-
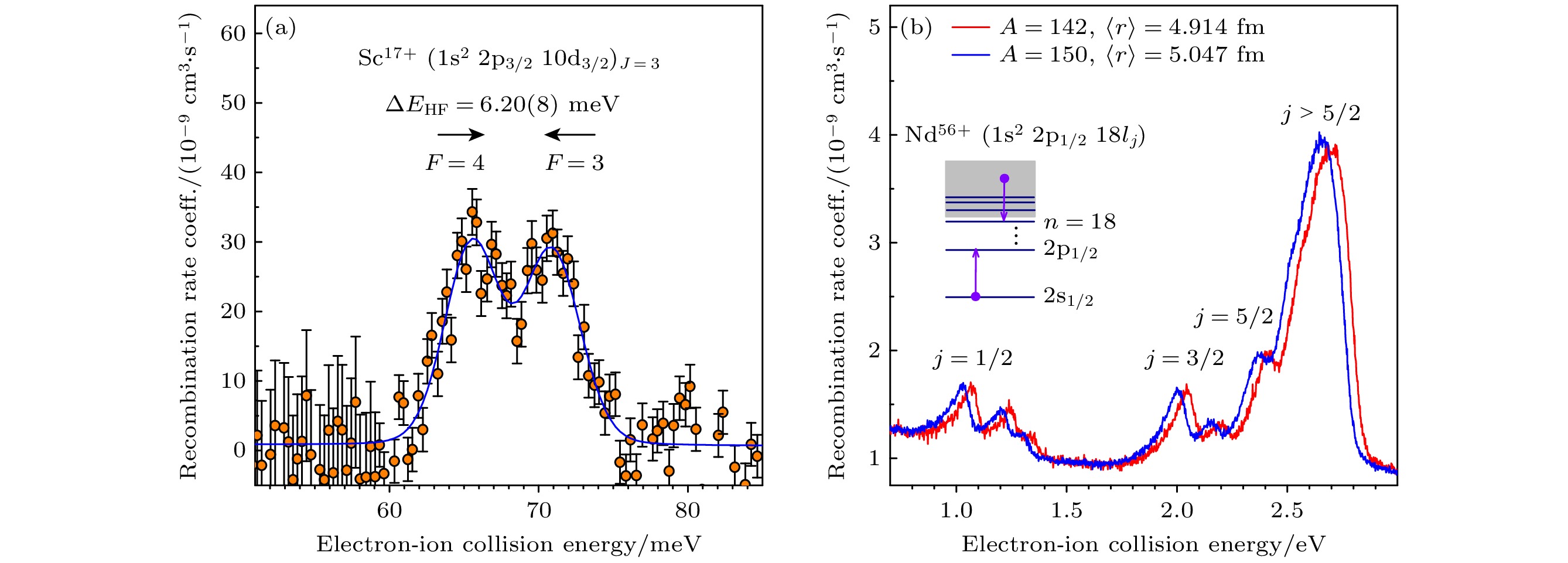
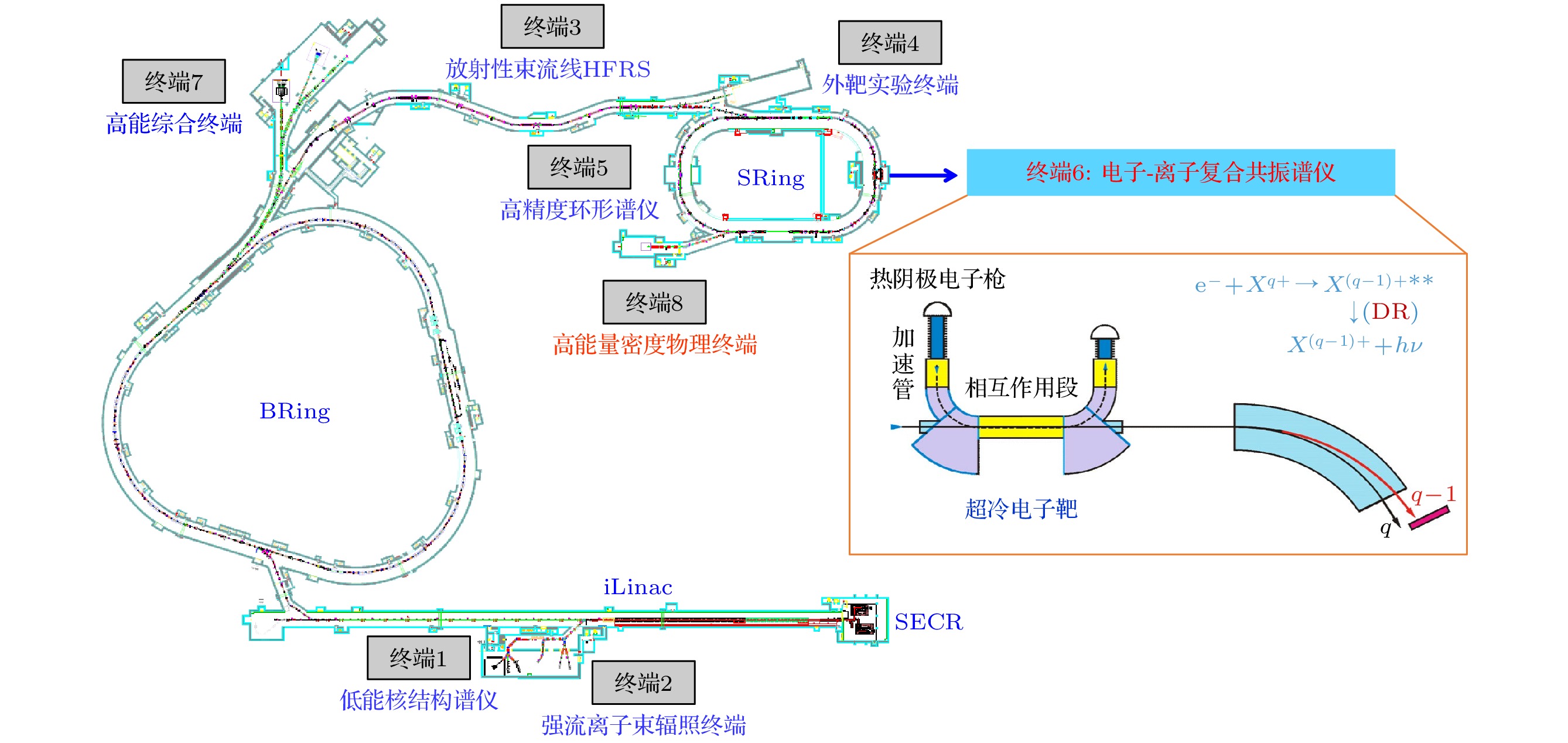
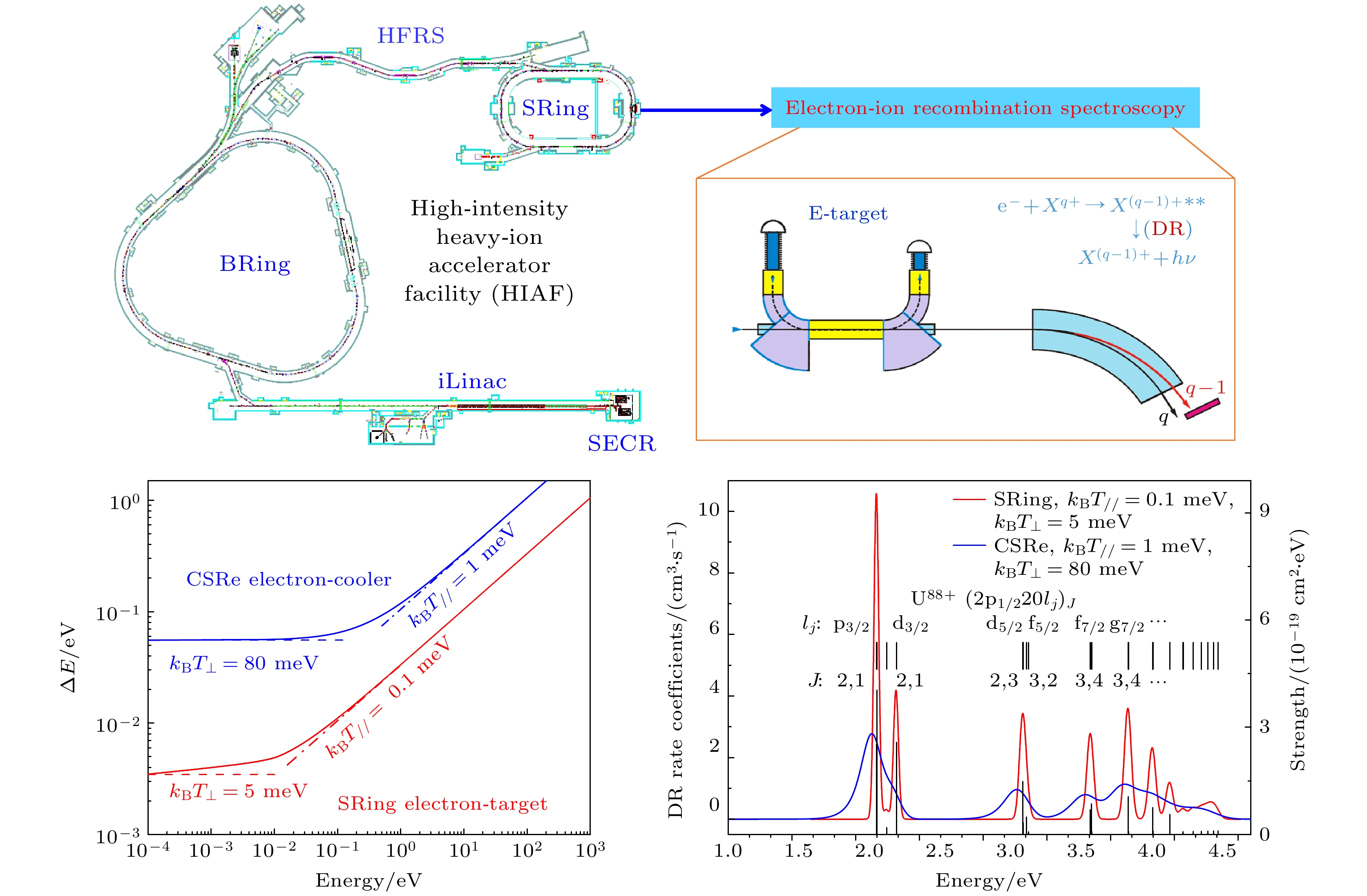
Dielectronic recombination (DR) experiments of highly charged ions not only provide essential atomic benchmark data for astrophysical and fusion plasma research but also serve as a stringent test for strong-field quantum electrodynamics (QED) effects, relativistic effects, and electron correlation effects. High-intensity heavy-ion accelerator facility (HIAF), currently under construction at Huizhou, China, will have a high-precision spectrometer ring (SRing) equipped with a 450 kV electron-cooler and an 80 kV ultracold electron-target. This advanced setup facilitates precise measurements of the DR process for highly charged ions in a broad range of center-of-mass energy, from meV to tens of keV. In this work, we carry out the molecular dynamics simulation of the electron beam temperature distribution of the ultracold electron-target at the SRing. The simulation results indicate that after treatment by the designed adiabatic magnetic field and acceleration field, the transverse and longitudinal electron beam temperature generated by the thermionic electron gun can be reduced from 100 meV to below 5 meV and 0.1 meV, respectively. Furthermore, we analyze the influence of this ultracold electron beam temperature on the resonance peak and energy resolution in DR experiment. The resolution gain at the SRing electron-target is particularly pronounced at small electron-ion collision energy, which provides unique experimental conditions for the DR experiments. Taking lithium-like $ {}_{~\,54}^{129}{{\mathrm{X}}{\mathrm{e}}}^{51+} $ and $ {}_{~\,92}^{238}{{\mathrm{U}}}^{89+} $ ions for example, we simulate the DR resonance spectra at the SRing and compare them with the simulated results from the experimental cooler storage ring CSRe. The results reveal that the SRing experiments can resolve fine DR resonance structures with ultra-high energy resolution compared with those from the CSRe. This work lays a solid foundation for precise DR spectroscopy of highly charged ions at the SRing to stringent test of strong field QED effect and extraction nuclear structure information.
-
Keywords:
- highly charged ions /
- storage ring /
- dielectronic recombination /
- ultracold electron-target /
- strong-field quantum electrodynamics effect
[1] Savin D W, Bartsch T, Chen M H, Kahn S M, Liedahl D A, Linkemann J, Müller A, Schippers S, Schmitt M, Schwalm D, Wolf A 1997 Astrophys. J. 489 L115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Savin D W, Behar E, Kahn S M, Gwinner G, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Muller A, Schippers S, Badnell N R, Chen M H, Gorczyca T W 2002 Astrophys. J. 138 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Savin D W, Gwinner G, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schnell M, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Zhou S G, Kieslich S, Muller A, Schippers S, Colgan J, Loch S D, Badnell N R, Chen M H, Gu M F 2006 Astrophys. J. 642 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Gwinner G, Grieser M, Repnow R, Saathoff G, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Muller A, Schippers S, Zavodszky P A, Chen M H, Gorczyca T W, Zatsarinny O, Gu M F 2003 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 147 421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Linkemann J, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Brandau C, Hoffknecht A, Muller A, Schippers S, Chen M H, Badnell N R 1999 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 123 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Linkemann J, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Muller A, Schippers S, Chen M H, Badnell N R, Gorczyca T W, Zatsarinny O 2002 Astrophys. J. 576 1098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Schmidt E W, Schippers S, Müller A, Lestinsky M, Sprenger F, Grieser M, Repnow R, Wolf A, Brandau C, Lukić D, Schnell M, Savin D W 2006 Astrophys. J. 641 L157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Larsson M 1995 Rep. Prog. Phys. 58 1267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Phaneuf R A, Havener C C, Dunn G H, Müller A 1999 Rep. Prog. Phys. 62 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lindroth E, Danared H, Glans P, Pešić Z, Tokman M, Vikor G, Schuch R 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 5027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Müller A, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 073202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang S X, Brandau C, Fritzsche S, Fuchs S, Harman Z, Kozhuharov C, Müller A, Steck M, Schippers S 2024 Eur. Phys. J. D 78 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Lestinsky M, Müller A, Schippers S, Stöhlker T 2015 Phys. Scr. 2015 014022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bates D R, Massey H S W 1943 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 239 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Badnell N R, Pindzola M S, Andersen L H, Bolko J, Schmidt H T 1991 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 24 4441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] LaGattuta K, Hahn Y 1981 Phys. Rev. A 24 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brooks R, Datla R, Griem H R 1978 Phys. Rev. Lett. 41 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Müller A, Belić D, DePaola B, Djurić N, Dunn G, Mueller D, Timmer C 1987 Phy. Rev. A 36 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schippers S 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. B 350 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shevelko V, Tawara H 2012 Atomic Processes in Basic and Applied Physics (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer) pp283–306
[21] Schuch R, Böhm S 2007 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88 012002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Xu X, Zhu L F, Chuai X Y, Yuan Y J, Zhu X L, Han X Y, Mao L J, Li J, Ma X M, Yan T L, Yang J C, Xiao G Q, Xia J W, Ma X 2015 Phys. Scr. T166 014023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Huang Z K, Wang S X, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Ma W L, Chen C Y, Zhang C Y, Chen D Y, Huang H K, Shao L, Liu X, Zhou X P, Mao L J, Li J, Ma X M, Tang M T, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Zhang S F, Zhu L F, Ma X W 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 073401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Danared H, Andler G, Bagge L, Herrlander C J, Hilke J, Jeansson J, Källberg A, Nilsson A, Paál A, Rensfelt K G, Rosengård U, Starker J, af Ugglas M 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 3775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lestinsky M, Lindroth E, Orlov D A, Schmidt E W, Schippers S, Böhm S, Brandau C, Sprenger F, Terekhov A S, Müller A, Wolf A 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 033001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schippers S, Schmidt E W, Bernhardt D, Yu D, Muller A, Lestinsky M, Orlov D A, Grieser M, Repnow R, Wolf A 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 033001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Harman Z, et al. 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 073201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Xu X, et al. 2018 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 235 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang S X, Xu X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Khan N, Preval S P, Badnell N R, Schippers S, Mahmood S, Dou L J, Chuai X Y, Zhao D M, Zhu X L, Mao L J, Ma X M, Li J, Mao R S, Yuan Y J, Tang M T, Yin D Y, Yang J C, Ma X, Zhu L F 2018 Astrophys. J. 862 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang S X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, et al. 2019 Astron. Astrophys. 627 A171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang S X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, et al. 2022 Phys. Rev. A 106 042808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang S X, Khan N, Wang H B, Chen C Y, Zhang C Y, Preval S P, Badnell N R, Ma W L, Liu X, Chen D Y, Zhu X L, Zhao D M, Mao L J, Ma X M, Li J, Tang M T, Mao R S, Yin D Y, Yang W Q, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Zhu L F, Ma X 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 邵林, 黄忠魁, 汶伟强, 汪书兴, 黄厚科, 马万路, 刘畅, 汪寒冰, 陈冬阳, 刘鑫, 周晓鹏, 赵冬梅, 张少锋, 朱林繁, 马新文 2024 73 123402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao L, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang S X, Huang H K, Ma W L, Liu C, Wang H B, Chen D Y, Liu X, Zhou X P, Zhao D M, Zhang S F, Zhu L F, Ma X W 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 123402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 马余刚, 赵红卫 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 112001
Ma Y G, Zhao H W 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 50 112001
[35] 马新文, 张少锋, 汶伟强, 杨杰, 朱小龙, 钱东斌, 闫顺成, 张鹏鸣, 郭大龙, 汪寒冰, 黄忠魁 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma X W, Zhang S F, Wen W Q, Yang J, Zhu X L, Qian D B, Yan S C, Zhang P M, Guo D L, Wang H B, Huang Z K 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 50 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Xu X, Wang H B, Dou L J, Chuai X Y, Zhu X L, Zhao D M, Li J, Ma X M, Mao L J, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Xu W Q, Xie L Y, Xu T H, Yao K, Dong C Z, Zhu L F, Ma X 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 408 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Danared H 1995 Phys. Scr. T59 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zaghloul M R 2017 ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 44 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Dou L, Xie L, Zhang D, Dong C, Wen W, Huang Z, Ma X 2017 Euro. Phys. J. D 71 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 李传莹, 刘晓菊, 孟广为, 王建国 2010 59 6044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C Y, Liu X J, Meng G W, Wang J G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 6044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Danared H 1993 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 335 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 张平文, 李铁军 2007 数值分析 (北京: 北京大学出版社) 第161页
Zhang P W, Li T J 2007 Numerical Analysis (Beijing: Beijing University Press) p161
[43] Danared H 1998 Hyperfine Interact. 115 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Zubova N A, Kozhedub Y S, Shabaev V M, Tupitsyn I I, Volotka A V, Plunien G, Brandau C, Stöhlker T 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 啜晓亚, 黄忠魁, 汶伟强, 汪寒冰, 许鑫, 汪书兴, 李冀光, 豆丽君, 赵冬梅, 朱小龙, 冒立军, 殷达钰, 杨建成, 原有进, 马新文 2018 原子核物理评论 35 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chuai X Y, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Xu X, Wang S X, Li J G, Dou L J, Zhao D M, Zhu X L, Mao L J, Yin D Y, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Ma X W 2018 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 35 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
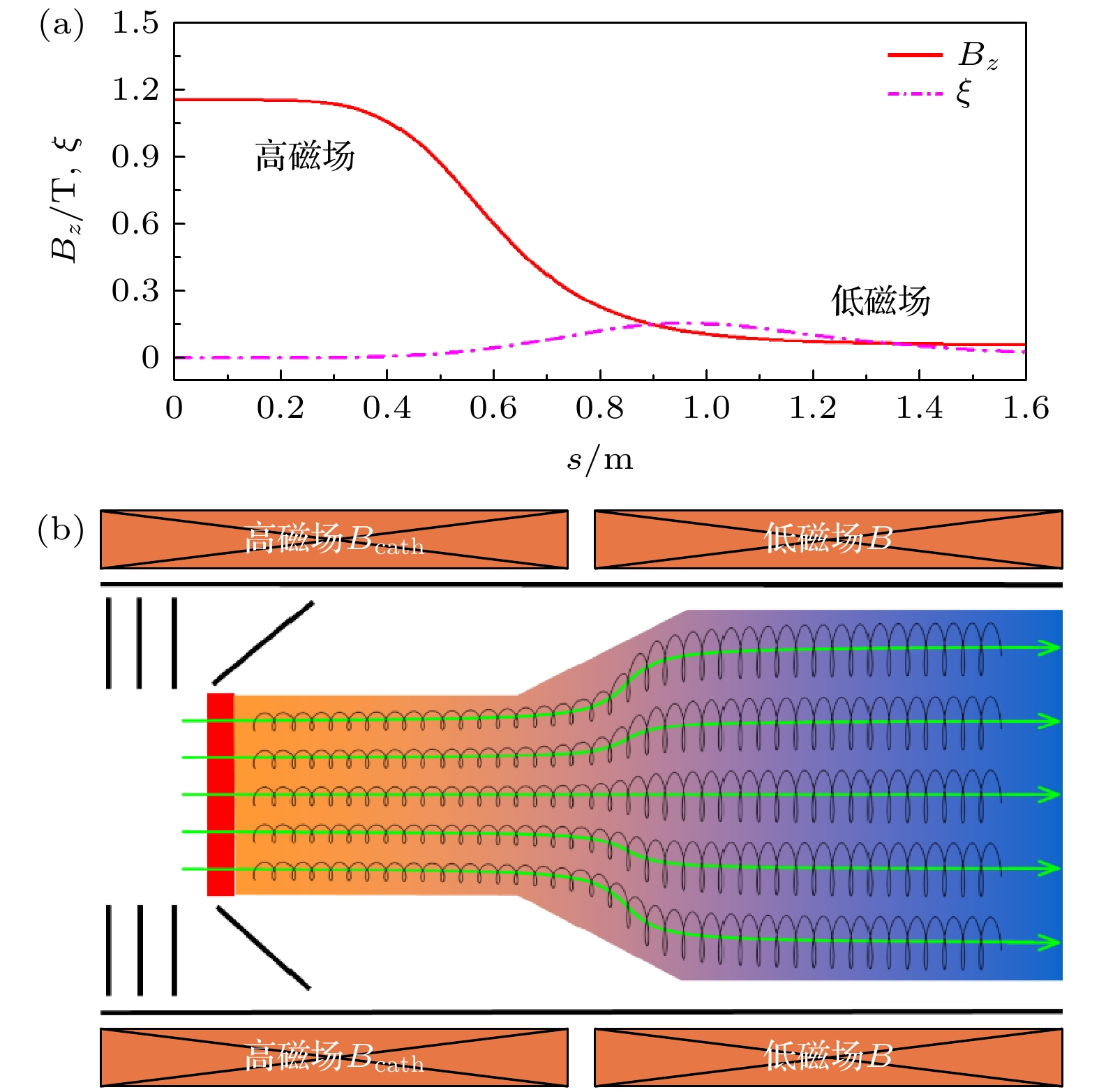
图 4 (a)超冷电子靶装置设计的绝热磁场$ {B}_{z} $和绝热参数$ \xi $的分布图; (b)超冷电子靶的电子束从热阴极发射后, 通过绝热磁场膨胀的示意图. 在引导磁场的作用下, 电子进行拉莫尔进动并经历绝热膨胀. 绿色箭头表示电子的运动轨迹
Figure 4. (a) Designed adiabatic magnetic field $ {B}_{z} $ and adiabatic parameter $ \xi $ of ultracold electron-target as a function of position in the electron-target; (b) schematic illustration of an electron beam emitted from a thermionic cathode within an ultracold electron-target as it traverses the magnetic field. Under the influence of the guiding magnetic field, the electrons undergo Larmor precession and adiabatic expansion. The green arrows indicate the direction of electron motion.
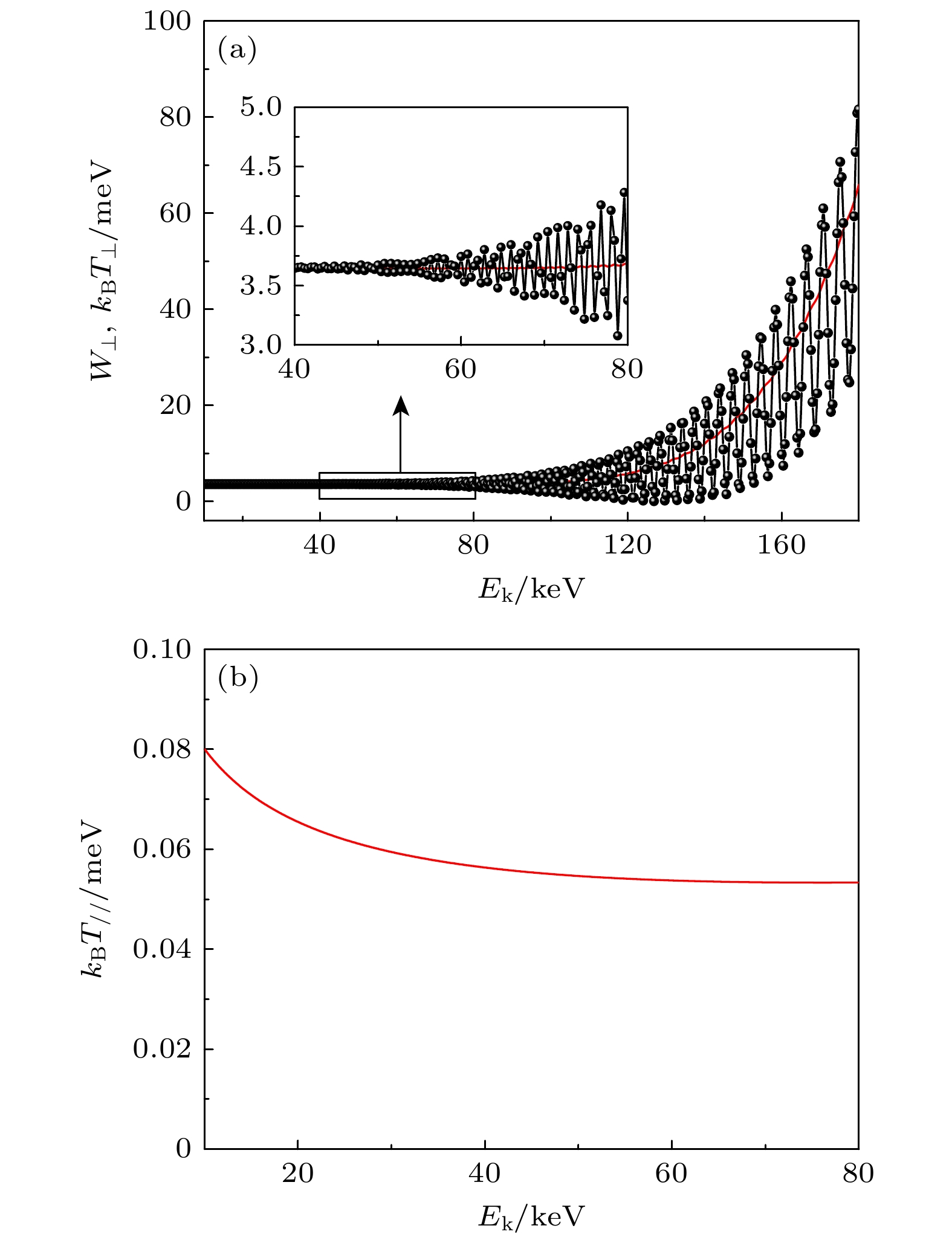
图 5 (a) 单个电子横向动能、电子束横向温度随着电子束能量的变换关系. 黑色点线表示单个电子的横向动能, 红色曲线代表电子束的横向温度. 当电子束的能量低于80 keV时, 电子束在磁场中保持绝热运动状态. (b) 电子束纵向温度随着电子束能量的变换关系
Figure 5. (a) Transverse kinetic energy of the individual electron and transverse temperature of the electron beam as a function of electron beam energy. The black dashed line indicates the transverse kinetic energy of individual electrons, while the red curve represents the transverse temperature of the electron beam. The electron beam maintains adiabatic motion within the magnetic field when the energy of the electron beam is below 80 keV. (b) The longitudinal temperature of the electron beam as a function of electron beam energy.
图 6 SRing (红色实线)和CSRe (蓝色实线)上双电子复合实验的能量分辨率与电子-离子碰撞能量之间的关系. 图中分别标出了横向温度(kBT⊥)、纵向温度(kBT//)对实验分辨的贡献. SRing在低能电子离子碰撞区域(meV级)展现出极高的能量分辨
Figure 6. Energy resolution of DR experiments as a function of electron-ion collision energy at the storage SRing (red solid line) and CSRe (blue solid line). The figure also shows the contributions of transverse temperature (kBT⊥) and longitudinal temperature (kBT//) to the experimental resolution. The DR experiment demonstrates ultra-high energy resolution in the low-energy electron-ion collision region (meV-level).
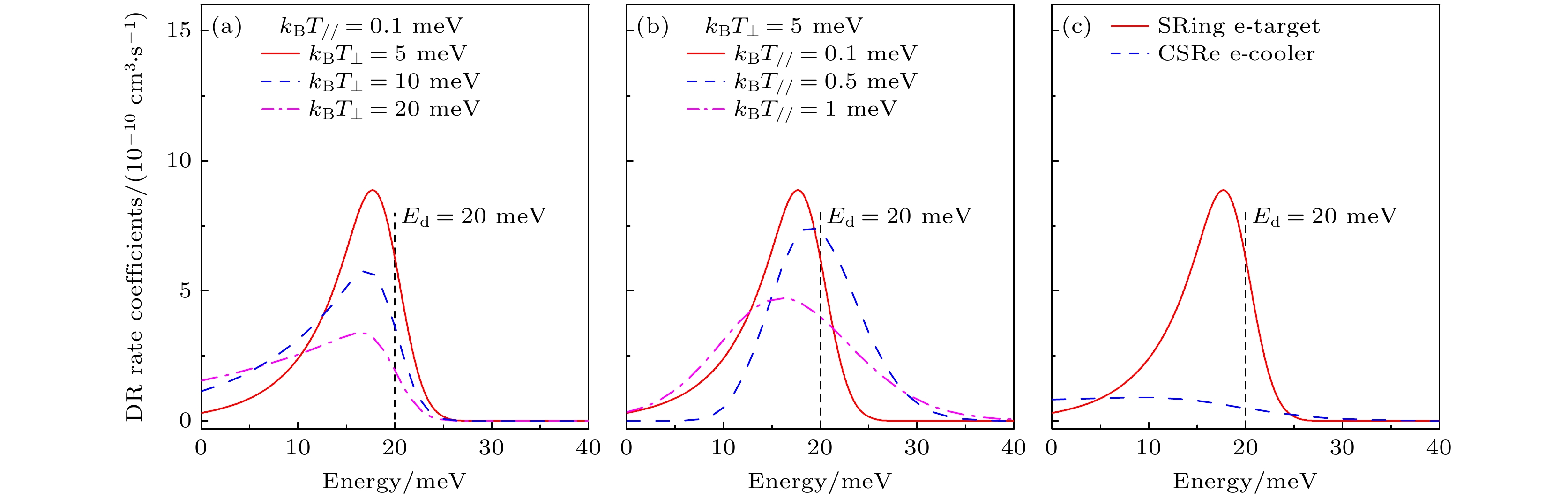
图 7 (a)电子束纵向温度$ {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1\;{\mathrm{meV}} $不变, 不同的电子束横向温度$ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5, {\mathrm{ }}10, {\mathrm{ }}20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $对双电子复合峰型和速率系数的影响, 其中共振峰的能量$ {E}_{{\mathrm{d}}}=20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $, 强度$ S=1\times10^{-18}~\mathrm{cm^2{\cdot}eV} $. (b)电子束横向温度$ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5\;{\mathrm{meV}} $不变, 不同的电子束纵向温度$ {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1, 0.5, 1~{\mathrm{eV}} $对双电子复合峰型和速率系数的影响, 其中共振峰的能量$ {E}_{{\mathrm{r}}{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{s}}}=20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $, 强度$ S=1\times10^{-18}~\mathrm{cm^2{\cdot}eV} $. (c) SRing和CSR在相同共振位置上的共振峰, 其中SRing上的电子束温度为$ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5\;{\mathrm{meV}}, {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1\;{\mathrm{meV}} $, 而CSRe上的电子束温度为$ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=80\;{\mathrm{meV}}, {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=1~{\mathrm{meV}} $
Figure 7. (a) Effect of different transverse temperatures of the electron beam, $ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5, {\mathrm{ }}10, {\mathrm{ }}20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $, on the DR peak shape and rate coefficient when the longitudinal temperature $ {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1\;{\mathrm{meV}} $ is constant, with the resonance energy $ {E}_{{\mathrm{d}}}=20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $ and strength $ S=1\times10^{-18}~\mathrm{cm^2{\cdot}eV} $. (b) Effect of different longitudinal temperatures of the electron beam, $ {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1, 0.5, 1~{\mathrm{meV}} $, on the DR peak shape and rate coefficient when the transverse temperature $ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5\;{\mathrm{meV}} $ is constant, with the resonance energy $ {E}_{{\mathrm{d}}}=20\;{\mathrm{meV}} $ and strength $ S=1\times10^{-18}~\mathrm{cm^2{\cdot}eV} $. (c) Simulation peaks of SRing and CSRe at the same resonance energy, the temperatures used for SRing and CSRe are $ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=5\;{\mathrm{meV}}, {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=0.1\;{\mathrm{meV}} $ and $ {k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}{T}_{\perp }=80\;{\mathrm{meV}}, {{k}_{{\mathrm{B}}}T}_{/ / }=1\;{\mathrm{meV}} $, respectively.
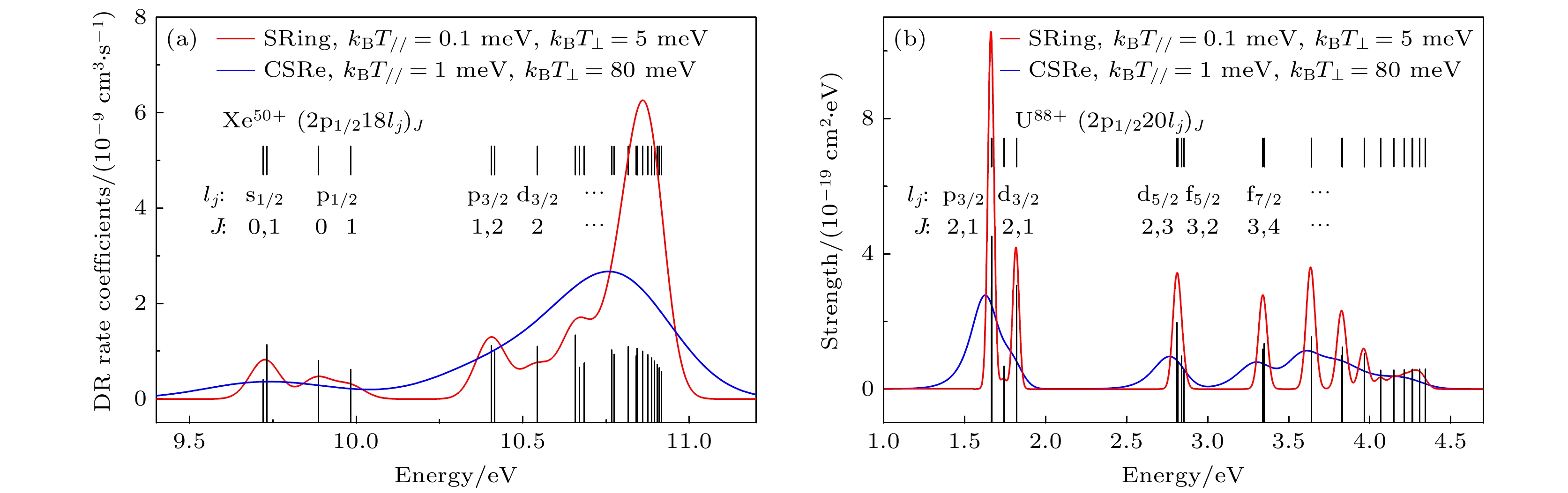
图 8 双电子复合实验模拟谱 (a)类锂$ {}_{54}^{129}{{\mathrm{X}}{\mathrm{e}}}^{51+} $离子; (b) 类锂$ {}_{92}^{238}{{\mathrm{U}}}^{89+} $离子. 图中红色实线代表SRing的模拟结果, 蓝色实线代表CSRe的模拟结果, 而黑色竖线表示由FAC程序计算得出的双电子复合共振位置和强度
Figure 8. DR experimental simulation spectra: (a) Li-like $ {}_{54}^{129}{{\mathrm{X}}{\mathrm{e}}}^{51+} $ ions; (b) Li-like $ {}_{92}^{238}{{\mathrm{U}}}^{89+} $ ions. The red solid line represents the simulation results at SRing, the black solid line represents the simulation results at CSRe, and the black vertical lines represent the positions and strengths of DR resonances calculated by the FAC code.
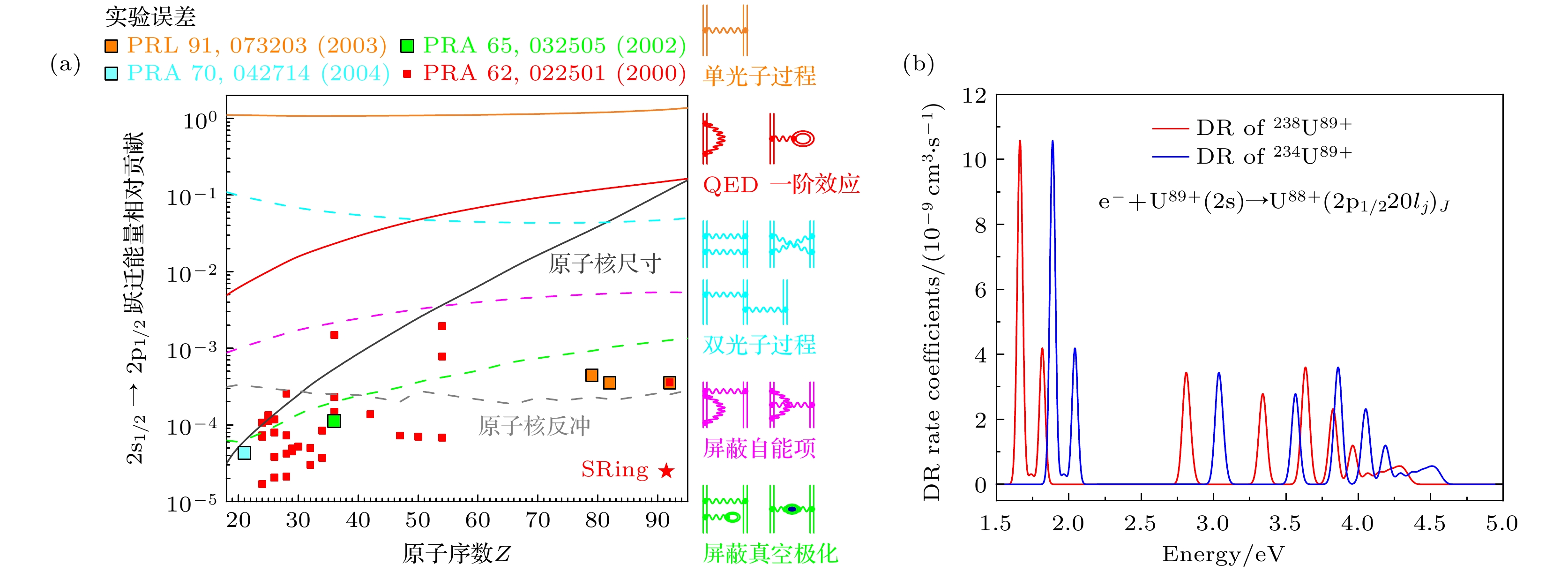
图 9 (a) 类锂离子$ {2{\mathrm{s}}}_{1/2}—{2{\mathrm{p}}}_{1/2} $能级跃迁中的各种效应贡献及相关实验测量结果. 使用SRing电子靶可以在高精度下测量类锂238U89+离子的$ {2{\mathrm{s}}}_{1/2}—{2{\mathrm{p}}}_{1/2} $跃迁能, 从而为严格检验强场下的高阶QED效应提供可能. (b) 类锂238, 234U89+同位素离子对应的双电子复合谱
Figure 9. (a) Contributions of various effects to the transition energy of $ {2{\mathrm{s}}}_{1/2}—{2{\mathrm{p}}}_{1/2} $ and the results of current experimental measurements. By utilizing the electron-target of SRing, we can measure the $ {2{\mathrm{s}}}_{1/2}—{2{\mathrm{p}}}_{1/2} $ transition energy in 238U89+ ions with high-precision, which provides an opportunity for a stringent test of higher-order QED effects in strong-field. (b) DR spectrum for lithium-like 238, 234U89+ isotopes.
表 1 超冷电子靶的主要物理设计参数
Table 1. Main physical design parameters of the ultracold electron-target.
物理量 参数 阴极半径/mm 4 电子束能量/keV 10—80 相互作用区电子束密度/(106 cm–3) 2 电子束最大流强/A 0.2 电子枪区最大磁场强度/T 1.2 相互作用段最大磁场强度/T 0.04 最大绝热参数 0.2 最大绝热展开因子 30 最大加速电场/(kV·cm–1) 2.3 -
[1] Savin D W, Bartsch T, Chen M H, Kahn S M, Liedahl D A, Linkemann J, Müller A, Schippers S, Schmitt M, Schwalm D, Wolf A 1997 Astrophys. J. 489 L115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Savin D W, Behar E, Kahn S M, Gwinner G, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Muller A, Schippers S, Badnell N R, Chen M H, Gorczyca T W 2002 Astrophys. J. 138 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Savin D W, Gwinner G, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schnell M, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Zhou S G, Kieslich S, Muller A, Schippers S, Colgan J, Loch S D, Badnell N R, Chen M H, Gu M F 2006 Astrophys. J. 642 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Gwinner G, Grieser M, Repnow R, Saathoff G, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Muller A, Schippers S, Zavodszky P A, Chen M H, Gorczyca T W, Zatsarinny O, Gu M F 2003 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 147 421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Linkemann J, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Brandau C, Hoffknecht A, Muller A, Schippers S, Chen M H, Badnell N R 1999 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 123 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Savin D W, Kahn S M, Linkemann J, Saghiri A A, Schmitt M, Grieser M, Repnow R, Schwalm D, Wolf A, Bartsch T, Muller A, Schippers S, Chen M H, Badnell N R, Gorczyca T W, Zatsarinny O 2002 Astrophys. J. 576 1098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Schmidt E W, Schippers S, Müller A, Lestinsky M, Sprenger F, Grieser M, Repnow R, Wolf A, Brandau C, Lukić D, Schnell M, Savin D W 2006 Astrophys. J. 641 L157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Larsson M 1995 Rep. Prog. Phys. 58 1267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Phaneuf R A, Havener C C, Dunn G H, Müller A 1999 Rep. Prog. Phys. 62 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lindroth E, Danared H, Glans P, Pešić Z, Tokman M, Vikor G, Schuch R 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 5027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Müller A, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 073202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang S X, Brandau C, Fritzsche S, Fuchs S, Harman Z, Kozhuharov C, Müller A, Steck M, Schippers S 2024 Eur. Phys. J. D 78 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Lestinsky M, Müller A, Schippers S, Stöhlker T 2015 Phys. Scr. 2015 014022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bates D R, Massey H S W 1943 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 239 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Badnell N R, Pindzola M S, Andersen L H, Bolko J, Schmidt H T 1991 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 24 4441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] LaGattuta K, Hahn Y 1981 Phys. Rev. A 24 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brooks R, Datla R, Griem H R 1978 Phys. Rev. Lett. 41 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Müller A, Belić D, DePaola B, Djurić N, Dunn G, Mueller D, Timmer C 1987 Phy. Rev. A 36 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schippers S 2015 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. , Sect. B 350 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shevelko V, Tawara H 2012 Atomic Processes in Basic and Applied Physics (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer) pp283–306
[21] Schuch R, Böhm S 2007 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88 012002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Xu X, Zhu L F, Chuai X Y, Yuan Y J, Zhu X L, Han X Y, Mao L J, Li J, Ma X M, Yan T L, Yang J C, Xiao G Q, Xia J W, Ma X 2015 Phys. Scr. T166 014023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Huang Z K, Wang S X, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Ma W L, Chen C Y, Zhang C Y, Chen D Y, Huang H K, Shao L, Liu X, Zhou X P, Mao L J, Li J, Ma X M, Tang M T, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Zhang S F, Zhu L F, Ma X W 2023 Chin. Phys. B 32 073401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Danared H, Andler G, Bagge L, Herrlander C J, Hilke J, Jeansson J, Källberg A, Nilsson A, Paál A, Rensfelt K G, Rosengård U, Starker J, af Ugglas M 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 3775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lestinsky M, Lindroth E, Orlov D A, Schmidt E W, Schippers S, Böhm S, Brandau C, Sprenger F, Terekhov A S, Müller A, Wolf A 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 033001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schippers S, Schmidt E W, Bernhardt D, Yu D, Muller A, Lestinsky M, Orlov D A, Grieser M, Repnow R, Wolf A 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 033001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Brandau C, Kozhuharov C, Harman Z, et al. 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 073201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Xu X, et al. 2018 Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 235 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang S X, Xu X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Khan N, Preval S P, Badnell N R, Schippers S, Mahmood S, Dou L J, Chuai X Y, Zhao D M, Zhu X L, Mao L J, Ma X M, Li J, Mao R S, Yuan Y J, Tang M T, Yin D Y, Yang J C, Ma X, Zhu L F 2018 Astrophys. J. 862 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang S X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, et al. 2019 Astron. Astrophys. 627 A171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wang S X, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, et al. 2022 Phys. Rev. A 106 042808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang S X, Khan N, Wang H B, Chen C Y, Zhang C Y, Preval S P, Badnell N R, Ma W L, Liu X, Chen D Y, Zhu X L, Zhao D M, Mao L J, Ma X M, Li J, Tang M T, Mao R S, Yin D Y, Yang W Q, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Zhu L F, Ma X 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 邵林, 黄忠魁, 汶伟强, 汪书兴, 黄厚科, 马万路, 刘畅, 汪寒冰, 陈冬阳, 刘鑫, 周晓鹏, 赵冬梅, 张少锋, 朱林繁, 马新文 2024 73 123402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao L, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang S X, Huang H K, Ma W L, Liu C, Wang H B, Chen D Y, Liu X, Zhou X P, Zhao D M, Zhang S F, Zhu L F, Ma X W 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 123402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 马余刚, 赵红卫 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 112001
Ma Y G, Zhao H W 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 50 112001
[35] 马新文, 张少锋, 汶伟强, 杨杰, 朱小龙, 钱东斌, 闫顺成, 张鹏鸣, 郭大龙, 汪寒冰, 黄忠魁 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma X W, Zhang S F, Wen W Q, Yang J, Zhu X L, Qian D B, Yan S C, Zhang P M, Guo D L, Wang H B, Huang Z K 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 50 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Xu X, Wang H B, Dou L J, Chuai X Y, Zhu X L, Zhao D M, Li J, Ma X M, Mao L J, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Xu W Q, Xie L Y, Xu T H, Yao K, Dong C Z, Zhu L F, Ma X 2017 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 408 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Danared H 1995 Phys. Scr. T59 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zaghloul M R 2017 ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 44 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Dou L, Xie L, Zhang D, Dong C, Wen W, Huang Z, Ma X 2017 Euro. Phys. J. D 71 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 李传莹, 刘晓菊, 孟广为, 王建国 2010 59 6044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C Y, Liu X J, Meng G W, Wang J G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 6044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Danared H 1993 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 335 397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 张平文, 李铁军 2007 数值分析 (北京: 北京大学出版社) 第161页
Zhang P W, Li T J 2007 Numerical Analysis (Beijing: Beijing University Press) p161
[43] Danared H 1998 Hyperfine Interact. 115 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Zubova N A, Kozhedub Y S, Shabaev V M, Tupitsyn I I, Volotka A V, Plunien G, Brandau C, Stöhlker T 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 啜晓亚, 黄忠魁, 汶伟强, 汪寒冰, 许鑫, 汪书兴, 李冀光, 豆丽君, 赵冬梅, 朱小龙, 冒立军, 殷达钰, 杨建成, 原有进, 马新文 2018 原子核物理评论 35 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chuai X Y, Huang Z K, Wen W Q, Wang H B, Xu X, Wang S X, Li J G, Dou L J, Zhao D M, Zhu X L, Mao L J, Yin D Y, Yang J C, Yuan Y J, Ma X W 2018 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 35 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4338
- PDF Downloads: 233
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: