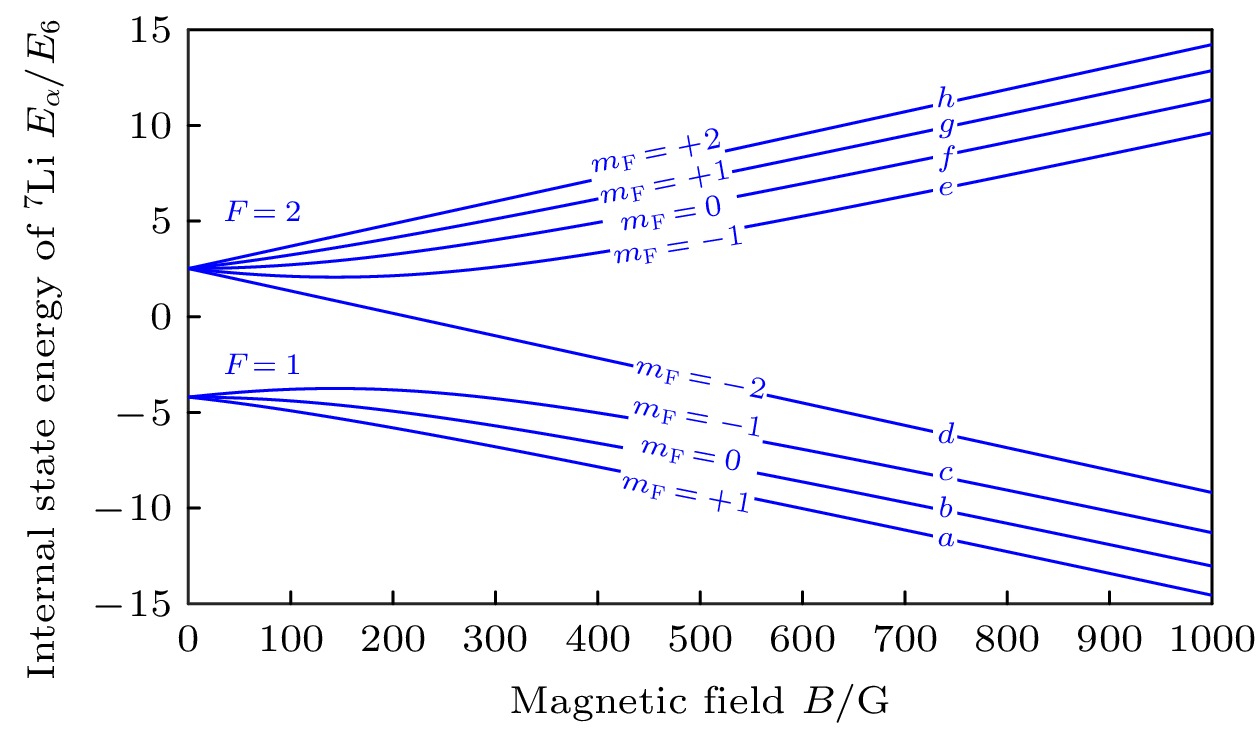
-
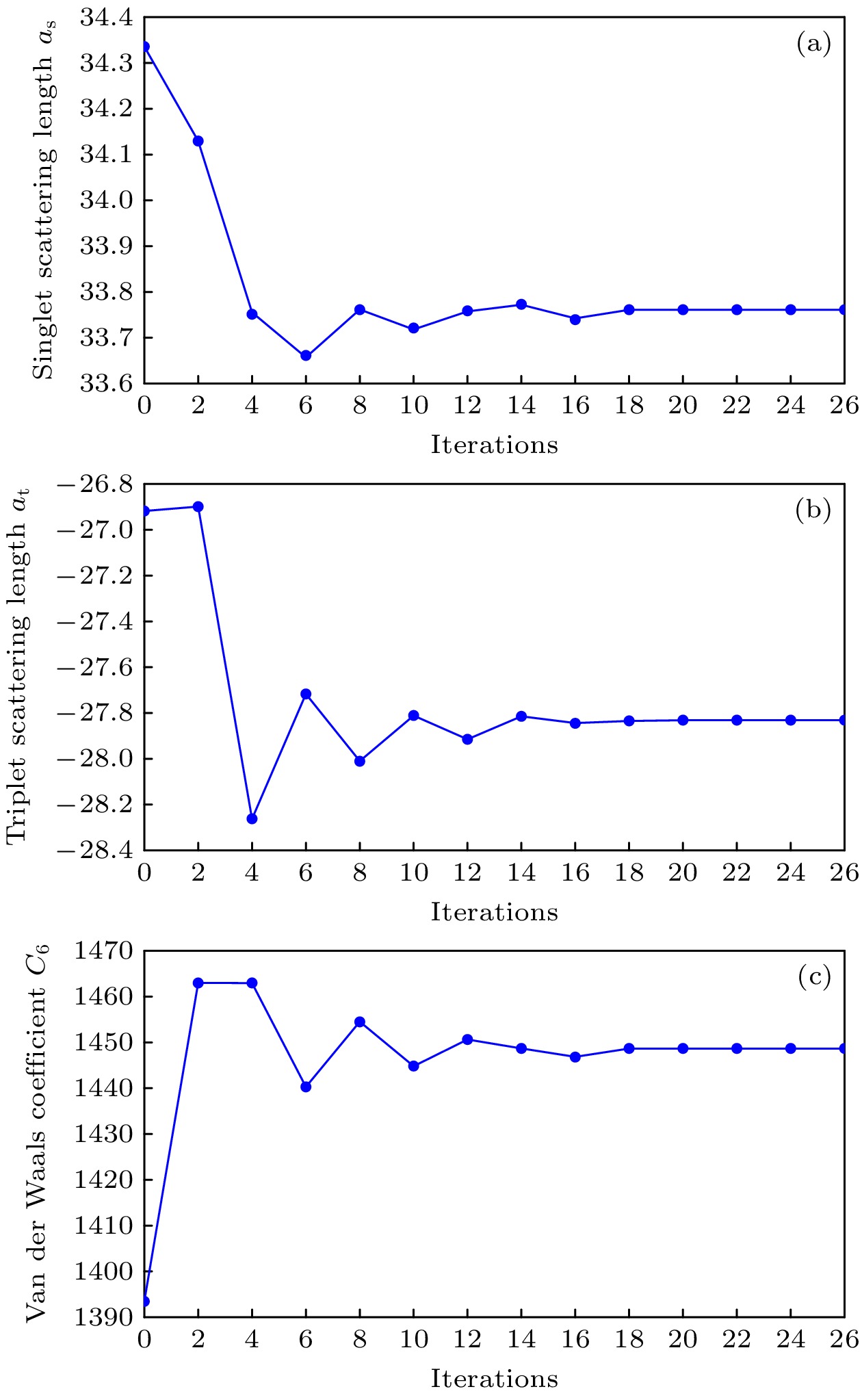
Feshbach resonance is a fundamental phenomenon in cold atomic physics, where interatomic interactions can be precisely changed into a scattering resonance by varying an external magnetic field. This effect plays a crucial role in ultracold atomic experiments, enabling the control of interaction strength, the formation of molecular bound states, and the realization of strongly correlated quantum systems. With the rapid development of cold atom experiments, numerous Feshbach resonances corresponding to different partial waves, such as s-wave, p-wave, and even higher partial wave ones, have been experimentally identified. While s-wave resonances have been widely utilized due to their isotropic nature and strong coupling, and higher partial-wave resonances (including p-wave and d-wave resonances), provide unique opportunities for exploring anisotropic interactions and novel quantum phases. In this study, by using the multichannel quantum defect theory (MQDT), we predict that two d-wave Feshbach resonances are existent in 7Li at 1039.24 G and 1055.64 G, repectively. Physical properties of the two resonances are presented, such as the resonance width and closed channel dimer energy. In addition, we optimize the computational parameters by using the Nelder-Mead algorithm and investigate the possible resonance splitting induced by dipole-dipole interactions in higher partial waves. The presence of these d-wave resonances at high magnetic fields provides a new platform for investigating the interplay between higher-order partial wave interactions and quantum many-body effects. Our results provide opportunities for investigating the effects of higher partial wave Feshbach resonances in high magnetic fields. Our theoretical predictions thus serve as a useful reference for future experimental studies of higher-order resonance phenomena in lithium and other atomic species.
-
Keywords:
- Feshbach resonance /
- multichannel quantum defect theory
[1] Schrödinger E 1926 Annalen der Physik 79 734
[2] Chu S, Bjorkholm J E, Ashkin A, Cable A 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Phillips W D, Metcalf H 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 48 596
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Moerdijk A J, Verhaar B J, Axelsson A 1995 Phys. Rev. A 51 4852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Feshbach H 1958 Ann. Phys. 5 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yao X C, Qi R, Liu X P, Wang X Q, Wang Y X, Wu Y P, Chen H Z, Zhang P, Zhai H, Chen Y A, Pan J W 2019 Nat. Phys. 15 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bartenstein M, Altmeyer A, Riedl S, Geursen R, Jochim S, Chin C, Denschlag J H, Grimm R, Simoni A, Tiesinga E, Williams C J, Julienne P S 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Strecker K E, Partridge G B, Hulet R G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 080406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Regal C A, Ticknor C, Bohn J L, Jin D S 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 053201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang R, Yan S, Song H, Guo H, Ning C 2024 Nat. Commun. 15 3858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Schwartz I, Shimazaki Y, Kuhlenkamp C, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Kroner M, Imamoğlu A 2021 Science 374 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Koch J, Menon K, Cuestas E, Barbosa S, Lutz E, Fogarty T, Busch T, Widera A 2023 Nature 621 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Margulis B, Horn K P, Reich D M, Upadhyay M, Kahn N, Christianen A, van der Avoird A, Groenenboom G C, Meuwly M, Koch C P, Narevicius E 2023 Science 380 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yudkin Y, Elbaz R, D’ Incao J P, Julienne P S, Khaykovich L 2024 Nat. Commun. 15 2127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Köhler T, Góral K, Julienne P S 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bruun G M, Pethick C J 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 140404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Aymar M, Greene C H, Luc-Koenig E 1996 Rev. Mod. Phys. 68 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Makrides C, Gao B 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 062718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Julienne P S, Hutson J M 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 052715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Stoof H T C, Koelman J M V A, Verhaar B J 1988 Phys. Rev. B 38 4688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gao B 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cavagnero M J 1994 Phys. Rev. A 50 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gao B 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 2778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gao B, Tiesinga E, Williams C J, Julienne P S 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 042719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gao B 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 012702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao B 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 012702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gao B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 022706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Góral K, Köhler T, Gardiner S A, Tiesinga E, Julienne P S 2004 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 37 3457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chin C, Grimm R, Julienne P, Tiesinga E 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 1225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gaebler J P, Stewart J T, Bohn J L, Jin D S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 200403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Weckesser P, Thielemann F, Wiater D, Wojciechowska A, Karpa L, Jachymski K, Tomza M, Walker T, Schaetz T 2021 Nature 600 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fey C, Schmelcher P, Imamoglu A, Schmidt R 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 195417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Strecker K E, Partridge G B, Truscott A G, Hulet R G 2002 Nature 417 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Inouye S, Andrews M, Stenger J, Miesner H J, Stamper-Kurn D M, Ketterle W 1998 Nature 392 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lagarias J C, Reeds J A, Wright M H, Wright P E 1998 SIAM J. Optim. 9 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pollack S E, Dries D, Junker M, Chen Y P, Corcovilos T A, Hulet R G 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 090402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
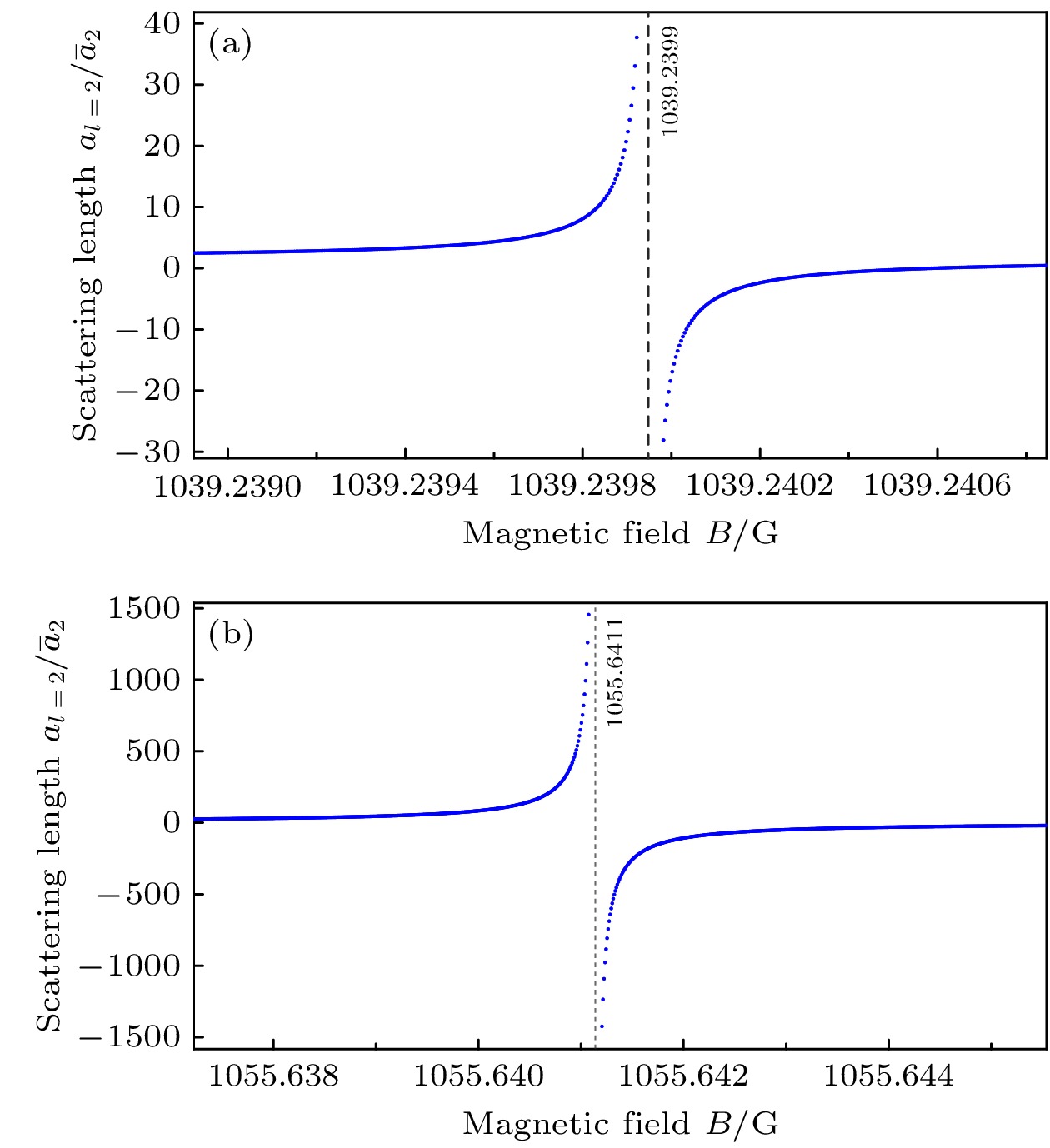
图 2 7Li原子d波广义散射长度$ a_2 $在两个共振磁场(a) 1039.24和(b) 1055.64 G附近随磁场的变化. 图中黑色虚线标注出了共振的位置
Figure 2. The d-wave generalized scattering length $ a_2 $ for 7Li atoms vs. the external magnetic field B in the vicinity of two resonances at (a) 1039.24 and (b) 1055.64 G. The black dashed lines represent the resonance points.
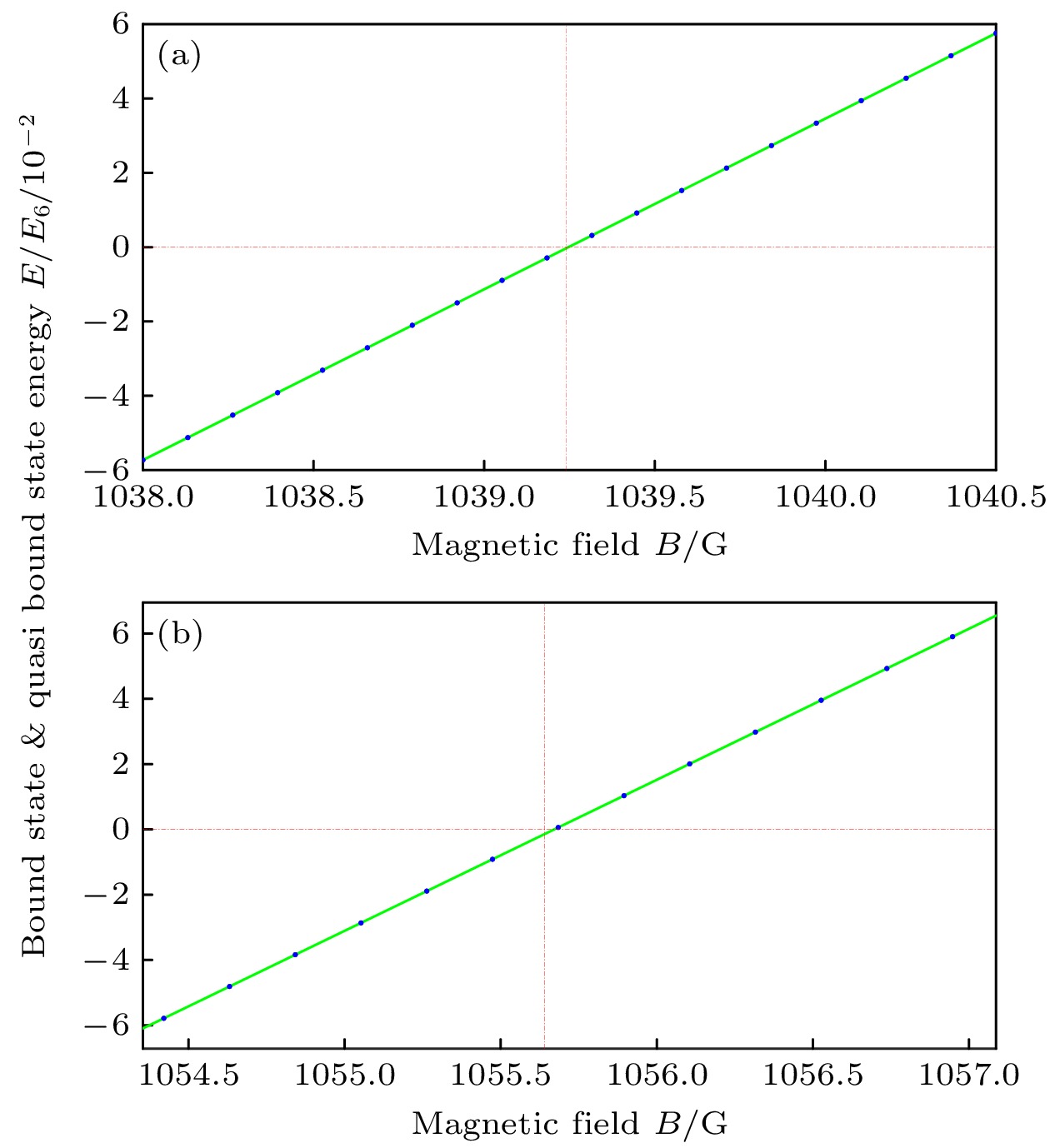
图 3 闭通道中低能束缚态能量$ E_{\mathrm{b}} $在两个共振磁场(a) 1039.24和(b) 1055.64 G附近随磁场的变化. 蓝色点为计算的数据点, 绿色线是线性拟合的数据, 红色虚线标记共振点的位置
Figure 3. Energy $ E_{\mathrm{b}} $ of the low energy bound state in the closed channels vs. the external magnetic field B in the vicinity of the two resonances at (a) 1039.24 and (b) 1055.64 G
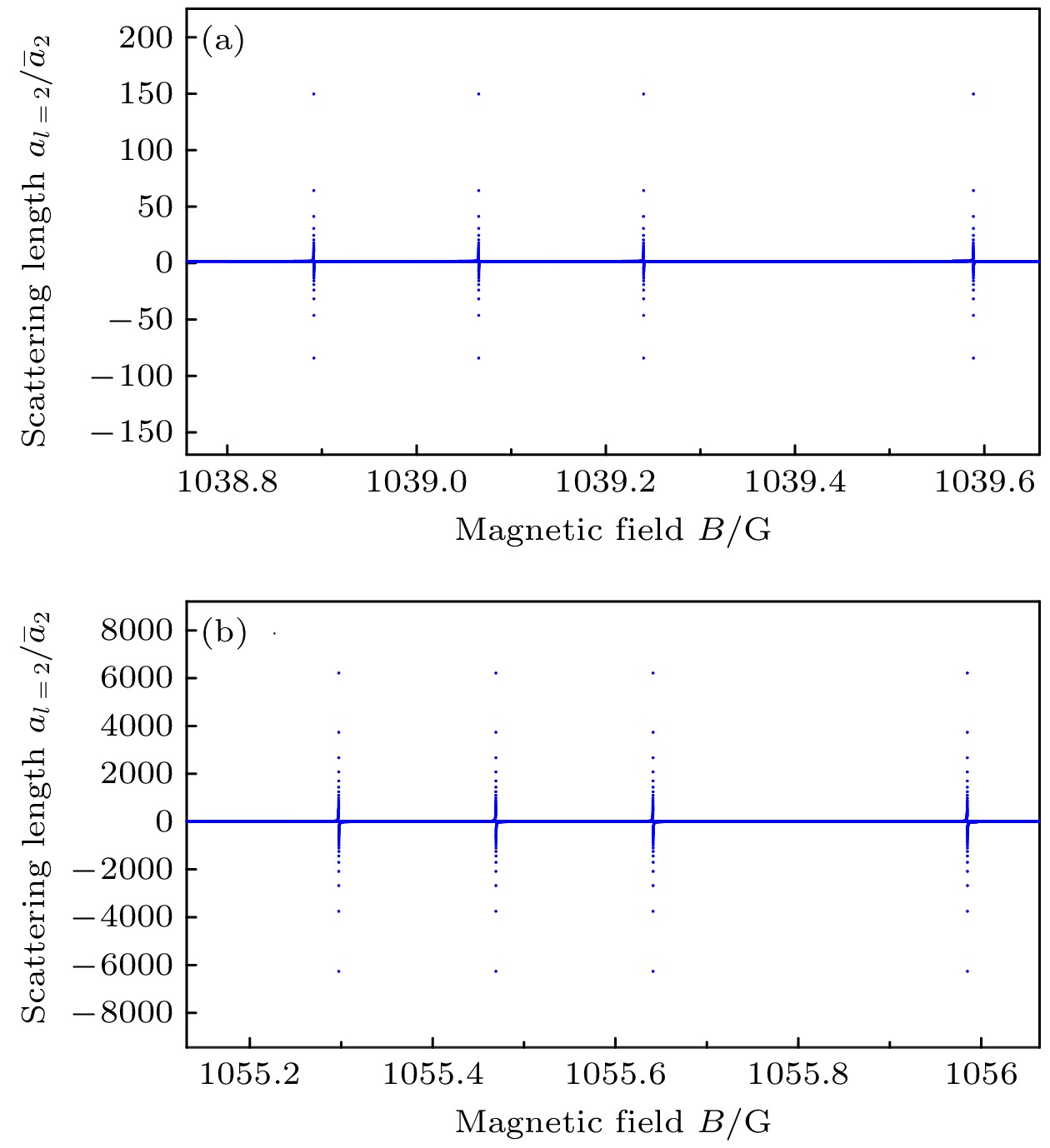
图 4 磁偶极矩相互作用导致的共振点劈裂. 两子图中$ a_2 $发散的磁场从小到大分别对应于$ m = 0 $, $ m = 1 $, 不考虑劈裂, $ m = 2 $的共振点位置
Figure 4. Resonance splittings due to the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction. In the plots the divergences of $ a_2 $ correspond to the resonances of $ m = 0 $, $ m = 1 $, no splitting, and $ m = 2 $ from small B to big B.
表 1 7Li的d波Feshbach共振
Table 1. d-wave Feshbach resonances in 7Li
B0 /G $ {a}_{2, {\mathrm{bg}}} $/$ \bar a_{2} $ Δ/G $ {\text{δ}}\mu/\mu_0 $ sres ζ 1039.24 1.529 $ 6.397 \times 10^{-4} $ 3.924 $ 2.19 \times 10^{-4} $ $ 6.49 \times 10^{-11} $ 1055.64 1.529 0.0615 3.953 0.021 $ 6.29 \times 10^{-9} $ 表 A1 7Li和23Na的Feshbach共振
Table A1. Feshbach resonances in 7Li and 23Na.
表 C1 不同原子的Feshbach共振
Table C1. Feshbach resonances in other alkali atoms.
元素 入射通道 l $ B_{0} $/G $ a_{l, {\mathrm{bg}}}/\bar a_l $ Δ/G 7Li ab p 977.12 1.1 121.1 d 72.9 2.63 148.3 7Li bc p 514.3 –1.235 –61.07 1083 –1.3 –15.85 23Na aa d 578.7 –1.179 –0.04575 656.2 –8.462 –0.1149 23Na ab s 977.1 1.464 $ 3.689\times 10^{-3} $ p 880.1 1.753 0.1491 d 694.3 –1.147 –0.05086 23Na bc s 1017 –1.152 –0.0523 -
[1] Schrödinger E 1926 Annalen der Physik 79 734
[2] Chu S, Bjorkholm J E, Ashkin A, Cable A 1986 Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Phillips W D, Metcalf H 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 48 596
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Moerdijk A J, Verhaar B J, Axelsson A 1995 Phys. Rev. A 51 4852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Feshbach H 1958 Ann. Phys. 5 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yao X C, Qi R, Liu X P, Wang X Q, Wang Y X, Wu Y P, Chen H Z, Zhang P, Zhai H, Chen Y A, Pan J W 2019 Nat. Phys. 15 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bartenstein M, Altmeyer A, Riedl S, Geursen R, Jochim S, Chin C, Denschlag J H, Grimm R, Simoni A, Tiesinga E, Williams C J, Julienne P S 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Strecker K E, Partridge G B, Hulet R G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 080406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Regal C A, Ticknor C, Bohn J L, Jin D S 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 053201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang R, Yan S, Song H, Guo H, Ning C 2024 Nat. Commun. 15 3858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Schwartz I, Shimazaki Y, Kuhlenkamp C, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Kroner M, Imamoğlu A 2021 Science 374 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Koch J, Menon K, Cuestas E, Barbosa S, Lutz E, Fogarty T, Busch T, Widera A 2023 Nature 621 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Margulis B, Horn K P, Reich D M, Upadhyay M, Kahn N, Christianen A, van der Avoird A, Groenenboom G C, Meuwly M, Koch C P, Narevicius E 2023 Science 380 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yudkin Y, Elbaz R, D’ Incao J P, Julienne P S, Khaykovich L 2024 Nat. Commun. 15 2127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Köhler T, Góral K, Julienne P S 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bruun G M, Pethick C J 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 140404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Aymar M, Greene C H, Luc-Koenig E 1996 Rev. Mod. Phys. 68 1015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Makrides C, Gao B 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 062718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Julienne P S, Hutson J M 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 052715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Stoof H T C, Koelman J M V A, Verhaar B J 1988 Phys. Rev. B 38 4688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gao B 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cavagnero M J 1994 Phys. Rev. A 50 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gao B 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 2778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gao B, Tiesinga E, Williams C J, Julienne P S 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 042719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gao B 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 012702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao B 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 012702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gao B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 022706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Góral K, Köhler T, Gardiner S A, Tiesinga E, Julienne P S 2004 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 37 3457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chin C, Grimm R, Julienne P, Tiesinga E 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 1225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gaebler J P, Stewart J T, Bohn J L, Jin D S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 200403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Weckesser P, Thielemann F, Wiater D, Wojciechowska A, Karpa L, Jachymski K, Tomza M, Walker T, Schaetz T 2021 Nature 600 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fey C, Schmelcher P, Imamoglu A, Schmidt R 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 195417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Strecker K E, Partridge G B, Truscott A G, Hulet R G 2002 Nature 417 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Inouye S, Andrews M, Stenger J, Miesner H J, Stamper-Kurn D M, Ketterle W 1998 Nature 392 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Lagarias J C, Reeds J A, Wright M H, Wright P E 1998 SIAM J. Optim. 9 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pollack S E, Dries D, Junker M, Chen Y P, Corcovilos T A, Hulet R G 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 090402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2321
- PDF Downloads: 70
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: