-
In the last two decades, a wide variety of plasmoids events have been observed, ranging from space and astrophysical phenomenon to magnetically confined laboratory plasmas, in which there are a lot of evidence of observational plasmoid-like features supported by direct large-scaled computer simulations. A super-Alfvénic instability, named plasmoid instability, occurs in an extended current sheet, when the Lundquist number exceeds a critical value. The large-aspect-ratio current sheet is fragmented by generating, growing, coalescing and ejecting of plasmoids so that this phenomenon has been proposed as a possible mechanism for fast reconnection scenario. This super-Alfvénic plasmoid instability has been usedin the significant new development of reconnection theory, and thus can provide alternative and more convincing mechanism for fast reconnection. In this work, a “driving” kind of shear flow in the out-of-plane direction is imposed on a two-dimensional, three-component magnetohydrodynamic model with a current sheet system to study the dynamic process of the plasmoids in a current sheet system. The effect of the width and strength of the driving flow on the reconnection rate of plasmoids are numerically analyzed in detail. It is found that the plasmoids are easily formed in the case of strong and wide out-of-plane driving flow. The reconnection rate and the number of the plasmoids increase with the driving flow width and/or driving flow strength increasing. In the presence of guiding field, it is found that the symmetry of the plasmoids is broken in the reconnection plane. In addition, for the fixed guiding field, the growth rate of plasmoids increases much faster when the strength of driving flow increases.
-
Keywords:
- magnetic reconnection /
- plasma driving flow /
- plasmiods /
- guiding field
[1] Parker E N 1963 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 8 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sweet P A 1969 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astr. 7 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yokoyama T, Akita K, Morimoto T, Inoue K, Newmark J 2001 Astrophys. J. Lett. 546 L69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dungey J W 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bhattacharjee A 2004 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astr. 42 365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hastie R J 1997 Astrophys. Space Sci. 256 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chapman I T, Scannell R, Cooper W A, Graves J P, Hastie R J, Naylor G, Zocco A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 255002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wei L, Wang Z X, Fan D M, Wang F, Liu Y 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 042503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang C L, Ma Z W 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 122113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jin S P, Yang H A, Wang X G 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 042902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ishizawa A, Waelbroeck F L, Fitzpatrick R, Horton W, Nakajima N 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 072312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Biskamp D 1986 Phys. Fluids. 29 1520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Daughton W, Scudder J, Karimabadi H 2006 Phys. Plasmas 13 072101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Drake J F, Swisdak M, Che H, Shay M A 2006 Nature 443 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Loureiro N F, Schekochihin A A, Cowley S C 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 100703
[16] Lapenta G 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lin J, Cranmer S R, Farrugia C J 2008 J. Geophys. Res. 113 D11107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bhattacharjee A, Huang Y M, Yang H, Rogers B 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 112102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Daughton W, Roytershteyn V, Albright B J, Karimabadi H, Yin L, Bowers K J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang Y M, Bhattacharjee A, Sullivan B P 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 072109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L, Selim B I 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 012106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Samtaney R, Loureiro N F, Uzdensky D A, Schekochihin A A, Cowley S C 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 105004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pritchett P L, Lee Y C, Drake J F 1980 Phys. Fluids 23 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ishii Y, Azumi M, Kishimoto Y 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 205002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Z X, Wang X, Dong J Q, Kishimoto Y, Li J Q 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 082109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang Z X, Wang X G, Dong J Q, Lei Y A, Long Y X, Mou Z Z, Qu W X 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 185004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bierwage A, Hamaguchi S, Wakatani M, Benkadda S, Leoncini X 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 065001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bowers K, Li H 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 035002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L 2016 Astrophys. J. 821 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L 2017 Astrophys. J. 835 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] La BelleHamer A L, Otto A, Lee L C 1994 Phys. Plasmas 1 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang J, Xiao C, Wang X 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 032905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang L, Wang X Q, Wang X G, Liu Y 2014 Chin. Phys. B 23 025203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
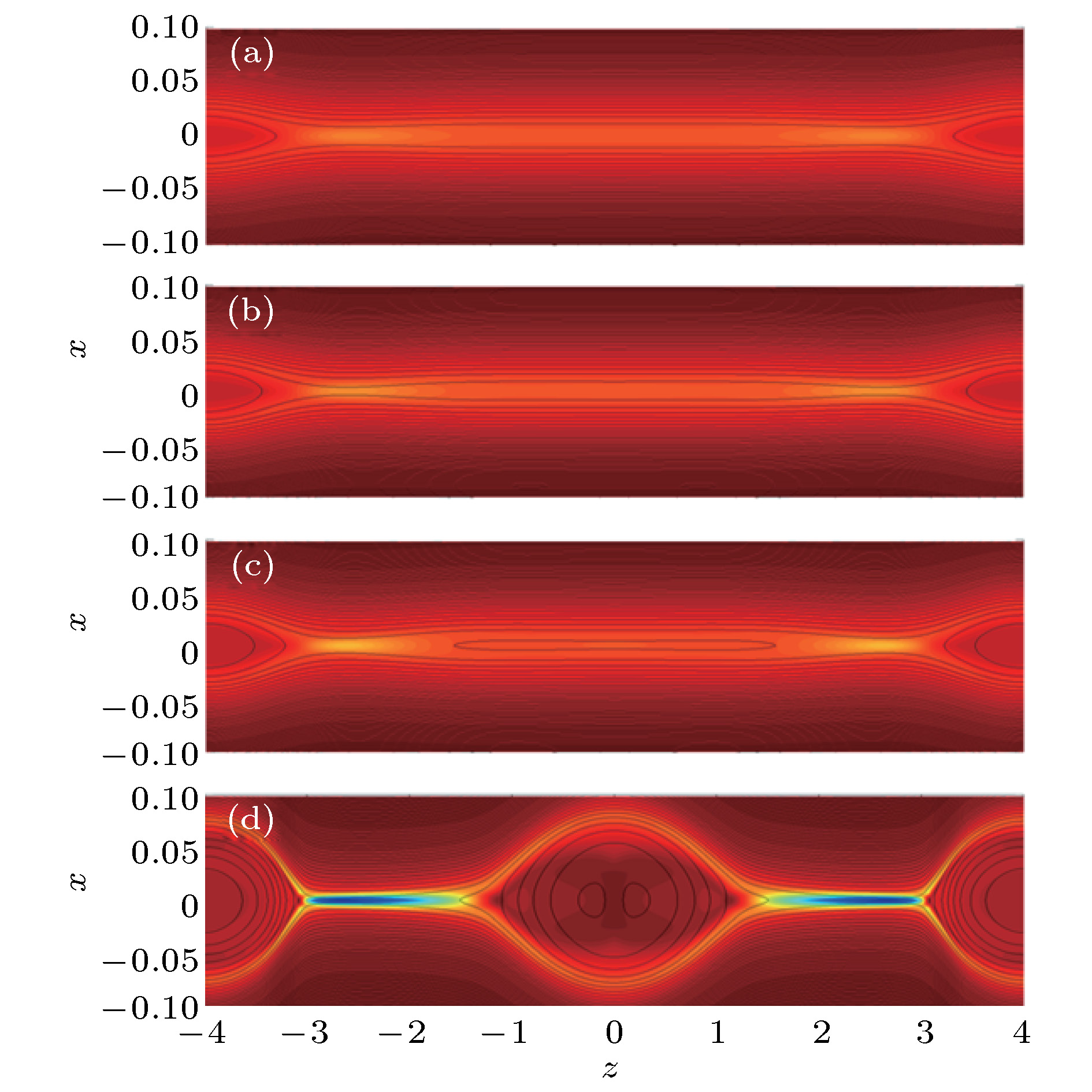
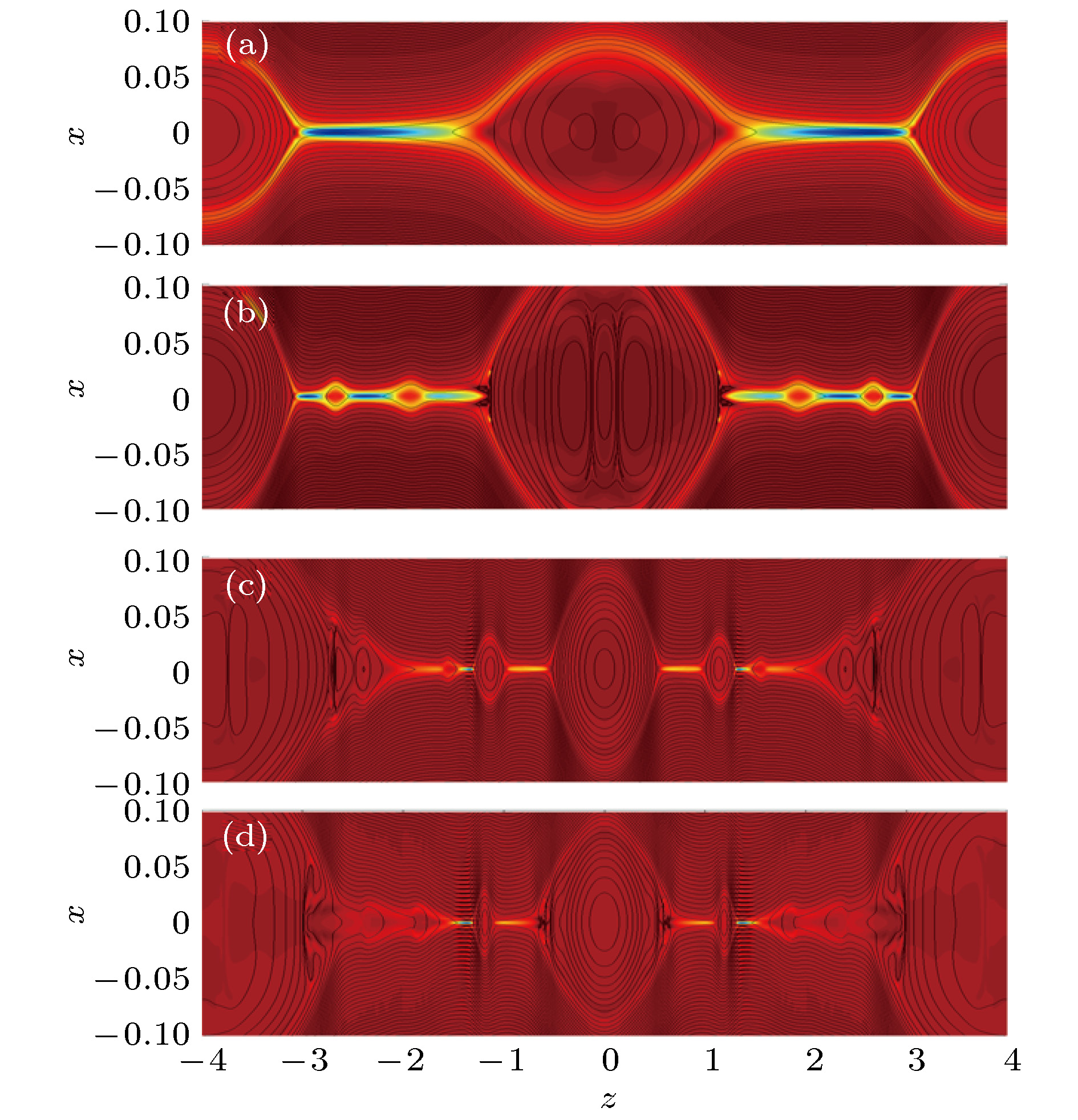
图 2 无驱动流情况下的磁岛位型 (a), (b), (c), (d)分别为时间t = 70, t = 74, t = 80和t = 120的结构, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度
Figure 2. The magnetic configuration without driving flow at (a) t = 70, (b) t = 74, (c) t = 80, (d) t = 120. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respectively.
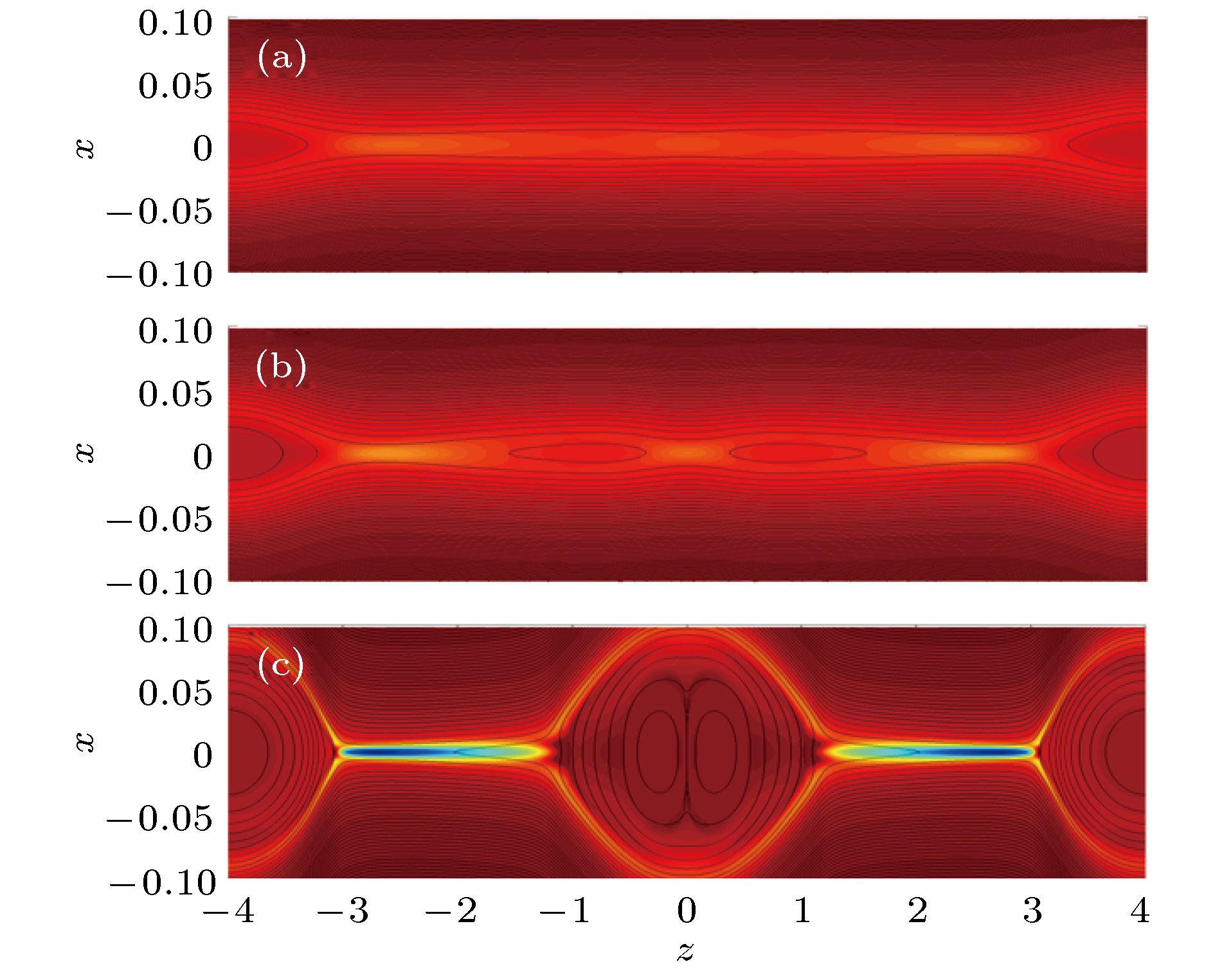
图 3 加入宽度LS = 0.05、强度U0 = 0.1的驱动流时, 磁岛链的演化过程 (a), (b), (c)分别为时间t = 70, t = 80和t = 110的结构, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度
Figure 3. Evolution of magnetic configuration with out-of-plane driving flow for LS = 0.05, U0 = 0.1 at (a) t = 70, (b) t = 80, (c) t = 110. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respec-tively.
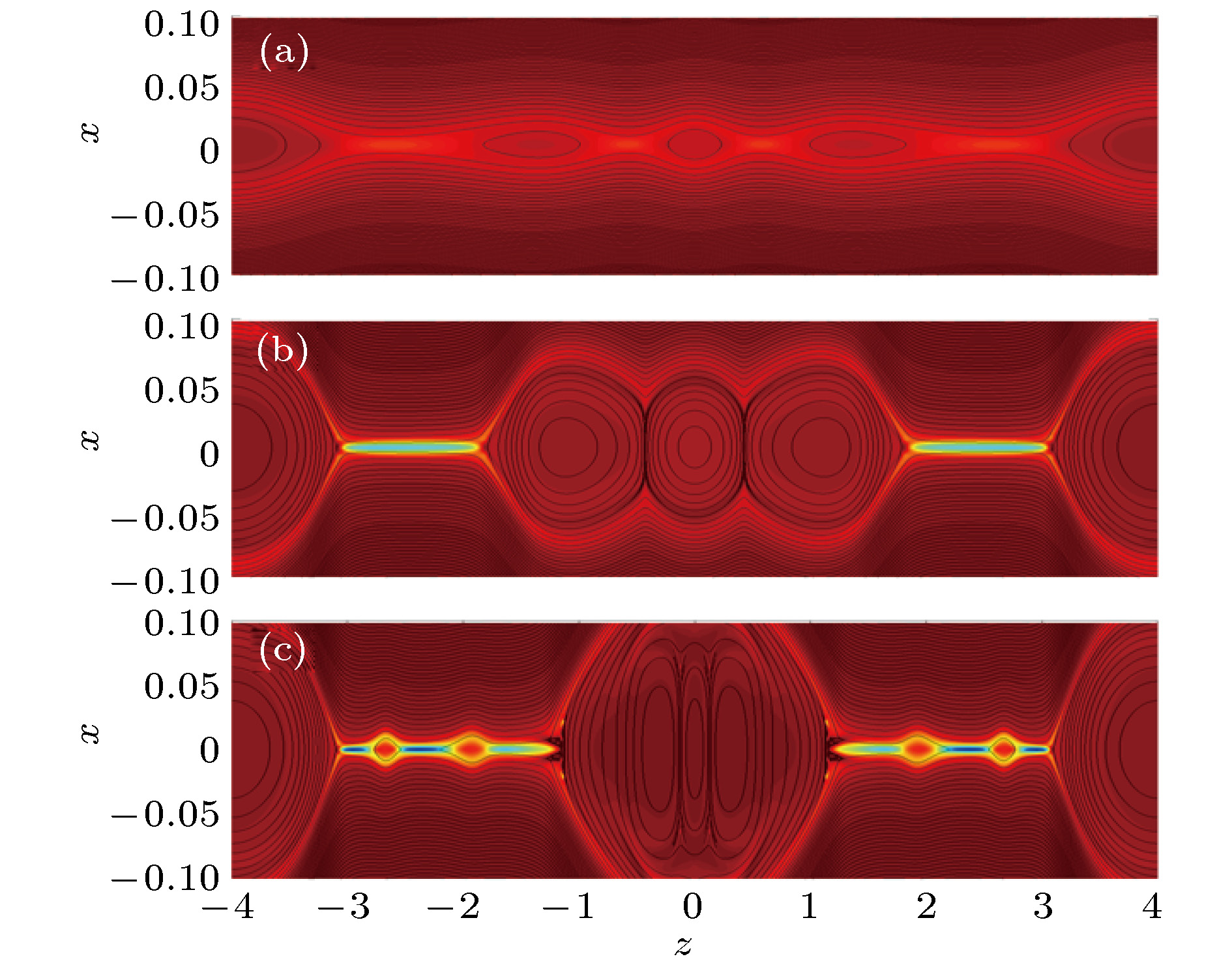
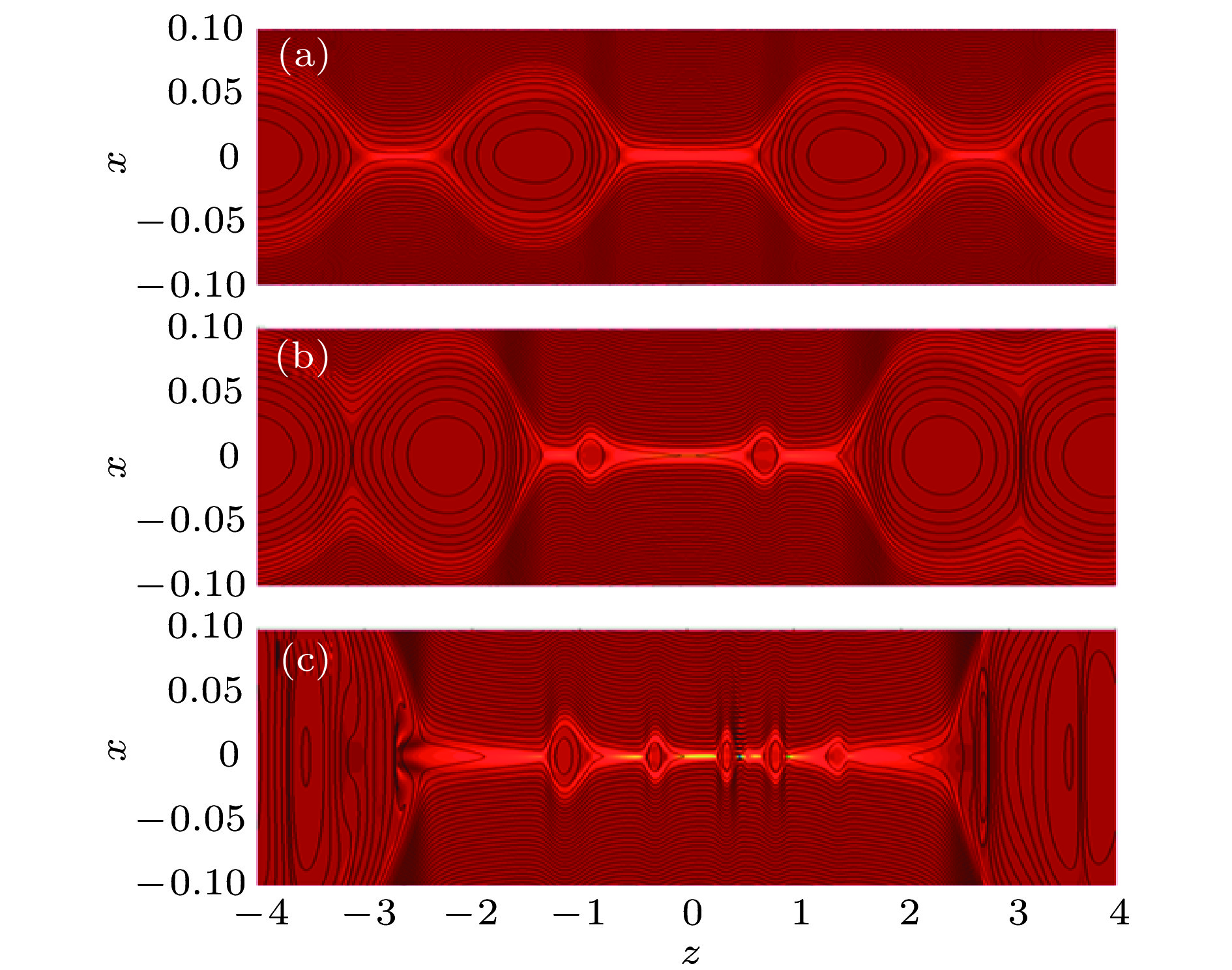
图 4 加入宽度LS = 0.3, 强度U0 = 0.1 驱动流情况下的磁岛位型 (a), (b), (c)为时间t = 80, t = 110和t = 118的结构, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度
Figure 4. The magnetic configuration with out-of-plane dri-ving flow for LS = 0.3, U0 = 0.1 at (a) t = 80, (b) t = 110, (c) t = 118. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respectively.
图 6 加入相同宽度LS = 0.3, 不同强度的驱动流时的典型磁岛位型, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度 (a)无驱动流的情况t = 120的结构; (b)加入强度U0 = 0.1的情况在t = 118的结构; (c)加入强度U0 = 0.2的情况在t = 97的结构; (d)加入强度U0 = 0.3的情况在t = 88的结构
Figure 6. The magnetic configuration with out-of-plane dri-ving flow with different strength for LS = 0.3 in the same phase. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respectively: (a) Without driving flow at t = 120; (b) with U0 = 0.1 at t = 118; (c) with U0 = 0.2 at t = 97; (d) with U0 = 0.3 at t = 88.
图 7 导向场By = 0.1, 驱动流宽度LS = 0.05、强度U0 = 0.1情况下的磁岛位型 (a), (b), (c)分别为时间t = 100, t = 110和t = 119的结构, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度
Figure 7. The magnetic configuration is effected by out-of-plane driving flow with LS = 0.05, U0 = 0.1 and guilding field By = 0.1 at (a) t = 100, (b) t = 110, (c) t = 119. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respectively.
图 8 驱动流宽度LS = 0.3, 强度U0 = 0.1, 导向场By = 0.1的情况下, 磁岛位形的演化 (a), (b), (c)分别为时间t = 70, t = 80和t = 88的结构, 黑线和背景颜色分别为重联平面的磁力线分布和垂直平面的电流密度
Figure 8. Evolution of the magnetic configuration with out-of-plane driving flow for LS = 0.3, U0 = 0.1 and guilding field By = 0.1 at (a) t = 70; (b) t = 80; (c) t = 88. The black lines and background colors indicate the magnetic field line in the reconnection plane and the current density in out-of-plane direction, respectively.
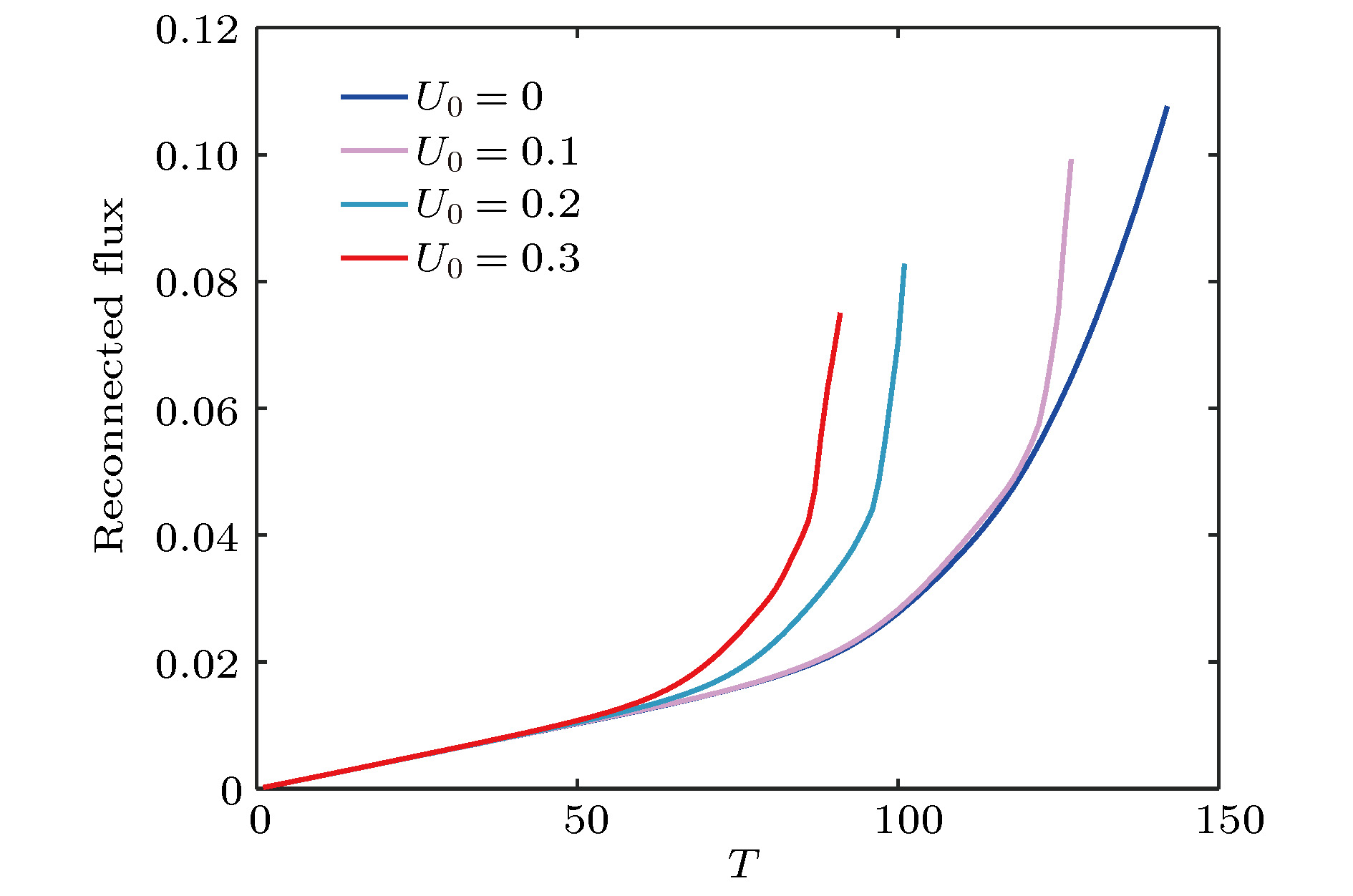
图 9 (a)驱动流宽度LS = 0.05, 强度U0 = 0.1时, 不同导向场By重联通量随时间的演化; (b)导向场By = 0.1, 驱动流宽度LS = 0.05时, 不同强度U0下重联通量随时间的演化; (c)导向场By = 0.1, 驱动流宽度LS = 0.05时, 小磁岛宽度的增长速度对强度U0的依赖关系
Figure 9. (a) Evolution of the reconnection flux with out-of-plane driving flow for LS = 0.05, U0 = 0.1 and different guilding field; (b) evolution of the reconnection flux with different driving flow strength and guilding field By = 0.1; (c) dependence of the growth rate of plasmoid on different driving flow strength with guilding field By = 0.1.
-
[1] Parker E N 1963 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 8 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sweet P A 1969 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astr. 7 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yokoyama T, Akita K, Morimoto T, Inoue K, Newmark J 2001 Astrophys. J. Lett. 546 L69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dungey J W 1961 Phys. Rev. Lett. 6 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bhattacharjee A 2004 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astr. 42 365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hastie R J 1997 Astrophys. Space Sci. 256 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chapman I T, Scannell R, Cooper W A, Graves J P, Hastie R J, Naylor G, Zocco A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 255002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wei L, Wang Z X, Fan D M, Wang F, Liu Y 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 042503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang C L, Ma Z W 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 122113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jin S P, Yang H A, Wang X G 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 042902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ishizawa A, Waelbroeck F L, Fitzpatrick R, Horton W, Nakajima N 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 072312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Biskamp D 1986 Phys. Fluids. 29 1520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Daughton W, Scudder J, Karimabadi H 2006 Phys. Plasmas 13 072101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Drake J F, Swisdak M, Che H, Shay M A 2006 Nature 443 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Loureiro N F, Schekochihin A A, Cowley S C 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 100703
[16] Lapenta G 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lin J, Cranmer S R, Farrugia C J 2008 J. Geophys. Res. 113 D11107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bhattacharjee A, Huang Y M, Yang H, Rogers B 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 112102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Daughton W, Roytershteyn V, Albright B J, Karimabadi H, Yin L, Bowers K J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 065004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Huang Y M, Bhattacharjee A, Sullivan B P 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 072109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L, Selim B I 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 012106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Samtaney R, Loureiro N F, Uzdensky D A, Schekochihin A A, Cowley S C 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 105004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pritchett P L, Lee Y C, Drake J F 1980 Phys. Fluids 23 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ishii Y, Azumi M, Kishimoto Y 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 205002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Z X, Wang X, Dong J Q, Kishimoto Y, Li J Q 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 082109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang Z X, Wang X G, Dong J Q, Lei Y A, Long Y X, Mou Z Z, Qu W X 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 185004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bierwage A, Hamaguchi S, Wakatani M, Benkadda S, Leoncini X 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 065001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bowers K, Li H 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 035002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L 2016 Astrophys. J. 821 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Nemati M J, Wang Z X, Wei L 2017 Astrophys. J. 835 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] La BelleHamer A L, Otto A, Lee L C 1994 Phys. Plasmas 1 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang J, Xiao C, Wang X 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 032905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang L, Wang X Q, Wang X G, Liu Y 2014 Chin. Phys. B 23 025203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14008
- PDF Downloads: 91
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: