-
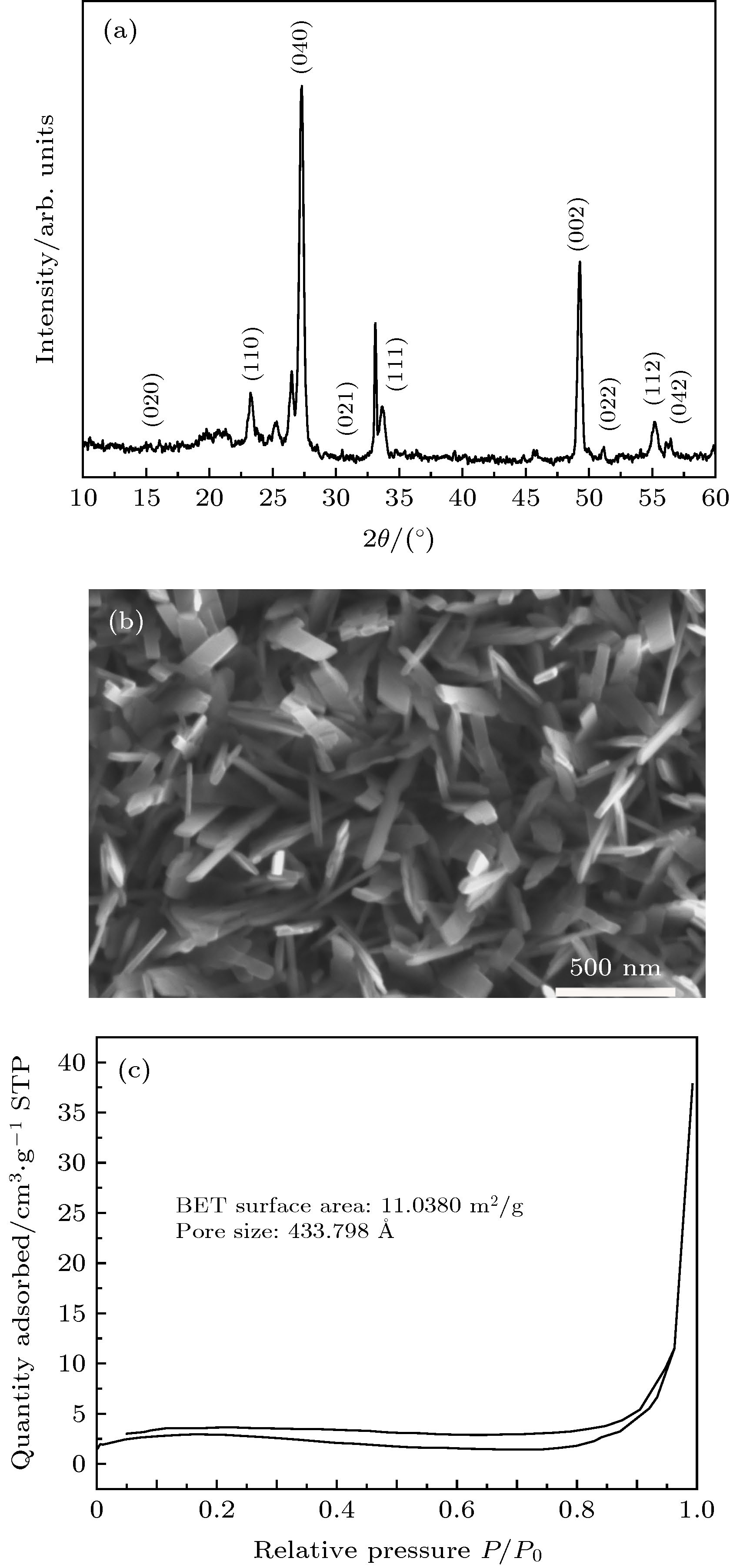
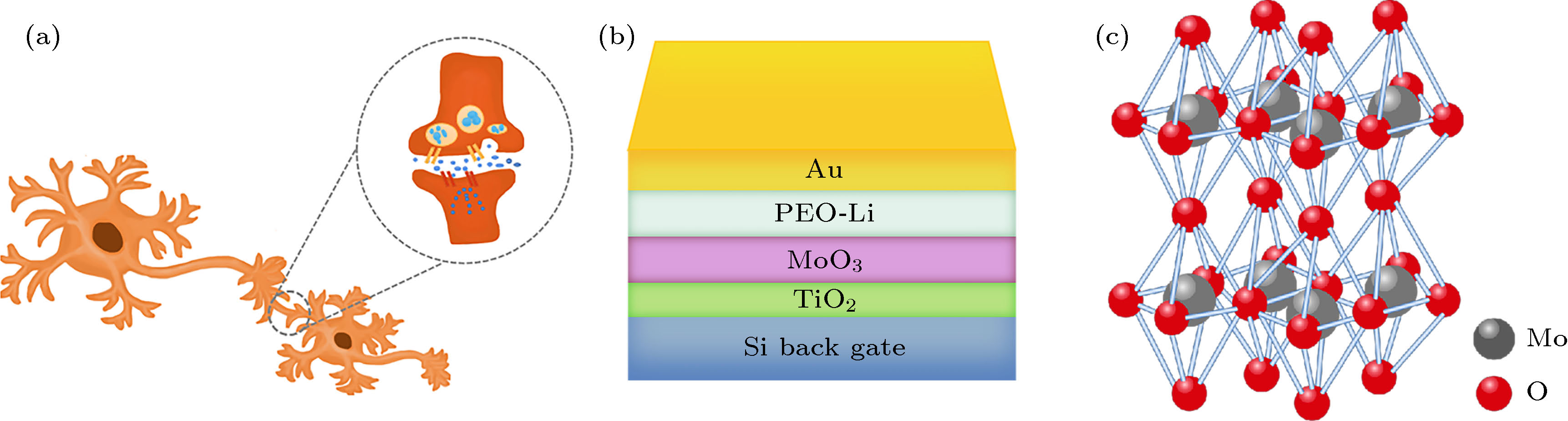
Recently, neuromorphic systems capable of parallel information processing have attracted increasing attention. A neuromorphic system is desired to emulate a human brain, which consists of hundreds of billions of neurons connected with even more synapses. Synapses are important connection parts between neurons to transmit information through release and reception of neurotransmitters. A neuromorphic system could replicate brain learning, cognition and computation of a human brain to process huge data with 1016 floating point numbers per second. The high computing efficiency has attracted many researchers to study artificial synapses for application in future artificial intelligence. The synaptic weight could be adjusted by the received information. This provides a basis for the learning and computing capability of artificial synapses. So far, a number of semiconductor materials have been used in artificial synaptic devices, like some organic materials, e.g. Poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl)(P3HT), [1]Benzothieno[3,2-b][1]benzothiophene, 2,7-dioctyl-(C8-BTBT) etc, some inorganic oxides such as zinc oxide, indium zinc oxide(IZO), indium gallium zinc oxide(IGZO), transition metal oxides, etc, and two-dimensional materials, e.g. graphene, black phosphorus, and organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials. Among them, transition metal oxides are attractive due to their unique layered structure and inherent properties, which are important in photohydrolysis, lithium ion batteries, and field-effect transistors. MoO3, as a typical transition-metal oxide, has been used in artificial synaptic devices, with different preparation methods, such as mechanical exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and chemical vapor transportation (CVT), pulse-laser deposition (PLD). Here, we report the preparation of a semiconductor layer of MoO3 nanosheets by hydrothermal method, and the use of a TiO2 nanoparticle seed layer to improve the adhesion of MoO3 nanosheets. This is a cost-effective and controllable process. The high surface-to-volume ratio of the material provides large contact area at the interface to allow easy ion diffusion. The device emulates important synaptic functions, such as excitatory post-synaptic current (EPSC), paired-pulse facilitation (PPF), spike-duration dependent plasticity (SDDP), spike-voltage dependent plasticity (SVDP) and spike-rate dependent plasticity (SRDP). This work could be an important addition to the neuromorphic research field. -
Keywords:
- artificial synapse /
- hydrothermal synthesis /
- molybdenum trioxide nanosheets /
- synaptic plasticity
[1] 王洋昊, 刘昌, 黄如, 杨玉超 2020 科学通报 65 46
Wang Y H, Liu C, Huang R, Yang Y C 2020 Chin. Sci. Bull. 65 46
[2] 姜珊珊, 聂莎, 何勇礼, 刘锐, 万青 2019 现代电子技术 42 181
Jiang S S, Nie S, He Y L, Liu R, Wan Q 2019 Modern Electronic Technology 42 181
[3] Yao Y, Huang X, Peng S, Zhang D, Shi J, Yu G, Liu Q, Jin Z 2019 Adv. Electron. Mater. 5 1800887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kim S G, Kim S H, Park J, Kim G S, Park J H, Saraswat K C, Kim J, Yu H Y 2019 ACS Nano 13 10294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shi C, Wang J, Sushko M L, Qiu W, Yan X, Liu X Y 2019 Adv. Funct. Mater. 29 1904777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kandel E R 2001 Science 294 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang S N, Tang Y G, Zucker R S 1999 J. Neurophysiol. 81 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shouval H Z, Bear M F, Cooper L N 2002 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99 10831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fang L, Dai S, Zhao Y, Liu D, Huang J 2020 Adv. Electron. Mater. 6 1901217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fuller E J, Keene S T, Melianas A, Wang Z, Agarwal S, Li Y, Tuchman Y, Jame C D, Marinella M J, Yang J J, Salleo A 2019 Science 364 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lee Y, Lee T W 2019 Accounts Chem. Res. 52 964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan C, Chen G, Fu Y, Wang M, Matsuhisa N, Pan S, Pan L, Yang H, Wan Q, Zhu L, Chen X 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1801291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Han H, Xu Z, Guo K, Ni Y, Ma M, Yu H, Wei H, Gong J, Zhang S, Xu W 2020 Adv. Intell. Syst. 2 1900176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Balakrishna Pillai P, De Souza M M 2017 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 1609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wan C J, Liu Y H, Zhu L Q, Feng P, Shi Y, Wan Q 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 9762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Y, Wen J, Guo L, Wan X, Du P, Feng P, Wan Q 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 30281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun J, Oh S, Choi Y, Seo S, Oh M J, Lee M, Lee W B, Yoo P J, Cho J H, Park J H 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1804397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yan X, Zhao J, Liu S, Zhou Z, Liu, Q, Chen J, Liu X Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Murase S, Yang Y 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 2459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y, Brenner K, Murali R 2012 Carbon 50 1727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schedin F, Lidorikis E, Lombardo A, Kravets V G, Geim A K, Grigorenko A N, Novoselov K S, Ferrari A C 2010 ACS Nano 4 5617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li X, Zhu H, Wang K, Cao A, Wei J, Li C, Jia Y, Li Z, Li X, Wu D 2010 Adv. Mater. 22 2743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian H, Guo Q, Xie Y, Zhao H, Li C, Cha J J, Xia F, Wang H 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 4991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kim S I, Lee Y, Park M H, Go G T, Kim Y H, Xu W, Lee H D, Kim H, Seo D G, Lee W, Lee T W 2019 Adv. Electron. Mater. 5 1900008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li M., Cui Z, Li E 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 14449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ji W, Shen R, Yang R, Yu G, Guo X, Peng L, Ding W 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 699
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu F, Tian J, Su Y, Guan Y, Jin Y, Wang Z, He T, Bao L, Chen S 2014 J. Power Sources 269 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu E, Fu Y, Wang Y, et al. 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li H, Wu J, Yin Z, Zhang H 2014 Accounts Chem. Res. 47 1067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang C S, Shang D S, Chai Y S, Yan L Q, Shen B G, Sun Y 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 4190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang C S, Shang D S, Liu N, Fuller E J, Agrawal S, Talin A A, Li Y Q, Shen B G, Sun Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1804170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang Z, Yang R, Huang H M, He H K, Shaibo J, Guo X 2020 Adv. Electron. Mater. 6 1901290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 于焕芹 2018 硕士学位论文 (山东: 济南大学)
Yu H Q 2018 M. S. Thesis (Shandong: Jinan University) (in Chinese)
[34] Galatsis K, Li Y X, Wlodarski W, Comini E, Faglia G, Sberveglieri G 2001 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 77 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu Y, Yang S, Lu Y, Chen W, Zakharova G S 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 359 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 徐英明, 王敏, 程晓丽, 霍丽华, 张现发 2016 中国专利 CN 105439202A
Xu Y M, Wang M, Cheng X L, Huo L H, Zhang X F 2016 CN Patent CN 105439202A (in Chinese)
[37] Zhang C, Chen Y, Yi M. Zhu Y, Li T, Liu L, Wang L, Xie L, Huang W 2018 Scientia Sinica Informationis 48 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zucker R S, Regehr W G 2002 Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jiang J, Hu W, Xie D, Yang J, He J, Gao Y, Wan Q 2019 Nanoscale 11 1360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Jo S H, Chang T, Ebong I, Bhadviya B B, Mazumder P, Lu W 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Yang C S, Shang D S, Liu N, Shi G, Shen X, Yu R C, L Y Q, Sun Y 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1700906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Bi G Q, Poo M M 2001 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Yu H Y, Gong J D, Wei H H, Huang W, Xu W T 2019 Mater. Chem. Front. 3 941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Yu S, Wu Y, Jeyasingh R, Kuzum D, Wong P H S 2011 IEEE Trans Electron Devices 58 2729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Gao B, Kang J, Zhou Z, Chen Z, Huang P, Liu L F, Liu X Y 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 04EA06
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Hsieh C C, Roy A, Chang Y F, Shahrjerdi D, Banerjee S K 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 223501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Zhu Y, Shin B, Liu G, Shan F 2019 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 40 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Zhu L Q, Wan C J, Guo L Q, Shi Y, Wan Q 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 1
-
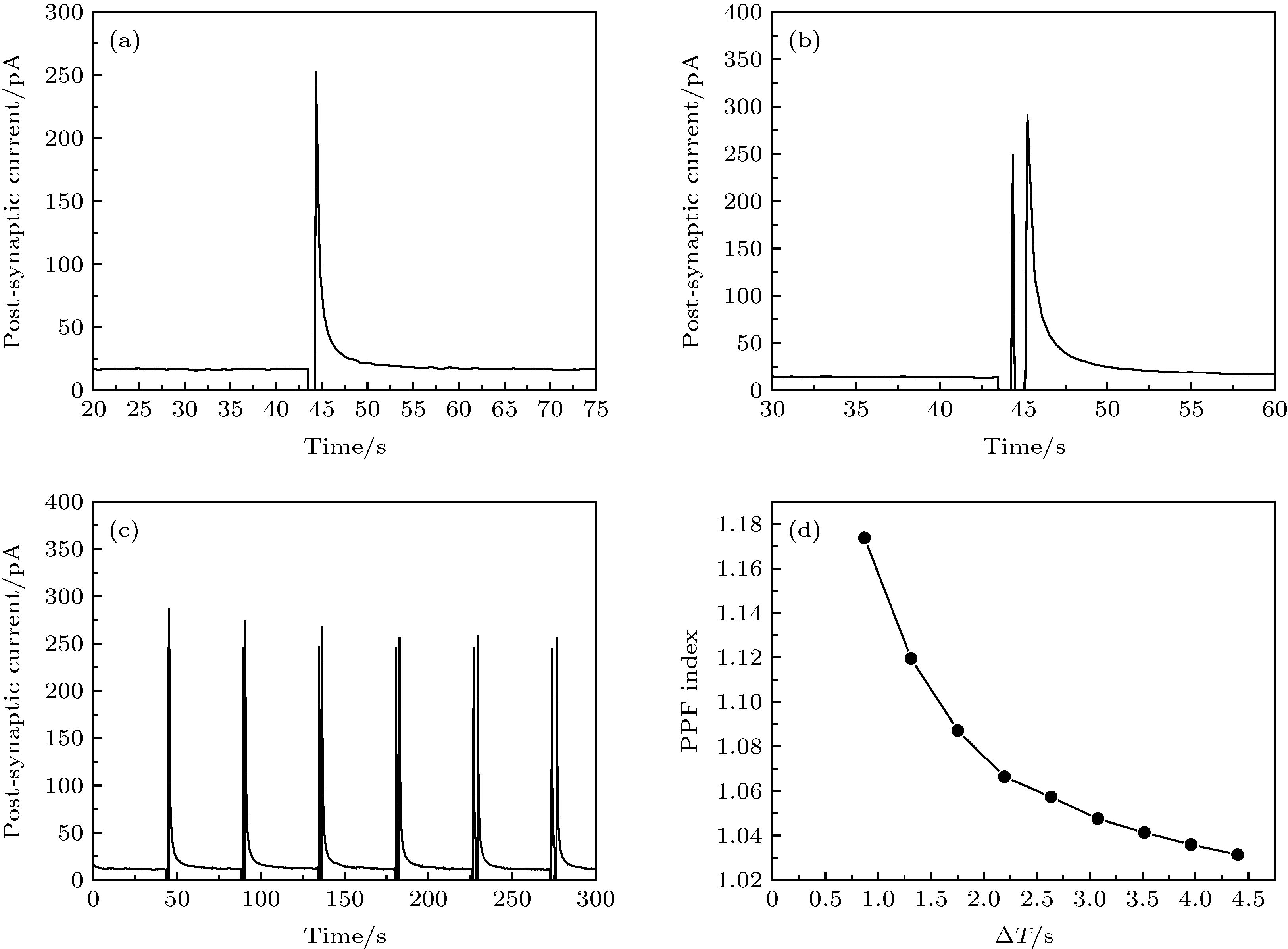
图 3 (a) 单个幅值为1 V的刺激在MoO3人工神经突触上引起的EPSC; (b)一对幅值为1 V的刺激在MoO3人工神经突触上引起的PPF; (c)和(d) 多对时间间隔不同, 幅值为1 V的脉冲引起的PPF及PPF Index
Figure 3. (a) EPSC triggered by a single 1 V spike at a MoO3 artificial synapse; (b) PPF triggered by a pair of 1 V spikes at a MoO3 artificial synapse; (c) and (d) PPF and PPF index triggered by spikes with different time intervals and same amplitudes of 1 V.
图 4 (a) 施加幅值为1 V刺激个数分别为1, 2, 3, 5, 8在MoO3突触器件上引起的的SRDP; (b) 相同幅值不同刺激持续时间造成的SDDP; (c) 幅值分别为0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 V的刺激在突触器件上引起的SVDP; (d)为施加幅值为0.2 V时所获得的兴奋性突触后电流及完成一次信号传递所消耗的能量
Figure 4. (a) SRDP on MoO3 synapses triggered by the number of spikes of 1 V applied at 1, 2, 3, 5, and 8; (b) SDDP triggered by different spike duration time with the same amplitude; (c) SVDP triggered by spikes with amplitudes of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 V, and 2.0 V on synaptic devices; (d) the excitatory postsynaptic current when the applied spike is 0.2 V and the energy consumed to complete a signal transmission.
表 1 不同金属氧化物人工突触器件能量消耗
Table 1. Energy consumption of different metal oxide artificial synaptic devices.
-
[1] 王洋昊, 刘昌, 黄如, 杨玉超 2020 科学通报 65 46
Wang Y H, Liu C, Huang R, Yang Y C 2020 Chin. Sci. Bull. 65 46
[2] 姜珊珊, 聂莎, 何勇礼, 刘锐, 万青 2019 现代电子技术 42 181
Jiang S S, Nie S, He Y L, Liu R, Wan Q 2019 Modern Electronic Technology 42 181
[3] Yao Y, Huang X, Peng S, Zhang D, Shi J, Yu G, Liu Q, Jin Z 2019 Adv. Electron. Mater. 5 1800887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kim S G, Kim S H, Park J, Kim G S, Park J H, Saraswat K C, Kim J, Yu H Y 2019 ACS Nano 13 10294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shi C, Wang J, Sushko M L, Qiu W, Yan X, Liu X Y 2019 Adv. Funct. Mater. 29 1904777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kandel E R 2001 Science 294 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang S N, Tang Y G, Zucker R S 1999 J. Neurophysiol. 81 781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shouval H Z, Bear M F, Cooper L N 2002 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99 10831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fang L, Dai S, Zhao Y, Liu D, Huang J 2020 Adv. Electron. Mater. 6 1901217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fuller E J, Keene S T, Melianas A, Wang Z, Agarwal S, Li Y, Tuchman Y, Jame C D, Marinella M J, Yang J J, Salleo A 2019 Science 364 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lee Y, Lee T W 2019 Accounts Chem. Res. 52 964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan C, Chen G, Fu Y, Wang M, Matsuhisa N, Pan S, Pan L, Yang H, Wan Q, Zhu L, Chen X 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1801291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Han H, Xu Z, Guo K, Ni Y, Ma M, Yu H, Wei H, Gong J, Zhang S, Xu W 2020 Adv. Intell. Syst. 2 1900176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Balakrishna Pillai P, De Souza M M 2017 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 1609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wan C J, Liu Y H, Zhu L Q, Feng P, Shi Y, Wan Q 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 9762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Y, Wen J, Guo L, Wan X, Du P, Feng P, Wan Q 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 30281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun J, Oh S, Choi Y, Seo S, Oh M J, Lee M, Lee W B, Yoo P J, Cho J H, Park J H 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1804397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yan X, Zhao J, Liu S, Zhou Z, Liu, Q, Chen J, Liu X Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1705320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Murase S, Yang Y 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 2459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y, Brenner K, Murali R 2012 Carbon 50 1727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schedin F, Lidorikis E, Lombardo A, Kravets V G, Geim A K, Grigorenko A N, Novoselov K S, Ferrari A C 2010 ACS Nano 4 5617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li X, Zhu H, Wang K, Cao A, Wei J, Li C, Jia Y, Li Z, Li X, Wu D 2010 Adv. Mater. 22 2743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian H, Guo Q, Xie Y, Zhao H, Li C, Cha J J, Xia F, Wang H 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 4991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kim S I, Lee Y, Park M H, Go G T, Kim Y H, Xu W, Lee H D, Kim H, Seo D G, Lee W, Lee T W 2019 Adv. Electron. Mater. 5 1900008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li M., Cui Z, Li E 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 14449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ji W, Shen R, Yang R, Yu G, Guo X, Peng L, Ding W 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 699
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wu F, Tian J, Su Y, Guan Y, Jin Y, Wang Z, He T, Bao L, Chen S 2014 J. Power Sources 269 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu E, Fu Y, Wang Y, et al. 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li H, Wu J, Yin Z, Zhang H 2014 Accounts Chem. Res. 47 1067
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang C S, Shang D S, Chai Y S, Yan L Q, Shen B G, Sun Y 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 4190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yang C S, Shang D S, Liu N, Fuller E J, Agrawal S, Talin A A, Li Y Q, Shen B G, Sun Y 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1804170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang Z, Yang R, Huang H M, He H K, Shaibo J, Guo X 2020 Adv. Electron. Mater. 6 1901290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 于焕芹 2018 硕士学位论文 (山东: 济南大学)
Yu H Q 2018 M. S. Thesis (Shandong: Jinan University) (in Chinese)
[34] Galatsis K, Li Y X, Wlodarski W, Comini E, Faglia G, Sberveglieri G 2001 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 77 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu Y, Yang S, Lu Y, Chen W, Zakharova G S 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 359 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 徐英明, 王敏, 程晓丽, 霍丽华, 张现发 2016 中国专利 CN 105439202A
Xu Y M, Wang M, Cheng X L, Huo L H, Zhang X F 2016 CN Patent CN 105439202A (in Chinese)
[37] Zhang C, Chen Y, Yi M. Zhu Y, Li T, Liu L, Wang L, Xie L, Huang W 2018 Scientia Sinica Informationis 48 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zucker R S, Regehr W G 2002 Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jiang J, Hu W, Xie D, Yang J, He J, Gao Y, Wan Q 2019 Nanoscale 11 1360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Jo S H, Chang T, Ebong I, Bhadviya B B, Mazumder P, Lu W 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Yang C S, Shang D S, Liu N, Shi G, Shen X, Yu R C, L Y Q, Sun Y 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1700906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Bi G Q, Poo M M 2001 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Yu H Y, Gong J D, Wei H H, Huang W, Xu W T 2019 Mater. Chem. Front. 3 941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Yu S, Wu Y, Jeyasingh R, Kuzum D, Wong P H S 2011 IEEE Trans Electron Devices 58 2729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Gao B, Kang J, Zhou Z, Chen Z, Huang P, Liu L F, Liu X Y 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 04EA06
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Hsieh C C, Roy A, Chang Y F, Shahrjerdi D, Banerjee S K 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 223501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Zhu Y, Shin B, Liu G, Shan F 2019 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 40 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Zhu L Q, Wan C J, Guo L Q, Shi Y, Wan Q 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 1
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10337
- PDF Downloads: 315
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: