-
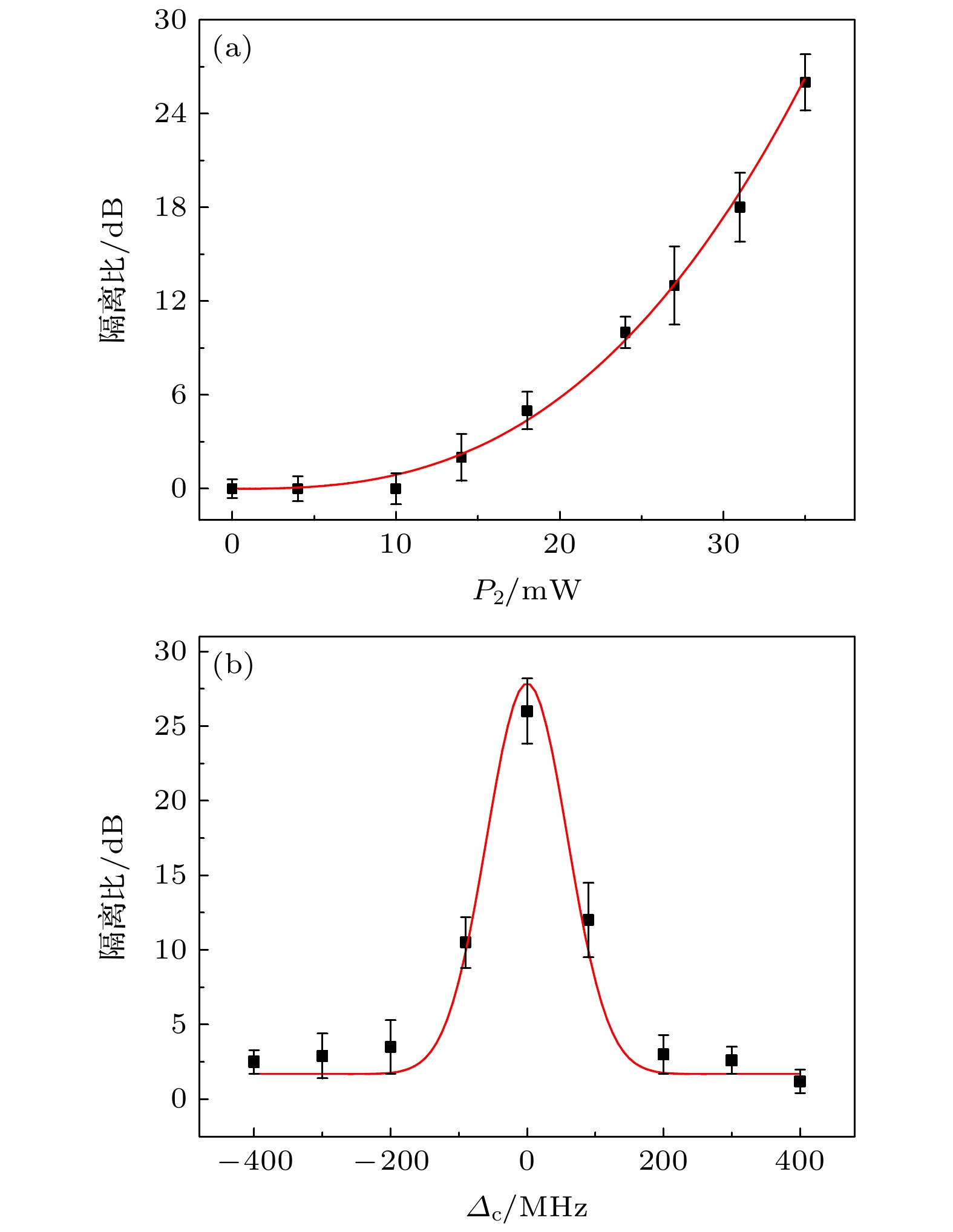
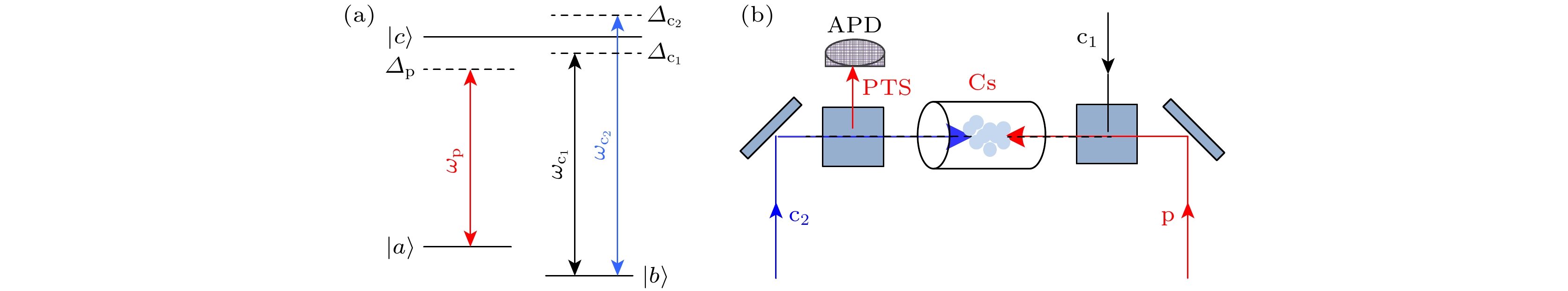
Non-magnetic optical non-reciprocal devices are conducive to constructing optical information processing networks for weak signals without using any external magnetic field. In this work, the non-reciprocal transmission of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) in a cesium atomic gas through laser exciting a Λ-type three-level atomic system is observed experimentally. With the help of cesium atoms, which have several advantages over other alkali atoms, such as a rich and readily adjustable energy level structure, bigger ground state hyperfine energy levels, and lower saturation light intensity. An 894.596 nm laser, as probe light, excites energy level from 6S1/2 (F = 4) to 6P3/2 (F = 5), and an 894.594 nm laser, as coupling light, is divided into two beams to excite energy level from 6S1/2 (F = 3) to 6P3/2 (F = 5). The coupling light enters the cesium atomic gas cell in two directions: either collinearly incident in the same direction as the probe light, or in the opposite direction. The probing light that interacts with the coupling light inside the cesium atomic gas and then is detected by the detector avalanche photodiode, and the outcomes are shown and measured on an oscilloscope. The experimentally observed non-reciprocal transmission of EIT proves optical signal isolation in a cesium atomic system. Under the experimental conditions, a series of experiments is conducted on the regulation of the optical non-reciprocal isolation ratio at room temperature by adjusting the power of the probe light and coupling light as well as the detuning. The influence of adjustable parameters on the non-reciprocal isolation ratio is analyzed. The results show that moderate probe light power helps maintain the intensity of EIT in the absorption intensity curve, ensuring a high isolation ratio, which provides a reference for implementing the performance metrics of optical isolators. The observed isolation ratio increases with the increase of coupling power, which is consistent with the theoretical calculation. Within a certain range of coupling light power, a high-performance optical non-reciprocal system is achieved. This trend is exactly in line with that of EIT signal strength variation during co-directional coupling light excitation. A maximum isolation ratio 26 dB is obtained when many parameters are appropriate. The results indicate that in the coherently prepared cesium atom systems, optically tunable parameters can provide an effective means for achieving ideal optical isolation with a high isolation ratio. Compared with existing research on high isolation ratio cavity-free non-reciprocity based on atomic coherence, our proposed experimental scheme can be conducted by using a three-level system at room temperature. With the development of chip-level integrated gas cells, the achieving miniaturization and system integration become easier, which provides experimental support for achieving the miniaturization and integration. This work provides a certain basis for exploring high-performance non-reciprocal devices with high isolation ratios and new perspective for designing the next generation of optical equipment. [1] Huang X Y, Lu C C, Liang C, Tao H G, Liu Y C 2021 Light 10 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Khanikaev A B, Alù A 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lodahl P, Mahmoodian S, Stobbe S, Rauschenbeutel A, Schneeweiss P, Volz J, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Nature 541 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cirac J I, Zoller P, Kimble H J, Mabuchi H 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 3221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Estep N A, Sounas D L, Soric J, Alù A 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Staliunas K, Herrero R 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 016601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Buddhiraju S, Song A, Papadakis G T, Fan S H 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 257403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y F, Qin L G, Huang J H, Wang L L, Tian L J, Wang Z Y, Gong S Q 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 194401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xia K Y, Lu G W, Lin G W, Cheng Y Q, Niu Y P, Gong S Q, Twamley J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 043802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Michael S, Adèle H, Elisa W, Jürgen V, Arno R 2016 Science 354 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xia K Y, Nori F, Xiao M 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 203602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tang L, Tang J S, Chen M Y, Nori F, Xiao M, Xia K Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 083604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2010 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 16 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tang J S, Nie W, Tang L, Chen M Y, Su X, Lu Y Q, Nori F, Xia K Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 203602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng Z H, Ning T Y, Tian N, Zhao Y F 2023 Opt. Express 31 31108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu G G, Gao Z, Wang Q, Xi X, Hu Y H, Wang M R, Liu C Q, Lin X, Deng L J, Yang S Y A, Zhou P H, Yang Y H, Chong Y D, Zhang B L 2022 Nature 609 925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王子尧, 陈福家, 郗翔, 高振, 杨怡豪 2024 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Chen F J, Chi X, Gao Z, Yang Y H 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Harris S E 1997 Physics Today 50 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y P, Brown, A W, Xiao M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 123603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Che J L, Xu W Q, Wang H, Gao Y H, Wang L, Lan H Y, Wei Z Y, Hu M L 2022 Infrared Phys. Techn. 127 104449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang S C, Hu Y Q, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Xia K Y, Gong J B, Gong S Q 2018 Nat. Photonics 12 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang S C, Hu Y Q, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Gong J B, Gong S Q 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 033902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y Q, Zhang S C, Kuang X Y, Qi Y H, Lin G W, Gong S Q, Niu Y P 2020 Opt. Express 28 38710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Fan S F, Qi Y H, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Gong S Q 2020 Opt. Commun. 462 125343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dong M X, Xia K Y, Zhang W H, Yu Y C, Ye Y H, Li E Z, Zeng L, Ding D S, Shi B S, Guo G C, Nori F 2021 Sci. Adv. 7 eabe8924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hu Y Q, Qi Y H, You Y, Zhang S C, Lin G, Li X L, Gong J B, Gong S Q, Niu Y P 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 16 014046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu H D, Ruan Y P, Li Z X, Dong M X, Cai M, Tang J S, Tang L, Zhang H, Xiao M, Xia K Y 2022 Laser Photonics Rev. 16 2100708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李鑫, 解舒云, 李林帆, 周海涛, 王丹, 杨保东 2022 71 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Xie S Y, Li L F, Zhou H T, Wang D, Yang B D 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Daniel A S 1998 Cesium D Line Data (University of Oregon: Open Publication License) p19
[31] Daniel A S 2008 Rubidium 85 D Line Data (University of Oregon: Open Publication License) p19
[32] Berman P R, Malinovsky V S 2011 Priciples of Laser Spectroscopy and Quantum Optics (Princeton: Princeton University Press
[33] 郭嘉豪 2024 博士学位论文 (上海: 华东理工大学)
Guo J H 2024 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology
-
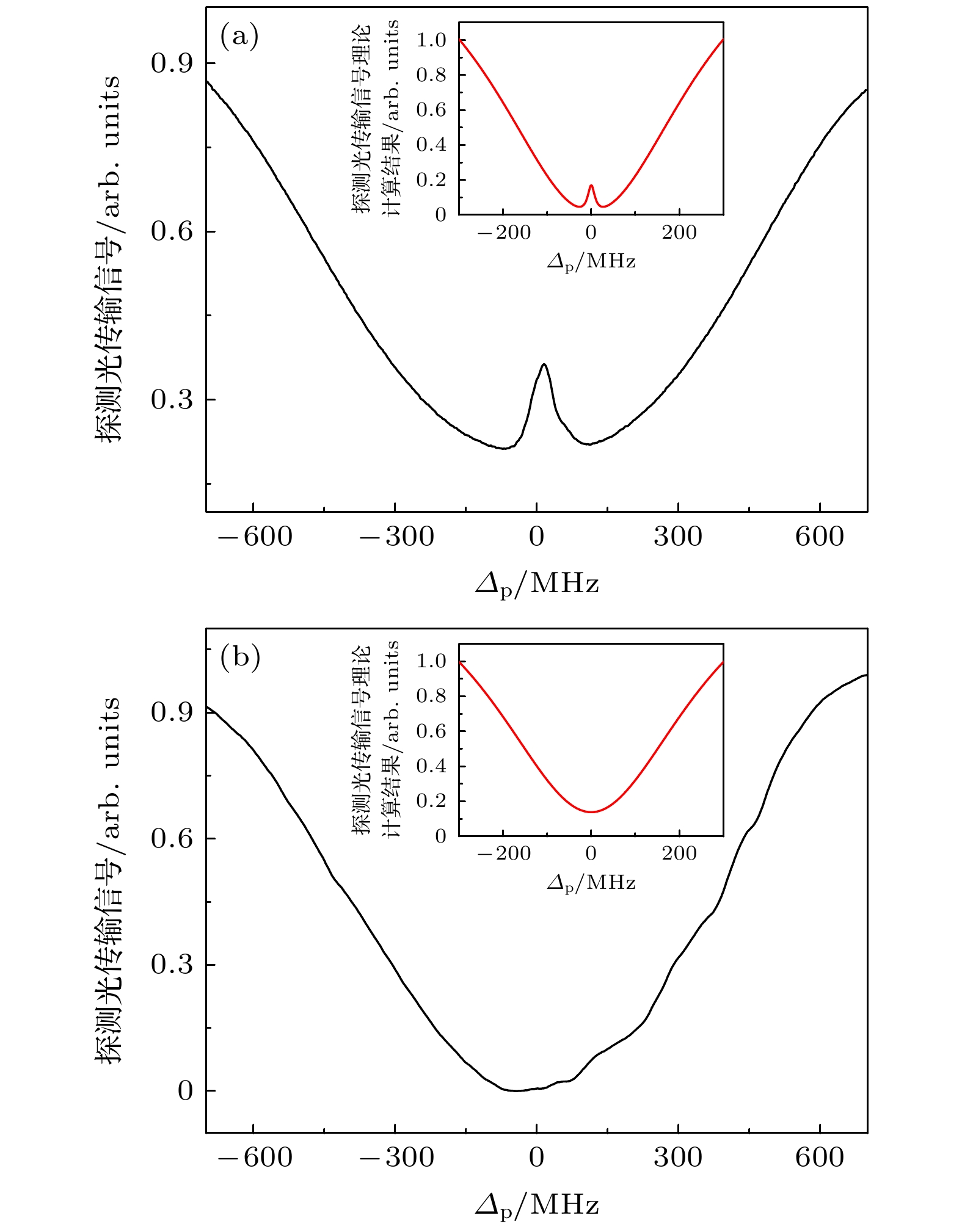
图 2 (a)同向耦合光激发时的探测光光谱实验结果图和理论模拟计算图; (b)反向耦合光激发时的探测光光谱实验结果图和理论模拟图
Figure 2. (a) Experimental spectrum and theoretical simulation results of probe transmission when the couple field is excited in the same direction; (b) experimental spectrum and theoretical simulation results of probe transmission when the couple field is excited in the opposite direction.
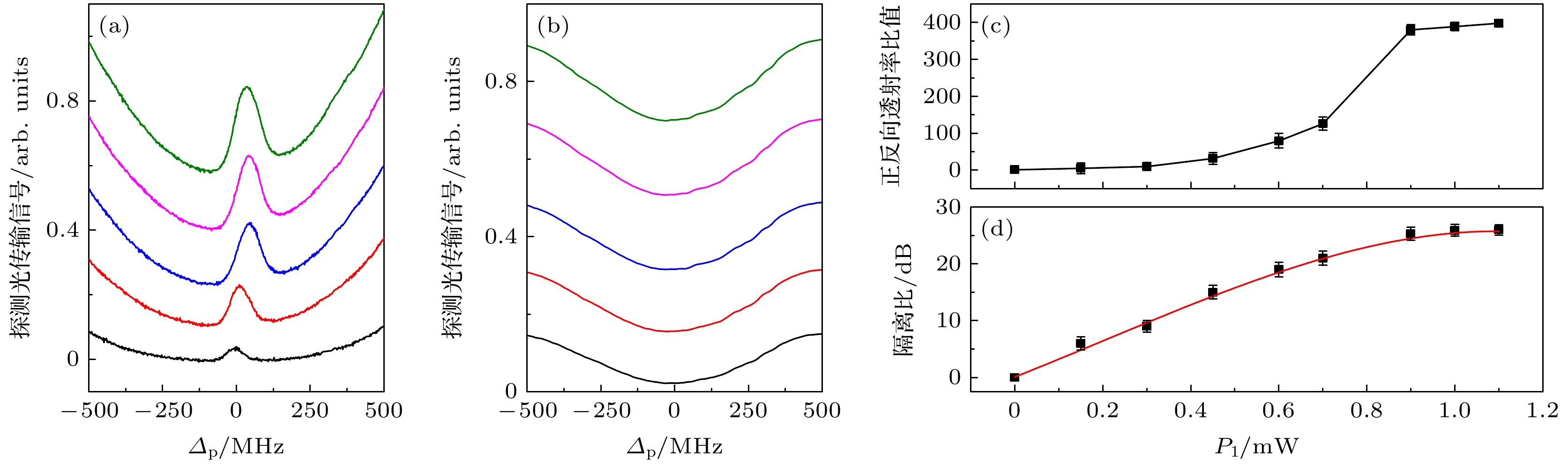
图 3 (a)同向耦合光作用下, 不同探测光功率下的探测光光谱图; (b)反向耦合光作用下, 不同探测光功率下的探测光光谱图; (c)正反向透射率比随着探测光功率的变化; (d)隔离比随着探测光功率的变化, 图中的误差棒是根据每个数据标准差的重复测得
Figure 3. (a) Experimental probe transmission spectra under different probe field power when the couple field is excited in the same direction; (b) experimental probe transmission spectra under different probe field power when the couple field is excited in the opposite direction; (c) variation of forward and backward transmission ratio with the power of probe field; (d) variation of isolation ratio with the power of probe field, where the error bars represent the standard deviations of repeated measurements.
-
[1] Huang X Y, Lu C C, Liang C, Tao H G, Liu Y C 2021 Light 10 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Khanikaev A B, Alù A 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lodahl P, Mahmoodian S, Stobbe S, Rauschenbeutel A, Schneeweiss P, Volz J, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Nature 541 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cirac J I, Zoller P, Kimble H J, Mabuchi H 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 3221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Estep N A, Sounas D L, Soric J, Alù A 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Staliunas K, Herrero R 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 016601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Buddhiraju S, Song A, Papadakis G T, Fan S H 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 257403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y F, Qin L G, Huang J H, Wang L L, Tian L J, Wang Z Y, Gong S Q 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 194401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xia K Y, Lu G W, Lin G W, Cheng Y Q, Niu Y P, Gong S Q, Twamley J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 043802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Michael S, Adèle H, Elisa W, Jürgen V, Arno R 2016 Science 354 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xia K Y, Nori F, Xiao M 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 203602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tang L, Tang J S, Chen M Y, Nori F, Xiao M, Xia K Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 083604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2010 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 16 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tang J S, Nie W, Tang L, Chen M Y, Su X, Lu Y Q, Nori F, Xia K Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 203602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng Z H, Ning T Y, Tian N, Zhao Y F 2023 Opt. Express 31 31108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu G G, Gao Z, Wang Q, Xi X, Hu Y H, Wang M R, Liu C Q, Lin X, Deng L J, Yang S Y A, Zhou P H, Yang Y H, Chong Y D, Zhang B L 2022 Nature 609 925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王子尧, 陈福家, 郗翔, 高振, 杨怡豪 2024 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Chen F J, Chi X, Gao Z, Yang Y H 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Harris S E 1997 Physics Today 50 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y P, Brown, A W, Xiao M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 123603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Che J L, Xu W Q, Wang H, Gao Y H, Wang L, Lan H Y, Wei Z Y, Hu M L 2022 Infrared Phys. Techn. 127 104449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang S C, Hu Y Q, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Xia K Y, Gong J B, Gong S Q 2018 Nat. Photonics 12 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang S C, Hu Y Q, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Gong J B, Gong S Q 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 033902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu Y Q, Zhang S C, Kuang X Y, Qi Y H, Lin G W, Gong S Q, Niu Y P 2020 Opt. Express 28 38710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Fan S F, Qi Y H, Lin G W, Niu Y P, Gong S Q 2020 Opt. Commun. 462 125343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dong M X, Xia K Y, Zhang W H, Yu Y C, Ye Y H, Li E Z, Zeng L, Ding D S, Shi B S, Guo G C, Nori F 2021 Sci. Adv. 7 eabe8924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hu Y Q, Qi Y H, You Y, Zhang S C, Lin G, Li X L, Gong J B, Gong S Q, Niu Y P 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 16 014046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu H D, Ruan Y P, Li Z X, Dong M X, Cai M, Tang J S, Tang L, Zhang H, Xiao M, Xia K Y 2022 Laser Photonics Rev. 16 2100708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李鑫, 解舒云, 李林帆, 周海涛, 王丹, 杨保东 2022 71 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Xie S Y, Li L F, Zhou H T, Wang D, Yang B D 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Daniel A S 1998 Cesium D Line Data (University of Oregon: Open Publication License) p19
[31] Daniel A S 2008 Rubidium 85 D Line Data (University of Oregon: Open Publication License) p19
[32] Berman P R, Malinovsky V S 2011 Priciples of Laser Spectroscopy and Quantum Optics (Princeton: Princeton University Press
[33] 郭嘉豪 2024 博士学位论文 (上海: 华东理工大学)
Guo J H 2024 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2669
- PDF Downloads: 68
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: