-
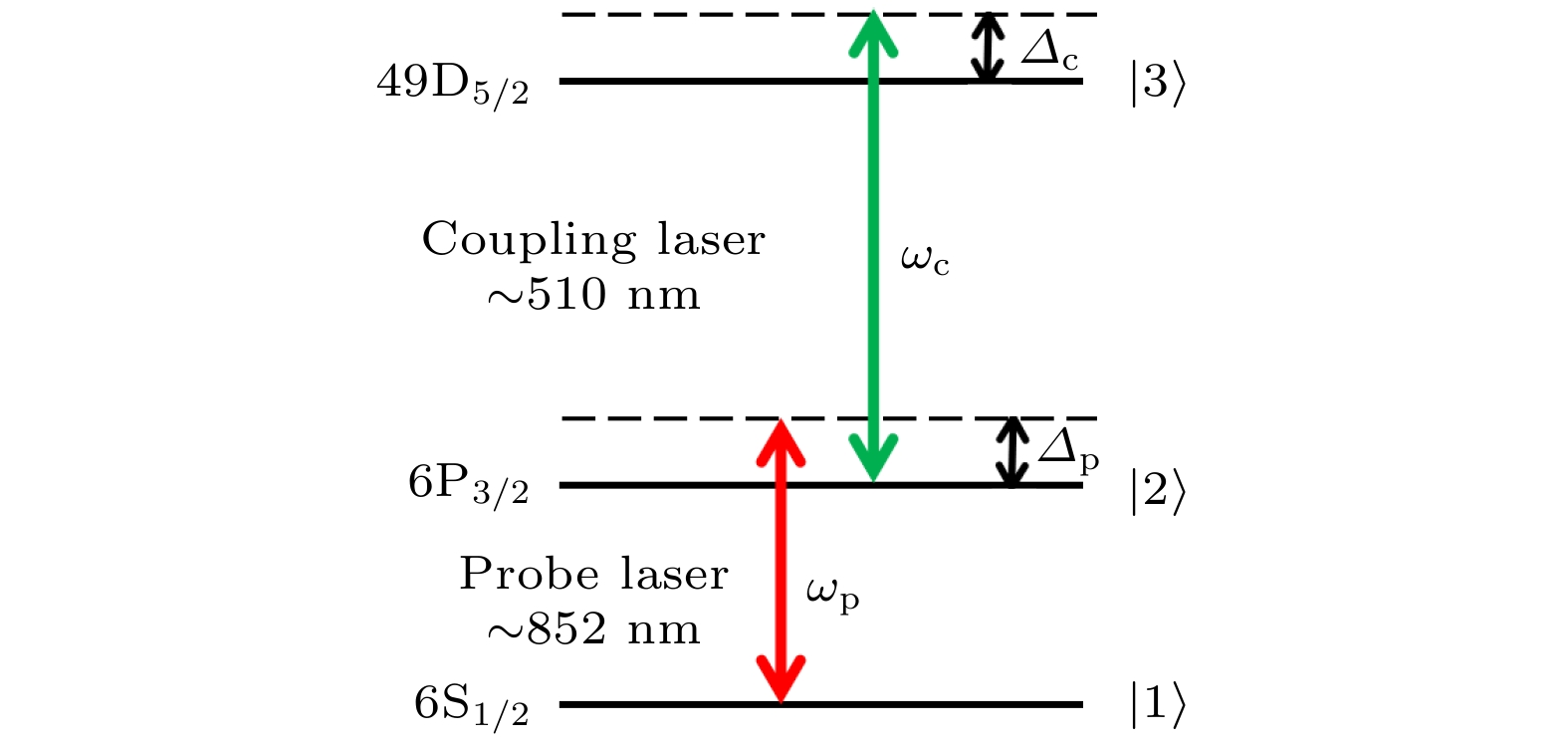
基于铯里德伯原子的电磁诱导透明效应, 当光与原子能级频率共振时, 色散将剧烈变化, 吸收减弱. 此时光脉冲在原子介质中传播时, 将会出现减速. 在铯原子阶梯型三能级
$6 {\rm S}_{1/2}\rightarrow6 {\rm P}_{3/2}\rightarrow49 {\rm D}_{5/2} $ 系统中, 观察到由色散曲线陡峭变化导致的探测光脉冲减速现象, 并系统研究了耦合光强度和原子气室温度对光脉冲减慢的影响. 实验结果表明, 耦合光越弱, 延迟时间越长; 原子气室温度越高, 减速效应越明显, 与理论计算相符. 实验结果为之后进行的通过光脉冲减速效应测量微波电场提供了实验基础.Based on the Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency (EIT) effect of cesium Rydberg atoms, the dispersion of the probe light will experience a drastically change while the absorption is diminished, as the frequency of it is resonated with that of the corresponding atomic transition. In this case, as the light pulse propagates in the atomic medium, the group velocity of the pulse will be slowed. In the cesium atoms 3-ladder-level system ($ 6{\rm S}_{1/2}\rightarrow6{\rm P}_{3/2}\rightarrow49{\rm D}_{5/2} $ ),the frequency of the probe light is locked at the resonance transition of$ 6{\rm S}_{1/2}\rightarrow6{\rm P}_{3/2} $ , while the transmission signal of 852 nm probe light is measured by scanning the coupling light frequency near the transition of$ 6{\rm P}_{3/2}\rightarrow49{\rm D}_{5/2} $ , We observed the EIT phenomenon and explored the relationship between the power of coupling laser and linewidth of the EIT signal. The experimental results show that the linewidth of the EIT signal is proportional to the power of the coupling laser. Then under the two-photon resonance condition, the deceleration of the probe light pulse caused by the steep change of the dispersion curve is observed. We also systematically investigate the influences of coupling optical power and temperature of vapor cell on the slowing down of light pulse. The experimental results show that the weaker the coupled light was, the longer the delay time; and the higher the temperature of the atomic gas chamber was, the more obvious the deceleration effect would be observed, those of which are consistent with the theoretical calculations. The investigation of the deceleration of optical pulses based on the Rydberg Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency is important for understanding the coherence mechanism of 3-ladder-level system and some potential applications, such as in Rydberg-atom-based electric field metrology. This research provides a new tool for the measurement of pulsed microwave electric field through the optical pulse deceleration effect.-
Keywords:
- Rydberg atoms /
- electromagnetically-induced-transparency /
- 3-ladder-level-system /
- deceleration of optical pulses
[1] Harris S E, Field J E, Imamoglu A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Boller K, Imamolu A, Harris S E 1991 Phys. Rev. Lett. 66 2593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Harris S E, Field J E, Kasapi A 1992 Phys. Rev. A 46 R29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xiao M, Li Y, Jin S, Gea-Banacloche J 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chanelière T, Matsukevich D N, Jenkins S D, Lan S Y, Kennedy T A B, Kuzmich A 2005 Nature 438 833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Eisaman M D, André A, Massou F, Fleischhauer M, Zibrov A S, Lukin M D 2005 Nature 438 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gorshkov A V, Andre A, Fleischhauer M, Sorensen A S, Lukin M D 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 123601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Phillips D F, Fleischhauer A, Mair A, Walsworth R L, Lukin M D 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 窦建鹏, 李航, 庞晓玲, 张超妮, 杨天怀, 金贤敏 2019 68 030307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou J P, Li H, Pang X L, Zhang C N, Yang T H, Jin X M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 030307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gorshkov A V, André A, Lukin M D, Sø rensen A S 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 033805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu C, Dutton Z, Behroozi C H, Hau L V 2001 Nature 409 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kasapi A, Jain M, Yin G Y, Harris S E 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 2447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hau L V, Harris S E, Dutton Z, Behroozi C H 1999 Nature 397 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杜丹, 胡响明 2006 55 5232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du D, Hu X M 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 5232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李琴, 郭红 2011 60 054204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Guo H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 054204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang K J, Deng L, Payne M G 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 041803(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mohapatra A K, Jackson T R, Adams C S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 113003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li L, Kuzmich A 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Maxwell D, Szwer D J, Paredes-Barato D, Busche H, Pritchard J D, Gauguet A, Weatherill K J, Jones M P A, Adams C S 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Distante E, Padrón-Brito A, Cristiani M, Paredes-Barato D, de Riedmatten H 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 113001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dudin Y O, Kuzmich A 2012 Science 336 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sedlacek J A, Schwettmann A, Kübler H, Löw R, Pfau T, Shaffer J P 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sedlacek J A, Schwettmann A, Kübler H, Shaffer J P 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 063001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Holloway C L, Gordon J A, Jefferts S, Schwarzkopf A, Anderson D A, Miller S A, Thaicharoen N, Raithel G 2014 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 62 6169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Holloway C L, Gordon J A, Schwarzkopf A, Anderson D A, Miller S A, Thaicharoen N, Raithel G 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 244102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jing M, Hu Y, Ma J, Zhang H, Zhang L, Xiao L, Jia S 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 闫丽云, 刘家晟, 张好, 张临杰, 肖连团, 贾锁堂 2017 66 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan L Y, Li J S, Zhang H, Zhang L J, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Javan A, Kocharovskaya O, Lee H, Scully M O 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 013805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 理论得到归一化后的色散和吸收曲线 (a)打开(虚线)和关上(实线)耦合光时原子系综的色散; (b)打开(虚线)和关上(实线)耦合光时原子系综对探测光的吸收
Fig. 2. Theoretical plots of normalized absorption and dispersion: (a) Dispersion of cesium atoms ensemble with coupling laser on (dashed line) and off (solid line); (b) absorption of probe laser with coupling laser on (dashed line) and off (solid line)
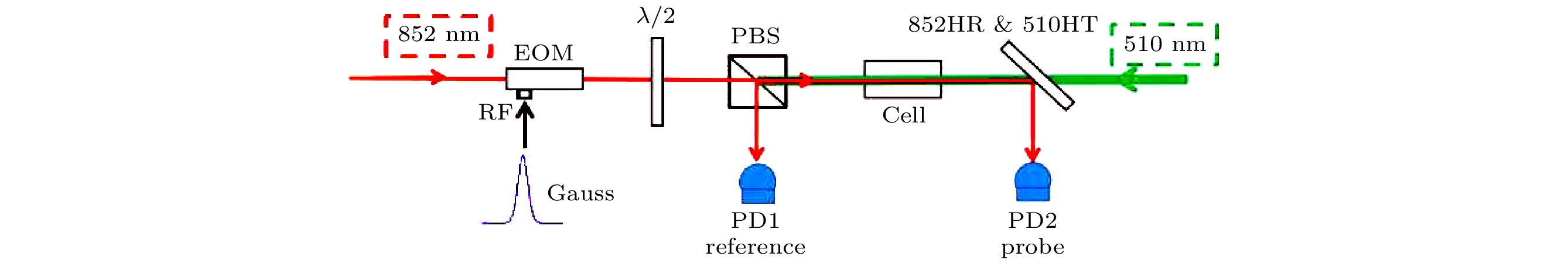
图 3 实验装置示意图(EOM为强度型电光调制器;
$ \lambda/2 $ 为二分之一波片; PBS为偏振分束棱镜; Cell为铯原子气室; 852 HR/510 HT: 852 nm高反510 nm 高透镜; PD为探测器)Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. (EOM, electro-optic intensity;
$ \lambda/2 $ , half-wave plate; PBS, polarization beam splitter; Cell, Cesium vapor cell; 852 HR/510 HT, Dichroic beam splitter; PD, photoclectric detector).图 5 耦合光功率和温度对输出光脉冲的影响 (a) 耦合光功率为5mW时输出光脉冲与参考光脉冲的对比(强度上归一化); (b)温度为40℃时输出光脉冲与参考光脉冲的对比(强度上归一化); (c) 延迟时间随耦合光功率的变化; (d)延迟时间随原子密度的变化
Fig. 5. Change of output pulse with coupling power and tempreature: (a) Comparison of the output optical pulse and the reference optical pulse when the coupling optical power is 5mW (Normalization of intensity); (b) Comparison of the output optical pulse and the reference optical pulse when the temperature is 40℃(Normalization of intensity); (c) delay time vary with coupling power; (d) delay time vary with atom density.
表 1 铯原子气室温度与密度的关系
Table 1. Relationship between cesium vapor cell temperature and density
T/$^{\circ}\mathrm{C}$ 25 30 35 40 N/($10^{11}\mathrm{cm^{-3}}$) 0.49 0.80 1.27 1.98 表 2 系统误差
Table 2. Systematic errors
误差来源 光程差 铯原子气室 示波器通道 探测器 延迟时间/ns 0.49 3.27 1.38 0.64 -
[1] Harris S E, Field J E, Imamoglu A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Boller K, Imamolu A, Harris S E 1991 Phys. Rev. Lett. 66 2593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Harris S E, Field J E, Kasapi A 1992 Phys. Rev. A 46 R29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xiao M, Li Y, Jin S, Gea-Banacloche J 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chanelière T, Matsukevich D N, Jenkins S D, Lan S Y, Kennedy T A B, Kuzmich A 2005 Nature 438 833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Eisaman M D, André A, Massou F, Fleischhauer M, Zibrov A S, Lukin M D 2005 Nature 438 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gorshkov A V, Andre A, Fleischhauer M, Sorensen A S, Lukin M D 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 123601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Phillips D F, Fleischhauer A, Mair A, Walsworth R L, Lukin M D 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 窦建鹏, 李航, 庞晓玲, 张超妮, 杨天怀, 金贤敏 2019 68 030307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou J P, Li H, Pang X L, Zhang C N, Yang T H, Jin X M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 030307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gorshkov A V, André A, Lukin M D, Sø rensen A S 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 033805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu C, Dutton Z, Behroozi C H, Hau L V 2001 Nature 409 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kasapi A, Jain M, Yin G Y, Harris S E 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 74 2447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hau L V, Harris S E, Dutton Z, Behroozi C H 1999 Nature 397 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杜丹, 胡响明 2006 55 5232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du D, Hu X M 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 5232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李琴, 郭红 2011 60 054204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Guo H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 054204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang K J, Deng L, Payne M G 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 041803(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Mohapatra A K, Jackson T R, Adams C S 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 113003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li L, Kuzmich A 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Maxwell D, Szwer D J, Paredes-Barato D, Busche H, Pritchard J D, Gauguet A, Weatherill K J, Jones M P A, Adams C S 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Distante E, Padrón-Brito A, Cristiani M, Paredes-Barato D, de Riedmatten H 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 113001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dudin Y O, Kuzmich A 2012 Science 336 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sedlacek J A, Schwettmann A, Kübler H, Löw R, Pfau T, Shaffer J P 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sedlacek J A, Schwettmann A, Kübler H, Shaffer J P 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 063001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Holloway C L, Gordon J A, Jefferts S, Schwarzkopf A, Anderson D A, Miller S A, Thaicharoen N, Raithel G 2014 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 62 6169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Holloway C L, Gordon J A, Schwarzkopf A, Anderson D A, Miller S A, Thaicharoen N, Raithel G 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 244102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jing M, Hu Y, Ma J, Zhang H, Zhang L, Xiao L, Jia S 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 闫丽云, 刘家晟, 张好, 张临杰, 肖连团, 贾锁堂 2017 66 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan L Y, Li J S, Zhang H, Zhang L J, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Javan A, Kocharovskaya O, Lee H, Scully M O 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 013805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7159
- PDF下载量: 170
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: