-
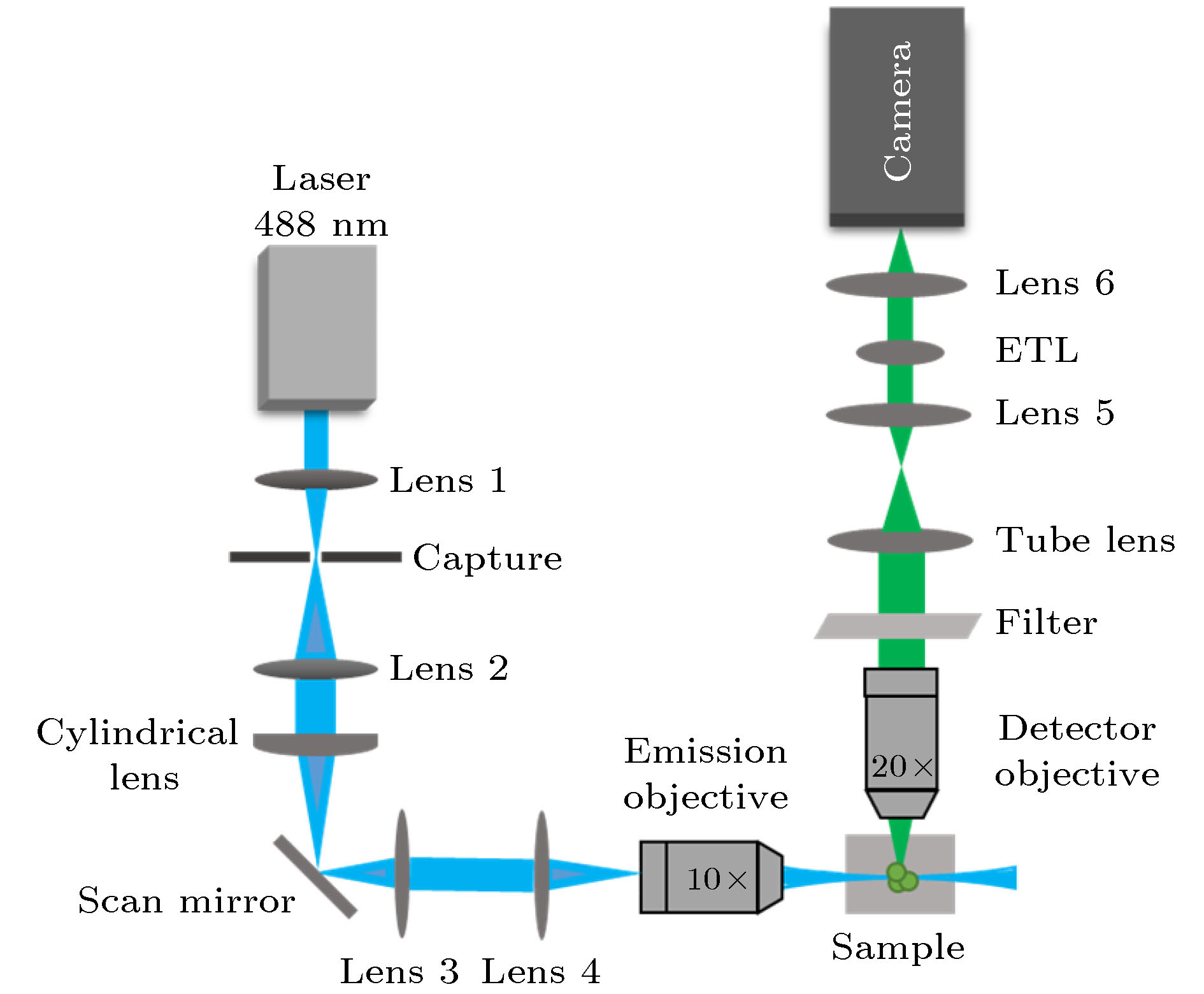
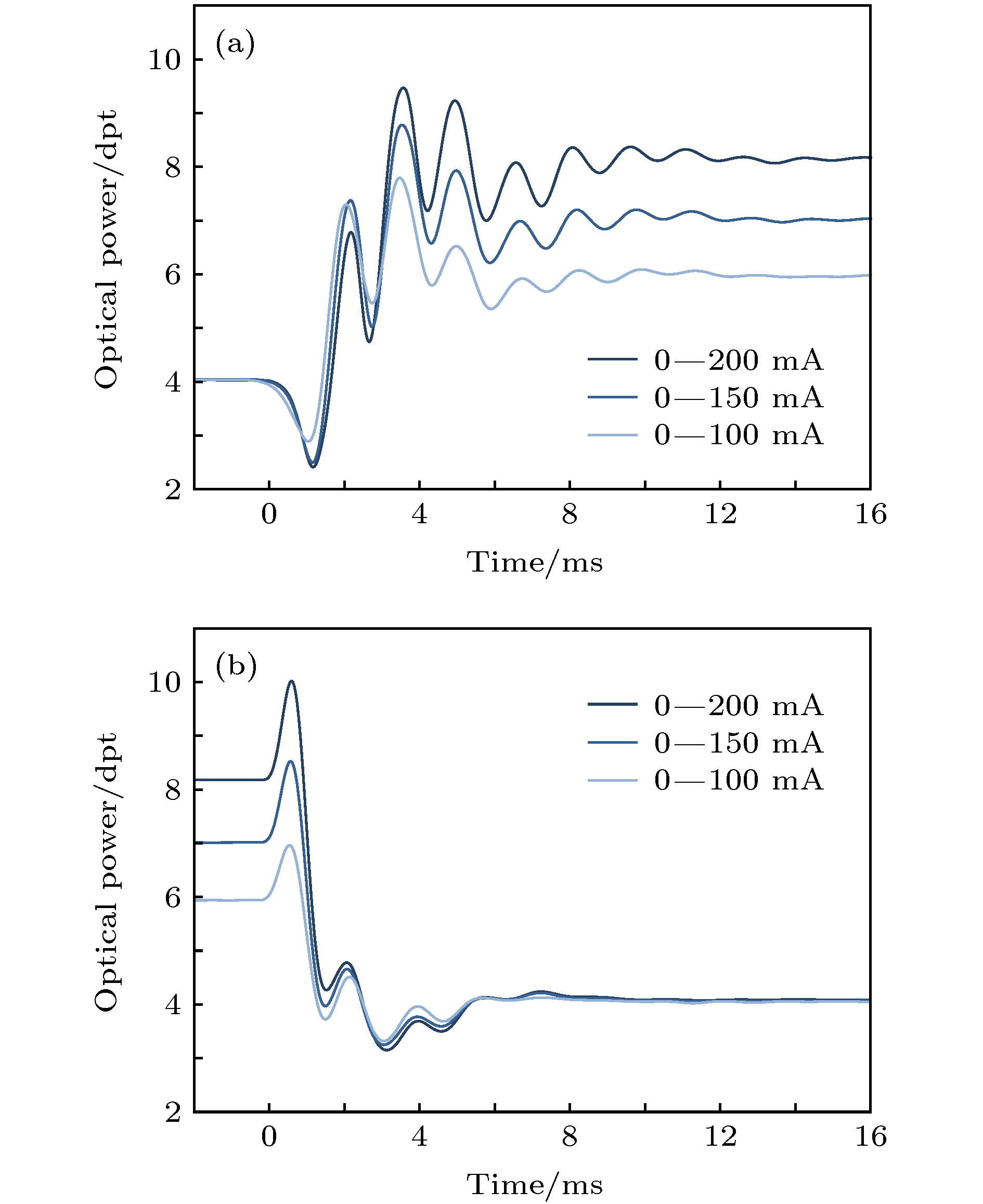
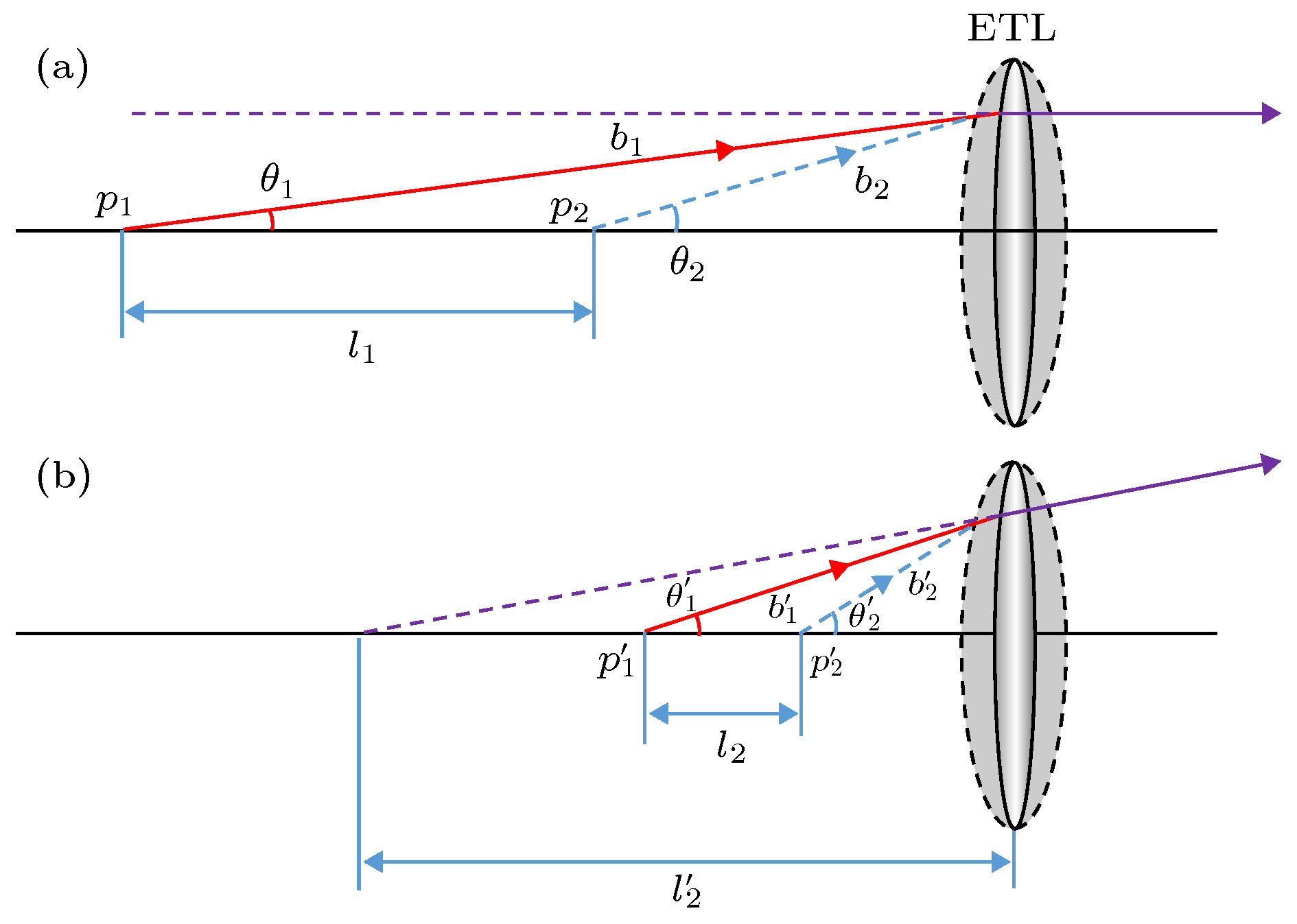
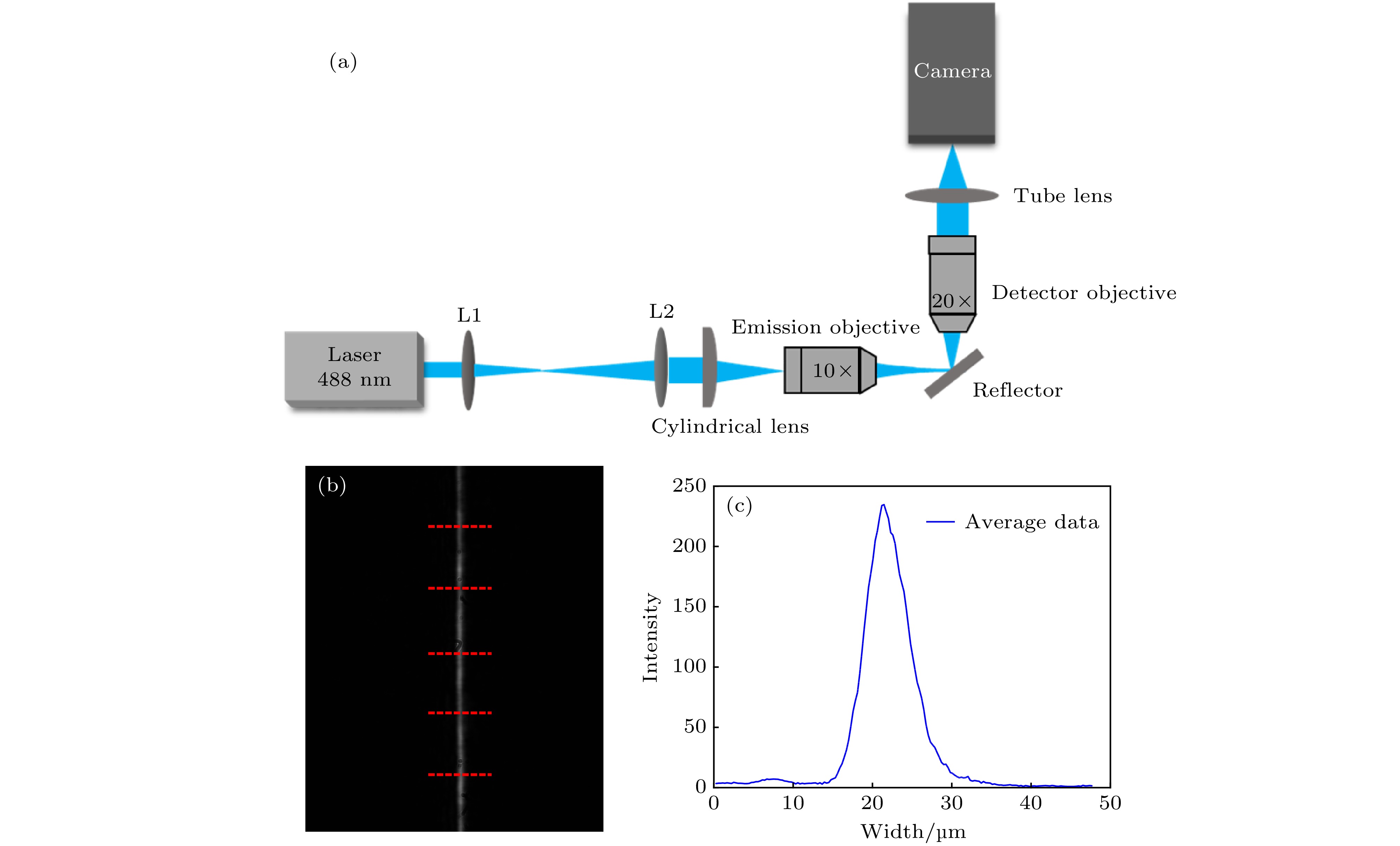
Fluorescence microscopic imaging technology realizes specific imaging by labeling biological tissue with fluorescence molecules, which has a high signal-to-noise ratio and has been widely used in the field of medical biology research. Some typical fluorescence microscopy techniques, such as confocal microscopy and two-photon microscopy, have high fluorescence intensity, but the long exposure can cause phototoxicity and photobleaching of biological tissue, which is difficult to meet the demand for long-time observation or noninvasive imaging. Then, light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) has become a hot research topic in fluorescence micro-imaging in recent years due to its fast speed, high resolution, low photobleaching and low phototoxicity. The imaging speed of a typical light sheet microscopy is not fast enough to observe fast biological activities such as transmission of neural signals, blood flow, and heart beats. At present, many reported light-sheet fluorescence microscopies still have some problems such as fixed imaging surface, slow imaging speed, small imaging depth or residual artifacts. Therefore, in this paper, a rapid light-sheet fluorescence microscopy based on electrically tunable lens is built. To achieve the rapid movement of the focal plane of the detection objective lens, the electrically tunable lens is introduced to meet the reqirement for fast changing of the diopter. Similarly, the rapid movement of light sheet is achieved by introducing one-dimensional galvanometer to change the rotation angle. Fast imaging requires the light sheet and focal plane to overlap in real time, which is then combined with a high-speed sCMOS receiving fluorescence to complete the whole imaging. In the experiment, the vertical depth significantly increases by modifying the optical path, and the LABVIEW programming is used to coordinate and improve the dynamic imaging quality, which effectively reduces the artifacts generated in rapid imaging. Finally, an imaging speed of 275 frames/s with a lateral resolution of ~0.73 μm, vertical resolution of ~5.5 μm, and an imaging depth of ~138 μm is achieved. This is of significance for developing the real-time and non-invasive imaging of living biological tissues.
[1] Zhang M X, Zhang J, Wang J, Achimovich A M, Aziz A A, Corbitt J, Acton S T, Gahlmann A 2019 Biophys. J. 116 25a
[2] Rocha M D, During D N, Bethge P, Voigt F F, Hildebrand S, Helmchen F, Pfeifer A, Hahnloser R H R, Gahr M 2019 Front. Neuroanat. 13 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ahrens M B, Orger M B, Robson D N, Li J M, Keller P J 2013 Nat. Methods 10 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huisken J, Swoger J, Del Bene F, Wittbrodt J, Stelzer E H 2004 Science 305 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Huisken J, Stainier D Y R 2009 Development 136 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rasmi C K, Madhangi M, Nongthomba U, Mondal P P 2016 Microsc. Res. Techniq. 79 455
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu Y C, Ghitani A, Christensen R, Santella A, Du Z, Rondeau G, Bao Z R, Colon-Ramos D, Shroff H 2011 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 17708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lemon W C, Pulver S R, Hockendorf B, McDole K, Branson K, Freeman J, Keller P J 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 7924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kumar S, Wilding D, Sikkel M B, Lyon A R, MacLeod K T, Dunsby C 2011 Opt. Express 19 13839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu D, Zhou X, Yao B L, Li R Z, Yang Y L, Peng T, Lei M, Dan D, Ye T 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ma P, Chan D C, Gu S, Watanabe M, Jenkins M W, Rollins A M 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 5120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 安坤, 王晶, 梁东, 刘军 2017 中国激光 44 274
An K, Wang J, Liang D, Liu J 2017 Chin. J. Lasers 44 274
[13] Hedde P N, Gratton E 2018 Microsc. Res. Techniq. 81 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fei P, Lee J, Packard R R S, Sereti K I, Xu H, Ma J G, Ding Y C, Kang H, Chen H, Sung K, Kulkarni R, Ardehali R, Kuo C C J, Xu X L, Ho C M, Hsiai T K 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 22489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haslehurst P, Yang Z Y, Dholakia K, Emptage N 2018 Biomed. Opt. Express 9 2154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kashekodi A B, Meinert T, Michiels R, Rohrbach A 2018 Biomed. Opt. Express 9 4263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fahrbach F O, Voigt F F, Schmid B, Helmchen F, Huisken J 2013 Opt. Express 21 21010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Landry J R, Itoh R, Li J M, Hamann S S, Mandella M, Contag C H, Solgaard O 2019 J. Biomed. Opt. 24 4
[19] Guan Z, Lee J, Jiang H, Dong S Y, Jen N, Hsiai T, Ho C M, Fei P 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ritter J G, Veith R, Siebrasse J P, Kubitscheck U 2008 Opt. Express 16 7142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Engelbrecht C J, Stelzer E H 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张球, 梁东, 白丽华, 刘军 2019 中国激光 46 279
Zhang Q, Liang D, Bai L H, Liu J 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 279
-
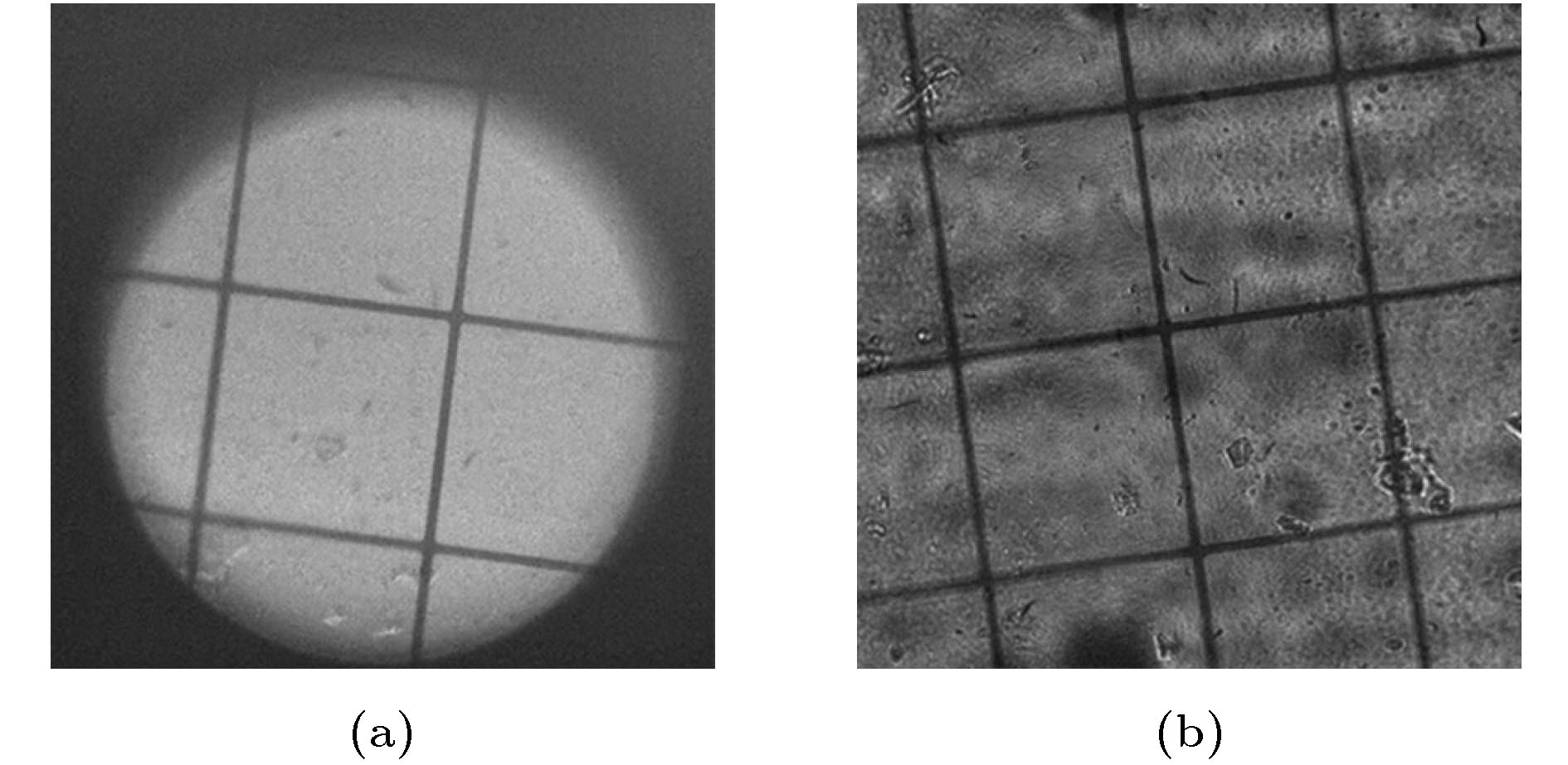
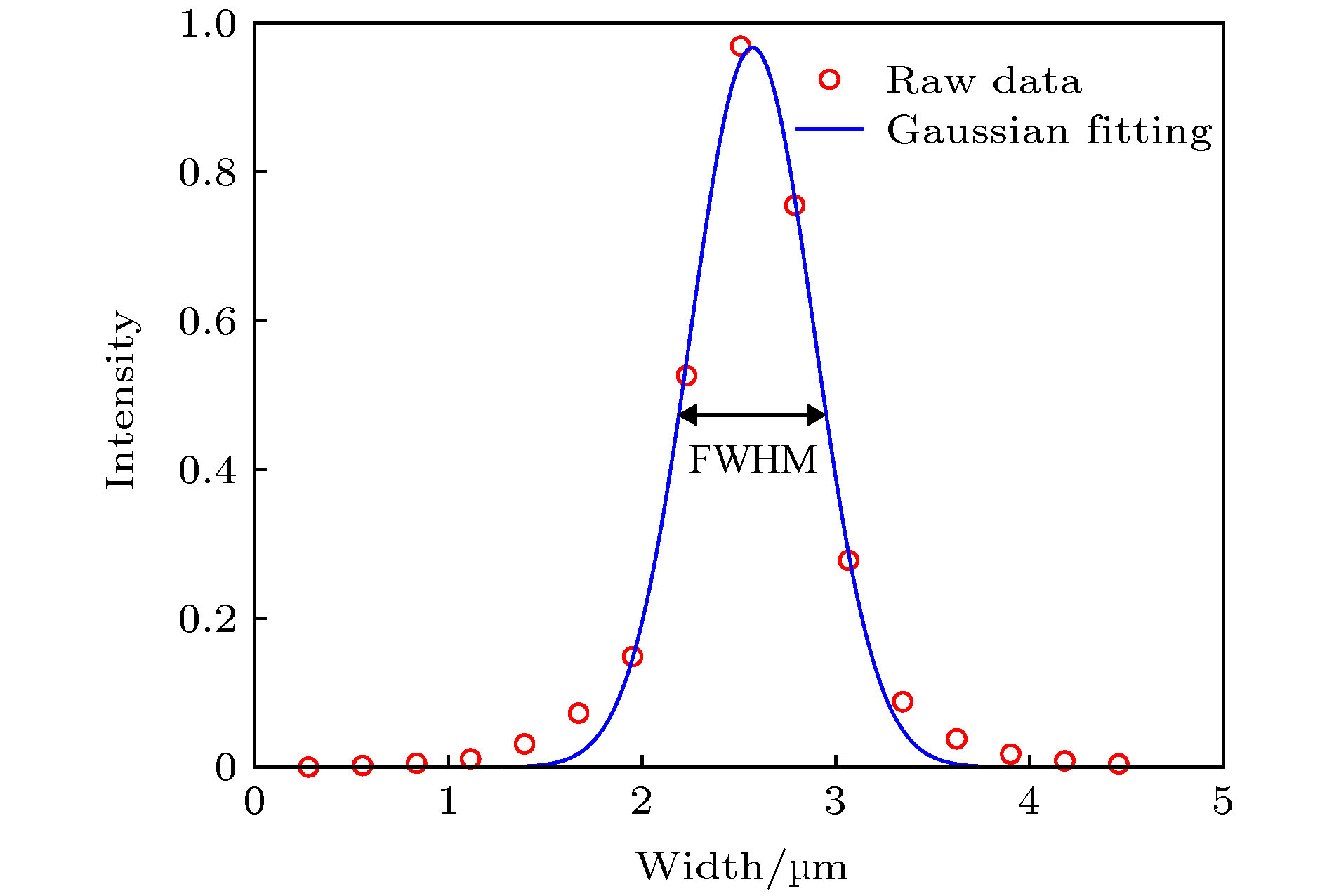
图 6 100 nm荧光微球的分析 (a) 100 nm荧光微球的拍摄图像; (b)−(f) 5个光强最大的荧光小球; (g)−(k) 分别是(b)−(f)中荧光小球的灰度剖面线; (l) (g)−(k)的归一化并平均化之后的曲线
Figure 6. Analysis of 100 nm fluorescent spheres: (a) Image of 100 nm fluorescent spheres; (b)−(f) five fluorescent spheres with the largest intensity; (g)−(k) intensity profile of a horizontal line passing through the center of fluorescent sphere in (b)−(f); (l) the normalized and averaged curves of (g)−(k).
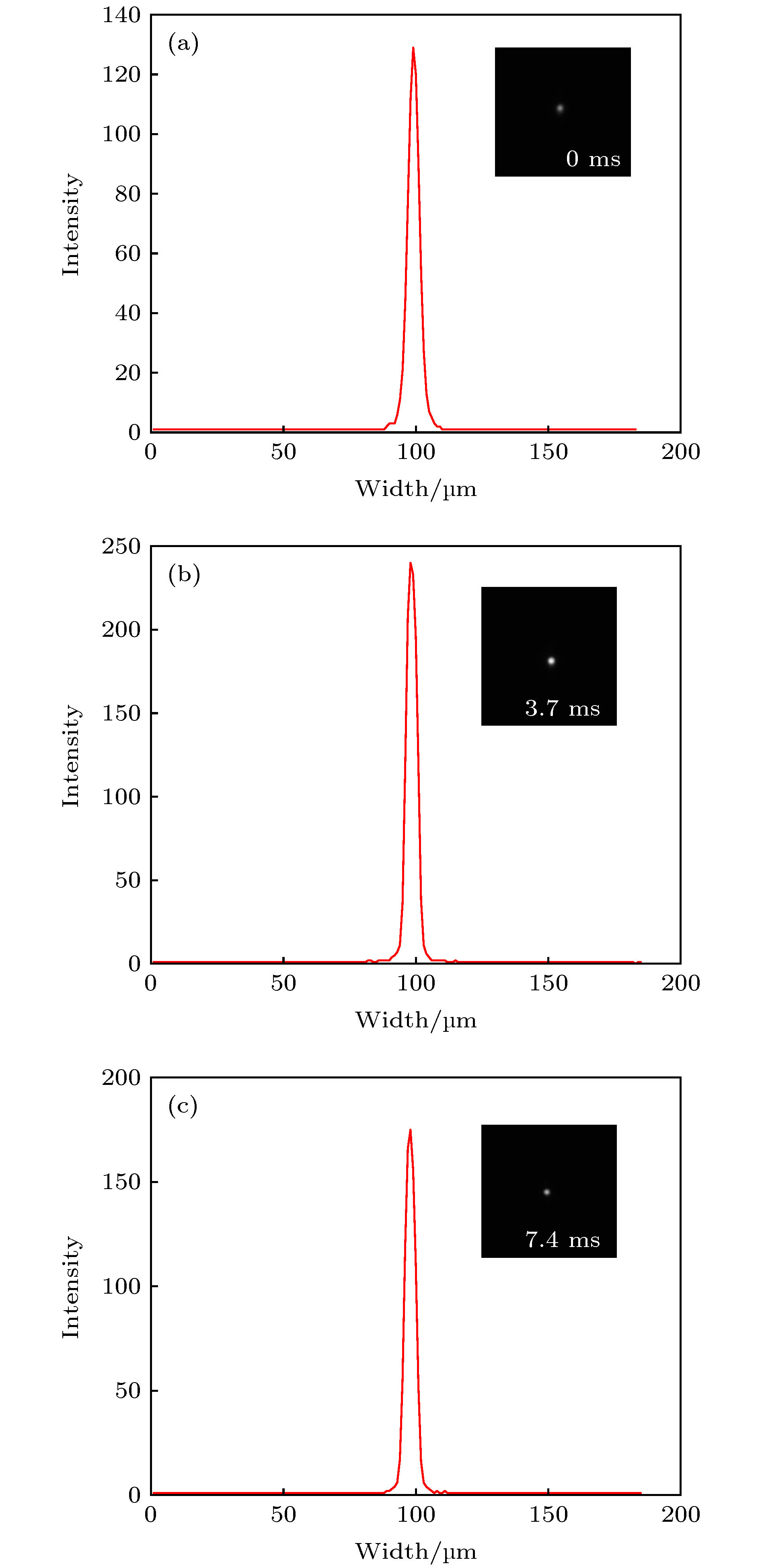
图 11 本实验结果的伪像分析 (a) 0 ms时经过荧光小球中心的灰度剖面线; (b) 3.7 ms时经过荧光小球中心的灰度剖面线; (c) 7.4 ms时经过荧光小球中心的灰度剖面线
Figure 11. The artifacts analysis of the experimental results: (a) Intensity profile of a line passing through the center of fluorescent sphere captured at 0 ms; (b) intensity profile of a line passing through the center of fluorescent sphere captured at 3.7 ms; (c) intensity profile of a line passing through the center of fluorescent sphere captured at 7.4 ms.
-
[1] Zhang M X, Zhang J, Wang J, Achimovich A M, Aziz A A, Corbitt J, Acton S T, Gahlmann A 2019 Biophys. J. 116 25a
[2] Rocha M D, During D N, Bethge P, Voigt F F, Hildebrand S, Helmchen F, Pfeifer A, Hahnloser R H R, Gahr M 2019 Front. Neuroanat. 13 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ahrens M B, Orger M B, Robson D N, Li J M, Keller P J 2013 Nat. Methods 10 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huisken J, Swoger J, Del Bene F, Wittbrodt J, Stelzer E H 2004 Science 305 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Huisken J, Stainier D Y R 2009 Development 136 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Rasmi C K, Madhangi M, Nongthomba U, Mondal P P 2016 Microsc. Res. Techniq. 79 455
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu Y C, Ghitani A, Christensen R, Santella A, Du Z, Rondeau G, Bao Z R, Colon-Ramos D, Shroff H 2011 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 17708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lemon W C, Pulver S R, Hockendorf B, McDole K, Branson K, Freeman J, Keller P J 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 7924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kumar S, Wilding D, Sikkel M B, Lyon A R, MacLeod K T, Dunsby C 2011 Opt. Express 19 13839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu D, Zhou X, Yao B L, Li R Z, Yang Y L, Peng T, Lei M, Dan D, Ye T 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ma P, Chan D C, Gu S, Watanabe M, Jenkins M W, Rollins A M 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 5120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 安坤, 王晶, 梁东, 刘军 2017 中国激光 44 274
An K, Wang J, Liang D, Liu J 2017 Chin. J. Lasers 44 274
[13] Hedde P N, Gratton E 2018 Microsc. Res. Techniq. 81 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fei P, Lee J, Packard R R S, Sereti K I, Xu H, Ma J G, Ding Y C, Kang H, Chen H, Sung K, Kulkarni R, Ardehali R, Kuo C C J, Xu X L, Ho C M, Hsiai T K 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 22489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haslehurst P, Yang Z Y, Dholakia K, Emptage N 2018 Biomed. Opt. Express 9 2154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kashekodi A B, Meinert T, Michiels R, Rohrbach A 2018 Biomed. Opt. Express 9 4263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fahrbach F O, Voigt F F, Schmid B, Helmchen F, Huisken J 2013 Opt. Express 21 21010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Landry J R, Itoh R, Li J M, Hamann S S, Mandella M, Contag C H, Solgaard O 2019 J. Biomed. Opt. 24 4
[19] Guan Z, Lee J, Jiang H, Dong S Y, Jen N, Hsiai T, Ho C M, Fei P 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ritter J G, Veith R, Siebrasse J P, Kubitscheck U 2008 Opt. Express 16 7142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Engelbrecht C J, Stelzer E H 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张球, 梁东, 白丽华, 刘军 2019 中国激光 46 279
Zhang Q, Liang D, Bai L H, Liu J 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 279
-
 20191908-video1.mp4
20191908-video1.mp4
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11234
- PDF Downloads: 155
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: