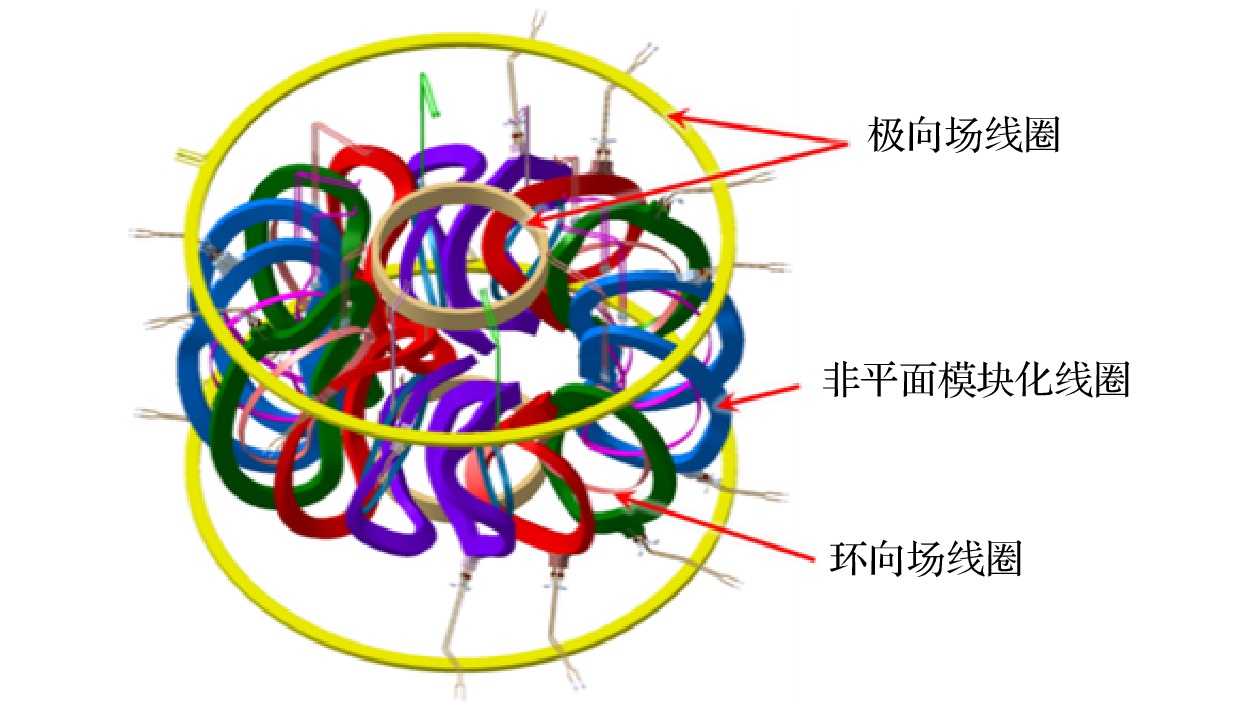
-
In stellarators, error fields arise from the inevitable deviations in the fabrication and assembly of complex coil systems. The magnetic configurations of stellarators are predominantly generated by external coils and are highly sensitive to these error fields. Therefore, assessing the impact of coil deformations on stellarator magnetic topology is important. The purpose of this study is to explore the influence of error fields, caused by modular coil (MC) perturbations, on the magnetic topology of the Chinese First Quasi-axisymmetric Stellarator (CFQS). In this work, by changing the Fourier coefficients that represent the current-carrying surface (CCS) and the coil, two types of deformation coils, i.e. “in-surface” and “out-of-surface” disturbance on each MC can be obtained. Subsequently, three kinds of magnetic islands (ι = 2/4, 2/5 and 2/6) are used to identify coil deviations that have a significant influence on the CFQS magnetic configuration. Several important results are obtained as follows. i) The same deformation of a coil gives rise to various resonant error fields with different amplitudes. ii) The sensitivity of a resonant error field to the deformation of each coil is different. The in-surface disturbance of the most complex coil may not have a significant influence on the magnetic topology structure. iii) The sensitivity of the resonant error field to out-of-surface disturbance in the coil is higher than that to in-surface disturbance.
-
Keywords:
- quasi-axisymmetric stellarator /
- coil deformations /
- error fields /
- magnetic configuration
[1] Rummel T, Risse K, Viebke H, Braeuer T, Kisslinger J 2004 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 14 1394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiong G Z, Xu Y H, Isobe M, Shimizu A, Ogawa K, Kinoshita S, Liu H F, Wang X Q, Cheng J, Liu H, Huang J, Zhang X, Zhang Y C, Yin D P, Wang A Z, Okamura S, Tang C J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 035020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shoji M, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Xu Y H, Liu H F 2023 Plasma Fusion Res. 18 2405026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boozer A H 2005 Rev. Mod. Phys. 76 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Waelbroeck F L 2009 Nucl. Fusion 49 104025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lazerson S A, Bozhenkov S, Israeli B, Otte M, Niemann H, Bykov V, Endler M, Andreeva T, Ali A, Drewelow P, Jakubowski M, Sitjes A P, Pisano F, Cannas B, W7-X Team 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 124002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kißlinger J, Andreevab T 2005 Fusion Eng. Des. 74 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Andreeva T, Bräuer T, Endler M, Kißlinger J, Toussaint U V 2009 Fusion Eng. Des. 84 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yamazaki K, Yanagi N, Ji H, Kaneko H, Ohyabu N, Satow T, Morimoto S, Yamamoto J, Motojima O, the LHD Design Group 1993 Fusion Eng. Des. 20 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Strykowsky R L, Brown T, Chrzanowski J, Cole M, Heitzenroeder P, Neilson G H, Rej D, Viol M 2009 23rd IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering San Diego, CA, USA, June 01–05, 2009 p1
[11] Brooks A, Reiersen W 2003 20th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering San Diego, CA, USA, 14–17 October, 2003 p553
[12] Nührenberg J, Sindoni E, Lotz W, Troyon F, Gori S, Vaclavik J 1994 Proceedings of the Joint Varenna Lausanne International Workshop on Theory of Fusion Plasmas Varenna, Italy, August 22–26, 1994 p3
[13] Garabedian P 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 2483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Huang J, Nakata M, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Isobe M, Okamura S, Liu H F, Wang X Q, Zhang X, Liu H, Cheng J, Tang C J 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 052505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu Y H, Liu H F, Xiong G Z, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Nakata M, Yin D, Wan Y, Wilfred, Cooper A, Zhu C X, Liu H, Zhang X, Huang J, Wang X Q, Tang C J 2018 27th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference Ahmedabad, India, October 22–27, 2018 p5
[16] Isobe M, Shimizu A, Liu H F, Liu H, Xiong G Z, Yin D P, Ogawa K, Yoshimura Y, Nakata M, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Tang C J, Xu Y H, the CFQS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3402074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang X Q, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Isobe M, Okamura S, Todo Y, Wang H, Liu H F, Huang J, Zhang X 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 036021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 黄捷, 李沫杉, 覃程, 王先驱 2022 71 185202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J, Li M S, Qin C, Wang X Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 185202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 苏祥, 王先驱, 符添, 许宇鸿 2023 72 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su X, Wang X Q, Fu T, Xu Y H 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhu C X, Gates D A, Hudson S R, Liu H F, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Okamura S 2019 Nucl. Fusion 59 126007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shimizu A, Liu H F, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Ogawa K, Nakata M, Satake S, Suzuki C, Xiong G Z, Xu Y H, Liu H, Zhang X, Huang J, Wang X Q, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y, the CFQS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3403151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 065008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Lazerson S A, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 054016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Okamura S, Liu H F, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Xiong G Z, Xu Y H 2020 J. Plasma Phys. 86 815860402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Ogawa K, Nakata M, Yoshimura Y, Suzuki C, Osakabe M, Murase T, Nakagawa S, Tanoue H, Xu Y H, Liu H F, Liu H, Huang J, Wang X Q, Cheng J, Xiong G Z, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 016010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu H F, Shimizu A, Xu Y H, Okamura S, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Li Y B, Xiong G Z, Wang X Q, Huang J, Cheng J, Liu H, Zhang X, Yin D P, Wang Y, Murase T, Nakagawa S, Tang C J 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 016014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li Y B, Liu H F, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Isobe X, Xiong G Z, Luo Y, Cheng J, Liu H, Wang X Q, Huang J, Zhang X, Yin D P, Wan Y, Tang C J 2020 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 62 125004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu H F, Zhang J, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Cooper W A, Okamura S, Isobe M, Wang X Q, Huang J, Cheng J, Liu H, Zhang X, Tang C J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 026018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kinoshita S, Shimizu A, Okamura S, Isobe M, Xiong G Z, Liu H F, Xu Y H, the CQFS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3405097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu H F, Shimizu A, Isobe m, Okamura S, Nishimura s, Suzuki C, Xu Y H, Zhang X, Liu B , Huang J, Wang X Q, Liu H, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y, the CFQS Team 2018 Plasma Fusion Res. 13 3405067
[31] Boozer A H 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 025001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pedersen T S, Otte M, Lazerson S, Helander P, Bozhenkov S, Biedermann C, Klinger T, Wolf R C, Bosch F S, the Wendelstein 7-X Team 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Merkel P 1987 Nucl. Fusion 27 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 016008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Drevlak M 1998 Fusion Technol. 33 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wechsung F, Giuliani A, Landreman M, Cerfon A, Stadler G 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 105021
-
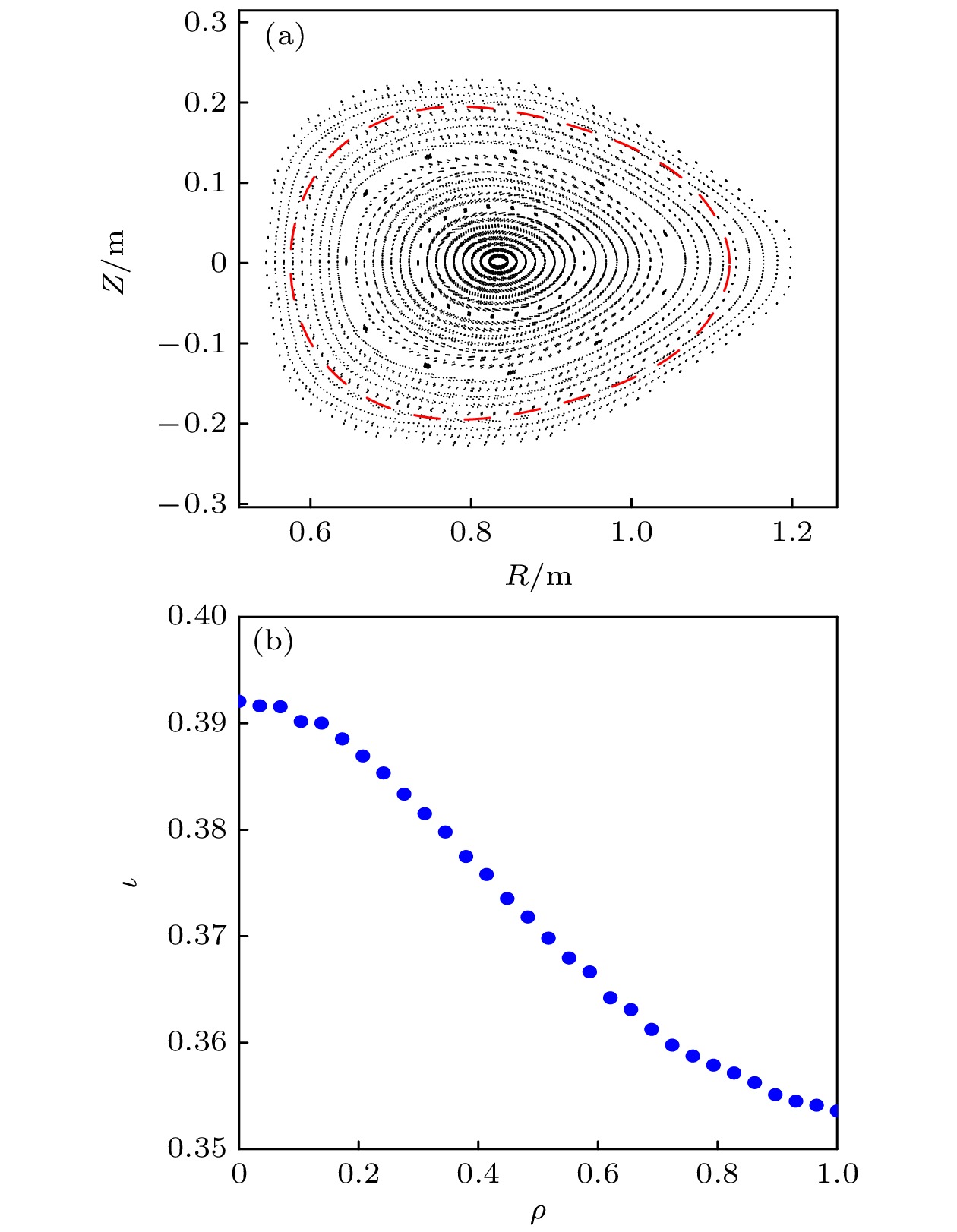
图 2 (a) 由磁力线追踪计算得到的理想MC线圈产生的磁场在环向角ξ = 90°横截面处的庞加莱图(黑色虚线)和目标等离子体边界(红色虚线), 追踪的初始位置在Z = 0, R∈[0.5446, 0.8359]处, 追踪周期为270; (b) 与该磁场截面对应的旋转变换剖面, 横坐标为归一化半径
Figure 2. (a) Poincaré plots (black dots) based on tracing field lines in the magnetic configuration produced by the designed MCs and the target plasma boundary (red dashed) at the triangular-shaped cross-section, field lines with initial positions R∈ [0.5446, 0.8359] and Z = 0 are traced 270 periods; (b) the corresponding rotational transform profile with the normalized radius as its abscissa.
图 3 由理想线圈产生的n/m = 2/4 (a), 2/5 (b)和2/6 (c) 的3种磁岛位形的庞加莱截面图及旋转变换剖面, 横坐标表示从主磁轴到磁场外侧的半径, 每个磁面的追踪周期为540, 追踪的初始位置为 (a) Z = 0, R∈[0.54, 0.81]; (b) Z = 0, R∈[0.56, 0.83]; (c) Z = 0, R∈[0.44, 0.76]
Figure 3. Poincaré plots of three island configurations with n/m = 2/4 (a), 2/5 (b) and 2/6 (c) and their rotational transform profiles produced by undeformed coils, the abscissa denotes radius from the main magnetic axis to the outboard side, field lines with initial positions R∈[0.54, 0.81] and Z = 0 (a), R∈[0.56, 0.83] and Z = 0 (b), R∈[0.44, 0.76] and Z = 0 (c) are traced 540 periods.
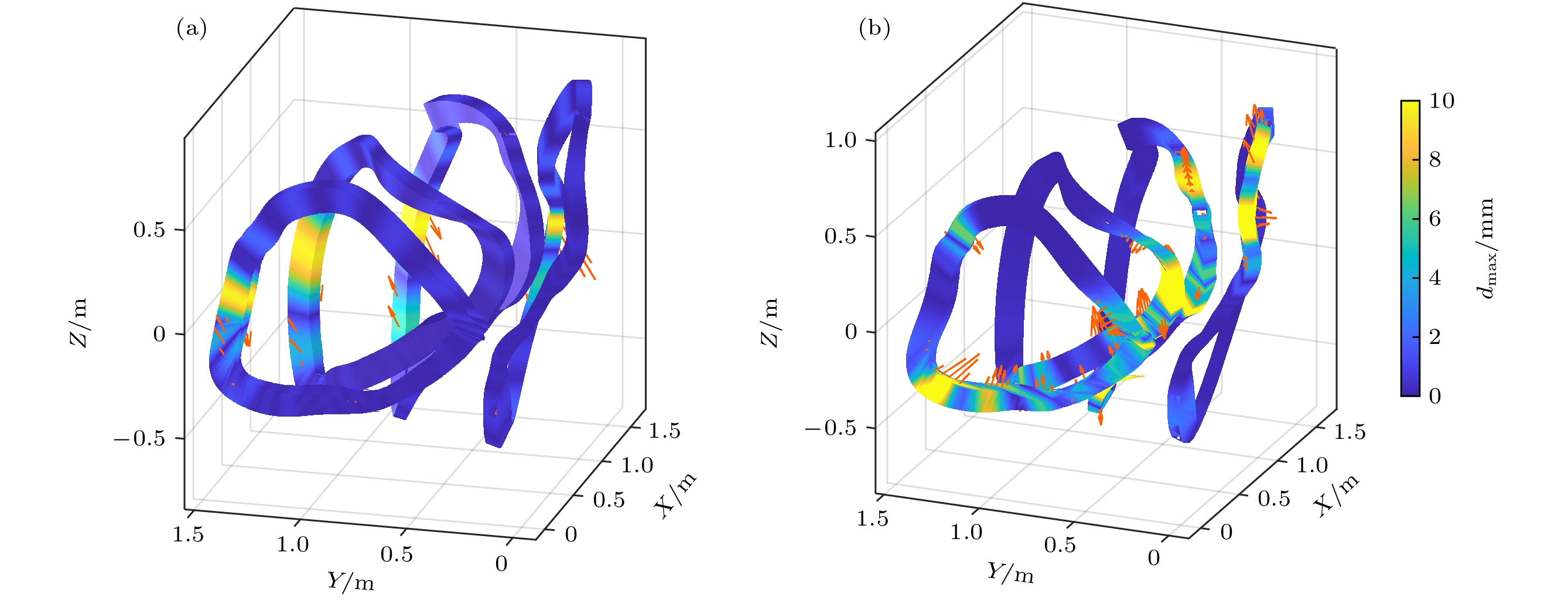
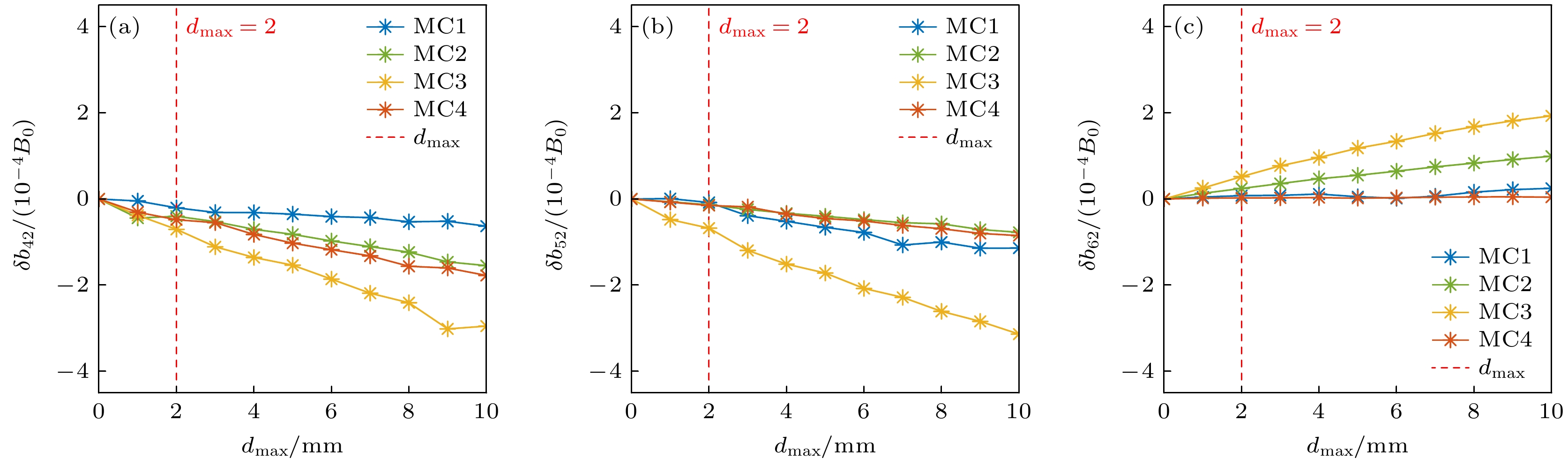
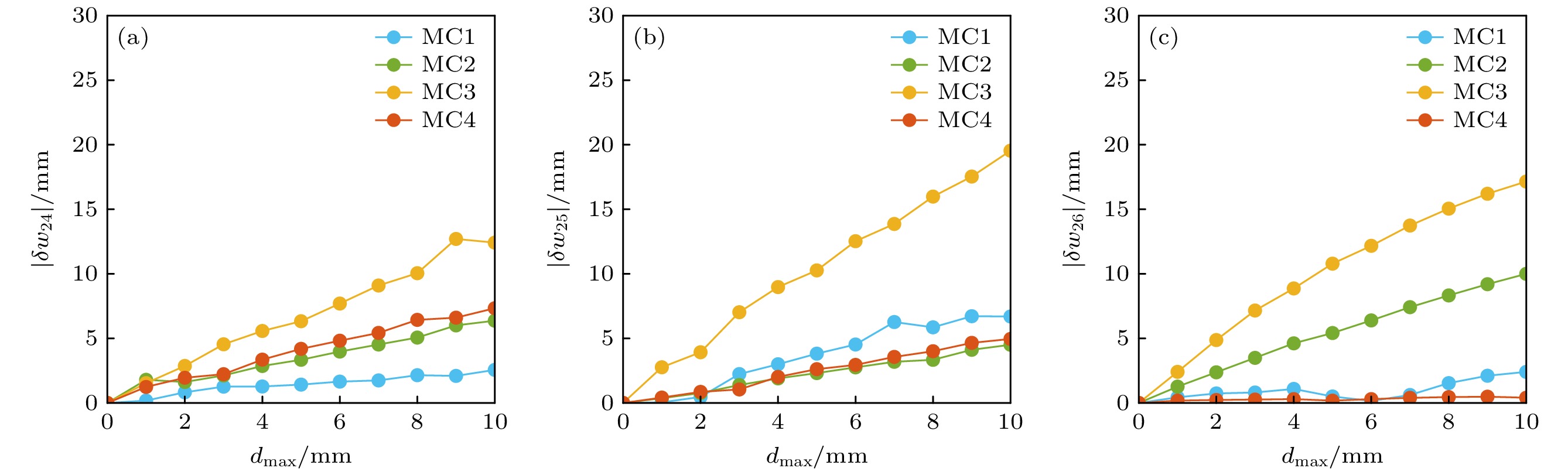
图 4 四种不同类型MC线圈的面内(a)和面外(b)形变分布, 在MC1, MC2, MC3和MC4上设置($ {\delta }_{1} $, $ {\delta }_{2} $) = (0.00003, 0.0001), (0.00002, 0.00009), (0.00002, 0.00009), (0.00004, 0.000095)以产生线圈的面内扰动, 在CCS上设置$ {\delta }_{3} $ = 0.0113, 0.086, 0.094, 0.074以产生面外线圈扰动, 在这两种情况下, 每个MC的最大形变量均为10 mm, $ {\delta }_{1} $, $ {\delta }_{2} $, $ {\delta }_{3} $的数值均为随机选取
Figure 4. Local (a) and broad (b) deformation distributions on four different types of MCs, ($ {\delta }_{1} $, $ {\delta }_{2} $) = (0.00003, 0.0001), (0.00002, 0.00009), (0.00002, 0.00009), (0.00004, 0.000095) are set on MC1, MC2, MC3 and MC4 to produce local perturbations of coils and $ {\delta }_{3} $ = 0.0113, 0.086, 0.094, 0.074 are set on MC1, MC2, MC3, MC4 to produce broad perturbations of coils. For these two cases the maximum deformation of each MC is 10 mm.
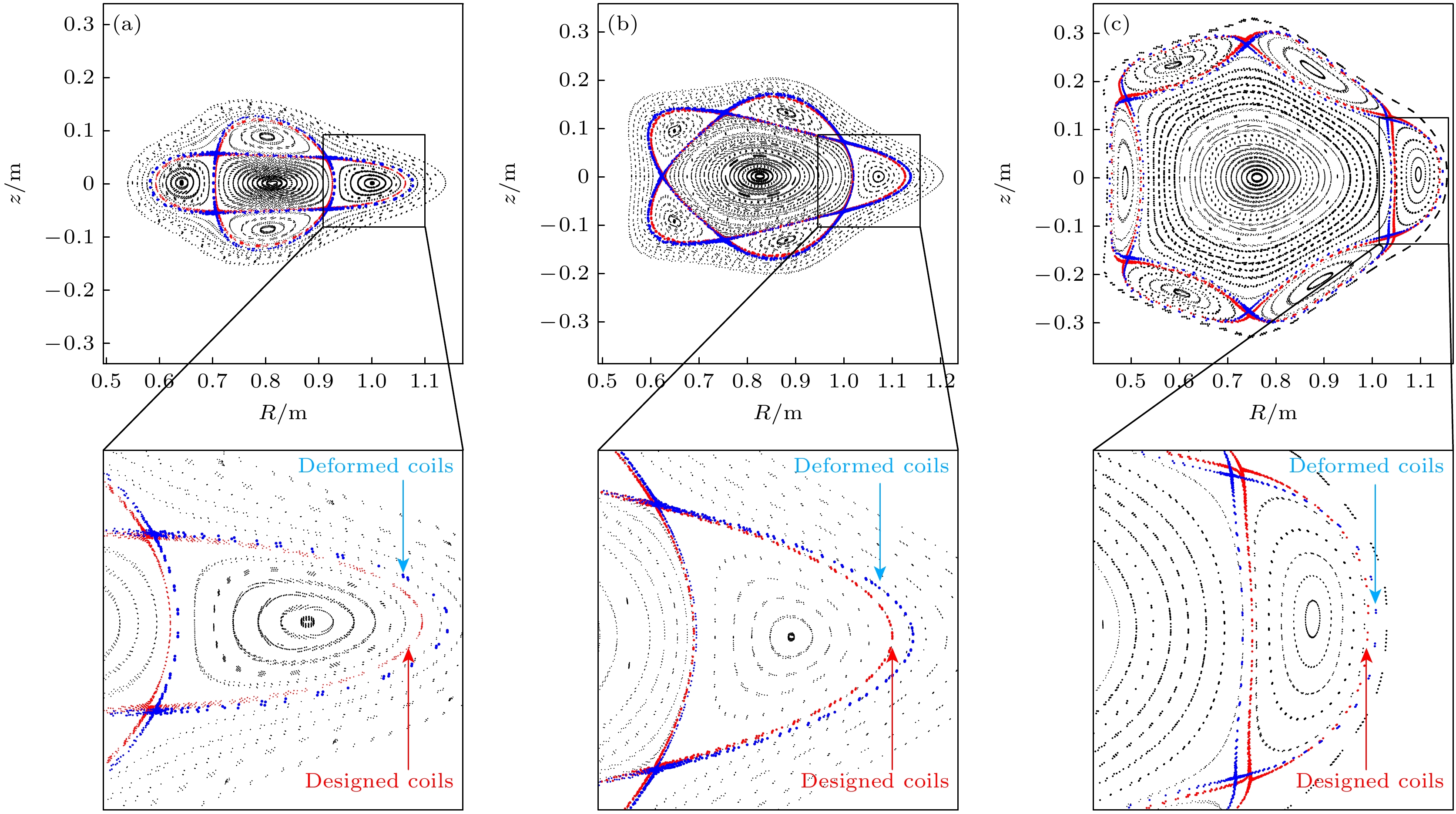
图 5 扰动MC1线圈使其产生最大形变量为10 mm时的3种 (n/m = 2/4 (a), 2/5 (b), 2/6 (c))磁岛位形的庞加莱截图, 红色虚线和蓝色虚线分别表示由理想线圈产生的磁岛边界和MC1线圈发生形变时的磁岛边界. 场线数值与图4相同
Figure 5. Poincaré plots of three island configurations with n/m = 2/4 (a), 2/5 (b), 2/6 (c) produced by perturbed MC1 with the maximum deviations of 10 mm (other coils sustain undeformed). Red and blue dots denote boundaries of the island chains induced by designed coils and the deformed MCs. Numerical details for field line tracing are the same as shown in Fig. 4.
表 1 CFQS中3种磁岛位形下, 模块化线圈、环向场线圈和极向场线圈的电流设置
Table 1. Coil currents in MCs, TFCs, and PFCs for n/m = 2/4, 2/5, and 2/6 magnetic island configurations of CFQS.
磁岛位形(n/m) 2/4 2/5 2/6 线
圈
电
流IMC/kA MC1 312.5 312.5 406.3 MC2 312.5 312.5 281.6 MC3 312.5 312.5 281.6 MC4 312.5 312.5 281.6 ITFC/kA TFC_10 –60 –24 0 TFC_32 –90 –36 0 TFC_70 –90 –36 0 IPFC/kA PFC_OV 0 0 –82 PFC_IV 0 0 41 -
[1] Rummel T, Risse K, Viebke H, Braeuer T, Kisslinger J 2004 IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 14 1394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiong G Z, Xu Y H, Isobe M, Shimizu A, Ogawa K, Kinoshita S, Liu H F, Wang X Q, Cheng J, Liu H, Huang J, Zhang X, Zhang Y C, Yin D P, Wang A Z, Okamura S, Tang C J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 035020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shoji M, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Xu Y H, Liu H F 2023 Plasma Fusion Res. 18 2405026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boozer A H 2005 Rev. Mod. Phys. 76 1071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Waelbroeck F L 2009 Nucl. Fusion 49 104025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lazerson S A, Bozhenkov S, Israeli B, Otte M, Niemann H, Bykov V, Endler M, Andreeva T, Ali A, Drewelow P, Jakubowski M, Sitjes A P, Pisano F, Cannas B, W7-X Team 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 124002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kißlinger J, Andreevab T 2005 Fusion Eng. Des. 74 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Andreeva T, Bräuer T, Endler M, Kißlinger J, Toussaint U V 2009 Fusion Eng. Des. 84 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yamazaki K, Yanagi N, Ji H, Kaneko H, Ohyabu N, Satow T, Morimoto S, Yamamoto J, Motojima O, the LHD Design Group 1993 Fusion Eng. Des. 20 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Strykowsky R L, Brown T, Chrzanowski J, Cole M, Heitzenroeder P, Neilson G H, Rej D, Viol M 2009 23rd IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering San Diego, CA, USA, June 01–05, 2009 p1
[11] Brooks A, Reiersen W 2003 20th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering San Diego, CA, USA, 14–17 October, 2003 p553
[12] Nührenberg J, Sindoni E, Lotz W, Troyon F, Gori S, Vaclavik J 1994 Proceedings of the Joint Varenna Lausanne International Workshop on Theory of Fusion Plasmas Varenna, Italy, August 22–26, 1994 p3
[13] Garabedian P 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 2483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Huang J, Nakata M, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Isobe M, Okamura S, Liu H F, Wang X Q, Zhang X, Liu H, Cheng J, Tang C J 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 052505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu Y H, Liu H F, Xiong G Z, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Nakata M, Yin D, Wan Y, Wilfred, Cooper A, Zhu C X, Liu H, Zhang X, Huang J, Wang X Q, Tang C J 2018 27th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference Ahmedabad, India, October 22–27, 2018 p5
[16] Isobe M, Shimizu A, Liu H F, Liu H, Xiong G Z, Yin D P, Ogawa K, Yoshimura Y, Nakata M, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Tang C J, Xu Y H, the CFQS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3402074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang X Q, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Isobe M, Okamura S, Todo Y, Wang H, Liu H F, Huang J, Zhang X 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 036021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 黄捷, 李沫杉, 覃程, 王先驱 2022 71 185202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J, Li M S, Qin C, Wang X Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 185202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 苏祥, 王先驱, 符添, 许宇鸿 2023 72 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su X, Wang X Q, Fu T, Xu Y H 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 215205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhu C X, Gates D A, Hudson S R, Liu H F, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Okamura S 2019 Nucl. Fusion 59 126007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shimizu A, Liu H F, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Ogawa K, Nakata M, Satake S, Suzuki C, Xiong G Z, Xu Y H, Liu H, Zhang X, Huang J, Wang X Q, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y, the CFQS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3403151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 065008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Lazerson S A, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 054016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Okamura S, Liu H F, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Xiong G Z, Xu Y H 2020 J. Plasma Phys. 86 815860402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Okamura S, Ogawa K, Nakata M, Yoshimura Y, Suzuki C, Osakabe M, Murase T, Nakagawa S, Tanoue H, Xu Y H, Liu H F, Liu H, Huang J, Wang X Q, Cheng J, Xiong G Z, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y 2022 Nucl. Fusion 62 016010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu H F, Shimizu A, Xu Y H, Okamura S, Kinoshita S, Isobe M, Li Y B, Xiong G Z, Wang X Q, Huang J, Cheng J, Liu H, Zhang X, Yin D P, Wang Y, Murase T, Nakagawa S, Tang C J 2021 Nucl. Fusion 61 016014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li Y B, Liu H F, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Kinoshita S, Okamura S, Isobe X, Xiong G Z, Luo Y, Cheng J, Liu H, Wang X Q, Huang J, Zhang X, Yin D P, Wan Y, Tang C J 2020 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 62 125004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu H F, Zhang J, Xu Y H, Shimizu A, Cooper W A, Okamura S, Isobe M, Wang X Q, Huang J, Cheng J, Liu H, Zhang X, Tang C J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 026018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kinoshita S, Shimizu A, Okamura S, Isobe M, Xiong G Z, Liu H F, Xu Y H, the CQFS Team 2019 Plasma Fusion Res. 14 3405097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu H F, Shimizu A, Isobe m, Okamura S, Nishimura s, Suzuki C, Xu Y H, Zhang X, Liu B , Huang J, Wang X Q, Liu H, Tang C J, Yin D P, Wan Y, the CFQS Team 2018 Plasma Fusion Res. 13 3405067
[31] Boozer A H 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 025001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pedersen T S, Otte M, Lazerson S, Helander P, Bozhenkov S, Biedermann C, Klinger T, Wolf R C, Bosch F S, the Wendelstein 7-X Team 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Merkel P 1987 Nucl. Fusion 27 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhu C X, Hudson S R, Song Y T, Wan Y X 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 016008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Drevlak M 1998 Fusion Technol. 33 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Wechsung F, Giuliani A, Landreman M, Cerfon A, Stadler G 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 105021
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 1659
- PDF Downloads: 55
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: