (${S_{\rm{3}}}$ ) and blizzard (${S_{\rm{1}}}$ ). When the snow is falling in the air, it has an energy absorption effect on the light quantum signal, which is called the extinction effect. The different intensities of snow extinction have different effects on free space optical quantum signal. In this paper, first, a mathematical model for the extinction effects on optical quantum signal at different levels of snowfall is presented; then the quantitative relationship between snowfall and free space extinction attenuation, as well as the relationship between snowfall and channel limit survival function is established, channel capacities under different snowfall intensities, and quantum bit error rate are also given. Finally, the mathematical models of snowfall intensity, transmission distance and link attenuation, amplitude damping channel capacity, channel survival function and channel error rate are established. Simulation results show that when the snowfall intensity is 2.1 mm/d (${S_{\rm{1}}}$ ) and the transmission distance is 2.2 km, the communication link attenuation is 0.0362, the channel capacity is 0.7745, the channel survival function is 0.2329, and the channel error rate is 0.0105. When the snowfall intensity is 3.8 mm/d (${S_{\rm{2}}}$ ) and the transmission distance is 3.5 km, the communication link attenuation is 0.1326, the channel capacity is 0.4922, the channel survival function is 0.2099, and the channel error rate is 0.019. Thus, different snowfall intensity has different influence on the performance of free space quantum communication. Therefore, in practical applications, the communication parameters should be adjusted adaptively based on the snowfall intensity to improve the reliability of free space quantum communication.[1] Diamanti E, Lo H, Qi B, Yuan Z L 2016 NPJ Quantum Inf. 2 16025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Smania M, Elhassan A, Tavakoli A, Bourennane M 2016 NPJ Quantum Inf. 2 16010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bäuml S, Azuma S, Kato G, Elkouss D 2020 Commun. Phys. 3 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bhaskar M K, Riedinger R, Machielse B, Levonian D S, Nguyen C T, Knall E N, Park H, Englund D, Lončar M, Sukachev D D, Lukin M D 2020 Nature 580 7801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jin X M, Ren J G, Yang B, Yi Z H, Zhou F, Xu X F, Peng C Z, Wang S K, Yang D, Pan J W, Hu Y F, Jiang S 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liao S K, Cai W Q, Handsteiner J, et al. 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 030501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liao S K, Yong H L, Liu C, et al. 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yin J, Li Y, Liao S, et al. 2020 Nature 582 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 聂敏, 任家明, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2016 65 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Ren J M, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 聂敏, 唐守荣, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2017 66 070302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Tang S R, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 070302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 聂敏, 尚鹏钢, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2014 63 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Shang P G, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 聂敏, 王允, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2016 65 020303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Wang Y, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 聂敏, 卫容宇, 杨光, 张美玲, 孙爱晶, 裴昌幸 2019 68 110301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Wei R Y, Yang G, Zhang M L, Sun A J, Pei C X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 110301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘西川, 高太长, 刘磊, 张伟, 杨树臣, 李涛 2010 应用气象学报 21 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X C, Gao T C, Liu L, Zhang W, Yang S C, Li T 2010 J. Appl. Meteorl. Sci. 21 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘玉莲, 任国玉, 于宏敏 2012 地理科学 32 1176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y L, Ren G Y, Yu H M 2012 Scientia Geographica Sin. 32 1176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wolf D, David A 2001 Radio Sci. 36 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gunn K L S, Marshall J S 1958 J. Meteorl. 10 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孙学金, 王晓蕾, 李浩, 张伟星, 严卫 2009 大气探测学 (第1版) (北京: 气象出版社) 第68页
Sun X J, Wang X L, Li H, Li H, Zhang W X, Yan W 2009 Atmospheric Observation (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Meteorological Press) p68 (in Chinese)
[19] 高太长, 刘西川, 张云涛, 杨树臣, 熊超超 2011 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版) 12 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao T C, Liu X C, Zhang Y T, Yang S C, Xiong C C 2011 J. PLA Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 12 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 宋飞虎, 许传龙, 王式民 2012 中国电机工程学报 32 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song F H, Xu C L, Wang S M 2012 Proc. Chin. Soc. Elect. Eng. 32 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 尹浩, 韩阳 2013 量子通信原理与技术 (第1版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第76−83页
Yin H, Han Y 2013 Quantum Communication Theory and Technology (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Electronics Industry Publishing) pp76−83 (in Chinese)
[22] 尹浩, 马怀新 2006 军事量子通信概论 (北京: 军事科学出版社) 第227页
Yin H, Ma H X 2006 Introduction to Military Quantum Communication (Beijing: Military Science Press) p227 (in Chinese)
[23] 张琳, 聂敏, 刘晓慧 2013 62 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L, Nie M, Liu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘堂昆, 王继锁, 柳晓军, 詹明生 2000 光学学报 20 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T K, Wang J S, Liu X J, Zhan M S 2000 Acta Opt. Sin. 20 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 马晶, 张光宇, 谭立英 2006 光学技术 32 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma J, Zhang G Y, Tan L Y 2006 Opt. Techn. 32 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 张光宇, 于思源, 马晶, 谭立英 2007 光电工程 34 126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G Y, Yu S Y, Ma J, Tan L Y 2007 Opto-Electronic Engineering 34 126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 降雪强度划分标准
Table 1. Criteria for classification of snowfall intensity.
降雪量/mm 降雪强度等级 < 2.5 小雪(${S_{\rm{1}}}$) 2.5—5 中雪(${S_{\rm{2}}}$) 5—10 大雪(${S_{\rm{3}}}$) > 10 暴雪(${S_{\rm{4}}}$) 表 2 信道误码率各参数含义和取值
Table 2. Meaning and values of the parameters of the channel bit error rate.
参数 含义 取值 $\tau $ 量子探测器时间窗口 1 $n$ 探测器数目 1 $\mu $ 平均光子数 1 ${P_{\rm a}}$ 单光子捕获率 0.5 ${T_{\rm a}}$ 系统装置传输率 1 ${\eta _{\rm d}}$ 单光子探测器效率 0.65 ${F_{\rm m}}$ 测量因子 1 -
[1] Diamanti E, Lo H, Qi B, Yuan Z L 2016 NPJ Quantum Inf. 2 16025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Smania M, Elhassan A, Tavakoli A, Bourennane M 2016 NPJ Quantum Inf. 2 16010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bäuml S, Azuma S, Kato G, Elkouss D 2020 Commun. Phys. 3 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bhaskar M K, Riedinger R, Machielse B, Levonian D S, Nguyen C T, Knall E N, Park H, Englund D, Lončar M, Sukachev D D, Lukin M D 2020 Nature 580 7801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jin X M, Ren J G, Yang B, Yi Z H, Zhou F, Xu X F, Peng C Z, Wang S K, Yang D, Pan J W, Hu Y F, Jiang S 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liao S K, Cai W Q, Handsteiner J, et al. 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 030501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liao S K, Yong H L, Liu C, et al. 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yin J, Li Y, Liao S, et al. 2020 Nature 582 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 聂敏, 任家明, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2016 65 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Ren J M, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 聂敏, 唐守荣, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2017 66 070302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Tang S R, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 070302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 聂敏, 尚鹏钢, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2014 63 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Shang P G, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 240303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 聂敏, 王允, 杨光, 张美玲, 裴昌幸 2016 65 020303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Wang Y, Yang G, Zhang M L, Pei C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 聂敏, 卫容宇, 杨光, 张美玲, 孙爱晶, 裴昌幸 2019 68 110301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie M, Wei R Y, Yang G, Zhang M L, Sun A J, Pei C X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 110301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘西川, 高太长, 刘磊, 张伟, 杨树臣, 李涛 2010 应用气象学报 21 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X C, Gao T C, Liu L, Zhang W, Yang S C, Li T 2010 J. Appl. Meteorl. Sci. 21 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘玉莲, 任国玉, 于宏敏 2012 地理科学 32 1176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y L, Ren G Y, Yu H M 2012 Scientia Geographica Sin. 32 1176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wolf D, David A 2001 Radio Sci. 36 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gunn K L S, Marshall J S 1958 J. Meteorl. 10 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孙学金, 王晓蕾, 李浩, 张伟星, 严卫 2009 大气探测学 (第1版) (北京: 气象出版社) 第68页
Sun X J, Wang X L, Li H, Li H, Zhang W X, Yan W 2009 Atmospheric Observation (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Meteorological Press) p68 (in Chinese)
[19] 高太长, 刘西川, 张云涛, 杨树臣, 熊超超 2011 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版) 12 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao T C, Liu X C, Zhang Y T, Yang S C, Xiong C C 2011 J. PLA Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 12 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 宋飞虎, 许传龙, 王式民 2012 中国电机工程学报 32 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song F H, Xu C L, Wang S M 2012 Proc. Chin. Soc. Elect. Eng. 32 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 尹浩, 韩阳 2013 量子通信原理与技术 (第1版) (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第76−83页
Yin H, Han Y 2013 Quantum Communication Theory and Technology (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Electronics Industry Publishing) pp76−83 (in Chinese)
[22] 尹浩, 马怀新 2006 军事量子通信概论 (北京: 军事科学出版社) 第227页
Yin H, Ma H X 2006 Introduction to Military Quantum Communication (Beijing: Military Science Press) p227 (in Chinese)
[23] 张琳, 聂敏, 刘晓慧 2013 62 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L, Nie M, Liu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 150301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘堂昆, 王继锁, 柳晓军, 詹明生 2000 光学学报 20 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T K, Wang J S, Liu X J, Zhan M S 2000 Acta Opt. Sin. 20 1449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 马晶, 张光宇, 谭立英 2006 光学技术 32 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma J, Zhang G Y, Tan L Y 2006 Opt. Techn. 32 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 张光宇, 于思源, 马晶, 谭立英 2007 光电工程 34 126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G Y, Yu S Y, Ma J, Tan L Y 2007 Opto-Electronic Engineering 34 126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7873
- PDF Downloads: 92
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: