-
The study of the interaction between highly charged ions and solid surfaces not only has great significance for basic scientific research such as atomic physics, astrophysics, and high energy density physics but also has promising application prospects in biomedicine, nanotechnology, surface analysis, and microelectronics. In this paper, the intermediate Rydberg states formed during highly charged
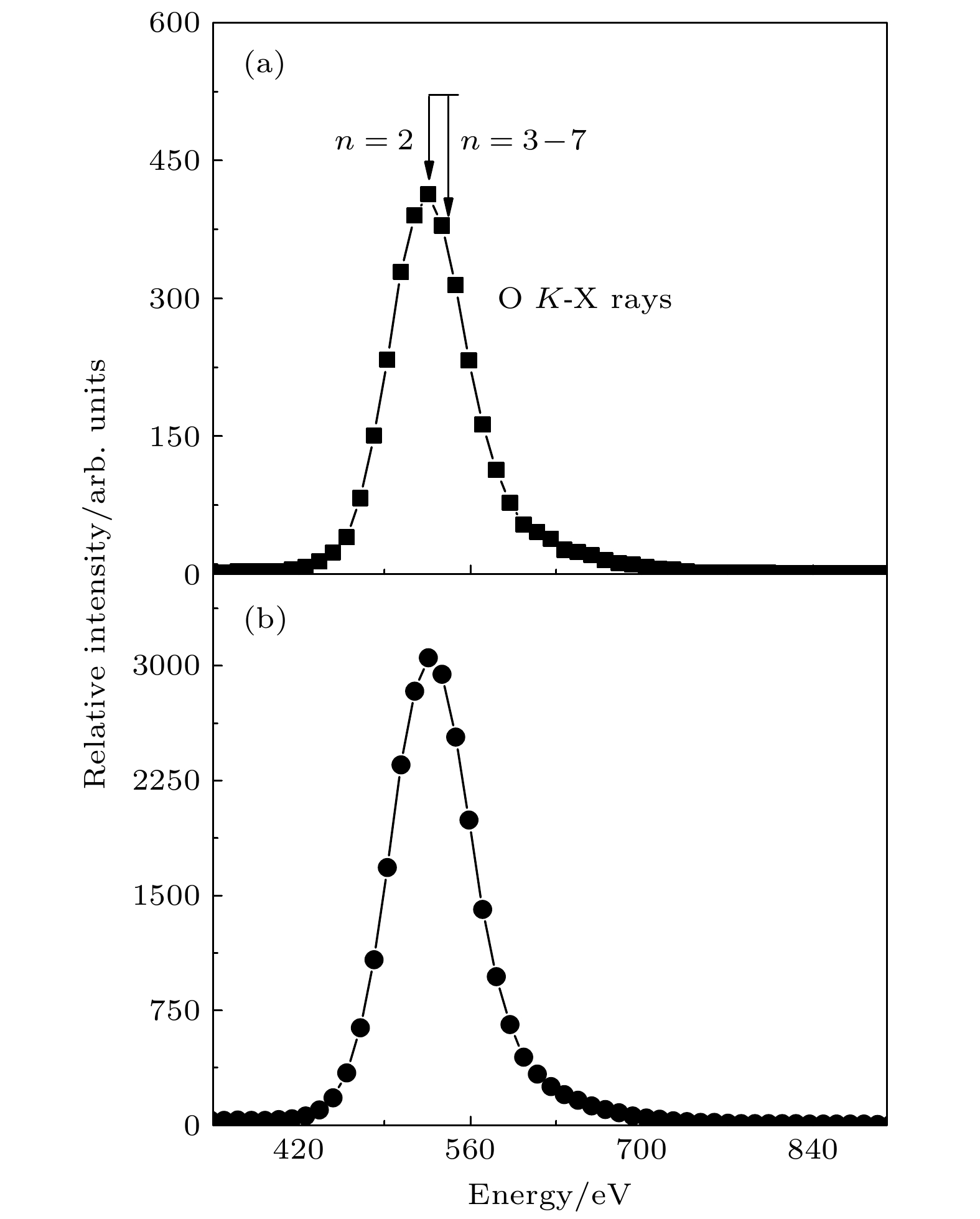
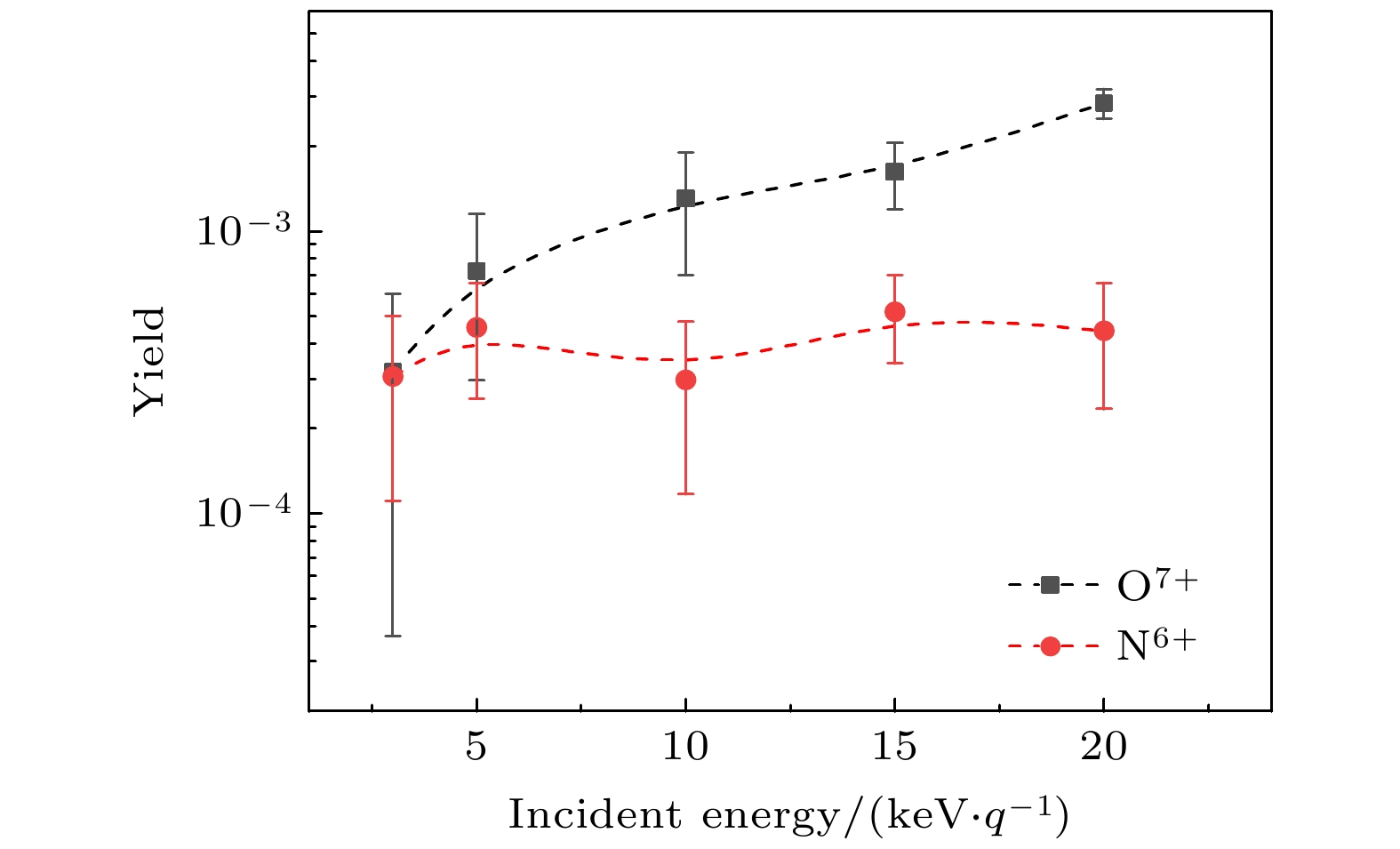
${\rm{O}}^{7+}$ and${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ ions incident on Al surface are studied theoretically by using the two-state vector model. Both the probability of electron capture into different Rydberg states$\left(n_{A}=2-7\right)$ and the most probable neutralization distances are given. The calculation shows that the larger principal quantum number$n_{A}$ is relevant to smaller probability. Therefore, the X-rays emitted by${\rm{O}}^{7+}$ and${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ ions incident on the Al surface come mainly from the de-excitation of the smaller$n_{A}$ to the ground state. In order to confirm the calculations, we measured the X-ray emission spectra of${\rm{O}}^{7+}$ and${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ ions in collisions with the Al surface in the energy range of 3–20 keV/q. The experiments were performed at an ECR ion source located in Institute of modern physics. We also calculated the transition energies (np–1s) from different high Rydberg states to the ground state by using the FAC code. The center of the measured K X-ray peak is close to the calculated transition energy from the principal quantum number n = 2 to n = 1, it is consistent with our results obtained by the two-state vector model as well. In addition, we found the experimental K X-ray yield for${\rm{O}}^{7+}$ ions incidence at lower energy collisions is almost the same with${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ ions, but larger at higher energy collisions. When the ion incident kinetic energy is low, the X-ray emission is mainly owing to the decay of “above the surface” hollow atoms. Because of the small difference in the critical distances for the capture of electrons by${\rm{O}}^{7+}$ and${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ to form hollow atoms, the X-ray yields produced in both cases are almost the same at low energy collisions. In contrast, as increasing the incident energy, the ions have a long-range in the target, so the contribution from the decay of “above the surface” and “below the surface” hollow atoms need to be considered at the same time.-
Keywords:
- highly charged ions /
- Rydberg states /
- the two-state vector model /
- X-rays
[1] Arnau A, Aumayr F, Echenique P M, Grether M, Heiland W, Limburg J, Morgenstern R, Roncin P, Schippers S, Schuch R, Stolterfoht N, Varga P, Zouros T J M, Winter H 1997 Surf. Sci. Rep. 27 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schenkel T, Hamza A V, Barnes A V, Schneider D H 1999 Prog. Surf. Sci. 61 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Winter H, Aumayr F 1999 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 3 2
[4] Song Z Y, Yang Z H, Xiao G Q, Xu Q M, Chen J, Yang B, Yang Z R 2011 Eur. Phys. J. D 64 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao Y T, Xiao G Q, Zhang X A, Yang Z H, Zhan W L, Chen X M, Li F L 2006 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 245 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao Y T, Xiao G Q, Zhang X A, Yang Z H, Zhang Y P, Zhan W L, Chen X M, Li F L 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 258 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张小安, 梅策香, 张颖, 梁昌慧, 周贤明, 曾利霞, 李耀宗, 柳钰, 向前兰, 孟惠, 王益军 2020 69 213301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X A, Mei C X, Zhang Y, Liang C H, Zhou X M, Zeng L X, Li Y Z, Liu Y, Xiang Q L, Meng H, Wang Y J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 213301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lei Y, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Wang X, Wang Y Y, Ren J R, Zhao Y T, Ma X W, Xiao G Q 2018 Eur. Phys. J. D 72 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张小安, 李耀宗, 赵永涛, 梁昌慧, 程锐, 周贤明, 王兴, 雷瑜, 孙渊博, 徐戈, 李锦玉, 肖国青 2012 61 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Zhao Y T, Liang C H, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Wang X, Lei Y, Sun Y B, Xu G, Li J Y, Xiao G Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang H, Chen X, Yang Z, Xu J, Cui Y, Shao J, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Xiao G 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268 1564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nedeljković L D, Nedeljković N N, Božanić D K 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 032901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Borisov A G, Zimny R, Teillet-Billy D, Gauyacq J P 1996 Phys. Rev. A 53 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Burgdörfer J, Lerner P, Meyer F W 1991 Phys. Rev. A 44 5674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Iwai Y, Murakoshi D, Kanai Y, Oyama H, Ando K, Masuda H, Nishio K, Nakao M, Tamamura T, Komaki K, Yamazaki Y 2002 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 193 504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kanai Y, Nakai Y, Iwai Y, Ikeda T, Hoshino M, Nishio K, Masuda H, Yamazaki Y 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 233 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tökési K, Wirtz L, Lemell C, Burgdörfer J 2000 Phys. Rev. A 61 020901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ninomiya S, Yamazaki Y, Koike F, Masuda H, Azuma T, Komaki K, Kuroki K, Sekiguchi M 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 4557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ninomiya S, Yamazaki Y, Azuma T, Komaki K, Koike F, Masuda H, Kuroki K, Sekiguchi M 1997 Phys. Scr. T73 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Aumayr F, Kurz H, Schneider D, Briere M A, McDonald J W, Cunningham C E, Winter H 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Song Z Y, Yang Z H, Zhang H Q, Shao J X, Cui Y, Zhang Y P, Zhang X A, Zhao Y T, Chen X M, Xiao G Q 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 042707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 042902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Nedeljković N N, Nedeljković L D, Mirković M A 2003 Phys. Rev. A 68 012721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gillaspy J D, Pomeroy J M, Perrella A C, Grube H 2007 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 58 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tona M, Watanabe H, Takahashi S, Nakamura N, Yoshiyasu N, Sakurai M, Terui T, Mashiko S, Yamada C, Ohtani S 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 256 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Heller R, Facsko S, Wilhelm R A, Moller W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 096102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] El-Said A S, Wilhelm R A, Heller R, Facsko S, Lemell C, Wachter G, Burgdorfer J, Ritter R, Aumayr F 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 117602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D, Božanić D K, Dojčilović R J 2016 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 49 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D, Galijaš S M D 2012 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kramida A, Ralchenko Y, Reader J, NIST ASD Team 2021 NIST Atomic Spectra Database [EB/OL] https://physics.nist.gov/asd [2021-12-27]
[30] 张秉章, 宋张勇, 刘璇, 钱程, 方兴, 邵曹杰, 王伟, 刘俊亮, 徐俊奎, 冯勇, 朱志超, 郭艳玲, 陈林, 孙良亭, 杨治虎, 于得洋 2021 70 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang B Z, Song Z Y, Liu X, Qian C, Fang X, Shao C J, Wang W, Liu J L, Xu J K, Feng Y, Zhu Z C, Guo Y L, Chen L, Sun L T, Yang Z H, Yu D Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1
$ {\rm{O}}^{7+} $ 离子俘获电子至里德伯态$v_{{\rm{A}}}(n_{{\rm{A}}}=3 ; \; l_{{\rm{A}}}= $ $ 0, 1, 2, 3)$ 的几率, 其中$l_{{\rm{A}}}=2$ 和$l_{{\rm{A}}}=3$ 的几率相等. 虚线对应点状核模型Figure 1. Probability for the
$ {\rm{O}}^{7+} $ ion capturing an electron into the Rydberg states$\left(n_{{\rm{A}}}=3 ;\; l_{{\rm{A}}}=0, 1, 2, 3\right)$ , where the values of$l_{{\rm{A}}}=2$ and$l_{{\rm{A}}}=3$ are equal. Dashed curves correspond to the case of the pointlike core图 3
$ {\rm{O}}^{7 + } $ 离子入射Al表面发射的X射线谱, 其中(a)为3 keV/q, (b) 为20 keV/q. 图中箭头标示了FAC程序计算的不同里德堡态退激到基态的跃迁能Figure 3. X-ray spectra induced by
${\rm{O}} ^{7 + } $ ions impact on aluminum surfaces at (a) 3 keV/q and (b) 20 keV/q collisional energy. The arrows indicate the calculated X-ray energies for different Rydberg states to the ground state by FAC code图 4
${\rm{N}} ^{6 + } $ 离子入射Al表面发射的X射线谱, 其中(a)为3 keV/q, (b) 为20 keV/q. 图中箭头标示了FAC程序计算的不同里德堡态退激到基态的跃迁能Figure 4. X-ray spectra generated by
$ {\rm{N}}^{6 + } $ ions incident on aluminum surfaces at (a) 3 keV/q and (b) 20 keV/q collisional energy. The arrows indicate the calculated X-ray energies for different Rydberg states to the ground state by FAC code表 1
${\rm{O}}^{7 + }$ ,${\rm{N}}^{6 + }$ 离子在考虑离子极化下的能级参数$\widetilde{\gamma}_{{\rm{A}}}$ (arb. units), 及不考虑离子极化下的参数$\gamma_{{\rm{A}} 0}= $ $ Z / n_{{\rm{A}}}$ (arb. units)Table 1. Energy parameter
$\widetilde{\gamma}_{{\rm{A}}}$ (arb. units) and$\gamma_{{\rm{A}} 0} = $ $ Z / n_{\rm A}$ (arb. units) for the ions${\rm{O}}^{7 + }$ and${\rm{N}}^{6 + }$ , separately correspond to the cases with and without polarization of the ionic core$n_{{\rm{A}}}$ $l_{{\rm{A}}} = 0$ $l_{{\rm{A}}} = 1$ $l_{{\rm{A}}} = 2$ $l_{{\rm{A}}} = 3$ $\gamma_{{\rm{A}} 0}$ ${\rm{O} }^{7 + }({{Z} } = 7)$ 2 3.540 3.487 3.500 3 2.352 2.328 2.334 2.334 2.333 4 1.760 1.748 1.751 1.751 1.750 5 1.399 1.400 1.401 1.400 6 1.166 1.167 1.168 1.167 7 1.003 1.000 ${\rm{N} }^{6+}({{Z} }=6)$ 2 3.040 2.987 3.000 3 2.018 1.994 2.000 2.000 4 1.510 1.497 1.500 1.500 5 1.207 1.195 1.200 1.200 6 0.999 1.000 7 0.855 0.857 表 2 TVM模型计算的
${\rm{O}}^{7 + }$ ,${\rm{N}}^{6 + }$ 离子的中和距离. 括号中的值代表点状核模型的中和距离Table 2. The neutralization distances for the
${\rm{O}}^{7 + }$ and${\rm{N}}^{6 + }$ ions calculated by TVM. Numbers in parentheses are the neutralization distances for the pointlike ionic core case$n_{{\rm{A}}}$ $l_{{\rm{A}}}=0$ $l_{{\rm{A}}}=1$ $l_{{\rm{A}}}=2$ $l_{{\rm{A}}}=3$ ${\rm{O}}^{7 + }$ 2 1.27 (1.28) 1.28 (1.28) (1.28) (1.28) 3 2.68 (2.74) 2.75 (2.74) 2.69 (2.74) 2.69 (2.74) 4 4.60 (4.62) 4.63 (4.62) 4.62 (4.62) 4.62 (4.62) 5 (7.01) 7.02 (7.01) 7.01 (7.01) 7.01 (7.01) 6 (9.87) 9.88 (9.87) 9.87 (9.87) 9.81 (9.87) 7 (13.30) 13.21(13.30) (13.30) (13.30) ${\rm{N}}^{6+}$ 2 1.45 (1.51) 1.52 (1.51) (1.51) (1.51) 3 3.15 (3.18) 3.18 (3.18) 3.18 (3.18) (3.18) 4 5.36 (5.39) 5.45 (5.39) 5.39 (5.39) (5.39) 5 8.13 (8.22) 8.25 (8.22) 8.22 (8.22) (8.22) 6 (11.65) 11.66 (11.65) (11.65) (11.65) 7 (16.29) 16.37 (16.29) (16.29) (16.29) 表 3 基于FAC程序计算的不同高里德堡态退激到基态的跃迁能(np −1s)
Table 3. Calculated transition energy for different Rydberg states to the ground state using FAC code (np −1s)
O ion $2 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $3{\rm{ p}}-1{\rm{ s}}$ $4 {\rm{p}}-1{\rm{ s}}$ $5 {\rm{p}}-1{\rm{ s}}$ $6 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $7 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ Energy/eV 526.4 541.5 543.5 543.9 544.1 544.2 N ion $2 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $3 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $4 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $5 {\rm{p}}-1{\rm{ s}}$ $6 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ $7 {\rm{p}}-1 {\rm{s}}$ Energy/eV 395.8 407.8 409.7 410.1 410.3 410.4 -
[1] Arnau A, Aumayr F, Echenique P M, Grether M, Heiland W, Limburg J, Morgenstern R, Roncin P, Schippers S, Schuch R, Stolterfoht N, Varga P, Zouros T J M, Winter H 1997 Surf. Sci. Rep. 27 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schenkel T, Hamza A V, Barnes A V, Schneider D H 1999 Prog. Surf. Sci. 61 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Winter H, Aumayr F 1999 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 3 2
[4] Song Z Y, Yang Z H, Xiao G Q, Xu Q M, Chen J, Yang B, Yang Z R 2011 Eur. Phys. J. D 64 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao Y T, Xiao G Q, Zhang X A, Yang Z H, Zhan W L, Chen X M, Li F L 2006 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 245 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao Y T, Xiao G Q, Zhang X A, Yang Z H, Zhang Y P, Zhan W L, Chen X M, Li F L 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 258 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张小安, 梅策香, 张颖, 梁昌慧, 周贤明, 曾利霞, 李耀宗, 柳钰, 向前兰, 孟惠, 王益军 2020 69 213301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X A, Mei C X, Zhang Y, Liang C H, Zhou X M, Zeng L X, Li Y Z, Liu Y, Xiang Q L, Meng H, Wang Y J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 213301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lei Y, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Wang X, Wang Y Y, Ren J R, Zhao Y T, Ma X W, Xiao G Q 2018 Eur. Phys. J. D 72 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张小安, 李耀宗, 赵永涛, 梁昌慧, 程锐, 周贤明, 王兴, 雷瑜, 孙渊博, 徐戈, 李锦玉, 肖国青 2012 61 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Zhao Y T, Liang C H, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Wang X, Lei Y, Sun Y B, Xu G, Li J Y, Xiao G Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 113401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang H, Chen X, Yang Z, Xu J, Cui Y, Shao J, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Xiao G 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268 1564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nedeljković L D, Nedeljković N N, Božanić D K 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 032901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Borisov A G, Zimny R, Teillet-Billy D, Gauyacq J P 1996 Phys. Rev. A 53 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Burgdörfer J, Lerner P, Meyer F W 1991 Phys. Rev. A 44 5674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Iwai Y, Murakoshi D, Kanai Y, Oyama H, Ando K, Masuda H, Nishio K, Nakao M, Tamamura T, Komaki K, Yamazaki Y 2002 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 193 504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kanai Y, Nakai Y, Iwai Y, Ikeda T, Hoshino M, Nishio K, Masuda H, Yamazaki Y 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 233 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tökési K, Wirtz L, Lemell C, Burgdörfer J 2000 Phys. Rev. A 61 020901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ninomiya S, Yamazaki Y, Koike F, Masuda H, Azuma T, Komaki K, Kuroki K, Sekiguchi M 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 4557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ninomiya S, Yamazaki Y, Azuma T, Komaki K, Koike F, Masuda H, Kuroki K, Sekiguchi M 1997 Phys. Scr. T73 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Aumayr F, Kurz H, Schneider D, Briere M A, McDonald J W, Cunningham C E, Winter H 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Song Z Y, Yang Z H, Zhang H Q, Shao J X, Cui Y, Zhang Y P, Zhang X A, Zhao Y T, Chen X M, Xiao G Q 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 042707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 042902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Nedeljković N N, Nedeljković L D, Mirković M A 2003 Phys. Rev. A 68 012721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gillaspy J D, Pomeroy J M, Perrella A C, Grube H 2007 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 58 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tona M, Watanabe H, Takahashi S, Nakamura N, Yoshiyasu N, Sakurai M, Terui T, Mashiko S, Yamada C, Ohtani S 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 256 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Heller R, Facsko S, Wilhelm R A, Moller W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 096102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] El-Said A S, Wilhelm R A, Heller R, Facsko S, Lemell C, Wachter G, Burgdorfer J, Ritter R, Aumayr F 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 117602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D, Božanić D K, Dojčilović R J 2016 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 49 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Nedeljković N N, Majkić M D, Galijaš S M D 2012 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45 215202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kramida A, Ralchenko Y, Reader J, NIST ASD Team 2021 NIST Atomic Spectra Database [EB/OL] https://physics.nist.gov/asd [2021-12-27]
[30] 张秉章, 宋张勇, 刘璇, 钱程, 方兴, 邵曹杰, 王伟, 刘俊亮, 徐俊奎, 冯勇, 朱志超, 郭艳玲, 陈林, 孙良亭, 杨治虎, 于得洋 2021 70 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang B Z, Song Z Y, Liu X, Qian C, Fang X, Shao C J, Wang W, Liu J L, Xu J K, Feng Y, Zhu Z C, Guo Y L, Chen L, Sun L T, Yang Z H, Yu D Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6182
- PDF Downloads: 80
- Cited By: 0




























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: