-
In this paper, we propose a hybrid subwavelength broadband sound absorber based on micro perforated plate and multiple coiled channels. And the mechanism of low frequency broadband sound absorption of the hybrid sound absorber is analyzed in detail. Based on this, the theoretical analysis model and the finite element numerical analysis model are established, and the mutual verification of theoretical and numerical solutions is completed. The structure can theoretically achieve the low-frequency and high-efficiency sound absorption with an average absorption coefficient of 0.8 in a frequency band of 200–500 Hz when the overall thickness of the sound absorbing structure is 60 mm. At the same time when the overall thickness is 90 mm, quasi-perfect sound absorption with peaks up to 0.95 in a frequency range of 180–350 Hz is realized theoretically. The composite sound absorption structure has a certain application prospect in engineering low frequency noise in future.
-
Keywords:
- micro-perforated plate /
- coiled channels /
- hybrid sound absorber /
- low frequency sound absorption
[1] 陈文炯, 刘书田 2012 噪声与振动控制 032 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W J, Liu S T 2012 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 032 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Maa D Y 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huang S B, Li S M, Wang X, Mao D X 2017 Appl. Acoust. 126 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ma G C, Sheng P 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Long H Y, Cheng Y, Tao J C, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 023502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma G C, Yang M, Xiao S W, Yang Z Y, Sheng P 2014 Nat. Mater. 13 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu X X, Fu C X, Li X, Meng Y, Gao Y B, Tian J X, Wang. L, Huang Y Z, Yang Z Y Wen W J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 043501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cheng Y, Zhou C, Yuan B G, Wu D J, Wei Q, Liu X J 2015 Nat. Mater. 14 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Y, Zhao H G, Yang H B, Zhong J, Wen J H 2017 Europhys. Lett. 120 54001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Y, Zhao H G, Yang H B, Zhong J, Zhao D, Lu Z L, Wen J H 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 123 185109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang M, Chen S Y, Fuab C X, Sheng P 2017 Mater. Horiz. 4 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jiang X, Liang B, Li R Q, Zou X Y, Yin L L, Cheng J C 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 243505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yang M, Sheng P 2017 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 47 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhu Y F, Fan X D, Liang B, Cheng J C, Jing Y 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 021034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang S B, Zhou Z L, Li D T, Liu T, Wang X, Zhu J, Li Y 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhu Y F, Donda K, Fan S W, Cao L Y, Assouar B 2019 Appl. Phys. Express 12 114002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen W Y, Wu F, Wen J H, Ju Z G, Yao L Y, Zhao H G, Wang Y, Xiao Y 2020 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 59 045503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu F, Xiao Y, Yu D L, Zhao H G, Wang Y, Wen J H 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 151901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang H, Liang B, Zou X Y, Yang J, Cheng J C 2017 Appl. Phys. Express 10 027201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu L, Chang H T, Zhang C, Hu X H 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 083503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 复合声学超材料的结构及理论模型 (a) 微穿孔板; (b) 折曲通道; (c)吸声结构三维模型; (d) 吸声结构二维理论模型
Figure 1. Structure and theoretical model of composite acoustic metamaterial: (a) The top micro-perforated panel (thickness
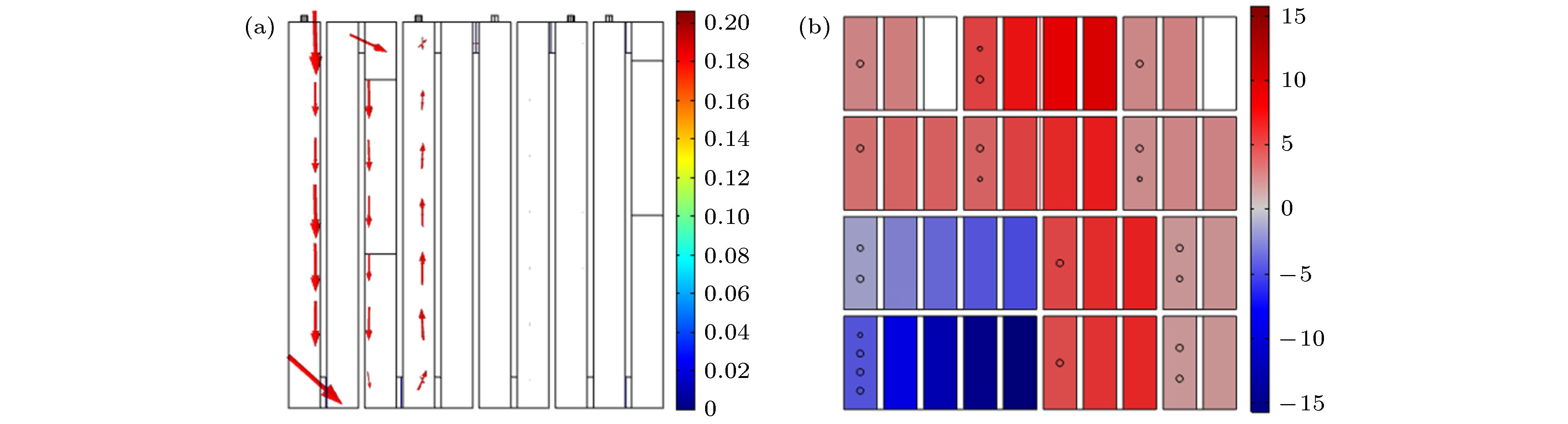
$t$ , diameter$d$ , perforation rate$p$ ); (b) multiple coiled FP channels; (c) schematic of the hybrid metamaterial absorber composed of a microperforated panel (MPP) as a top face sheet and coiled-up Fabry–Perot (FP) channels with folding number n; (d) an approximate analytical two dimensional (2 D) model of one unit cell of a space-coiled metamaterial. All the widths of the channels in the YZ plane are$L$ . The height of the channel along the Z axis is$H$ .图 2 230 Hz声波传入时吸声器内声速与声压 (a)声速分布(m/s); (b)声压分布(Pa)
Figure 2. Sound velocity and sound pressure in a sound absorber when a 230 Hz sound wave is introduced: (a) Sound velocity distribution (m/s); (b) sound pressure distribution (Pa). The absorbers are constructed using the coiled-up channel with geometric parameters:
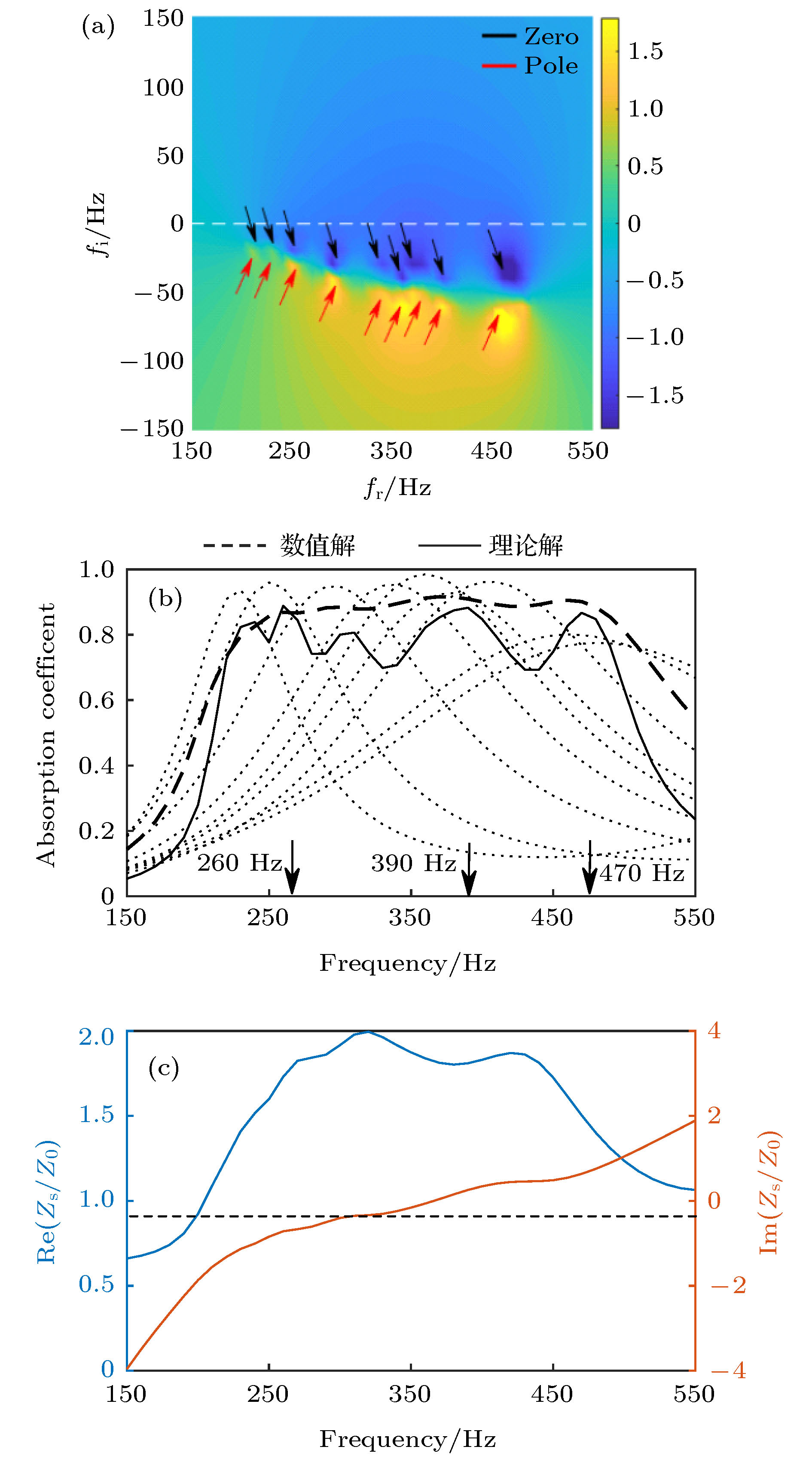
$H = {\rm{59\;mm}}$ ,${L_1} = {L_2} = {L_3} = {L_4} = {L_5} = 4.8{\rm{5\;mm}}$ and$W = 13.6\;{\rm{ mm}}$ and$d = {t_0} = {t_1} = 1\;{\rm{ mm}}$ .图 3 复合吸声结构的吸声特性 (a) 反射系数零、极点分布; (b)吸声性能曲线; (c)声阻抗的实部与虚部
Figure 3. Sound absorption characteristics of composite sound absorption structure: (a) Zero and pole distributions of reflection coefficients on complex frequency plane; (b) sound absorption performance curve. The dotted line is the theoretical solution and the solid line is the numerical solution, the black dotted line is the theoretical solution of each unit (Gradually increase the equivalent sound absorption length from left to right); (c) real and imaginary parts of relative impedance.
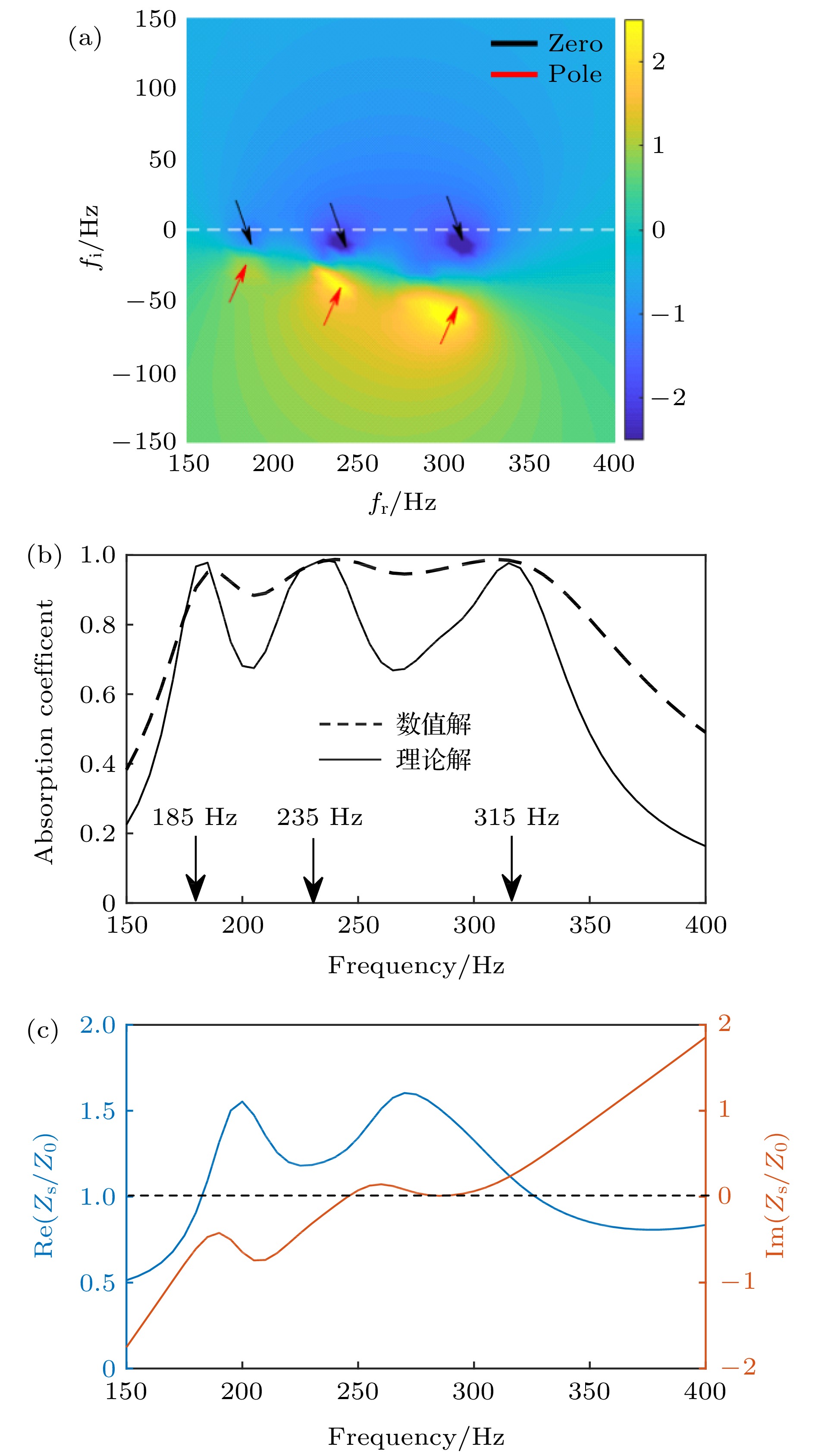
图 4 复合吸声结构的准完美吸声特性 (a) 反射系数零、极点分布; (b)吸声性能曲线; (c)声阻抗的实部与虚部
Figure 4. Quasi-perfect sound absorption characteristics of composite sound absorption structure: (a) Zero and pole distributions of reflection coefficients on complex frequency plane; (b) sound absorption performance curve, The dotted line is the theoretical solution and the solid line is the numerical solution; (c) real and imaginary parts of relative impedance.
表 1 准完美吸声结构各吸声单元结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of each sound absorption unit of quasi-perfect sound absorption structure.
序号 ${t / {{\rm{mm}}}}$ ${d / {{\rm{mm}}}}$ ${D / {{\rm{mm}}}}$ $p$ 1 1 1 360 0.048 2 1 1 360 0.048 3 1 1 360 0.048 4 1 1 360 0.048 5 1 1 270 0.035 6 1 1 270 0.035 7 1 1 270 0.060 8 1 1 240 0.030 9 1 1 180 0.023 10 1 1 180 0.038 11 1 1 180 0.035 12 1 1 180 0.040 -
[1] 陈文炯, 刘书田 2012 噪声与振动控制 032 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W J, Liu S T 2012 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 032 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Maa D Y 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huang S B, Li S M, Wang X, Mao D X 2017 Appl. Acoust. 126 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ma G C, Sheng P 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Long H Y, Cheng Y, Tao J C, Liu X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 023502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma G C, Yang M, Xiao S W, Yang Z Y, Sheng P 2014 Nat. Mater. 13 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu X X, Fu C X, Li X, Meng Y, Gao Y B, Tian J X, Wang. L, Huang Y Z, Yang Z Y Wen W J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 043501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cheng Y, Zhou C, Yuan B G, Wu D J, Wei Q, Liu X J 2015 Nat. Mater. 14 1013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Y, Zhao H G, Yang H B, Zhong J, Wen J H 2017 Europhys. Lett. 120 54001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Y, Zhao H G, Yang H B, Zhong J, Zhao D, Lu Z L, Wen J H 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 123 185109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang M, Chen S Y, Fuab C X, Sheng P 2017 Mater. Horiz. 4 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jiang X, Liang B, Li R Q, Zou X Y, Yin L L, Cheng J C 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 243505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yang M, Sheng P 2017 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 47 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhu Y F, Fan X D, Liang B, Cheng J C, Jing Y 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 021034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang S B, Zhou Z L, Li D T, Liu T, Wang X, Zhu J, Li Y 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhu Y F, Donda K, Fan S W, Cao L Y, Assouar B 2019 Appl. Phys. Express 12 114002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen W Y, Wu F, Wen J H, Ju Z G, Yao L Y, Zhao H G, Wang Y, Xiao Y 2020 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 59 045503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu F, Xiao Y, Yu D L, Zhao H G, Wang Y, Wen J H 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 151901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang H, Liang B, Zou X Y, Yang J, Cheng J C 2017 Appl. Phys. Express 10 027201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu L, Chang H T, Zhang C, Hu X H 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 083503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10728
- PDF Downloads: 338
- Cited By: 0




















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: